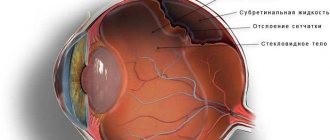
With astigmatism, after refraction in the optical system of the eye, light rays do not converge into one point, but are projected onto the retina in the form of several points, segments of different lengths, circles or ovals. As a result, instead of a normal image, you get something deformed and unclear. Moreover, a person suffering from astigmatism sees both close and distant objects equally poorly.
According to ophthalmologists, almost all inhabitants of the planet have one degree or another of astigmatism, but for most people (85%) it is characterized by a small amount (up to 1 diopter), which does not affect visual acuity. At the same time, about 15% of the population needs astigmatism correction with the help of special glasses (or lenses) or surgery.
Mechanism of disease development
Humans perceive visual images using the lens and cornea. Normally, they have a smooth spherical surface, allowing light rays to focus at one point. Thanks to this, the visible object is perceived as clear, distinct, without blurry spots.
Astigmatism is a violation of the sphericity of the cornea or lens, and therefore the refractive power of light becomes different, as a result, the image of an object is not clearly focused. This happens this way because some elements of the object are focused in front of the retina, others in different places behind it.
The disease is often combined with other ailments of visual function such as myopia, farsightedness, and the more pronounced they are, the more difficult the treatment process will be.
Types and degrees of astigmatism
In ophthalmology, the following types are distinguished, each of them has its own individual characteristics:
- Simple myopic. It is distinguished by changes in refraction that develop in one meridian. That is, on one meridian there is myopia, and on the other there is normal vision. Therefore, some of the light rays are focused in front of the retina, while others are focused on the retina.
- Complex myopic. It appears on different meridians with varying degrees of refractive error. Patients quickly lose their vision, the outlines of objects are distorted when looking at them, they stretch out and bifurcate. A person has to tilt his head, stretch his eyelids, squint.
- The mixed view combines two types of refractive error, that is, the image is focused twice: behind the retina and in front of it. Such a person simultaneously suffers from farsightedness and myopia.
- Simple hypermetropic. It is observed with farsightedness and is marked by emmetropia in one eye, and meridian in the other.
- Complex hypermetropic. It can be observed with varying degrees of farsightedness. In this form, the disease is focused precisely in front of the retina.
Changes in vision with astigmatism
Differences in structure:
- general,
- corneal,
- lenticular,
- interior.
This depends, first of all, on the changed shape of the area of the eye, but the general appearance combines several types at once, for example, lens and cornea.
In addition to the variety, it is divided into types according to the degree of disturbances occurring in the tissues of the visual system, representing a difference in the refractive power of the meridians.
The degrees of astigmatism are distinguished:
- weak – up to 3 diopters,
- average – 3-6 diopters,
- high – more than 6 diopters.
With the disease, changes are observed not only in the lens or cornea of the eye, but also in the muscles of the visual system. There may also be a displacement of several degrees of the eyeball, which leads to increased intraocular pressure and the development of glaucoma.
Specifics of the pathology
Astigmatism is a vision disorder in which the shape of the lens, cornea, or eyeball is deformed, resulting in loss of clarity. This is due to the fact that when the normal structure of the eyes changes, the image of objects is not focused correctly. With astigmatism, a person begins to see objects as distorted or blurry.
The optical system of the eye includes the cornea and lens. These are two lenses that are responsible for the refraction of light rays and their position on the retina. Depending on the cause, corneal, lenticular and general astigmatism are distinguished.
High visual acuity is provided by the macula, the central region of the retina. The cornea and lens must focus light rays so that they fall into the macular area.
High visual acuity requires a spherical cornea. Passing through such a surface, light rays are refracted with equal strength and fall into a strictly defined point. Distortion of the shape of the cornea leads to the fact that the rays are refracted chaotically.
The word “astigmatism” is translated from Greek as “no point”. This is due to improper focusing of light rays at several points in the presence of pathologies of the cornea or lens. These points lie before and after the retina, but do not specifically fall on it. What appears in the macula is not a clear image, but a blurred spot, information about which is transmitted to the brain.
With astigmatism, caused by changes in the shape of the cornea, light in different sections is refracted with different strengths. The image cannot be focused on the retina, so it appears blurry to the person.
There are two main meridians in the human eye, which are perpendicular to each other - strong and weak. With astigmatism, light rays from different meridians hit different points that are not focused on the retina. Only the light scattering circle falls into this area.
Causes of pathology
The causes of astigmatism in adults can be acquired or congenital. The acquired form develops as a result of exposure to various external factors on the visual system; in the congenital form, damage to the refractive system occurs as a result of impaired development of the lens or cornea in the prenatal period.
The main reason is the incorrect configuration of the optical vision system: an irregularly shaped lens or uneven curvature of the cornea. Most often this is a hereditary pathology. It can develop due to congenital uneven pressure of the extraocular muscles, orbital bones, and eyelids.
Also, the congenital form can occur as a result of: an unhealthy lifestyle or injury to the mother during pregnancy; birth of a baby prematurely; genetic predisposition - if one of the parents or both have a similar disease, then there is a high risk of developing a disorder of the shape of the cornea or lens.
Acquired astigmatism can have different causes: eye injuries resulting in scarring of the cornea or subluxation of the lens; structural anomalies and injuries of the dental system – congenital absence of teeth, prognathia, open bite; eye surgery; keratoconus, keratoglobus; inflammatory processes.
Predisposing factors contributing to the development of the acquired type may be: arterial hypertension, increased intraocular pressure, diabetes mellitus, other diseases of the visual system - cataracts, glaucoma.
It should be noted that when treating this type, in some cases it is enough to eliminate the root cause and vision will return to normal. Basically, one eye is affected, but if the development is caused by complications after surgery or injury, then both eyes are affected by the disease.
Differences in what is visible in various eye diseases
Causes of astigmatism
Most often, the cause of distortion of the shape of the cornea and lens is a hereditary factor, although the pathology can also be acquired. In a family where at least one parent has astigmatism, the child’s chance of developing the disease is almost 100%. As a rule, astigmatism is combined with refractive pathologies (myopia and farsightedness).
Causes of acquired astigmatism:
- injuries to the ocular system that cause scarring of the cornea;
- ophthalmological manipulations;
- inflammation;
- dystrophic processes;
- clouding of the corneal layer.
Congenital astigmatism can appear immediately after the baby is born. However, the presence of symptoms does not always indicate the pathological nature of the phenomenon. The fact is that all newborns have one degree or another of astigmatism due to the development of the visual system.
In children, astigmatism is not always caused by physiological defects. Sometimes the pathology does not affect visual function in any way and does not require treatment.
Symptoms, diagnostics to determine astigmatism
The clinical signs of astigmatism in adults are practically no different from the symptoms of other eye diseases. At the initial stage there are almost none. Eye fatigue may only increase due to muscle tension or slight defocus.
Symptoms in adults may be as follows: decreased clarity and acuity of vision; blurred contours; discomfort, pain in the eyes; double vision, itching and burning in the eyes; redness of the conjunctiva; feeling of increased fatigue; severe pain in the forehead and temple area.
The following symptoms may also appear: inability to clearly see horizontal and vertical lines at the same time; frequent blinking; curved lines appear straight and vice versa; difficulty concentrating on lines and letters; feeling of intolerance to glasses, irritation, discomfort; deterioration of twilight vision.
In order to understand the disease, you can take a photo without adjusting the sharpness of the lens. Then you can get an accurate idea of how people with astigmatism see. It is important to remember that these symptoms also occur with other eye diseases. It is the doctor who will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis.
It is important that in children the disease can be determined by other signs. The child turns or tilts his head to see more clearly. He does not recognize the text written on the board. He brings a book or notebook close to his eyes, changes and confuses the letters. If any symptoms are detected, you should immediately undergo diagnostic testing.
Astigmatism in children
Often, astigmatism is diagnosed even in the youngest patients, who are not even a year old. Astigmatism in preschool age is always a hereditary factor. If parents suffer from this disease or have vision problems, the risks increase. To prevent problems with the development of this pathology, you should monitor the time that the child spends in front of the computer or TV screen.
It is easy to diagnose astigmatism in a child: he often misses when he takes the desired object, brings pictures too close to his eyes, squints when watching TV, and complains of headaches. All these symptoms are a reason to consult a doctor.
Until the age of 18, astigmatism is not treated, but only corrected with glasses or contact lenses, since until adolescence, the organs of vision grow and change. If astigmatism is no more than 1 diopter, glasses are not prescribed.
Video: How to treat astigmatism in children
Diagnosis of astigmatism by an ophthalmologist
Diagnosis includes, first of all, a consultation with an ophthalmologist. Only he can carry out a competent, comprehensive assessment of the state of the functions of the visual system: examination of the eye structures, determination of the value of refraction, methods of indirect visualization.
Correct diagnosis of the disease is not so simple. Traditionally used examination methods do not always provide a complete and correct picture of the disease, and therefore the use of special diagnostic equipment is also required.
This applies especially to children and young patients, in whom defects in the visual organ of the optical system are masked by muscle tension, as a result of which glasses may be selected incorrectly, which will lead to aggravation of the situation.
Based on the patient’s complaints, an experienced doctor will suspect this disease, but to clarify the diagnosis and determine the form and type of the disease, a number of additional instrumental and clinical examinations will be required. The doctor may also prescribe tests to help identify the cause of the disease:
measurement of visual acuity; refractometry; skiascopy - determination of the degree of refraction; ophthalmometry - determination of corneal curvature; biomicroscopy; computer keratotopography; determination of the degree of astigmatism; measurement of intraocular pressure.
Based on research data, the doctor will draw up a complete picture of the disease, determine the stage and degree, identify the cause, and prescribe appropriate effective treatment. Remember, if you do not seek help in a timely manner, treatment will take more time and effort, and advanced forms cannot be treated at all.
HAPPY END
The patient and I are best friends. He periodically asks the question: “Maybe I should still have a cornea transplant? After all, I will be able to see even better.” Which, of course, I’m trying to dissuade him from for now. The eye looks like this under a microscope:
Fortunately, everything ended well. Finally
: the eye is not a constructor that can be taken apart in parts and replaced; it has a complex structure, all structures are interconnected. Although, the further we go in the development of ophthalmology, the more we can do: take something apart, change something.
This must be done in experienced hands, choosing specialists not of a “narrow” profile, but those who see the eye as a whole, knowing all its departments. And the clinic - with a full range of surgical operations and equipment for performing them, so that the “professional outlook” is sufficient and does not limit the choice of technique.
Also, a good doctor can fix a lot of things, but it’s good if you contact him right away.
Yes, the main thing is that if these were our days and the patient underwent correction using the ReLEX SMILE method, the story would not have happened.
How to determine astigmatism using visometry
An experienced practicing ophthalmologist will easily make a diagnosis using visometry. This is one of the most common verification methods. The patient puts on a special frame, closes one eye with a shutter, and lenses with different refractive powers are placed in front of the other and the refraction in both meridians and visual acuity are determined.
It can be carried out using two methods: with correction or without correction. In the first case, a trial frame is used. One eye is covered with an opaque material, and cylindrical lenses, which have different refractive powers, are placed in front of the other, in order to achieve the best visual acuity.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of astigmatism is made by an ophthalmologist after examining the patient, checking visual acuity using special tables and determining the difference in the curvature of the cornea - special cylindrical lenses are used for this purpose.
For a person with astigmatism, the glasses prescription will contain the cryptic letters: sph (sphere), cyl (cylinder) and ax (axis). The sphere shows the amount of spherical astigmatism correction, and the cylinder and axis show its size and orientation. Such glasses are often called “complex” by patients, and cylindrical by doctors.
Testing for astigmatism with skiascopy
Another no less effective and accurate, but rather labor-intensive diagnostic method is skiascopy. However, it should be noted that during its implementation it is not always possible to determine the exact direction of the main meridians. Skiascopy – determines the refraction of the eye using shadow movement.
The essence of the method is as follows. Using a reflective mirror, light is directed directly into the pupil, hitting the retina, it begins to reflect from it. Then they begin to move the mirror, a shadow appears in the area of the pupil, which, depending on the state of the refractive force, will move in different directions.
The study is carried out in a darkened room. The patient sits down on a chair and a light source is placed on the side at eye level. At a distance of 1 meter from the patient, the doctor sits down opposite and begins to move the mirror along the horizontal and vertical axis, observing the movement of the shadow.
During the examination, the doctor determines the nature of the disorder - hypermetroric or myopic. Then lenses with different refractive powers are installed in front of the patient’s eye one by one until the shadow that appears disappears. Based on the examination, conclusions are drawn about the degree of refractive error.
Special astigmatic lenses can be used to examine patients with astigmatism. They are picked up until the shadow disappears when the mirror moves in both meridians. Then, based on the refractive power of the lenses used during the examination, conclusions are drawn about the extent and nature of the disease.
Siemens star for pathology detection
Astigmatism therapy
With timely, correct and complete correction of astigmatism, it is possible to completely restore vision, increase its sharpness and eliminate discomfort. Modern medicine offers patients conservative and surgical methods for eliminating astigmatism in adults and children.
Optical correction
This type of treatment for astigmatism involves wearing therapeutic optical systems. Glasses and contact lenses are considered the most common and safest way to correct childhood astigmatism.
To eliminate this pathology, patients are prescribed glasses with cylindrical lenses (positive or negative depending on the type of disease). Despite the fact that glasses are a simple and cheap way to correct vision, in severe forms of the disease they are ineffective.
Wearing glasses or lenses causes some inconvenience to the patient. Glasses do not allow you to play sports, and the lenses require constant care. Spectacle optical systems greatly limit lateral vision; the frame is always in the field of view. The stereoscopic effect (perception of the volume of objects), which is especially important when driving a vehicle, is also impaired.
A small degree of astigmatism can be corrected with contact lenses. Previously, only hard lenses were used, which were very uncomfortable and required getting used to. However, today astigmatism can be corrected with toric or spherical lenses. They do not cause severe discomfort and effectively increase visual acuity.
Modern ophthalmology also offers patients orthokeratolic lenses. They are made of gas-permeable plastic and are designed to be worn at night. During eight hours of sleep, these lenses normalize the curvature of the cornea, which persists throughout the next day.
Laser correction
Modern ophthalmology is increasingly turning to excimer laser correction to treat astigmatism. The procedure takes 10-15 minutes on an outpatient basis. The patient is under local anesthesia, and the doctor separates the top layer of the cornea using a microkeratotome. This provides access to the deep layers of the cornea. Then the doctor evaporates certain parts of the cornea with a laser and replaces the cut flap, securing it with collagen.
Laser correction does not require sutures: the epithelium of the cut flap is able to recover on its own. Rehabilitation after such an intervention takes a minimum of time, and after 1-2 hours the patient returns home. The effect after laser correction is immediate, but complete restoration of vision occurs only after a few weeks.
Astigmatomy
This method of treating astigmatism involves applying arc micro-incisions to the periphery of the cornea to reduce strong-axis refraction. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, and surgery on each eye takes up to 10 minutes. After astigmatomy, vision is blurred for several hours.
As a rule, the procedure is prescribed if astigmatism is accompanied by myopia, or the pathology is of a mixed nature. Indications for surgery will be a high degree of pathology, contraindications to laser correction, the thin structure of the cornea and the need to replace the lens.
Astigmatomy is safe for children, but surgery is prescribed only if spectacle correction is intolerable. This treatment helps prevent amblyopia.
Refractive lens replacement
This operation is most effective for high degrees of astigmatism. When a patient has a thin cornea and is at increased risk of deformation, refractive lens replacement may be recommended. During the operation, the lens is removed and an artificial lens is installed in its place, which will effectively correct disorders caused by astigmatism.
Replacing the lens with an intraocular lens is recognized as the safest and best way to cure astigmatism and refractive pathologies up to 5-6 diopters. Lens replacement also helps eliminate cataracts. The best are multifocal toric intraocular lenses, which provide visual acuity at all distances.
Phakic lenses are also used to correct astigmatism. They are implanted in front of or behind the iris so that the lens is positioned in front of the lens along the pathology axis.
Phakic lenses are rarely used because other correction methods are more common. It is also inconvenient that if cataracts develop, the operation will have to be repeated: first remove the lens and replace the lens.
How to check the diagnosis of astigmatism by refractometry
Refractometry provides more complete and accurate information about changes in refraction. It is performed with a dilated pupil, which allows you to get a quickly accurate result. Refractometry determines dystrophic and degenerative changes in the tissues of the organs of vision.
Today, many ophthalmology clinics have automatic refractometers. The patient is positioned in front of the device, his head is fixed and he is asked to look into the distance. The device independently performs all examinations, detects deviations from the norm and displays the obtained examination data on the monitor.
This is a completely objective, and most importantly reliable way to study the refractive power of the eye system.
Doctors at the Excimer Clinic will help you cope with astigmatism
All doctors
Pershin Kirill Borisovich
Leading ophthalmic surgeon and medical director of the Excimer clinics, doctor of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, professor, academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Pashinova Nadezhda Fedorovna
Chief physician of the Moscow ophthalmological clinic "Excimer", ophthalmic surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Plyukhova Olga Alexandrovna
Head of the laser therapy department, ophthalmic surgeon, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences
How does eye astigmatism differ from other diseases in terms of symptoms?
It should be noted that the clinical symptoms are very similar to those of other diseases of the organs of vision, but still have their own characteristics. For example, headaches, lacrimation, and increased fatigue do not occur immediately after heavy eye work, but after several hours.
Also not typical for the disease are swelling, redness, swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyeballs, and the appearance of dark circles around the eyes. Such signs are more related to the development of cataracts, glaucoma, and conjunctivitis.
A characteristic sign of the disease is that a person is unable to focus his gaze on objects located far or near. The picture most often becomes fuzzy and blurry. The patient can see a clear image if she focuses on one point, but the rest of the view will be blurry and without clear boundaries.
It is important to remember that any disorder of the visual system, including astigmatic vision, should not be left without the close attention of an ophthalmologist. The sooner a sick person turns to a doctor for help, the greater his chances of recovery.
MY HISTORY
So, a patient came to me after 12 operations
, with a thinned irregular cornea, the outer part of which was transplanted from a donor, low protective properties of the inner wall (endothelium), two crooked lenses in the eye, high intraocular pressure - this is like a complication of everything he has experienced and the desire to see.
They no longer wanted to see him anywhere in Moscow and the world for several reasons:
- To solve his problem, it was necessary to start with the removal (explantation) of two crooked lenses causing complications - no one took on this, because the rupture of the posterior capsule that occurred during the operation made this operation extremely risky and very expensive.
- It was difficult to calculate the optics of the new required lens - vast experience in calculations and surgical intuition were needed.
- The operation had to be performed in “poor visibility” conditions, as the cornea was cloudy due to pressure and scarring.
This is what the topography of the cornea of patient “A” looked like.
And something had to be done. Firstly, because high intraocular pressure would destroy the optic nerve. Secondly, the patient, as you already understood, loves to undergo surgery. That is, such people do not give up so easily, and once they begin to fight for their eyesight, they finish the job.
Thirteenth operation
(I don’t believe in superstitions, but still) – removal of both lenses from the eye and implantation of a monofocal aspheric IOL with the expectation of emmetropia (we call it “zero”). The operation went great, technically we managed to accomplish everything planned and the new lens was in the right place. The patient and I were happy – but it was too early. A complication arose that could nullify all efforts and lead to a fatal end.
As a result of multiple previous surgeries, an eye reaction in the form of inflammation occurred. Not just a small one - but a stormy one, with a large number of cells, with thick turbidity and loss of vision.
This is what an ultrasound picture looks like for inflammation in the posterior segment of the eye.
This is what the eye looked like under a microscope.
After a couple of days, he stopped seeing objects - only light, and I stopped distinguishing anything in his eye. Unfortunately, such a development is possible after numerous operations, when we have to enter the eye cavity. No vision. The consultation with colleagues did not add optimism - the general opinion is that the end will be the same - “an eye in a basin.” It's time to give up. There was no time to hesitate. The next operation followed.
Fourteenth operation
– introduction of drugs into the anterior chamber of the eye.
We took cultures for the presence of microbes (then we received a negative answer). In most cases, this helps, but in this case a fifteenth operation
- the injection of drugs into the posterior chamber of the eye - into the vitreous cavity, since such inflammation is dangerous for the retina and can destroy it. All this, of course, against the background of general therapy.
The fight went on day and night - we became allies in this battle. But by the third day it became clear that another major operation could not be avoided.
Sixteenth operation
– vitrectomy – a deep serious operation – removal of the cloudy vitreous body, which, like a sponge, absorbs all inflammatory cells, microbes (if any) and their decay products. If this operation is not performed on time, the eye will die. The operation is very difficult, “visibility is zero,” but I managed to do it. It brought relief, a gradual improvement in the patient’s vision and vision was already 60% by the end of the month. We celebrated the victory. Early.
After 2 months, “A” again experienced a relapse of inflammation and vision decreased to light perception. We went along the same path - the seventeenth operation
and
the eighteenth operation
- the introduction of medicinal drugs into the vitreous cavity.
And 6 months later, when everything had calmed down, another problem was found that interfered with vision and caused distortion.
The patient saw six lines. But there were complaints about distortion. The reason for this was the formation of an epiretinal membrane (similar to a cellophane film covering the retina) in the center. At the same time, the new lens stood perfectly, and the cornea remained stable.
The CT scan shows the correct position of the new lens under the iris.
I perform a large number of operations on the retina, including this type. But I can’t say that I wanted to have another operation then. On the one hand, there are risks of a recurrence of inflammation, on the other, there is a huge temptation to help the patient, to get rid of distortions; this is impossible without surgery. We decided together what we would do!
Nineteenth operation
– removal of the epiretinal and internal limiting membranes – looks like this: vitrectomy + work in the vitreous cavity with special tweezers for manually removing “cellophane”. Again, when it’s hard to see. But everything was successful - the result was 80% of vision, and the correction was 90-100% (corneal astigmatism still interferes).
The pressure is good, no drops. The position of the lens is normal. The cornea is still irregular, the density and quality of the endothelium is not very high. But the transparency is good and allows you to see 100%.
This is a tomogram of the membrane, causing distortion of the retinal relief
Tomogram of the retina after the 19th operation
Twentieth operation
– blepharoplasty is already aesthetic ophthalmology. The result is that the patient begins to see and looks 10-15 years younger.
Features of childhood astigmatism
It has been established that many newborn children have congenital astigmatism of the eyes with a degree of 1-2 diopters. By the age of one year, this figure decreases to 0.5-0.75. If the value does not decrease, then the baby needs urgent mandatory spectacle vision correction.
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to impaired binocular and stereoscopic vision, as well as strabismus; accommodative asthenopia - rapid eye fatigue; Amblyopia – lazy eye syndrome, when impaired vision can no longer be corrected with lenses or glasses.
It is important to remember that it is very difficult to independently determine the disease in children. From birth they get used to such features. Therefore, you should carefully monitor your child’s habits. If he: squints his eyes often; brings a book close to his eyes; If you get tired quickly, you urgently need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Since all the signs indicate pathology, one of which may be astigmatism of the cornea or lens of the eye. Increased stress on children's eyes will lead to the appearance of double vision of the objects in question, and without appropriate treatment to strabismus and irreversible loss of vision.
Astigmatism in children
Prevention of astigmatism
Delayed or improper treatment of astigmatism can lead to a severe deterioration in visual acuity. The patient may also develop amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome) or even strabismus.
Childhood astigmatism can cause blindness in one or both eyes. This occurs in cases where the retina ceases to perceive the image. Blindness may be variable or affect only one eye.
Preventive measures:
- Establishing the correct lighting mode for the workplace. The light should fall on the workspace from the left or right (depending on the leading hand).
- Compliance with the rules of reading, watching TV and working at the computer.
- Performing gymnastic exercises (several times a day or every 20 minutes with visual stress).
- Alternating visual stress and rest.
- Taking vitamin supplements with lutein.
- Products with vitamins A and D.
- Preventive examinations every six months.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the visual organs that increase the risk of developing astigmatism (keratoconus, lens distortion, corneal pathologies).
- Physiotherapy to relieve tension and improve blood supply to the eyes (color therapy, massage, Sidorenko glasses).
- Protect your eyes from injury, solar radiation and dust.
At first, astigmatism causes nothing but discomfort; over time, the pathology will lead to a decrease in visual acuity and the development of side conditions. Surgery for astigmatism does not take much time and provides good results for many years.
Sources used:
- Fundamentals of ophthalmoscopic diagnostics / D.I. Berezinskaya. - Moscow
- Eye and image / N.N. Blinov. - M.: Medicine, 2004.
- Clinical ophthalmology. Systematized approach / Jack Kansky. - M.: Logosphere, Elsevier Urban & Partner, 2009.
- Kursk State Medical University
Treatment methods for eye astigmatism
It should be noted that treatment can be done in various ways, using glasses, contact, or laser correction. The method of treatment is selected by the doctor individually, taking into account the type and stage of the disease.
In any case, a positive outcome can only be achieved through complex treatment prescribed by a doctor, after the results of ophthalmological examinations of the patient, taking into account the characteristics of his body.
Traditionally, treatment in adults occurs with glasses. These are special glasses that help you focus your gaze on the object in question, thereby making it clearer.
Unfortunately, the disease cannot be cured with glasses. Many refuse to wear them, citing discomfort. Therefore, the attending physician advises them to carry out vision correction using special toric contact lenses.
This is a fairly common method for treating eye astigmatism in adults. These lenses can only be used by adults. They do not cause discomfort; vision is focused precisely on the object, without distortion or blurred contours.
Today, laser correction is quite effective and popular. During the operation, a special device lifts the top layer, evaporates excess corneal cells and fixes the separated area in place. The laser effect lasts no more than 40 seconds, no stitches are required, and vision quickly improves.
During surgical treatment, deep incisions are created around the perimeter of the cornea, changing its curvature. However, the recovery period after such an intervention lasts a long time.
Medication method - vitamin eye drops are prescribed to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes. Their use helps reduce the symptoms of the disease and stop its progression. You can use them after consulting an ophthalmologist, so as not to cause further harm.
An important place in treatment is occupied by the patient’s diet and lifestyle. At this time, it is recommended to eat more foods containing vitamins - fresh vegetables, herbs, blueberries, as well as taking eye vitamins, since they contain all the necessary microelements.
Your doctor may also recommend special eye exercises. Such gymnastics will help stop further decline in vision, and in complex treatment will lead to a more effective result. But the treatment regimen is individual and depends on the degree of pathology, the presence of scar tissue, the patient’s age and the characteristics of his body.
Lenses for astigmatism
What to do with astigmatism
Only a qualified doctor can determine the presence of pathology and perform the necessary ophthalmological tests. The doctor decides which correction methods are suitable for a particular patient and evaluates the feasibility of therapeutic treatment. Eye exercises are often prescribed for astigmatism.
The main method of correcting astigmatism is surgical treatment. In some cases, laser correction will also be effective. Optical systems (glasses and contact lenses) only help correct vision, but do not in any way affect the cause of the pathology.
Lenses for astigmatism: types, advantages and disadvantages
Contact lenses during treatment are selected similarly to lenses for glasses.
Advantages of lenses:
- more effective correction;
- maintaining peripheral visibility;
- the ability to eliminate corneal astigmatism;
- creation of binocular vision;
- minimizing chromatic aberration;
- cosmetic effect.
The disadvantages of contact lenses are:
- increased myopia with chronic oxygen starvation of the cornea;
- the likelihood of inflammatory processes increases; eye pain and discomfort complicate the course of the disease;
- difficulties in installation, increased hygienic requirements for the maintenance of lenses do not make it possible to use them for small children;
- high prices for toric contact lenses.
For treatment can be used:
- hard contact lenses made of durable polymers, and therefore retain their constant shape;
- soft contact lenses made from soft materials; they can be spherocylindrical, cylindrical, spherical.
Contact lenses are invisible and cause almost no discomfort to those who wear them, and therefore they are an ideal solution to the problem for patients.
How to treat astigmatism with gymnastic exercises
In combination with other treatment methods, gymnastics plays an important role. It should be performed systematically and over a long period of time. Gymnastic exercises help restore tone to the eye muscles and relieve tension from them. It is impossible to recover using exercises, but their correct use makes the course of the disease easier.
Moderate or weak astigmatism can be corrected using special therapeutic exercises:
- alternately concentrate attention on objects located either near or far away;
- rotate alternately closed and open eyes clockwise and counterclockwise;
- close your eyelids and move your pupils left and right, up and down, then open your eyelids and repeat the movements;
- draw straight and curved lines, letters and numbers with your gaze;
- place your finger on the bridge of your nose and concentrate your gaze on it for 30 seconds;
- blink softly and frequently for several seconds;
- Close your eyes tightly for a few seconds, then open them, repeat several times, this will ensure good blood flow to the eyeballs.
The effectiveness of exercise in resting and relaxing muscles, improving metabolic processes and blood circulation. It is recommended to perform them at least three times a day, and with constant eye strain, every hour.
The set of exercises developed by the American ophthalmologist W. Bates is deservedly popular. According to his theory, the main cause of the manifestation of this disease is the uneven tension of the muscles of the optic apple. Many of his exercises have their roots in ancient Eastern treatises.
Here are just a few exercises from this unique complex:
- make a hundred big turns with your head;
- when reading small print, move your gaze between the lines, accompanying it with soft blinks;
- turn your head alternately and simultaneously move your gaze between the lines;
- Blink frequently and gently for a minute.
It is these special exercises that help reduce the load and prevent the development of the disease and its complications. The effectiveness of the exercises is explained by the fact that during their execution the eye muscles rest and relax, which ensures accommodation of the lens.
Treatment of astigmatism
NOT MY STORY
So, 1978 - the first operation
- radial keratotomy. This is an operation to manually apply incisions to the anterior surface of the cornea. In the 80s, its triumphant march began - it was widespread in the USSR and America. If the surgeon’s hand trembled, the cut would be crooked or, even worse, through. The middle of the cornea flattened, the optics of the eye became weaker. The number and shape of notches were calculated using formulas, but the accuracy was low. “A” got everything at once - perforation and curvature of the notch. The cornea “sank and became distorted.”
Second operation
– an attempt to straighten the resulting astigmatism with notches, but tangential (longitudinal).
Eye during keratotomy
Third operation
- thermokeratoplasty - an attempt to get rid of the resulting postoperative farsightedness - by applying thermal burns with an infrared optical laser on its periphery and subsequent reduction of collagen fibers. Like this:
Fourth operation
– 1998 – LASIK surgery.
Yes, such a now popular method was then pioneering - it was seen as getting rid of all the problems of eye optics. The patient’s cap was cut off from the upper layer of the cornea, and some thickness of the stroma was “evaporated” with an excimer laser of that generation to correct the optics, but alas, the cornea still remained crooked and vision was poor. How this is done is written here. Scheme of the LASIK operation
And we remember that the lid never grows back after LASIK - and there is a temptation to lift it again in a couple of months in order to “burn” it to the goal. Thus arose the fifth operation
– lifting the “lid” after LASIK and excimer laser evaporation of some more thickness of the corneal stroma. The result is that the cornea has become critically thin and keratectasia has occurred. Keratectasia is something that is very similar to keratoconus in its course and symptoms. I wrote about her here.
It was 2012
. By this time, “A” had not become a pilot, he had become a wealthy successful man and decided to undergo treatment in Switzerland - it cost him 1 million Swiss francs. A doctor from the French part of Switzerland, who took up the treatment, decided not to touch the cornea anymore, he went a different way (he generally understood little about the cornea, but he knew how to remove lenses). As a result, it was decided to remove the patient’s completely transparent natural lens and replace it with an artificial complex astigmatic one, which, according to the doctor’s understanding, was supposed to compensate for the irregularities of the cornea in the right direction. The idea, in my opinion, could not be successful, since the diseased, crooked, exhausted cornea was so irregular that there was no lens that could correct it.
Sixth operation
– phacoemulsification of cataract with implantation of a pre-ordered individual astigmatic lens. For those who understand something about lenses, its astigmatic part was +7.5 diopters, sphere +21.0. The operation in experienced hands takes 5 minutes; in the post “Implanting an artificial lens” you can read in detail how it is performed.
But something went wrong again - during the operation a rather serious complication occurred in the form of a rupture of the posterior capsule of the lens, the surgeon left the peripheral part of his own lens and somehow coped with the implantation. The tear creates problems for lens alignment. The decision was made at the moment of capsule rupture, and the surgeon considered that the rupture was not large enough to affect the position of the lens. I took a risk and bet. The idea was not the best from the very beginning: irregular astigmatism is poorly compensated, and the implantation axis did not coincide with the calculated one.
The problem was that the previously ordered complex astigmatic lens could no longer be placed in the defective bag, since correct orientation would be impossible.
But the lens was placed because the surgeon hoped for a “miracle.” A miracle did not happen - the optics became even crooked. Diagram of optics for irregular astigmatism
We remember that this surgeon did not deal with corneas, but only knew how to do cataracts and change lenses. And he suggested to the patient to add another lens (!) on top of the one already placed, to make such a “sandwich” of them, ordering an astigmatic one with alternative axes, a sphere -7.5, a cylinder +11.0.
Seventh operation
– implantation of this additional lens on top of the previous one. More precisely, he was afraid to take out the lens and put a new one in its place: this is a rather complicated and risky operation. As you might guess, the optics have become even crooked.
This is what ultrasound biomicroscopy looks like with two artificial lenses in the eye.
By the way, I use such additional lenses (lenses) quite often - they really help out in certain cases. They have an excellent ability - they can be rotated - rotated if necessary.
This is how you can “twist” the IOL in the eye clockwise or counterclockwise
. So, operation eight
- in fact, this is not one, but three operations - attempts to rotate an additional lens in order to reduce the optics to zero. Is it worth writing that all attempts were unsuccessful. And my colleague from the French part of Switzerland sent the patient to the German part of Switzerland to help solve the problem.
My colleague number two from the German part of Switzerland did not deal with cataracts and lenses, he only dealt with corneas - he transplanted them and did laser corrections. And so the ninth operation
- the surgeon honestly decided to correct the cornea in a simple, safe way - with tightening sutures. But they didn't help.
And we remember that this colleague’s specialty is corneal transplantation. the tenth anniversary operation was performed
– anterior lamellar keratoplasty – transplantation of the anterior wall of the cornea, which restored the thickness of the cornea.
Schematically, the operation looks like this.
After the cornea transplant, the optics, of course, did not become correct - after all, the transplanted cornea had the curvature and refraction of the donor (that is, the deceased person from whom it was transplanted). To make it clear, transplanting a cornea from a donor is like transplanting breasts from one woman to another - during transplantation, we do not figure out whether it is the right or left eye, where is the top and where is the bottom, the curvature is not taken into account at all. But the surgeon hoped that he would then perform a femtolaser correction and correct at least the corneal component. Let me remind you that he was not a specialist in lenses and was not tormented by the question of the two lenses in the eye with rather extraordinary optics.
Eleventh operation
– femtoLASIK on a transplant – 1st time. It didn’t work out - probably at that time the lenses in the eye moved and everything was askew. How femtoLASIK surgery works is written here.
Twelfth operation
– repeat femtoLASIK on the graft. It didn’t work out again, and it couldn’t have worked out. But the cornea thinned to 130 microns in its thinnest part (!), although it remained quite regular in the optical zone. This is what the keratotopogram looked like:
When the patient asked the Swiss surgeon, “What will we do next?”, he answered, “We will transplant the cornea again, and then sharpen it with a laser again.” Realizing that the circle had closed, “A” returned to Moscow.
How to treat astigmatism using traditional methods
First of all, remember that all folk remedies are only auxiliary therapy in the main treatment. None of these recipes can stop the deformation of the cornea or lens, but only slow down the pathological processes.
There are many recipes that can help stop the development of astigmatism. Among them, excellent results are achieved by using blueberries, which contain many beneficial substances for the eyes. You can use it in any quantity and form - raw, jam, preserves, freeze for the winter.
Traditional medicine over the centuries has accumulated a huge arsenal of recipes that can temporarily improve the trophism of the eyeball. But none of them will correct the incorrect focus of vision.
Natural vegetables and fruits also have beneficial properties. They contain a rich list of microelements and vitamins. These are: beets, carrots, cucumbers, celery, parsley, spinach, dill. These herbal remedies are useful in the form of salads with the addition of sour cream or vegetable oil.
There are many recipes that can be used for preventive and therapeutic purposes. But the doctor will suggest a treatment regimen after the examination. In any case, a positive result from treatment with traditional medicine can only be obtained at the initial stage of the disease. They will not help with dystrophic changes in the visual system.