Keratotopography (corneotopography, photokeratoscopy, videokeratography) is a non-invasive technique for obtaining a topographic map of the anterior surface of the cornea.
The very first device for detecting corneal surface abnormalities was the Placido disc , developed in 1880 by Portuguese ophthalmologist Antonio Placido. It is a flat disk with concentric alternating white and black rings. From a light source located behind the patient's head, rays reflected from the surface of the disk were projected onto the cornea. There was an aperture in the center of the disk through which the doctor could observe the image being formed on the surface of the cornea. The smaller the radius of curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea, the smaller this image is, and the rings of the Placido disc are located closer to each other. With astigmatism in the region of a steeper meridian, the rings will also be closer to each other.
The error during keratotopography is in the range of ±0.25 D or 2-3 µm, but in complex cases it can be ±0.50-1.00 D.
What is corneal keratotopography?
Keratotopography is a painless, non-contact diagnostic method. During the examination, eye contact with the equipment is excluded, which helps prevent injury and infection. The result of keratotopographic diagnosis is a color map of the ocular surface, on which healthy and pathologically altered areas of the cornea are marked. The importance of this study can be understood from the anatomy of the cornea.
It is the anterior, most convex part of the eyeball, which performs the important function of a light-refracting medium. Rays of light pass through it and are collected on the retina, forming a clear “picture”. Abnormal thickening of individual areas or the entire cornea, along with its irregular curvature, lead to disturbances in refractive power, which, in turn, cause deterioration in visual acuity.
Keratotopography of the cornea of the eye allows you to identify existing irregularities on the ocular surface, determine the direction of the visual meridians and the degree of their severity. Based on changes in the relief of the cornea, the ophthalmologist can accurately determine the causes of visual acuity disorders. Moreover: keratotopography is the only technique that allows us to identify keratoconus, in which the cornea takes on a cone shape.
Features of the study
This study is performed on an automated computer installation “Eye map”. Its working part is a conical keratograph, in which recording rings are located every 0.3 mm. Measuring area: 10.5 mm. The results of the study are presented in the form of a color-coded contour map of the corneal surface; they represent data on more than 8 thousand points on the surface of the cornea. To expand the volume of data, a standard international scale was introduced - a color code, it means:
- violet-blue - less strong cornea;
- orange-red - strong cornea.
The standard color code interval is usually 5 or 1.5D. A more accurate determination of corneal strength is indicated by numerical parameters. Normally, the cornea is steeper in the center, flatter towards the periphery, mirror-like, with an aspherical radial topography.
Indications and contraindications for corneal keratotopography
| Indications | Contraindications |
| The procedure has no contraindications for the eyes and can be performed even if the patient has ophthalmological diseases of various natures. However, it is not carried out if the patient is under the influence of alcohol or drugs, or if he suffers from severe mental disorders. |
Indications for examination
In ophthalmology, keratotopography is used for:
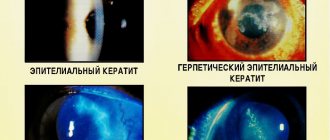
• early diagnosis of corneal pathologies: keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, Therrien's degeneration, epithelial dystrophy and other epithelopathies; • quantitative assessment of irregular astigmatism and corneal irregularity that are associated with contact lens wear; • assessment of the condition of the cornea during the period before and after surgical interventions (refractive surgery, keratoplasty). It is especially important to exclude the presence of keratoconus in patients who are preparing for laser vision correction; • selection of rigid gas permeable lenses (RGPL) and monitoring the effect of wearing them.
What does a keratotopogram show?
A diagnostic study is carried out using an ophthalmological apparatus - a keratograph. Its design provides for the presence of recording rings, which are designed to record the results obtained from 8 thousand positions, by which the condition of the cornea is assessed.
Based on these data, a special computer program constructs a topographic map on which you can see:
- areas of red or yellow color, displaying thickening of the cornea while maintaining its integrity and relief above normal;
- areas of purple and blue color, showing thinned areas with relief below normal.
Thus, the keratotopogram provides the ophthalmologist with all the data necessary to:
- make an accurate diagnosis;
- evaluate treatment results;
- determine the scope of the upcoming laser correction.
Based on these data, the curvature of the cornea, the power of refraction, and the degree of distortion of the visual meridians are identified.
Contraindications
Computer keratotopography does not involve direct contact with the tissues of the eye, as well as irradiation or any other impact. Accordingly, there are no absolute or relative contraindications.
It should be especially emphasized that the quality of keratotopography largely depends on the accuracy and resolution of diagnostic equipment. Thus, the Moscow Ophthalmological Center has precision Pentakam OCULUS equipment made in Germany. This system embodies the physical principle of the Scheimpflug chamber; mapping of the anterior surface of the cornea is carried out on the basis of computer processing of many high-precision stereometric measurements - 138,000 points are analyzed to construct the final image.
Topographic and pachymetric (thickness) indicators of a specific cornea are calculated, various geometric proportions are identified, and the density of the lens is assessed (densitometry is also one of the automatically performed functions). A virtual three-dimensional model of the eye is constructed, which can be rotated in any plane on the screen. It is obvious that in terms of the nature, volume and accuracy of the information obtained, also taking into account the absolute harmlessness of the procedure, keratotopography as a diagnostic method in a number of clinical situations has no alternative.
How is keratotopography performed?
This diagnostic procedure is simple and does not require special preparation from the patient. The use of anesthetic drops before the procedure is not necessary, since it is not only painless, but also non-contact. Despite the difference in the types of keratotopographic systems used, the scheme for performing a diagnostic study does not differ.
Before starting the study, the patient needs to remove contact lenses or glasses, as well as remove decorative cosmetics from the face. He will be asked to sit in front of the keratograph and fix his head on its stand. During the scan, which lasts several minutes, head and eye movements must be eliminated in order for the study results to be as accurate as possible.
There are various types of keratotopographic systems, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. One of the most modern and accurate systems is based on the use of the Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor. It allows you to analyze light waves at ten different points, which allows you to achieve the highest quality data obtained.
At the Sfera clinic we use just such a keratotopograph: “HRK-7000”, which allows you to obtain data even on the periphery of the eye, which, in turn, allows you to achieve the desired accuracy when selecting contact lenses.
How is keratotopography performed?
Before keratotopography, it is necessary to remove lenses and glasses. No special preparation is required - the examination can be carried out by a doctor as part of the initial examination if indicated.
The patient takes a comfortable position in front of the keratograph and fixes his head, resting his chin on a special stand. There is nothing complicated in the study - you just need to open your eyes and not move for a few seconds. The keratoscope scanner will perform an optical examination using two light sources. It is not painful, not harmful, and does not affect visual function.
It takes approximately 5-15 minutes to decipher the resulting color diagnostic card. The doctor will be able to clarify the location of pathological foci, their depth and size, severity, and general characteristics of “problem” areas of the cornea.
Interpretation of keratotopography results
Displaying data on a keratotopogram is carried out in different forms.
| In what form is the data displayed? | What does the information received say? |
| Numbers | The resulting diagram contains information about the corneal curvature in diopters (D) in ten concentric areas in 1 mm increments. |
| Profile view | The resulting image includes the flattest and steepest meridians of the cornea, and the difference between them in diopters (D). |
| Photokeratoscopy | The appearance of Placido rings on the cornea reveals the location of the apex of keratoconus. |
| Keratometry | Allows you to identify the symmetry of astigmatism and determines the decision on the need for laser correction. |
Decoding
The thickness of the cornea, the degree of curvature, and the “bulging” of surface areas on the topographic map are displayed in certain colors:
- areas of a cold shade (violet, blue, light blue) indicate low values relative to zero: lower value, lower level;
- areas of warm shades (red, orange, yellow) areas indicate high values of quantities, a higher level;
- green is always the zero level, set automatically or manually.
By studying the keratotopogram, the doctor evaluates the local radii of curvature of the corneal surface and the local thickness of the cornea. Color illustrations of different formats resemble geographical maps of the earth's surface. The location of the “lake” or “mountain” has its own coordinates and area. The obtained data is also presented in the form of digital information, allowing statistical processing of the results. As a result, in addition to early detection of the initial signs of diseases, the doctor has a very powerful tool for planning laser correction of impaired vision.
Advantages of keratotopography at the Sfera clinic
Diagnostics in this area in our clinic are carried out using a modern autorefractometer “HRK-7000”, manufactured at the production facilities of the South Korean company. This is a modern device that allows for a full analysis of possible violations of the optical system of the eyes, having a highly sensitive matrix and the “Super Luminescent Diode” system, which guarantee image clarity. Moreover: it is equipped with a special noise reduction system, which allows for the most accurate diagnostic studies even with pathologies such as cataracts, ametropia, and if the patient has an IOL.
Undoubtedly, even the most high-tech equipment will be useless without an experienced specialist who knows how to handle it... But the ophthalmologists of the Sfera clinic have been certified and work in accordance with international standards. If you want to be sure that the diagnosis will be carried out in the best possible way, contact us!
In order to get an appointment with our specialists, use the online form on our website or call us: +7 495 139‑09-81.
How is keratotopography performed?
The examination is carried out in several stages. But before you begin an eye examination, you need to visit an ophthalmologist for a general examination of your vision. It is advisable to take a referral from an eye doctor to conduct an examination of the cornea.
- The patient sits down on a chair. The optimal height is selected for him.
- The head must be placed in the place specified by the device and fixed. All nuances are corrected by the doctor.
- Next, the doctor warns about the start of the examination. The results are transferred to the computer.
Features of the event
An integral part of the optical refractive structure of the eye is the cornea. Its surface must be smooth, have the correct angle of refraction, as well as the necessary curvature. This is required for the purpose of clarity and correctness of visual functions. Diseases of this element of the visual system entail a deterioration in the ability to see, and sometimes even complete loss of vision.
What is a research method
Patients who are prescribed keratotopography are interested in what it is and how this examination is carried out. Keratotopography (or corneotopographic study) is a non-invasive (non-contact) method for studying the relief of the cornea of the eye. During the procedure, the cornea is scanned with a special keratotopograph device. The device consists of rings located at a short distance from each other, which “read” and record readings from 8000 points on the surface of the cornea.
The technique was developed and first used in the 19th century by an ophthalmologist from Portugal A. Placido. The inventor conducted the research using special optical instruments. Later, primitive ophthalmological instruments were replaced by devices consisting of a disk with black and white stripes. A lamp was installed behind the patient's back, the beam from which was directed to the disk and the reflection from it created projections on the cornea of the eye.
Modern examinations are carried out using the latest computer programs. This allows you to obtain maximum accuracy of the study and simplifies the procedure for examining the patient.
Currently, the following types of keratotopographic systems exist:
- Placido's rings. The device consists of 8-32 rings. The disadvantage of the method is that the central zone of the cornea is not examined, and the accuracy of the results depends on the condition of the tear film.
- Method using optical and scanning slit. Two light devices with light slits are placed at an angle of 45 degrees to the center of the eyeball. The device scans 20 pictures at slow speed. The procedure is lengthy compared to other methods.
- Schleimpflug chamber. The device, consisting of two cameras, rotates and takes 50 pictures in 2 seconds. The images clearly reflect all surfaces of the shell, which makes it possible to diagnose complex pathologies in keratoconus.
- Photokeratoscopy (Raster photography). The device transmits a grid consisting of cells of a certain caliber to the front of the cornea and reads the image from different angles. Tear film staining and cobalt light are used to obtain images.
- Laser holographic interferometry. Measurements are carried out using a three-dimensional image, the reflection of which depends on the shape of the cornea.
Useful video
More useful information can be found in these videos:
Keratotopography is a modern way of examining the condition of the eye. A specialist can record even the smallest curvatures of the cornea that are not amenable to other diagnostic methods. It is keratotopography that diagnoses ophthalmological pathologies at the earliest stage of its development. This helps not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to prescribe effective treatment that helps maintain the ability to see the world around us.
?
Keratotopography: how it works
The eye is a unique collection of completely different anatomical structures in the body: a strong outer sclera, an intermediate choroid, and an inner light-sensitive retina.
Light reflected from surrounding objects travels a long way from the cornea to special retinal cells in a very short time.
The outpost of the eyeball is the cornea, consisting of dozens of layers of specialized cells. It is the only structure in the human body that receives nutrition directly from the tear fluid and moisture of the anterior chamber of the eye. The latter is the second obstacle to the path of light to the retina. The third object is the lens of the eye. It consists of unique cells that have been separated from the immune system since the beginning of intrauterine life. Behind the lens is a gelatinous vitreous body. Having overcome it, the light reaches specialized cells of the retina.
The optical environment of the eye is extremely important for constructing the correct image on the retina
All of the listed structures have different transmission capacities for light waves. The optical density of the cornea is approximately 28 diopters, the lens of the eye is about 12–14.
Normally, the cornea has the same density in all radial directions. With various diseases, the shape and structure of its areas suffer. As a result, visual acuity disorders are observed. In addition, the cornea is extremely important when laser vision correction is needed. The essence of this method is to evaporate a layer of the cornea strictly defined in thickness with a directed light beam to restore a clear visual picture on the retina.
Keratotopography is a medical term that refers to the construction of a spatial picture of the surface of the cornea. For this, a laser is used - a directed beam of light waves of a certain length. A special device records the reflected beam, after which the computer processes the indicators obtained from eight thousand points of the cornea.
Keratopography involves examining the surface of the cornea of the eye.
The result is presented as a color image. The computer encodes the obtained indicators using different colors: depressions in blue, elevations in red-orange. Thanks to this technology, the surface of the cornea is accurately assessed by an ophthalmologist.