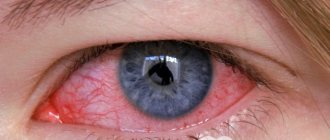
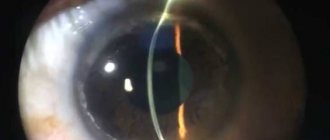
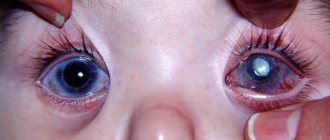
Any disease worries a person, especially one that is immediately visible from the outside. Diseases of the visual organs bother many people. Corneal clouding can occur to anyone at the most unexpected moment, and it is important to know how to recognize the disease and how to deal with it. The clouding is usually visible to the naked eye, appears as a white spot, can completely cover the pupil, or can be located in parts along the cornea. The disease is also called leukoma. Leukoma consists of remnants of the inflammatory infiltrate, elements of dystrophy and degeneration.
Clouding of the cornea: causes
Corneal opacity is a cataract, which is a scar change. Cloudiness can occur due to mechanical damage to the organs of vision (a speck, a branch poked, burns or other external damage) and viral infections (for example, conjunctivitis).
In the future, a bacterial infection may develop and infect the entire thickness of the cornea. Then vision begins to deteriorate. It should not be allowed to reach this state.
Vision begins to decline rapidly if the disease manifests itself in the central part of the pupil. Vision will deteriorate a little more slowly if the process occurs in the peripheral zone.
The cause of the appearance of a cataract may be a recent operation. After all, the cornea has non-renewable cells, which the patient may lack.
It is not possible to determine the number of such cells in advance. Therefore, as a result of surgical intervention, complete clouding or dystrophy of the cornea occurs. No one is immune from this. Unfortunately, it is impossible to prevent the appearance of a cataract after surgery.
Cloudiness appears after suffering keratitis (a disease associated with inflammation of the cornea); it can be formed from tuberculosis or syphilis. Here it is not the eyes that need to be treated, but the underlying disease, the cause is not in the cornea.
In case of eye injuries, serious problems may arise in addition to the appearance of a cataract; the cornea and iris may become soldered, which will lead to the development of another disease - glaucoma. Glaucoma is a serious disease of the organ of vision when the pupil becomes green in color.
Previously, doctors could not distinguish a cataract from a cataract, since the signs and symptoms are the same. But these are two completely different diseases. Cataracts also cause clouding of the lens, but the treatment required is completely different, because the disease affects the internal parts of the organ of vision.
With ordinary clouding of the cornea, the cataract appears only on the outer part of the cornea, therefore, the treatment is not so deep.
There are several reasons for clouding, but the most important is damage. If you don’t want to walk around with an eyesore, protect your visual organs from foreign objects getting into them, from burns and inflammation.
You can find out more information about clouding of the cornea in the video provided.
How to identify possible deviations
When a newborn’s eyes are still cloudy and cannot focus on an object due to the immature refractive function, the mother wants to know how to distinguish normality from pathology. In maternity hospitals, a mandatory procedure for treating infants' vision organs is to eliminate eye infections. Therefore, mothers should trust the health of their child to professionals and stop worrying about everything - it’s better to focus on lactation.
Why red eyes in a newborn baby - what to do
Eye pathologies are determined in the following ways:
- detection of suppuration in the lacrimal sac - when pressure is applied, it is not a tear that is released, but pus;
- excessive tearing also indicates a viral infection;
- During the examination, pronounced photophobia is detected;
- On examination, redness of the conjunctiva is revealed.
Important! As a result of the examination, the baby’s vision will be checked by a specialist in the postpartum department. After which a mother with a baby aged 1, 6 and 9 months should definitely visit an ophthalmologist.
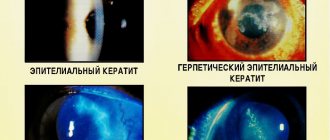
Kinds
There are several types of corneal opacities. They differ from each other in size, shape and intensity of turbidity. They do not look aesthetically pleasing at all; it is easy to determine the type of formation by their appearance.
Happens:
- cloud
- spot
- thorn
They represent three different degrees of turbidity. The first degree is not so terrible, but the last can cause blindness. When first-stage clouding is detected, it is important to take timely measures to prevent further development of the disease.
Cloud
This clouding is barely noticeable; it can only be seen upon careful examination; it looks like a gray, smoky speck. It has a negative effect on vision, but with such clouding one can see quite normally, only slight discomfort is felt, some patients do not even notice anything.
Spot
The spot looks brighter, such formation is immediately noticeable. The color of the spot is usually pearly. No matter where in the eye it is located, the patient’s vision becomes worse. If the spot appears in childhood, further development of strabismus is possible.
Belmo
The cataract is formed as a result of scarring of the cornea, after suffering from inflammation and ulcers. It appears as a white-gray or yellow formation and may have the color of frosted glass or porcelain.
The thorn can be congenital, caused by intrauterine inflammatory processes, but most often the disease is acquired, occurring as a result of injury or infection.
The cataract involves thinning of the cornea, affects intraocular pressure, and is often associated with vascular sprouting. A cataract is also called a bulging leukoma.
Cloudiness can be of different types, but the primary cause of its appearance is usually one - from external damage.
Inflammation, which causes a thorn, is also an external factor. Whatever the type of cloudiness, it is necessary to consult a specialist in any case.
Causes of blurred vision in the morning
After waking up, does it take you a few minutes for the world around you to become clear? Many people face this. There can be many reasons for blurred vision: from improper sleeping posture to diabetes. Today we will talk about them.
1. Some medications.
Antihistamines, sleeping pills, cold and high blood pressure medications can reduce tear production. If you take medications before bed, you may experience blurred vision and dry eyes in the morning. Be sure to discuss your medication regimen with your doctor.
2. Drinking alcohol before bed.
Alcohol causes dehydration of the body. This leads to dryness and cloudiness in the eyes.
Fuchs
endothelial
dystrophy . This condition causes the cornea to swell during sleep. After waking up, clarity of vision can take a long time to recover—during the day. Fuchs' dystrophy is more common in women than in men. Symptoms usually develop by age 50.
4. Sleep on your stomach face down.
This position can cause drooping of the upper eyelid. This not only causes blurred vision, but also watery eyes and burning sensation. An additional risk factor is being overweight.
5. Allergies.
It can cause itching, swelling and watery eyes, as well as dry eyes, which can cause blurry vision. If you experience a flare-up of allergies in the morning, the problem could be dust mites, laundry detergent, or pet hair. Determine the source of the allergy and eliminate it.
6. Sleeping in contact lenses.
Lenses prevent oxygen from reaching the eyes. This leads to blurred vision in the morning. Therefore, it is important to follow the instructions for wearing and caring for your lenses.
7. Problems with blood sugar levels.
Too much or too little sugar can cause blurred vision. In this case, you will also experience dizziness and weakness. If symptoms appear, do not delay going to the doctor.
8. Problems with the sebaceous glands.
Sometimes the sebaceous glands that are located next to the eyelashes produce too little sebum. This can cause irritation and blurred vision in the morning.
9. Dried tears.
Tears moisturize and protect the mucous membrane even during sleep. Sometimes they can dry out on the surface of your eyes and you won't be able to see well when you wake up.
In most cases, there is no need to worry - just wash or blink. But sometimes blurred vision persists for several days and is accompanied by other symptoms:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- tingling and numbness of the limbs;
- slurred speech;
- nausea;
- ringing in the ears;
- problems with coordination.
In this case, you should contact a specialist so that he can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Source
Symptoms of corneal clouding
People do not immediately notice problems with their visual organs. For example, a speck got in, it became difficult to blink and nothing was visible, the speck was taken out, but the discomfort continued.
It would seem that you should not pay attention to such nonsense as a speck, but you need to monitor other symptoms; it is possible that clouding is already beginning to appear. But you can’t start a disease, because no one wants to remain blind because of some speck.
Symptoms of corneal clouding may include the following:
- Pain, foreign body sensation.
- The eye begins to turn red, blood vessels burst.
- Excessive tearing occurs.
- It becomes difficult for the eye to perceive bright light, increased sensitivity in light.
- The cornea becomes cloudy, a white sore appears in the form of a scar or spot.
- Visual changes can be either at the edge or in the center of the pupil.
- Vision deteriorates. How strong depends on the area where the cloudiness spreads. If the entire cornea or its central part is damaged, then it is unlikely that you will be able to see anything with the affected eye; if a small part or a peripheral area of the cornea is affected, then it will be worse visible.
Having identified the symptoms of a cataract, you should take timely measures to treat this disease.
Having discovered the disease, you need to urgently contact a specialist for help so as not to be left without vision at all.
Causes and symptoms
Blurred vision is a symptom of ophthalmological diseases. In this case, the visual organ may remain visually normal, or may become cloudy. Visually, the whites of the eyes may become cloudy after hard work at a computer monitor or fatigue. This condition goes away after rest.
Additionally, symptoms may appear: floaters, decreased visual acuity, double vision, fatigue, foreign body sensation. Visually you can see lacrimation, an expanded vascular network, and loss of shine.
Overwork
The person notes eye fatigue, blurred vision, and a feeling of sand. Visually: redness of the sclera, lacrimation. This happens from lack of sleep, prolonged work at the computer, watching TV, or working with small objects. A cloudy look is characteristic of dry eye syndrome.
Ophthalmic diseases
External clouding occurs due to diseases associated with disruption of the structure and function of the visual organ. As a rule, they are accompanied by decreased visual acuity, blurred vision, and blurred vision.
- A cloudy pupil occurs with cataracts due to a clouded lens.
- Cloudiness of the cornea is characterized by the formation of a white spot - a cataract.
- Cloudy, reddened whites of the eyes in humans can be caused by inflammatory causes (conjunctivitis, uveitis and others).
- Vitreous opacities, glaucoma, myopia and hypermetropia are diseases characterized by blurred vision. However, the eye itself is visually normal.
- Mechanical damage. After an injury, a foreign body, or a burn, the protective film of the eyes is damaged, vision becomes cloudy, and the conjunctiva turns red.
- Age-related thinning of the membranes of the eyeball gives the sclera a blue tint.
General diseases
The sclera of the eyes become cloudy due to blood acidosis (a shift in blood pH to the acidic side). Acidosis is caused by intoxication of the body, kidney disease, decompensation of diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis. Externally from the visual organ: loss of shine, pale mucous membrane.
Improper care
After wearing lenses for a long time, your eyes become cloudy. Poor care, incorrectly selected glasses, as well as the use of low-quality cosmetics and makeup removers can cause a pathological symptom.
Natural periods
Cloudy eyes are possible in a newborn; later they become brighter and can change the color of the iris. Cloudiness occurs in pregnant women due to changes in the woman’s hormonal system.
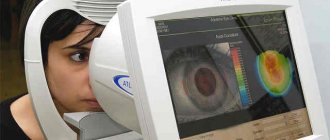
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will ask about the symptoms, previous injuries to the visual organs, and conduct a thorough examination to complete the picture.
Before the examination, eye drops are usually instilled half an hour before the examination, which help dilate the pupils, this will make it easier to see the problem and discern the reason for the patient’s visit. The doctor directs a special bright lamp to the organ of vision, takes a microscope and examines the condition of the problem organ.
Most often, the disease occurs in older people over 55 years of age, which often results in complete blindness.
The cells that sense light wear out over time, and in their place spots appear on the retina.
Initially, distorted vision or blurred perception appears. Straight lines appear wavy, and black dots appear in the field of vision. The listed signs are harbingers of complete loss of vision.
The doctor can even show the patient that he actually has this disease. The ophthalmologist has a special device called an Amsler grid.
The patient’s task is to focus his gaze on the indicated point in the grid; if the surrounding lines appear not straight, but wavy, then most likely, clouding of the cornea of the eye is present and its further development is expected. It is necessary to prescribe treatment immediately.
Fluorescein angiography allows you to examine the retina and confirm the diagnosis.
The disease, without proper attention, constantly progresses. If it is not diagnosed and treated in time, you can completely lose your vision.
Classification
There are different types of cataracts in children, they are distinguished depending on the reasons that led to the development of the disease:
- Congenital cataract . This type is diagnosed either immediately after the birth of the child or after a few weeks of his life. This pathology can be transmitted from parents, and also develop due to metabolic disorders in the newborn.
- Acquired cataract. This type appears for several months and even years after the baby is born. Pathology can appear due to eye injury or after surgery on the visual organ.
- Secondary cataract. Appears when complications occur after cataract surgery. In this case, clouding of the posterior capsule of the lens occurs, and surgical intervention is also required to treat this type of disease.
Due to its wide prevalence, congenital cataracts are classified into a separate classification based on the location of the opacification. There are the following types, which will be discussed below.
Spot
This species is quite rare, and the manifestations of pathology are not so noticeable. Vision, for example, decreases slightly. However, with a further increase in visual load, for example, at school, a child’s vision may deteriorate. This type of cataract develops pointwise and has the following symptoms:
- Cloudiness on the lens spreads in the form of individual dots or scattered areas of a heterogeneous type;
- The color of the protein does not change or becomes slightly lighter than usual;
- The decrease in vision is not severe, most often manifested by blurred images.
The development of this type of cataract is associated with one of the following reasons:
- Pathologies of chromosomes.
- Prematurity.
- Infection of the fetus during pregnancy.
- Systemic diseases of the background type (diabetes mellitus, problems with calcium metabolism, Wilson's disease, autosomal recessive syndrome, hypoglycemia).
Clouding of the cornea of the eye: treatment
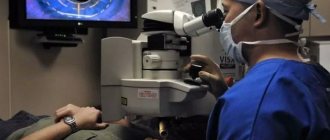
Only a doctor knows how to carry out treatment; by contacting him, the patient can receive some instructions and undergo treatment at home, but in most cases temporary hospitalization or a short hospital stay is required for a number of procedures. Treatment depends on the cause of the disease; drops, antibiotics or steroids may be prescribed.
At the initial stage of the disease, conservative treatment methods are used, injections, physiotherapy and ultrasound are performed.
More complex coarse opacities in the form of scars have to be dealt with only surgically. Laser surgeries and donor corneal transplants are performed if the patient has appropriate indications.
Regardless of how long the disease has been occurring, or whether an inflammatory process is present, anti-inflammatory and absorbable drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments or drops.
A solution of ethylmorphine hydrochloride, proteolytic enzymes and instillation of potassium iodide are used in the form of drops or injections for the best absorption of the drug. The course of treatment usually lasts 10 days.
Electrophoresis with hydrocortisone can smooth out the scars a little, make them less rough, which will at least allow you to move your pupils painlessly and see at least a little better.
This course of treatment is carried out every 2 months for 15 procedures lasting 15 minutes.
When the eyes are clouded from syphilis or tuberculosis, treatment is required not for the cataract, but for the underlying disease.
Having diagnosed the disease, in order to maintain your health, you need to undergo treatment. The ophthalmologist will prescribe how and what to take; in certain cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Consequences
Damage to the cornea of the eye is dangerous because you can completely lose your vision and become blind. This occurs if the disease is neglected and left untreated.
In the early stages of the disease, you can somehow manage with local treatment, but then you won’t be able to recover without surgery. You should worry about your health in advance.
During inflammation, discomfort occurs, nerve endings are irritated, eyelid spasms are caused, profuse lacrimation appears, the eyes turn red, pain occurs from bright light, and as a result, vision deteriorates significantly. Such symptoms occur when a large speck gets into the eye.
An inflamed cornea can have lesions of various shapes, which over time enlarge and grow, and the boundaries are blurred. When the inflammation subsides, a scar forms, which is a white thorn.
To avoid unpleasant consequences and not remain blind, you need to monitor your health and take action at the first symptoms of opacities.
Clouding of the cornea in children
Corneal opacity in pediatric ophthalmology is a fairly common disease. A tenth of the registered diseases associated with blindness in children are related to corneal opacities.
The appearance of a cataract in a child is influenced by several reasons:
- Congenital (occurs in utero).
- Hereditary (transmitted at the genetic level from parents).
- Traumatic (mechanical damage to the pupil).
- Inflammatory (due to inflammatory processes).
- Metabolic (disruption of normal processes).
Diagnosing clouding in children is quite difficult. There are no reliable methods for detecting the disease in children. Symptoms are visible only externally; the child may not complain because he either does not yet know how to speak or does not understand how to explain what is happening.
In treatment, conservative methods are ineffective, and surgical intervention is associated with great risk, and many technical difficulties arise. Adult diseases of the visual organs are much easier to treat.
Corneal transplant operations in children are less effective than in adults, which is why this method is not considered acceptable. The body's response to the donor cornea may be inadequate.
Clear actions for the treatment of childhood clouding of the eyes have not yet been developed, prognoses have not been studied, the principles of preparation for surgical intervention have not been worked out, and the timing of operations has not been determined. There is also no general system of visual rehabilitation.
Corneal clouding in children is difficult to treat, but if there is a chance of recovery, then it is imperative to carry out medical therapy.