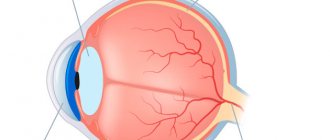
Cornea –
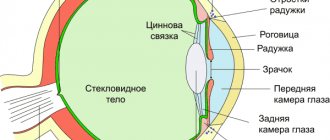
the transparent shell of the eye, which plays the role of light refraction and protects the eye from the effects of negative external factors. It consists of several layers, has the shape of a convex-concave lens and occupies 1/6 of the surface of the eyeball. Disorders most often develop in the endothelial layer of the cornea. Corneal edema is a fairly common complication of contact vision correction and develops as a result of a disorder of corneal metabolism and a decrease in the supply of oxygen to the cornea when using contact lenses. When the cornea edema, as a rule, a veil appears before the eyes, this complication is especially pronounced after a night's sleep, and by the evening it almost completely disappears. In some cases, the formation of bullae (bubbles) and microcysts is possible, causing photophobia, redness, and sharp, sudden pain in the eye.
Why does swelling occur?
Corneal edema can be caused by both external and internal causes. The most common are:
Diseases of the cornea of the eye + photo
- Allergic reaction. The surface of the eye may become swollen, red and irritated upon contact with chemicals, smoke or dust in the air, pollen, or animal hair.
- Ophthalmological diseases caused by bacterial or viral infections: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis.
- Injuries to the cornea - blows, burns, micro-abrasions when villi or particles of dirt get into the eye most often become the causes of severe swelling of the stratum corneum, which is additionally aggravated by the introduction of infection into the wound.
- Incorrect use of contact lenses or incorrectly selected contact lenses.
- Surgery on the organs of vision - the cornea swells after surgery to remove cataracts and replace the lens due to mechanical stress and due to the medicinal solution used in the surgical area. It usually occurs a day after the intervention.
- Increased intraocular pressure and development of glaucoma. With increased pressure inside the eye, the outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted. It accumulates in the eye structures and causes swelling of the surface layer.
Important: in newborns and infants, corneal edema can be a consequence of birth trauma or one of the signs of congenital endothelial dystrophy. In adults, sometimes the cornea swells due to inflammation of the optic nerve. This pathology is very serious, since it is the optic nerve that is responsible for transmitting visual impulses to the corresponding centers of the brain and for blood microcirculation in the organs of vision. If the optic nerve is damaged, the normal functioning of not only the eyes, but also the brain is threatened.
Reasons for appearance
There are several factors that influence the transparency of the shell:
- Viral infection. Ordinary conjunctivitis can lead to leukoma if accompanied by inflammatory processes affecting the cornea.
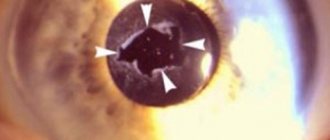
- Violation of the integrity of the shell. First, the surface layer is injured, then bacteria get involved. The infection eats away at the cornea and causes the formation of an ulcer, which over time transforms into a cataract.
- Surgical intervention. The inside of the shell is lined with endothelial cells that cannot regenerate after injury. With age, their concentration decreases. The operation leads to the fact that the lack of endothelium decompensates the cornea. As a result, degeneration of the membrane and its clouding.
A lack of vitamin A in the body and improper use of contact lenses also threatens the development of leukoma.
How it manifests itself
Symptoms of corneal edema vary depending on the cause. If it is a viral, bacterial or fungal infection, the symptoms will be similar:
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- burning, itching;
- pain of varying degrees;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- blurred vision;
- purulent discharge from the eyes, forming dense crusts on the eyelids overnight.
Swelling due to allergies manifests itself in almost the same way, with the difference that there is usually no pain, and if there is any discharge, it is insignificant and transparent.
If the cause of corneal edema is any neoplasms in the organs of vision or brain, or increased intraocular pressure, then the patient will complain of the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- distortion of the visual image;
- rapid eye fatigue.
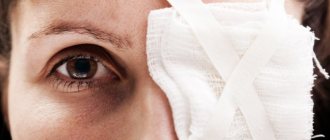
The photo shows what corneal edema looks like in a patient with advanced keratitis
Swelling of the cornea and eyes in general sometimes signals kidney dysfunction and congestion in the body. In this case, in addition to swollen eyes, the following symptoms are noted:
- lower back pain;
- difficulty or frequent urination;
- swelling of the limbs.
With edema, the cornea thickens and becomes denser, becoming less transparent. When the eyeball is illuminated with a slit lamp, folds and vertical lines are visible.
Symptoms of the condition
Corneal edema is sometimes asymptomatic, and a person may not even know that he has suffered from the disease. Or it may occur with clinical manifestations:
- blurred vision;
- distorted perception of objects;
- decreased visual acuity;
- foreign body sensation;
- photophobia;
- discomfort or pain;
- hemorrhages;
- corneal clouding.
Diagnostic methods
In order to accurately establish the cause of swelling of the cornea and differentiate possible pathologies, the following methods are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the eye (ophthalmoechography) - allows you to get a more complete picture of the condition of the eye not only on its surface, but also inside. Based on changes in the lens, retina, and vitreous body, the doctor can determine the extent of the lesions and make an accurate diagnosis.
- Optical pachymetry is the measurement of the thickness of the cornea of the eye using a non-contact method using a slit lamp.
- Schirmer test - during this procedure, the volume of tear fluid is determined.
- Bacteriological examination of purulent discharge or eye scraping if a bacterial infection is suspected to identify the type of pathogenic microorganisms.
Based on all the data obtained, the doctor draws up an anamnesis and determines treatment tactics.
An experienced doctor will be able to diagnose corneal edema by external signs; further diagnostics are carried out to differentiate or identify other pathologies
DO YOU STILL FIND THAT IT'S HARD TO GET CLEAR VISION BACK?
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against blurred vision is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the eyes are very important organs, and their proper functioning is the key to health and a comfortable life. Sharp pain in the eye, clouding, dark spots, sensation of a foreign body, dryness or, on the contrary, tearing... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
window.RESOURCE_O1B2L3 = 'kalinom.ru'; var m5c7a74e42d742 = document.createElement('script'); m5c7a74e42d742.src='https://www.sustavbolit.ru/show/?' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '= 13498&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + document.title +'&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000); function f5c7a74e42d742() { if(!self.medtizer) { self.medtizer = 13498; document.body.appendChild(m5c7a74e42d742); } else { setTimeout('f5c7a74e42d742()',200); } } f5c7a74e42d742(); window.RESOURCE_O1B2L3 = 'kalinom.ru';
Take an online visual acuity test right here and now ==> jQuery(document).on('click','.spoiler-trigger',function(e){e.preventDefault();jQuery(this).toggleClass(' active');jQuery(this).parent().find('.spoiler-block').first().slideToggle(300);}) jQuery('#ostrotazreniya').load('https://etoglaza .ru/test/1/test.html'); “+”ipt>
(function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-332662-1', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-332662-1', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks ');
EtoGlaza.ru » Eye diseases » Corneal diseases
How to treat
Treatment of corneal edema is carried out in two main directions:
- directly relieve swelling and other associated symptoms;
- eliminate the cause of these symptoms.
The methods of therapy and the drugs used are determined by the diagnosis and degree of damage to the cornea.
- In case of allergies caused by external pathogens, it is necessary to first eliminate the allergen irritant. Next, antihistamines of local and systemic action are used. Floxal drops have proven themselves well. In case of a severe allergic reaction, hydrocortisone ointment is applied to the eye. But the main point in successful treatment is identifying the allergen. Until it is detected and the patient’s contact with it is excluded, the allergy will not go away. It will bother you constantly, despite the medications used. Determination of potential allergenic substances is now carried out by testing blood from a vein in some laboratories.
- If your eyes become swollen and irritated from incorrectly fitted contact lenses, you should consult a specialist and choose the correct optical system. You can put on new contact lenses only after the inflammation and swelling have completely subsided. For this, eye drops with a moisturizing, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect are used for a course of 5–7 days - Ofloxacin, Tsiprolet, etc. In case of severe damage to the cornea and the development of keratitis, ointments that stimulate the restoration of eye tissue, for example, Korneregel, can be additionally prescribed. If the symptoms of infection do not decrease by day 3–4 of therapy, systemic antibiotics are added to the treatment regimen. Usually it is possible to relieve inflammation and swelling of infectious etiology in 5–14 days.
- Postoperative swelling of the stratum corneum is not considered a pathological condition and does not require systemic treatment. With successful healing of the sutures and tissue restoration, the swelling goes away on its own after 1–2 weeks. To speed up the process, vasoconstrictor and moisturizing eye drops may be prescribed.
- Swelling of the cornea, caused by increased intraocular pressure or a symptom of glaucoma, is treated in conjunction with the underlying disease. The standard treatment regimen involves the administration of Atropine or its analogues and B vitamins. The course of treatment must be completed comprehensively and to the end. Stable high pressure inside the eye provokes retinal detachment, disruption of its structure, as well as damage to the optic nerve, which leads to blindness if left untreated.
Anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antihistamine eye drops are the simplest and most convenient way to get rid of swelling of the eye structures
Swelling after injury is usually not treated if there is no mechanical damage to the eyeball. To eliminate external hematoma, ointments and gels are used that stimulate blood circulation - Troxevasin, Heparin, Bruise-off. Folk remedies that are effective in this case are various lotions and compresses. If the injuries are serious, treatment is determined by a traumatologist together with an ophthalmologist. In difficult cases, surgery will be required.
Surgical treatment of corneal swelling
Transplantation of an irreversibly damaged cornea is called keratoplasty in ophthalmology. The operation is performed if endothelial dystrophy develops after surgical removal of cataracts. With the help of keratoplasty, it is possible to restore the transparency of the cornea and clarity of vision, and completely eliminate the causes of the pathology.
Based on the area of the cornea that needs to be replaced, the following types of surgery are distinguished:
- total;
- subtotal;
- local.
Penetrating keratoplasty allows you to restore a person’s visual functions even with very deep and extensive damage to the eye tissue
Depending on the depth of penetration, keratoplasty can be:
- through;
- front;
- back layer.
The operation consists of removing the affected area layer by layer using special instruments and implanting an artificial flap. The procedure itself is usually performed under local anesthesia and does not take more than a quarter of an hour. But the sutures heal after surgery for at least six months. For the first time after surgery, the patient must wear a bandage and protective lenses. Then, until complete recovery, remember the precautions: do not overstrain your eyes, do not lift heavy objects, avoid both overheating and hypothermia.
Be careful with folk remedies against edema: they will not help with degenerative changes in tissues, and with allergic swelling they can only intensify unpleasant symptoms
What treatment does modern ophthalmology offer?
Therapy for leukoma can be carried out either conservatively or surgically. In the first case, the doctor prescribes the use of eye drops, physiotherapeutic procedures, eye exercises, and gives recommendations on nutrition and lifestyle.
Drug treatment may include the following medications:
- anti-inflammatory drops, ointments, which contain components containing corticosteroids;
- preparations for resorption of scar tissue - ethylmorphine hydrochloride and potassium iodide;
- agents that improve blood circulation to the retina with a vasodilating effect.
The choice of a specific drug, dose, frequency and duration of administration is determined by the doctor individually for each patient. Good effectiveness of treatment can be obtained with the help of physiotherapy: electrophoresis, phonophoresis in combination with hormonal medications or natural ingredients.
Conservative therapy is used in the earliest stages of the disease, when there are no pronounced pathological changes within the visual system. In cases where the disease is advanced or drug therapy has not brought the desired result, the doctor decides to perform an operation.
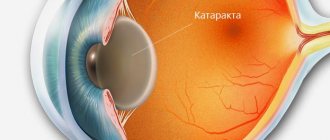
Video: Treating a cataract
Surgical treatment of clouding is considered more effective because it eliminates the pathology, stops its progression, reduces the risk of complications and restores vision. Modern ophthalmology has several ways to treat ocular leukoma:
- keratoplasty - excision of the clouded part of the cornea, with the further use of drug therapy to restore the cornea;
- transplantation - transplantation of a cornea from a donor (allows you to completely restore vision, but problems often arise when searching for a donor, which slows down the operation);
- cosmetic tattoos - eliminate the defect itself, but do not restore visual functions;
- implantation of an artificial lens - often performed when the cornea is injured (does not restore vision, but relieves constant discomfort).
It is important to understand that a small spot on the periphery of the cornea is not an indication for surgery. Such procedures are carried out only strictly according to indications and there is no effect from conservative treatment
If the patient has contraindications to any operation or the person himself refuses such treatment, the doctor may recommend cosmetic correction of the pathology using contact lenses.
The prognosis after treatment depends on how badly the cornea is damaged, so everything is individual. Doctors make every effort to preserve the patient’s vision and eliminate aesthetic discomfort.
How to cure an eyesore
Helpful tips for swollen eyes
Swelling of the cornea can be treated with improvised means if there are no contraindications to their use. You should not resort to traditional medicine recipes if the swelling is caused by allergies or open wounds of the eye. A bacterial infection that is accompanied by swelling of the stratum corneum cannot be cured with medicinal plants. In other cases, irritation and swelling can be relieved with gentle home remedies. The most popular, accessible and safe of them:
- Raw potatoes. Wash one medium tuber, peel it, grate it very quickly on a fine grater, and apply the resulting pulp to your eyes. For convenience, you can use gauze cuts, and for greater efficiency, add a spoonful of cold sour cream, cottage cheese or kefir to the potato pulp. Leave this compress on for 10 minutes, then remove any remaining residue and rinse your eyes with cool water. If you do this mask every two to three hours, the swelling and hematoma will go away very quickly.
- Honey solution. Pour two tablespoons of warm boiled water into a glass, add one spoon of natural honey, stir. Apply 2 drops of the resulting liquid to sore eyes in the morning and evening. This remedy can only be used if it is known for certain that there is no allergy to bee products.
- Onion broth. To prepare this medicine, one medium onion is peeled, a glass of water is poured into a fireproof container and put on fire. Cut the onion in half, put it in water, let it boil and cook over low heat for 10 minutes. Then cool the broth and strain off 50 ml. Add exactly 4 drops of boric acid to the onion broth. The resulting medicine is administered into the affected eyes, 1-2 drops two to three times a day.
If there is absolutely nothing available, you can wash your eyes with chamomile infusion or tea leaves, but at the first opportunity you should consult a doctor, undergo an examination and select an adequate treatment regimen.
The essence of pathology
This element of the organ of vision is highly sensitive and protects the eyes from debris by closing the eyelashes. In addition, polluting particles are washed out of the organ of vision with the help of tear fluid.
When an anomaly occurs, the characteristics of the cornea change, light transmission decreases, and photophobia occurs. This process is accompanied by loss of visual acuity, especially in the morning and evening. Due to abnormal changes, swelling in the cornea can lead to destruction of its substance. Subsequently, these zones undergo necrotic changes.
Prevention of corneal swelling
In most cases, corneal edema can be prevented or at least significantly reduced the risk of its development. To do this, it is enough to follow these simple preventive measures:
- Contact lenses for daily use must be removed at night, do not be lazy to clean and store only in a solution specially provided for this. If contact lenses or solution have expired, they are disposed of and replaced with new ones. All procedures - taking out and putting on, cleaning and disinfecting lenses - are performed only with clean hands.
- When swimming and diving in open water or public pools, use special masks and goggles, and in sunny weather protect your eyes with sunglasses.
- Try not to read in transport, do not work with texts and documents in poor lighting.
- Do not overload your eyes when working or relaxing at the computer, limit watching TV shows, especially before bed.
- Monitor the expiration dates of decorative cosmetics and personal hygiene products.
- If you are prone to allergies, remove potential irritant allergens from your diet: citrus fruits, red fruits, chocolate, seafood.
- If you are often bothered by irritation and redness of the eyes, the organs of vision quickly become tired, and visual acuity periodically decreases, do not put off visiting an ophthalmologist. The sooner a violation is detected, the faster you can get rid of it.
Thus, corneal edema is not such an innocent phenomenon as many people believe. Sometimes this is a symptom of eye irritation from poor-quality cosmetics or water. But also swelling of the stratum corneum can signal an increase in intraocular pressure and threaten very serious consequences, including loss of vision. Corneal edema should be treated depending on the cause of its development. Medications, physiotherapy, and folk remedies can be used. In complex cases, with deep and extensive injuries or irreversible tissue changes, surgical intervention is performed.
Causes
There are the following reasons why corneal edema may occur:
Allergic reaction to cosmetics, household chemicals, pet hair or plants. An inflammatory process caused by infection entering the eye. Eye injuries - a blow, a burn from chemical agents, foreign bodies getting into the eye due to negligence or failure to comply with safety precautions. Incorrectly selected contact lenses or their improper use in violation of hygiene rules. It is not uncommon for swelling to develop after cataract surgery. After replacing the lens, which is performed with this type of surgery, the cornea naturally swells due to the passage of a large amount of a special solution through it. Any eye inflammatory diseases: conjunctivitis, chronic blepharitis, keratitis, iritis.. Another possible reason is increased intraocular pressure, and glaucoma developing in connection with this.
Another possible reason is an increase in intraocular pressure, and glaucoma developing in connection with this.