Why do negative consequences occur after lens replacement?
If the operation to replace the lens for cataracts is performed by an experienced ophthalmic surgeon, then it does not entail any special problems. For professionals who have performed more than one surgical intervention, removing the lens and placing an implant in its place - an intraocular lens - is a simple and quick operation. The recovery process is smooth for most patients. The likelihood of complications occurs infrequently. But still they cannot be excluded, although they are quite rare phenomena.
Each type of complication has specific causes. After surgery, swelling of the eye often occurs. Many patients encounter this problem during the postoperative period. It is usually associated with a weakened cornea. Another reason is the peculiarity of the body’s reaction to ultrasound. It is used in cases where the patient seeks medical help too late. If the cataract has been advanced, then ophthalmic surgeons need to use more powerful ultrasound waves. This often has an increased impact on the eyeball.
A possible cause of complications after lens replacement for cataracts can also be medical error. Such situations are not so common in medical practice, but they cannot be excluded. Problems may arise due to technical or tactical errors of the doctor who performed the operation. Medical errors usually occur accidentally. Therefore, it is difficult to predict their risk. Cataract surgery is the only possible method of treatment and ophthalmic surgeons have sufficient experience in performing it. But this does not negate the likelihood of complications arising due to the doctor’s fault.
Principles of treatment of corneal edema
Edema is treated by eliminating the cause. If there is a bacterial or viral infection, antibacterial and antiviral drugs must be used. Hard lenses are replaced with breathable ones. They also reduce the time they are worn to give the eyes a rest.
If swelling causes dry eye syndrome, artificial tears are prescribed (Oftagel, Vidisik, Systane-ultra). Severe cases of corneal edema require the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Dexamethasone, Tobradex).
Choice of therapy for corneal edema
- Infectious lesions require the use of antibacterial drugs, additionally antiviral and antifungal drugs. In case of a calm course, ointments and eye drops are prescribed, and severe lesions are also treated with tablets and injections. During the treatment period, you should avoid using cosmetics and carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Allergic lesions are treated with antihistamines.
- Specifically, corneal edema requires the prescription of anti-inflammatory non-hormonal drugs. I stop the pronounced process with glucocorticoids (short course). It is better not to use contact lenses during treatment.
- For swelling of the conjunctiva, I prescribe anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor drops.
- If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment can be resorted to. If the cornea is damaged, it is transplanted or densified with ultraviolet light.
Incorrect use of lenses
The most common cause of corneal edema is improper use of contact lenses. Incorrect selection, prolonged wear, sleeping in lenses and using old ones that have expired - all this can cause swelling.
Eliminating these causes is simple; all you need to do is change the lenses, choose the right model that allows oxygen to pass through well, remove the lenses at night and when your eyes are tired, and additionally use moisturizing drops. It is important to care for your lenses and use special aseptic compounds to clean them.
An ophthalmologist may prescribe medications to speed up corneal recovery. Do not use contact lenses until swelling is eliminated. Exposure to a foreign body can aggravate the condition and injure the eye.
If the measures taken do not have the desired effect, and the swelling recurs, you must stop wearing contact lenses. Swelling caused by lenses should be treated by a qualified physician as there may be hidden risk factors. For swelling that is complicated by vascularization, on the contrary, it is recommended to wear hard lenses. Only an ophthalmologist can select and prescribe them.
Infection and allergy
For infectious corneal edema, diagnosis is aimed at identifying pathogens, and treatment at combating them. The patient is prescribed antimicrobial and antiviral drugs, usually drops with antibiotics (Levomycetin, Tobrex, Floxal, Tsiprolet). Additionally, eye ointments and tablets are prescribed.
If the cause of swelling is an allergic reaction, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and allergist. Contact with the allergen should be avoided and antihistamines should be used. Almost anything can be an allergen, so you need to conduct a test to identify the irritant in a specific patient.
With allergic edema, other symptoms usually also occur (itching, sneezing, runny nose, difficulty breathing). A comprehensive examination will reveal allergies in cases where swelling is the only symptom and there is constant contact with the allergen.
It is noteworthy that after surgical intervention in the eyeball, swelling is observed in almost all cases. If it does not disappear within 1-2 weeks, you should consult a doctor. Prolonged swelling after surgery, as a rule, does not disappear on its own. To eliminate swelling after surgery, drops are prescribed that accelerate tissue regeneration (Solcoseryl, Adgelon, Erisod, Emoxipin).
What are the intraoperative complications during lens replacement?
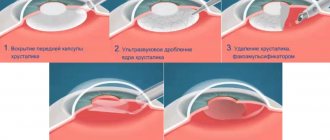
Lens replacement for cataracts is considered a well-established procedure. But even with this high-tech operation, complications are possible. One of them is the rupture of the wall of the capsule, inside of which the clouded lens of the eye was previously located, and the loss of its crushed particles into the area of the vitreous body. This complication often entails the development of glaucoma and retinal damage. Repeated surgery can help correct the situation. Typically, optometrists monitor the patient for 2-3 weeks. After this, the clogged vitreous is removed surgically.
Displacement of the intraocular lens towards the retina is another type of complications that are possible after replacing the lens for cataracts. This happens due to improper placement of the implant. This provokes swelling of the macula - the very center of the retina of the eye, in which light rays are focused. In this case, the only possible way to eliminate this problem is to perform a repeat operation and replace the “wrong” lens with a new one. A special type of complication is suprachoroidal hemorrhage. This is an accumulation of hemorrhagic contents in the space between the sclera - the white membrane of the eye - and the choroid. In most cases, hemorrhage due to cataracts occurs in patients of advanced age or concomitant diseases: glaucoma or hypertension. The danger of such a complication is that it can lead to a rapid decrease in vision and loss of the eye.
Inflammatory processes as complications after lens replacement
They should be used for 2-3 weeks. The regularity of use is selected individually.
If the patient’s immunity was weakened even before the diagnosis of cataract, then the usual signs of inflammation may be accompanied by symptoms of uveitis or iridocyclitis. With uveitis, various parts of the choroid of the eye become inflamed:
- iris;
- ciliary body;
- choroid.
This disease manifests itself as redness, pain in the visual organs, photosensitivity, blurred vision, and increased tearfulness. In some cases, floaters and floating spots may appear before the eyes. The basis of treatment for uveitis is the use of mydriatics, steroids, and immunosuppressive drugs.
Another ophthalmological disease that can be a consequence of the inflammatory process is iridocyclitis. This pathology affects the iris and ciliary body. The disease “makes itself felt” with swelling, redness, and pain. In particularly difficult cases and with advanced cataracts, the iris may change color, the pupil may narrow and become deformed.
Conservative treatment of iridocyclitis includes the following types of therapy:
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiviral.
Types of complications that can be treated conservatively
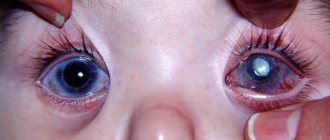
Hyphema is a negative consequence that can occur after cataract surgery. This is a hemorrhage into the anterior chamber of the eyeball, filled with intraocular fluid. That is, there is an accumulation of blood between the lens and the iris. Hyphema occurs due to the fact that during the operation the ophthalmic surgeon accidentally damaged the vessels of the ciliary body or the iris of the eye. This condition does not pose a serious danger to the patient, although it may persist for several months. Hyphema does not cause pain and does not impair vision. It is treated with additional rinses. Doctors most often prescribe hormonal drops, for example, Dexamethasone, and mydriatics, for example, Atropine.
Unsuccessful cataract surgery can cause increased intraocular pressure. This condition is often called "postoperative glaucoma."
Reasons that cause increased intraocular pressure include:
- inflammatory processes or hemorrhages inside the eye;
- gel-like suspensions used during surgery are not washed off well enough;
- displacement of the artificial lens closer to the iris and its pressure on the pupil;
- moisture entering the operated eye within a week after surgery;
- exposure to too much bright light on the iris.
Patients with postoperative glaucoma report pain in the eyes, increased lacrimation, and blurred vision. The pressure is normalized after using special drops, for example: Timolol, Brinzopt, Pilocarpine. If treatment with drops does not help, then the ophthalmologist prescribes a puncture with washing of the clogged ducts of the eyeball.
Postoperative astigmatism is another possible complication that can occur after cataract removal. When the lens is replaced, the shape of the cornea changes. Because of this, the refraction of the eye is impaired and vision becomes blurred. Postoperative astigmatism is corrected with contact lenses that have a toric design, cylindrical or spherocylindrical glasses. It is very important to distinguish between the symptoms of astigmatism, which can develop several months after implant placement, and diplopia, which is a side effect of surgery. With diplopia, the functions of the eye muscles are impaired, causing the image to appear in two. This condition resolves within a few days and does not require treatment.
Traditional medicine recipes for corneal edema
Self-medication for corneal edema can be very harmful and require serious and long-term therapy. Traditional medicine can only be used as an additional symptomatic effect, but only with the permission of the attending physician.
Proven methods for treating inflammation in the eye:
- Honey. Add a little honey to boiled water (1:2). Place 2 drops into eyes twice a day.
- Onions and horseradish. Grind the ingredients and dilute with water (1:1). Leave for 15 minutes until the bitterness goes away. Moisten a cotton pad and apply to your eyes.
- Mulberry. For swelling and pain in the eyes, a decoction of mulberry leaves and bark helps: boil a large spoonful of the ingredients (a glass of water) in a water bath for 15 minutes. Instill a few drops 3-5 times a day. Effective for dry eyes.
- Potato. Swelling can be eliminated with raw potatoes. You need to grate one tuber, put the pulp in gauze and put it on your eyes for 20 minutes.
- Onion. You can make an eye wash from onions. You need to boil a medium onion and add a couple of drops of boric acid to the broth. Use twice daily.
- Herbal mixture for severe pain. Mix flaxseed, cornflower and elderberry (a small spoon each), pour boiling water (2 cups), leave for 8 hours and strain. You should rinse your eyes several times a day.
- Prevention of corneal edema involves careful facial care and proper personal hygiene. It is necessary to use only high-quality and hypoallergenic cosmetics, as well as hygiene products. Contact lenses must be selected correctly and purchased at a specialized salon. People over 45 years of age should monitor intraocular pressure and protect their eyes from ultraviolet radiation. It is important to consult a doctor promptly if visual discomfort occurs.
Sources used:
- Modern pharmacotherapy of ulcerative lesions of the cornea / Olga Krivosheina and Igor Zapuskalov. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- New technologies in the treatment of corneal diseases / ed. H.P. Takhchidi. - Moscow: Mir, 2004.
- Cornea. Atlas / Jay Crutchmer, David Paley. - M.: Logosphere, 2007.
- National Eye Institute
What complications after lens replacement require surgery?
Serious complications may occur after cataract removal. They require repeated surgery. If the intraocular lens, which is placed inside the capsular bag instead of the clouded lens, is not properly fixed, the IOL can independently move back, forward or to the side. In such situations, the patient complains of a double image of distant objects and rapid fatigue of the visual organs. This type of complication is considered quite severe. Its danger is that if no measures are taken, the patient may develop glaucoma or retinal detachment. Conservative treatment in this case will be useless. The situation can only be corrected by repeating the operation. During this procedure, the ophthalmic surgeon will adjust the position of the artificial lens.
One of the complications that arise after cataract removal is rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. This is a rather serious pathology that requires surgical intervention. Rhegmatogenous detachment occurs because the retinal layer, when separated from the wall of the eyeball, loses access to nutrients and begins to die. This condition is dangerous because it can lead to complete loss of vision. It can be identified by the patient’s complaints about the appearance of a veil before the eyes. Treatment is carried out by:
- laser coagulation - a medical procedure with which ophthalmic surgeons eliminate dystrophic and degenerative changes in the retina;
- vitrectomy - a surgical operation used for hemorrhages in the vitreous body, retinal detachment, injuries to the visual analyzer;
- extrascleral filling - a method of treating retinal pathologies by squeezing it with a special filling fixed on the outside of the sclera.
A rare, but very dangerous complication after removal of cataracts is endophthalmitis. This is a severe inflammatory process in which pus accumulates in the vitreous body. It occurs due to infection entering the eye during surgery, when the tear ducts become infected. Endophthalmitis often develops in people with weakened immune systems and in those who have suffered other ophthalmic pathologies, for example: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, etc. Symptoms of the disease:
- sharp pain in the eyes;
- swelling in the eyelid area;
- significant decrease in vision;
- redness of the sclera.
In case of endophthalmitis, emergency hospitalization in the ophthalmology department is necessary. If the necessary measures to treat the disease are not taken in a timely manner, this may lead to loss of the eye or the development of meningitis.
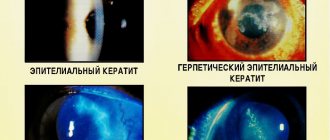
Symptoms of corneal edema
When the cornea edema, pain and pain in the eye are felt, lacrimation and photophobia increase. Blinking and moving your eyes causes discomfort. Vision may be blurred, making it difficult for the patient to see small details. Visual acuity decreases. Redness and inflammation are visually noted.
Chronic edema causes increased vascularization and impaired transparency of ocular structures. The condition, caused by the activity of bacteria, viruses and fungi, has similar symptoms. Discomfort with corneal edema is caused by its thickening and decreased transparency. Because the cornea is responsible for refracting light, clouding of the cornea causes a blurred or foggy sensation before the eyes. When wearing contact lenses, the discomfort increases.
Chronic edema is characterized by vascularization (the formation of blood vessels inside the cornea). It is very important to consult a doctor, because the complication does not manifest itself for a long time, and only an ophthalmologist can notice its signs during biomicroscopy.
Advanced vascularization affects the quality and acuity of vision. Often, surgical treatment is required to preserve visual function with chronic corneal edema.
Can complications arise after a few months?
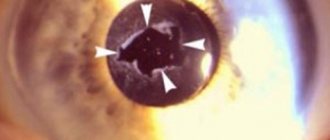
Some types of complications may “make themselves felt” several months after surgery. The main one is the development of secondary cataracts. This condition usually occurs after 6 months to a year. In this case, the cloudiness does not form on the lens. The capsule, inside of which the intraocular lens is located, suffers. Patients note symptoms typical of cataracts. The complication is characterized by:
- blurred image outlines;
- weakened color rendering of objects;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes.
Treatment of secondary cataracts is carried out using two methods. The first is surgical capsulotomy. This operation removes the clogged film of the capsular bag. The second method is to clean the back wall of the capsule using a laser. Another type of complication that can occur after replacing a lens that is clouded by a cataract is cystoid macular edema. The inflammatory process develops in the central part of the retina. It is caused by rupture of the lens capsule or infections in the vitreous. Cystoid macular edema involves damage to the corpus luteum, the most important part of the retina where light rays are focused. The danger of this condition is that early diagnosis is difficult. Symptoms are not clearly expressed. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by optical tomography of the eye and retinal angiography. Anti-inflammatory drugs play an important role in the treatment of the disease.
Surgical treatment of corneal edema
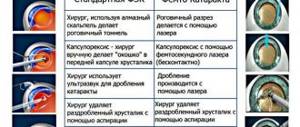
It is very important to monitor the patient's condition after cataract surgery, as the risk of endothelial dystrophy, which is characterized by corneal edema, increases. This complication is rare, but has dangerous consequences. The patient is prescribed long-term antiviral drugs or undergoes a corneal transplant. Keratoplasty restores the transparency of the cornea, stops its pathologies and ensures the functionality of the eye.
Based on the size of the area to be replaced, keratoplasty can be total, local, and subtotal, and based on the layers being replaced, there are end-to-end, anterior, and posterior layer-by-layer keratoplasty. During the operation, the doctor creates a flap using special instruments or a femtosecond laser. Donor material is implanted into the vacant space and sutured to the periphery of the cornea. After surgery, the patient must wear a bandage or protective lenses for some time.
Keratoplasty is performed in one procedure, most often under local anesthesia. A few hours after the operation, the patient is sent home. Recovery after a cornea transplant takes a year. The stitches are removed after 6-12 months. After keratoplasty, you should avoid heavy loads and aggressive effects on the eyes.
Modern medicine also offers an innovative method of cross-linking. The procedure promotes the fusion of collagen fibers, which are the basis of the cornea, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The shell becomes dense and withstands loads. The operation eliminates complications and swelling, as well as reduces astigmatism and improves vision.
How to avoid complications after lens replacement?
In order to avoid complications after cataract removal, you should follow the recommendations of the ophthalmologist. This will speed up the rehabilitation process and avoid complications.
- You should not tilt your head sharply.
- It is better to sleep on the side where the healthy eye is located.
- Make sure that no water gets into the operated eye during hygiene procedures.
- Avoid visual stress. Read less, watch TV, work on the computer.
- Take vitamins, eat more fruits and vegetables.
- Give up bad habits, especially smoking.
- Do not lift anything weighing more than 10 kg.
- Refuse to drive.
If you follow the recommendations given by your doctor after replacing the lens, complications can be avoided.