Corneal opacity
- an opaque formation in the layers of the cornea of the eye. Most often, opacities are white or gray in color, and differ in density and size. In some formations, vessels may grow - vascularization of the cornea. It is worth noting that when clouding occurs, vision can decrease to the point of blindness.
What is corneal clouding?
In ophthalmology, the deviation is called leukoma. The severe anomaly develops as a result of the formation of scar tissue on the cornea. This process disrupts the physiological arrangement of stromal fibers. As a result, the degree of transparency of the cornea decreases and a disruption in visual function occurs.
Usually, clouding is a consequence of damage to an element of the eye (burn, injury, surgery, infection of bacterial or viral origin). Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in elderly patients. However, young people are also not protected from developing leukoma. In exceptional situations, the disease is congenital.
| With a mild course of the disease and timely treatment, eye acuity suffers slightly. But large areas of clouding can cause blindness. |
Symptoms
The degrees of turbidity are usually distinguished by their intensity in accordance with the clinical picture:
- I degree of corneal opacity - cloud. It is detected during an ophthalmological examination with lateral illumination and has the appearance of a gentle smoky change in the transparency of the media, which practically does not affect the function of vision;
- II degree – spot. This is a clearly visible limited opacification of the cornea, which, when localized in the optical zone, leads to a significant decrease in visual acuity (up to 0.1 - 0.3). This degree of corneal clouding can cause a person to be unsuitable for many specialties. In early childhood, a spot on the cornea is often the reason why the child does not develop binocular vision, which leads to concomitant strabismus;
- III and IV degrees of corneal opacity are a real thorn. In this case, the cornea takes on the appearance of porcelain or frosted glass, often with blood vessels growing inside. This degree of corneal clouding is accompanied by a pronounced decrease in visual acuity to hundredths, thousandths, or even light perception.
The patient, as a rule, does not have any difficulty in independently establishing a direct connection between the previous inflammatory eye disease (for example, keratitis) and the subsequent development of corneal opacification, which led to a decrease in visual function. Such vision loss usually does not progress further.
Reasons for appearance
There are several factors that influence the transparency of the shell:
- Viral infection. Ordinary conjunctivitis can lead to leukoma if accompanied by inflammatory processes affecting the cornea.
- Violation of the integrity of the shell. First, the surface layer is injured, then bacteria get involved. The infection eats away at the cornea and causes the formation of an ulcer, which over time transforms into a cataract.
- Surgical intervention. The inside of the shell is lined with endothelial cells that cannot regenerate after injury. With age, their concentration decreases. The operation leads to the fact that the lack of endothelium decompensates the cornea. As a result, degeneration of the membrane and its clouding.
A lack of vitamin A in the body and improper use of contact lenses also threatens the development of leukoma.
Causes of cloudiness
Ocular leukoma is cloudiness of any structure of the eyes, and cloudiness of the stratum corneum of the eye is called corneal leukoma. The causes of cloudy eyes in humans are injuries that result in the formation of a scar. Such damage occurs in the following cases:
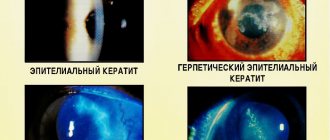
- keratitis (inflammatory process of the cornea);
- inflammatory processes that have spread to the cornea (trachomas, conjunctivitis);
- mechanical injuries;
- chemical injuries;
- surgical interventions on the eye;
- intrauterine fetal infection;
- genetic diseases leading to pathological changes in the organ of vision.
The main causes of cloudy cornea are exogenous factors (infection, injury, burns). Such factors act not only in adults, but also in children, even at the time of embryogenesis. Only genetic pathologies can be classified as endogenous factors. But it should be noted that in such cases the formation of a cataract is quite a rare occurrence and its diagnosis occurs immediately in the delivery room.
Varieties
The pathology is divided into three types depending on the area of turbidity and its intensity.
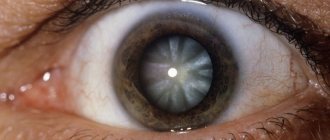
- Cloud. Most often they are located closer to the center of the shell. The cloudiness of a grayish tint has a limited scope. It is extremely difficult to notice it with the naked eye. Due to their minor parameters, clouds do not significantly affect the optical function.
- Spot. They are characterized by higher intensity and can be located in the center or on the sides of the cornea. They negatively affect the ability to clearly and clearly perceive the world around them.
- Belmo. The most dangerous form of pathology. Persistent clouding occurs when tissue scars. Occupies a certain area of the cornea or the entire surface. The cataract has a white or light gray tint and can lead to complete loss of vision.
Classification of leukoma
necessary therapeutic depend on the type of opacities of the cornea . There are three types of corneal transparency:
- Cloud. It looks like a smoky spot with uneven edges. It is difficult to diagnose. Often the patient exhibits a slight decrease in vision.
- Spot. It looks like a pearl-colored dot with clear edges. It is clearly visible and causes severe vision loss.
- Belmo. This is a strong clouding, in the place of which the cornea loses its transparency. Diagnosis of this degree of turbidity is simple; only an objective examination is enough. In this case, a white spot with clear edges is visualized, sometimes it may have a yellow tint.
Considering the location of leukoma, the following types are distinguished:
- Peripheral. It is placed along the peripheral edge of the cornea, as a result of which the field of vision in patients is reduced. If the cloudiness is in the form of a cloud or spot, then vision may not be impaired.
- Central. When the cataract is located in the area of the lens, blindness develops. In this case, the patient does not see anything, but can tell whether there is light or not. With slight clouding, visual acuity decreases.
- Total. Scarring occurs in both the central and peripheral areas of the cornea.
The degree of turbidity determines whether a person’s visual acuity will decrease or blindness will develop. There are also congenital and acquired cataracts . Congenital leukomas are quite rare and are detected only in newborns. The causes of their occurrence are genetic pathologies and intrauterine infection. Acquired ones arise as a result of the action of various exogenous factors on the cornea of adults and children.
Symptoms
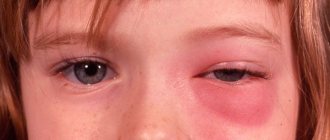
In addition to visible signs, patients often complain of the following manifestations of the disease:
- Blurred vision. People report the appearance of fog or a veil before their eyes.
- Loss of optical fields.
- Sensation of the presence of sand or a foreign object in the organ of vision.
- Redness of the sclera.
- Increased lacrimation.
- Intolerance to bright light.
- Rapid decline in eye acuity.
Any of the listed symptoms is a serious reason to visit a doctor.
Cataract treatment
For cataracts (treatment takes a long time, up to six months, but it helps without surgery!!). This is from experience:
My case is not uncommon. I worked for a quarter of a century in hazardous production involving nitrogen compounds. Toxins hit my whole body, but they came back to haunt me in the eyes. As a result, at the age of 55 - acquired cataracts. A gray star, as the ophthalmologist said. This is when you look at the lens under a microscope, and it is cloudy and star-shaped. There is good news - it’s still the initial stage, it’s too early to go under the knife, but the ophthalmologist prescribed absorbable medications, domestic drops. He said they were good. He only immediately warned that there would be no complete cure for them, they would only slow down the development of the disease. I told a friend at work about my illness, and he told me, try Kalmykov drops, they have already helped many. I say: what if they are so effective, doctors don’t prescribe them? So, this is a folk medicine, the comrade explained, you can make it yourself, at home. The next day he brought me the recipe, written down by hand on a piece of paper. There were only three ingredients: honey, silver water and aloe.
I had my doubts about silver water, but then I read that it is even more useful than regular water. And silvering plain water is not difficult. I had a silver spoon, I steeped it in a three-liter jar for a week. And then, according to the recipe, I first added aloe, boiled it in this water, and let it brew for a day. Then he put in the honey. When the honey has dissolved, the drops are ready. I admit, I was a little worried when I buried it for the first time. But they don’t promise a quick cure. It’s just charlatan drugs that cure everything in a week. And it took me almost six months. But the cataract went away, as promised, completely. The ophthalmologist recorded this fact; it turned out that he had heard about these drops, but was afraid to prescribe them because he did not want to experiment on his patients. But I wasn’t scared and I’m very glad that it turned out to my advantage.
M.Z. Rybakov.
Possible complications
If you start the disease, you increase the risk of encountering dangerous consequences of leukoma:
- Increased discomfort in the visual apparatus.
- Blindness of the damaged eye.
- Severe drop in visual acuity.
- The occurrence of pain, which intensifies when blinking.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease immediately after its detection. Return to contents
Experience in treating turbidity
One of my hopes
to restore the cornea and remove clouding - aqueous propolis extract (I haven’t tried it yet, I ordered it, it’s on its way by mail, I’ll try dripping it into the eye). I will also try dripping fir resin.
While I rub my eyes with a decoction of celandine, calendula and other herbs, I do eye exercises - but the cloudiness is strong and does not decrease, for example, it is impossible to read with this eye - I do not see the lines.
If someone managed to cure cloudiness, write what you used to treat it?..
LATER:
ATTENTION! A healer I know (website vashe-zdorovie.ru/) said that under no circumstances should you drip oleoresin - you could end up without eyes. Propolis - only INSIDE, not in the eye!
The same applies to celandine and, apparently, many other folk methods. You can really hurt yourself. BUT - here we are talking about a high concentration of resin and propolis. As it turned out, resin can be dripped into the eye at a content of no more than 2.5%.
Recommend:
Traditional medicines:
Fir resin in cedar decoction.
Start with a weak dilution! (I found an option not in decoction, but in cedar oil)
Golden mustache juice with honey. Start with a weak dilution! Usnea and cedar oil.
Additional tools:
HuaShen eye patch
On the Internet I found a version of oleoresin specifically for the eyes
is a 2.5% solution of oleoresin in
cedar
oil.
It is said that cedar oil is the only oil that can be dropped into the eye . It forms a film on the eye that dissolves after 10 minutes. You can drop either pure cedar oil into the eye, or the option cedar oil + resin
(2.5%).
It is also recommended to cleanse the body
- take a 10 or 15% solution of resin orally.
Gum balsams are found in ecotopia.
Cleansing (cleansing the body) with oleoresin (Siberian cleansing)
The recipe for this cleansing is here.
To carry out cleaning, you will need a 40 unit syringe without a needle (like a dispenser) and 200 ml of 10-15% resin. In general, the cleansing lasts 79 days
. On the side there is a table of dosages, listed for all days of cleaning, based on 5 units. If you weigh more than 80-100 kg, you can take more, at the rate of 7-8 units, up to ten.
- On the 1st day of cleansing, in the morning on an empty stomach, drink 5 units (0.125 ml) of oleoresin, then neither drink nor eat for 30 minutes. If you cannot stand the bitter taste, you can drink it with water. But it's better to just go and brush your teeth.
- The next day, drink 10 units (0.250 ml),
- On the third 15 (0.375 ml)
- Add 5 units (0.125 ml) every day.
- On day 40 you will reach 200 units (5 ml).
- From the next day you begin to reduce the dose, also by 5 units (0.125 ml) per day.
In the first 40 days, you gradually reach a new energy level, at this time the memory of your cells is revealed and restored, restoration processes are turned on at a very deep level, at the DNA level. Over the next 40 days you consolidate at this level. Usually it is at this time that a person feels the effect of cleansing. It manifests itself differently in different people.
Stone oil for eyes
What definitely won’t do any harm is rock oil – you can take it internally and drop it into the eye. But whether it cures a thorn is unknown. Plus Hua Shen's eye patch.
Healers also recommend:
Buy Riciniol base in Argo. This is an emulsion based on castor oil from seeds. Previously, they buried it in the Gulag in Khakassia in the eyes of imprisoned Poles at a gold mine. The juice of angelica (hogweed) was squeezed out from the seeds, mixed with fir resin and a drop into the eyes - the most important thing was to rinse the eyes with soap and hot water. Always hot
water - every morning.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Doctors use several common techniques to identify cloudiness, its size and intensity:
- Amsler lattice. The basic method, which involves the use of special equipment. The unit is designed in such a way that a person with healthy eyes sees the lines that form the grid as straight. A patient with degenerative changes in the cornea will say that they are crooked. However, this technique only helps confirm the fact that there are problems with the visual apparatus. An accurate diagnosis will require additional examination.
- Ultrasound of the eyes. A scan of the apple is carried out, which reveals leukoma and the disorders that it provoked.
- Biomicroscopy. The study affects only the anterior part of the visual apparatus, focusing directly on the cornea.
- Optical coherence tomography. The most complex and accurate type of diagnosis. Light pulses are sent to the eyes and the reaction of the tissues of the organ of vision to the waves is subsequently studied.
| All procedures are painless and do not cause discomfort. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid of them. |
Symptoms and diagnosis
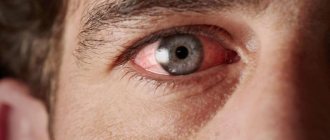
Cloudiness of the cornea can usually be seen with the naked eye: grayish areas appear on the surface, which are called clouds, spots and cataracts. The clouds resemble small smoke spots located in the center of the protein.
The spots are more intense, and cataracts are persistent and obvious opacities that occupy a large part of the cornea. Such manifestations are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- redness of the whites;
- photophobia;
- partial or complete loss of vision;
- tearfulness;
- discomfort or sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
If one or more symptoms develop, you should immediately consult a doctor, since modern diagnostic methods can detect the disease in the early stages.
Making a diagnosis begins with collecting anamnesis, visual examination of the organs of vision and checking the patient’s visual acuity. If corneal clouding is suspected, a special device called an Amsler grid is used.
The patient focuses his gaze on the point indicated by the ophthalmologist, and if the nearby lines seem wavy and not straight to him, this indicates degenerative changes in the eye.
To clarify the diagnosis, patients undergo ultrasound of the visual organs and biomicroscopy: the first procedure is aimed at studying the entire eye, and the second - its anterior part. The most accurate method for diagnosing corneal opacities is optical coherence tomography.
This simple study, which is based on the different display of light waves by the tissues of the visual organs, does not cause discomfort and allows you to make a diagnosis with great accuracy.
Treatment methods
Leukoma therapy is carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. The course of treatment is selected depending on the stage of the pathology, the person’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases. Traditional medicine recipes are allowed to be used as additional therapy. But under no circumstances should they replace any medications prescribed by your doctor.
Medications
Treatment of corneal opacities with medications makes sense only in the early stages of the development of the disease:
- To get rid of unpleasant symptoms and block inflammation, ointments and drops containing corticosteroids are prescribed. For example, "Hyphen."
- Resorption of scar tissue is facilitated by injections of ethylmorphine hydrochloride and potassium iodide. Injections of drugs with mercury and proteolytic enzymes are also recommended. Biogenic stimulants are prescribed for the same purpose.
- To normalize blood circulation, local vasodilating medications are prescribed.
Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis) using hormonal or natural drugs has a good effect.
Surgical intervention
The operation is prescribed for the development of total spots of increased density and central damage to the cornea. Also, you cannot do without the help of a surgeon if drug therapy does not bring results. You should not refuse the intervention; it is performed under anesthesia, so you will not feel pain.
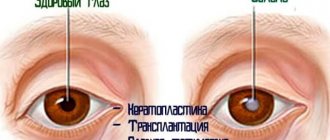
Of course, you will have to stay in the clinic for some time and walk around with an eye patch, but the reward will be getting rid of the defect and restoring your vision. Patients with leukoma undergo one of two types of surgery:
- Keratoplasty. As a result of the intervention, a piece of the cornea damaged by scar tissue is removed. In the future, you will have to undergo a course of medication to regenerate the epithelium.
- Transplantation. A healthy cornea is transplanted from a donor. The operation can be through or with preservation of its own epithelial layer.
| There may be contraindications for surgical intervention due to the patient’s age or the presence of certain pathologies. In such situations, you will have to use lenses to cosmetically mask the opacities and take medications to prevent the progression of the anomaly. |
Return to contents
Traditional medicine recipes
In addition to traditional treatment, do not forget about the “miracle” remedies from nature. Traditional recipes are sometimes highly effective. They are recommended to be used in combination with drug therapy.
- Medicinal eyebright has long been considered a herb that helps fight eye diseases. Take a tablespoon of dry eyebright and pour boiling water (two hundred milliliters). Leave for three hours. Then remove the herb and cool the solution to room temperature. Apply lotions to the eyelid that is in contact with the injured eye twice a day. You can use the infusion for internal use: once a day, a tablespoon.
- Grind the stem and leaves of the marsh calamus, squeeze out the juice and strain it through cheesecloth. It is necessary to ensure that there is no pulp in the liquid. Dilute the juice with boiling water (one tablespoon per two hundred milliliters of water). Cool to room temperature and drop into eye twice daily. Course of treatment: four weeks.
- Fir resin effectively fights leukoma, even in the most severe forms. Just don’t put it in your eyes under any circumstances! In addition to the unbearable burning sensation, you risk getting a burn. Apply the warm resin drop by drop onto the eyelid and leave for fifteen minutes. Then rinse carefully, being careful not to get anything into your eyes.
- Take homemade rye bread. It must be hot, otherwise there will be no effect. Make a hole in the bun and place a glass there upside down. After a few minutes, condensation will begin to settle on the glass. They need to be collected and buried twice a day.
Before using traditional recipes, do not forget to consult your doctor. Otherwise, you may experience allergic reactions, worsening cloudiness, or a burn to the cornea.
Modern diagnostic methods
If the development of leukoma of the eye is suspected, the ophthalmologist conducts an external examination, collects an anamnesis, and prescribes a number of studies, including:
- determination of visual acuity;
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision;
- biomicroscopy;
- Amsler lattice study;
- coherence tomography.
The results of the study help the doctor obtain a complete picture of the disease, assess the extent of damage, make a final diagnosis, and determine treatment tactics.
One of the informative diagnostic methods is the Amsler grid study, which consists of the use of a special apparatus that helps determine the degree of visual impairment. During the examination, the patient focuses on the point named by the doctor. If the lines inside the apparatus seem not straight, but wavy, this is a serious sign of disorders and degenerative changes.
Forecast
The prognosis for leukoma therapy is given individually for each patient. It depends on the age and state of health of the person, as well as on the cause of the disease.
- Minor opacities in the periphery do not require therapy because they do not interfere with normal vision. All you need is regular examination by a doctor.
- A large cataract caused by diseases (not ophthalmological) does not require surgical treatment, provided that the root cause is eliminated. If the patient has gotten rid of the disease, the clouding will go away after taking medication.
- Surgical intervention is prescribed for advanced forms of leukoma, as well as when drug intolerance is detected in the patient. The prognosis for this treatment is favorable, since the graft takes root well.
- If the cataract is formed as a result of a burn and serious damage, then it is impossible to restore full vision. Therapy comes down to minimizing the consequences of injury and combating unpleasant symptoms.
| Treatment of clouding will be successful if it is started at the initial stage of development of the disease. |
What it is?
History of appearance
Belmo is one of the oldest diseases of the organs of vision, which was mentioned in the works of Avicenna and medieval physicians.
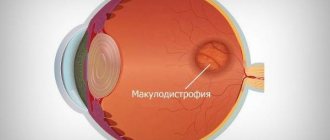
This phenomenon represents scarring changes in the retina of the eye, which is responsible for central vision.
For this reason, a person begins to see poorly even those objects that are directly in front of him, and the disease progresses over time.
Prevalence
285 million people worldwide suffer from eye pathologies , and corneal clouding occupies one of the leading places among such ailments.
With the advent of laser surgery and other innovative techniques to combat ophthalmic diseases, the incidence of blindness due to the development of cataracts has decreased significantly.
Who is affected?
Most often, corneal clouding develops as a result of age-related changes in the body, but there are a number of reasons and factors that can cause pathology in young people.
Prevention
In order not to encounter leukoma, you should follow simple rules:
- Give up cigarettes. A bad habit has a negative impact on health.
- Avoid direct sunlight exposure to your eyes.
- Don't forget about UV protection.
- Wear goggles and a mask when working with hazardous substances.
- Treat eye diseases in a timely manner.
- When you spend a long time at the computer, do not forget to take a break.
- Visit your eye doctor regularly for preventive examinations.
- Introduce into your diet foods that improve visual acuity (carrots, blueberries).
| If you use contact lenses, do not forget to remove them before going to bed and follow the storage rules. |
Treatment of keratitis with bee products
Recovery after operations and burns, after inflammation of the cornea (keratitis), with cataracts, with retinal dystrophy:
- Honey composition honey + royal jelly
- dilute 1:1 in cold boiled water and put in the eyes (possible lacrimation and burning) 2-3 times a day - Aqueous propolis extract
(the kind sold by those who make honey) - take 1 teaspoon orally 3 times a day, 20-30 minutes before meals.
For conjunctivitis, dilute the aqueous extract of propolis in water in a ratio of 1:2 (2 times more water than the balm extract), drop into the eyes 3-4 times a day.
Diseases of the cornea of the eye: inflammatory, dystrophic and congenital
Anyone reading these lines, of course, imagines what the anterior portion of the eyeball looks like. The white areas of the sclera, the dense spherical “casing” of the eye, are open to the external observer, as well as, which consists of a pupil capable of changing diameter and the iris surrounding it. The cornea, or simply the cornea, is the outer lens of the eye “lens”, which, firstly, must have a precisely adjusted surface curvature, secondly, be absolutely transparent and, thirdly, sufficiently strong.
These regulatory requirements are dictated by the functional purpose of the cornea: being a natural concave-convex lens with a diameter of about 1 cm and a thickness of 0.5-0.6 mm (in the center) to 1-1.2 mm (along the perimeter), it has an optical power of 40 diopters concentrates the light flux and directs it further onto the lens.
At the same time, it is designed to protect, as far as possible, the pupil, iris and the delicate internal autofocusing or accommodation system (ciliary body + lens) and the “photosensitive matrix” (retina), as well as other intraocular environments, tissues and fluids, which should, of course, , stay within the eyeball. Therefore, evolution reliably sealed the entrance hole of the eye, merging the corneal lens with the sclera in a smooth transition.
The multilayered structure of its substance allows the cornea to perform such different tasks: thus, there are epithelial layers - anterior and posterior (which is also called the endothelium, or internal layer), boundary membranes (external Bowman's and internal Descemet's). Several years ago, evidence was obtained in favor of the existence of another layer, previously known only at the level of assumptions. After the discoverer’s name, this ultra-thin (up to 20 microns) “stiffness membrane” was called the “Duha layer.” The bulk of the cornea is stroma, a transparent working substance made of tiny collagen fibers.
The versatility and unique natural properties of the cornea place special demands on its preservation. Any diseases, injuries and burns, any processes and conditions that can change the optical, geometric or mechanical characteristics of the cornea are dangerous for vision. Even a slightly deformed cornea will refract light incorrectly, which will lead to astigmatism (the inability of the eye to focus the image in the intended zone, or at least outside it, but at a single point); reducing transparency will create the effect of glasses with frosted tinted lenses; complete opacity is equally complete blindness; finally, a penetrating wound or other perforation of the cornea is fraught with such serious consequences as prolapse of the iris, destruction of the pupil, etc.
Our ophthalmology center is engaged in the diagnosis and effective treatment of corneal diseases using the most modern equipment and with the involvement of international specialists. An individual approach and advanced techniques guarantee high treatment results!
There are many diseases that negatively affect the functional state of the cornea. These include, first of all, infectious-inflammatory and infectious-allergic processes, which most often begin in adjacent tissues and systems, for example, in the conjunctiva, vascular network, eyelids, etc., then spreading to the cornea.
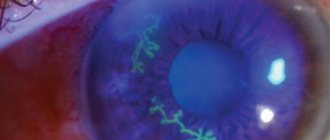
The most common inflammatory diseases of the cornea are keratitis of various nature (bacterial, viral, vitamin deficiencies, etc.) and corneal ulcer, which can be complicated by descemetocelle (“corneal hernia”).
However, a fairly large group of non-inflammatory keratopathies is known, caused by disorders of tissue nutrition and/or metabolism - these are corneal dystrophies (primary and secondary), keratoconus (keratoglobus) and keratectasia.
A special place is occupied by congenital malformations of the cornea - microcornea, megalocornea.
Traumatic damage to the cornea may also be present: erosion, foreign bodies (scale, etc.), burns and penetrating wounds. These pathologies can lead to complications such as neovascularization (vascular sprouting), corneal opacities (various localizations), the most pronounced of these conditions is cataract, when the transparency of the tissue is significantly reduced, which leads to a significant decrease in vision, up to blindness.
Diseases of the cornea (their causes, symptoms and treatment) are discussed in more detail in the relevant sections.
KERATOCONUS
SOIL (CLOSURE)
KERATITIS (INFLAMMATION)
DYSTROPHY
PTERIGIUM
CORNEAAL EROSION