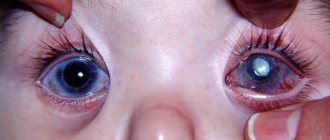
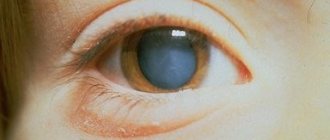
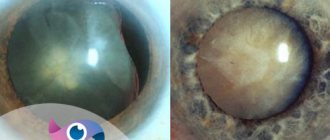
Diabetes mellitus is a systemic disease, affecting not only the kidneys, blood vessels, reproductive and nervous systems, but also the eyes. Diabetic cataracts are a common complication of the disease.
A cataract is a clouding of the lens. The disease is natural for older people, but in young people it can be a consequence of injury or a complication of systemic diseases, including diabetes.
The only way to cure cataracts is surgery. Modern phacoemulsification allows to minimize complications and achieve good quality of vision even in patients with diabetes. If previously every fourth diabetic was denied implantation of an artificial lens, now the operation is performed even with serious disorders in the visual system.
Surgery for cataracts in a patient with diabetes requires careful preparation and planning, physician care, and longer postoperative follow-up. However, when phacoemulsification is performed correctly, complications are observed no more often than in patients without diabetes.
What is cataract
Diabetic disease negatively affects the visual organs.
There are several common complications, not the least of which is diabetic cataracts. This means that all or part of the lens is cloudy. According to medical research, cataracts associated with diabetes progress to the final stage more quickly than those without an underlying disease.
The lens plays the role of a natural lens. When it becomes cloudy, vision deteriorates and then disappears altogether. As a rule, the cause of pathology is a change in the biochemical parameters of the lens.
Type 2 diabetes contributes to the malfunction of the body as a whole.
Metabolic disorders, altered blood circulation, and low immunity contribute to deformation of the visual system. Once blepharitis and conjunctivitis appear, they are not easy to cure; sometimes they develop into cataracts or glaucoma.
Cataracts go through several stages.
- Visual vigilance is not impaired, there are no obvious signs. The disease is diagnosed during the next medical examination.
- Vision begins to decline. The pathology moves to the center of the lens.
- The transparent body becomes cloudy entirely, acquiring a light gray tint. Visual acuity decreases to 0.1 - 0.2, but basic color perception remains.
- The fibers of the lens are destroyed, resulting in complete blindness.
There are metabolic and senile cataracts. Metabolic is a disease that develops with a significant increase in sugar content, senile - with senile visual impairment.
Types of disease and causes
The exact reasons for the development of cataracts in diabetics (as well as other groups of patients) are still unknown. But there are predisposing factors that could theoretically cause this disease. These mainly include age and heredity. 50% of people over 60 years of age are diagnosed with lens opacities, and over the age of 80 years, this disease is found in 90-100% of patients. Cataracts in diabetics can be divided into 2 types:
- a disease caused by age-related degenerative changes that progresses rapidly due to diabetes;
- a disease that arose precisely because of carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
The first type of cataract usually occurs in type 2 diabetes, since a person's eye health deteriorates with age. Against the background of elevated blood sugar, all pathological processes in the body are more severe. Due to diabetes, the normal blood supply to the eye is disrupted and the conductivity of nerve fibers in this area deteriorates. Without control and treatment, this can lead to serious visual impairment, including blindness.
Causes of diabetes
The lens is located inside the eyeball and is a vitreous body that transmits light rays. They, falling on the retina, show the images they saw.
In diabetics, excess sugar enters the visual organs. Glucose, after processing, becomes fructose, resulting in the production of sorbitol. As a result, osmotic pressure increases, metabolic processes and microcirculation are disrupted. All these indicators contribute to the lens becoming cloudy.
Diabetic cataracts are caused by the following reasons:
- impaired blood circulation in the eyeballs,
- insufficient insulin levels,
- eyelashes swell,
- acidosis,
- endocrine disorders,
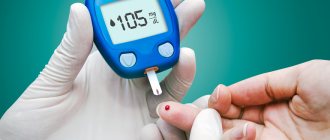
- increased sugar.
The disease progresses much more rapidly in insulin-dependent patients.
Cataracts can occur when excess sugar and acetone in the lens increase the light sensitivity of the protein. This causes the natural protein structure to change and the lens to become cloudy.
Clinical picture
The classic manifestation of symptoms of diabetic cataract development is clouding of the lens, rapid progression of pathological disorders of the visual organ, poor passage of light rays, loss of transparency of the natural eye lens.
The main symptoms of cataracts in diabetics:
- the presence of cloudiness appears in the visual apparatus, the vision becomes clouded, a whitened veil appears;
- visibility decreases;
- dark spots mixed with flakes appear before the eyes;
- difficult to work with small elements;
- distortion of color perception;
- objects begin to double;
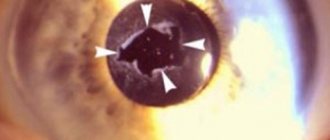
- the pupil becomes whitish in color.
Symptoms
Cataracts in diabetes are expressed in the occurrence of the following symptoms:
- a veil appears before the eyes,
- double image in the eyes,
- it is impossible to concentrate your gaze on an object,
- the surrounding reality appears fuzzy and dim,
- the pupil becomes not black, but cloudy and light,
- the fundus is difficult to examine.
Cataracts are manifested by mental disorders. The patient becomes nervous and restless because it is difficult for him to perform basic functions: working with a book, at the computer.
If you experience any symptoms associated with diabetes, it is best to immediately visit a doctor and get examined. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the sooner treatment begins, and there is a greater chance of returning normal vision.
Symptoms
At the beginning of the development of the disease, symptoms may be vague or even absent completely. As the disease progresses, the patient begins to worry about the following manifestations:
- the appearance of spots and sparks before the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- periodic bifurcation of objects;
- blurred vision when working at a computer, reading books and writing;
- decreased twilight vision;
- sensation of a slight veil before the eyes.
Signs of disease development
Diabetic cataract differs from age-related cataracts in that the clinical picture is detected in a young state. In the absence of glucose disorders, the first signs appear after 40 years, and if they are present, up to 25. The symptoms of ordinary clouding rapidly worsen; otherwise, the disease can develop over years and decades.
The initial sign is usually a veil before the eyes, blurriness of objects located against a bright background. Duality of the image appears, dimming of visible objects, as well as changes in the pupil. It turns out to be light and quite cloudy, which is identified by an ophthalmologist during a routine examination.
Symptoms of diabetic cataracts may be associated with nervous system disorders. Given the changes taking place, a person becomes irritable and restless. As visual functions worsen, these processes become more and more intense.
Diabetic fetopathy of the fetus and newborns
Diagnostics
Diagnosis consists of a routine ophthalmological examination.
- visual acuity is checked, the specialist measures the pressure of the eyeball,
- Ultrasound scanning is used to study all parts of the retina,
- using a three-mirror Goldmann lens, the fundus is examined,
- dystrophic disorders are examined by biomicroscopy using a slit paw.
In diabetics with 10 years of experience, the condition of the iris is carefully studied. After the doctor makes a valid diagnosis, treatment for cataracts in diabetes mellitus is prescribed.
How is diabetic cataract treated?
For this ophthalmological problem, conservative treatment usually does not bring any positive effect. To restore vision, the patient requires surgery. Such surgical interventions are currently performed routinely.
- The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
- Typically, 2 small punctures are made on the body of the eye, through which the naturally clouded lens is crushed and removed by aspiration. Removal of the damaged lens occurs in a low-traumatic manner.
- An artificial soft lens is inserted into the eye cavity through the existing holes.
Considering that all stages, surgical intervention is carried out with minimal trauma to the tissues of the eyeball. This ensures faster healing. As usual, after just a few hours the blindfolds can be removed, and the person can begin to lead a full life.
Surgical interventions of this type can eliminate even immature cataracts that develop in people suffering from diabetes. Early treatment helps prevent the development of severe complications.
Many people mistakenly believe that diabetic cataracts can be cured using folk remedies. For this purpose, recipes based on honey, medicinal chamomile, rose hips, burdock root, black currant and blueberries are often used.
Traditional methods of treatment cannot cure this complication of diabetes, although some patients still observe a possible positive effect. In addition, their use in some cases can cause significant harm.
Three stages of retinopathy
There are three stages of retinopathy.
First stage (also called non-proliferative)
This is the most common stage of retinopathy. At this stage, protrusions called microaneurysms form in the walls of the capillaries due to constant contact with glucose, and small hemorrhages may appear inside the retina.
Most often, there is no visual impairment, but due to changes in the capillary wall, the ability to properly nourish the retina deteriorates. If fluid begins to leak through the walls of the capillaries, swelling of the macula (the area of “best vision”) may occur - maculopathy - in this case, vision becomes blurred, unclear, and may almost disappear for a while.
Nonproliferative retinopathy usually requires no treatment, except for macular edema, which requires immediate treatment to prevent vision loss. You should consult an ophthalmologist for help.
Second stage (also called preproliferative)
At this stage, more pronounced changes in blood vessels and capillaries occur, and larger hemorrhages appear. Treatment is required for severe hemorrhages and the development of maculopathy.
Third stage (also called proliferative)
- The last stage of retinal damage;
- At this stage, complete closure (blocking) of a large number of vessels supplying the retina occurs;
- Instead of these vessels, new, thinner and weaker vessels begin to grow. These vessels can rupture at any time, causing hemorrhage into the vitreous body - this can lead to loss of vision;
- The growth of new blood vessels also causes the formation of connective tissue, which in turn can pull the retina out of place—a condition called retinal detachment, which can lead to vision loss.
An unpleasant fact: retinopathy is asymptomatic for a long time, and you can notice any changes only at the last - proliferative stage, when sometimes it is already too late. That is why it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist regularly, at least once a year, to examine the fundus with a dilated pupil!
Treatment
Therapeutic therapy begins with the fact that the main disease – diabetes mellitus – is first cured. To achieve this goal, the following tasks are solved:
- glucose levels are normalized,
- the optimal dose of insulin and medications that reduce sugar is selected,
- metabolism is adjusted,
- a healthy lifestyle without bad habits is organized.
Diabetics should visit an ophthalmologist at least once every 6 months.
To reduce high sugar levels, eye drops “Quinax” and “Catachrome” are used. For preventive purposes, they are used for a month, after which the same break is taken and the course is repeated. Sometimes therapy lasts a lifetime to prevent surgery. Eye drops are not able to stop the disease, they only slow down its progression.
Diabetic cataracts are completely eliminated through surgery; there are no other effective methods. It is recommended to remove the lens at earlier stages, without waiting for the disease to become advanced.
It develops quite quickly, so the patient may suddenly begin to see worse. The use of contact lenses and glasses in this situation does not correct vision.
If it is necessary to perform cataract surgery for diabetes mellitus at the onset of the disease, phacoemulsification is used. It should be borne in mind that visual acuity should not decrease by more than 50%. The advantage of this type of intervention is that there is no need to apply stitches; therefore, astigmatism does not develop after it.
Eye surgery consists of the following: a micro-incision is made with a laser or ultrasound, through which the deformed lens is removed, leaving the capsular bag. An intraocular lens is placed instead of the natural lens. The procedure is done using local anesthesia.
Patients note that improvement appears immediately, despite this, the recovery period lasts some time. If the lesion affects both eyes, first remove the film from one eye, then after about 3 months from the other.
There are some reasons prohibiting the operation:
- advanced stages of retinal pathologies,
- formation of a vascular network on the iris,
- blindness,
- inflammation of the visual organ.
Before surgery, it is necessary to confirm that blood glucose levels have returned to normal and that the patient does not have chronic diseases that could interfere with postoperative rehabilitation.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, the tissues and blood vessels of the eye are not injured, and vision is restored on the second day. After the procedure, it is recommended to use hormonal and non-steroidal drops.
Traditional and non-traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of diabetic cataracts requires a lot of effort and constant adherence to certain rules. As soon as a patient is diagnosed with diabetes, he is necessarily referred to an ophthalmologist. The doctor determines at what stage of development the cataract is.
Usually it can only be cured by surgery. But before surgery, you need to stabilize your blood sugar levels. To do this, the patient is prescribed insulin therapy, a diet, and recommended to lead a healthy and active lifestyle. After this stage of treatment has been completed, cataract surgery can be performed.
But not all patients with diabetes have such a critical situation that requires immediate surgical intervention. To avoid cataract surgery, many patients are forced to use eye drops or brew tinctures according to traditional medicine recipes that help improve vision throughout their lives.
But people with diabetic cataracts should consult a doctor when they want to be treated with one method or another. Below is a list of folk ingredients that can be used as treatment:
- liquid honey;
- blueberry;
- chamomile;
- burdock root;
- rose hip.
There are a huge number of recipes with these ingredients, but everyone needs to choose the one that suits them.
You should never forget about your health. It is necessary to carry out preventive measures and undergo routine examinations by specialists in various fields. After all, this is the only way to stay beautiful and healthy for many, many years.
Doctor of the Moscow Eye Clinic D.F. Pokrovsky about diabetic cataracts:
It is recommended to study:
Is it possible to treat cataracts without surgery: the secrets of recovery without surgery
Laser treatment of cataracts: recommendations, contraindications, complications
Surgical treatment of cataracts: types and details of each method
What to do with cataracts in both eyes - is there a way out of the situation?
Source of article: https://diabetystop.com/oslogneniya/diabeticheskaya-katarakta-mozhno-li-delat-operatsii-na-glaza-pri-saharnom-diabete/
Surgical intervention
The goal of the surgical procedure is to remove the cataract itself and replace the lens. It is performed under local anesthesia, most often it is phacoemulsification, which allows you to get rid of problems of any severity. Please note that:
- An ultrasonic probe is used to crush the cloudy area and provide aspiration of the structures;
- an implant, which is a tube, is inserted through a special incision using a syringe-injector;
- The duration of the operation is no more than 25-30 minutes.
Liver cirrhosis due to diabetes mellitus
The advantages of this tactic are safety, absence of pain, minimal likelihood of complications, and short duration of the intervention. The fast rehabilitation - up to 30 days and the macro-incision parameters (up to 2.5 mm) are noteworthy.
After the operation, non-steroidal and steroidal names are used for three to five weeks. Indocollir and Dexamethasone are administered (two drops four times a day). Within 10 days, installation of antibacterial compounds in a similar ratio is ensured.
Until the incision heals completely (within two to three weeks), the patient needs to monitor hygiene. This will help prevent the development of an infectious algorithm.
In this regard, it is not recommended to touch the eye, as well as wash it under running water. As part of the recovery phase, they avoid wearing makeup, playing sports and visiting the sauna.
Cataract surgery is contraindicated in cases of advanced retinopathy and the presence of scars on the eye structures. The same applies to inflammation of the problem area and the development of the vascular network on the iris.
Recovery after cataract removal
A common consequence of lens removal in diabetics is the progression of retinopathy. Deterioration of the retina is observed when:
- long-term course of the disease and insulin administration (from 10 years);
- concomitant kidney damage;
- glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye);
- in elderly patients (after 65 years);
- with decompensated diabetes with sudden changes in blood sugar.
Therefore, further observation by an endocrinologist and ophthalmologist, regular measurements of blood sugar levels and blood pressure are a prerequisite. To prevent inflammation, it is recommended to instill drops with dexamethasone, antibiotics, and non-steroidal drugs. Antibacterial therapy started in the preoperative period continues.
For a month it is prohibited:
- visual and physical stress;
- washing the eyes with running water (they are washed with a weak infusion of chamomile, calendula, tea);
- hot shower, bath, sauna, thermal treatments;
- look at the bright sun without glasses;
- apply cosmetics to the eyelid area;
- touch your eyes with unwashed hands, rub your eyelids.
A month later, a control examination of the operating surgeon is carried out and glasses for correction are selected.
Find out more about diabetes in children here.
Cataracts appear against the background of diabetes mellitus due to damage to the lens of the eye and microvascular circulatory disorders. For treatment at the initial stage, eye drops are prescribed, which slightly slow down the progression of the disease. To save vision, surgery is prescribed.
For the modern phacoemulsification method, diabetes is not a contraindication, but its course must be compensated. After preoperative preparation, patients have their lens destroyed with ultrasound or laser and a lens is inserted in its place. Due to the risk of progression of diabetic retinopathy, further observation by an ophthalmologist is necessary.
If diabetic foot has developed, treatment should be started as early as possible. At the initial stage, ointments, traditional medicine and laser are used to improve blood circulation and vascular condition. For ulcers, surgical treatment and some modern medications are suitable.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs quite often in diabetics. Depending on which form of the classification is identified - proliferative or non-proliferative - treatment depends. Reasons: high sugar, poor lifestyle. Symptoms are especially subtle in children. Prevention will help avoid complications.
Complications
Postoperative complications develop extremely rarely. As a rule, intraocular pressure may increase and inflammatory processes may occur.
If the iris is damaged during the procedure, hemorrhage occurs in the anterior chamber. It is very important to protect the eyes from traumatic effects in the postoperative period, because they provoke retinal detachment.