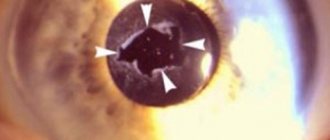
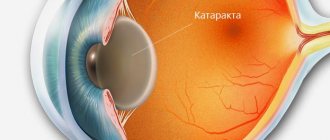
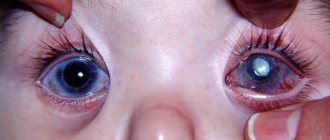
The most effective and safe method of surgical treatment of cataracts is replacing the eye lens using ultrasound or laser phacoemulsification. The recovery period after such treatment can be divided into three stages:
- first week after surgery;
- first postoperative month;
- six months after treatment.
At the first stage , immediately after surgery, the patient notes a significant increase in visual acuity. However, as after any other operation, some undesirable reactions to painkillers and the intervention itself may be observed (pain in the eye and surrounding areas, swelling of the eyelids, general weakness). To relieve such phenomena, non-steroidal painkillers can be prescribed, recommendations on nutrition and fluid intake, and head position during sleep are given.
At the second stage , vision improves even more noticeably, but its sharpness is unstable. In order to ultimately maximize the effect of treatment, you should follow a gentle eye regime in the first month after surgery. This applies to reading, watching TV, working at the computer. Temporary wearing of glasses to reduce eye strain may be indicated. As a rule, in the second period, eye drops are prescribed according to a specific individual scheme (anti-inflammatory and disinfectant solutions). By the end of the second rehabilitation period, the frequency of instillations is gradually reduced.
The third stage after ultrasound and laser phacoemulsification is characterized by maximum vision restoration at the beginning of this period. Only some restrictions remain, which are gradually being lifted. After vision has reached its maximum, it is possible to choose glasses or lenses for additional correction. Rehabilitation after extracapsular or intracapsular cataract extraction is longer. Only after the sutures are removed in the third postoperative period, vision is finally restored, and glasses or lenses can be prescribed.
The most common complications
There are the most common complications that occur in almost all patients. In this case, treatment may be completely absent or incorrect. Some of them are fixable, others cannot be eliminated. Therefore, it is necessary to find a competent specialist who will prescribe the right treatment that completely restores vision function.
To treat cataracts, medications and surgery are used. In both cases, the patient's condition may become more complicated.
Hemorrhage
Eye surgery is classified as microsurgery. It is carried out using magnifying devices that allow you to closely examine the internal structures of the eyes. If the doctor incorrectly installed the intraocular lens, applied excessive pressure to any element of the eye, or made an incorrect movement, hemorrhage may occur.
In some cases, it does not form immediately, but after the operation is completed. This is the most dangerous option, since the entire internal cavity of the eye can fill with blood, this will lead to irreparable phenomena for the eyes, which will cause blindness.
In some cases, minor hemorrhage occurs, which resolves on its own. These are minor complications that do not require correction.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases
The internal structure of the eyes is an aseptic environment. When the eyeball is opened, pathogenic microorganisms enter it. These include bacteria, viruses, and fungi. If their number is insignificant, antiseptic agents will completely remove these microorganisms. Otherwise, infection of the internal structures of the eyes develops, and pus forms.
Infection often develops on the superficial structures of the eyes; pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound. This forms an infectious-inflammatory disease that spreads over the entire surface. To prevent the condition, the doctor prophylactically prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of drops to all patients.
Corneal edema
To penetrate the lens area, the doctor must cut the cornea. After the procedure is completed, swelling and inflammation will form. If the patient's condition is stable, medications, ointments, and solutions are prescribed. In case of extensive inflammatory processes, keratoplasty is indicated. This is a procedure to completely replace the cornea.
Postoperative astigmatism
For surgery, the eyeball must be cut. This changes its shape. There are often cases when it is not restored to its previous size. Astigmatism is formed, that is, the wrong shape of the eyes.
The patient does not clearly see surrounding objects, their shape and size changes. To correct the condition, special glasses and lenses are indicated.
Increased intraocular pressure
This condition is called postoperative glaucoma. Secreted fluid begins to accumulate in the chambers of the eyes, which expands them. Gradually they increase in size, squeezing the surrounding structures. This condition can lead to retinal detachment or degeneration. The optic nerve is also affected, losing its signal transmission function.
Secondary cataract
There is a pathology of the lens, for example, nuclear cataract, when it is necessary to remove not the entire element, but only part of it. In this case, the doctor needs to be very careful not to leave pieces of clouded tissue. If this happens, a secondary cataract forms. This condition is less amenable to correction, and most surgical treatments are not suitable. The patient's visual function begins to decline again, and blindness may occur.
Increased eye dryness
In the postoperative period, tear production often decreases. The surface of the mucous membrane becomes dry. This forms microtraumas and cracks in the cornea. The condition goes away over time. To maintain eye moisture, use drops (Defislez, Slezin).
Formation of floaters, dots before the eyes
If the vitreous body is damaged or compressed during surgery, non-existent elements form in front of the eyes. These include dots, flies, lines, stripes, lightning. They can be bright yellow or black. If this condition occurs several times and goes away, there is no need to worry.
Corrections require the constant formation of these elements.
Failed lens replacement surgery
Hello!
I apologize in advance if my explanation is incomplete/incorrect or inconsistent; I learned the most unpleasant news a few hours ago. At the beginning of this week, my grandmother (she is 87 years old, hypertensive) was diagnosed with complete cataracts. For surgery to remove cataracts (installation of a new “lens”) at our local central district hospital. For a very long time she could not go to bed earlier, because she is an emotional person and as soon as the conversation turned to the hospital, the pressure rushed to around 200. But now she finally pulled herself together. After consulting with a doctor, they said that the left eye is in a deplorable state and an urgent operation is needed, with the right eye the situation is better and she can see in principle. According to the doctor, I ordered “the best American lens” for quite a lot of money, because... those that are free or cheaper are a bad option.
Today, when I came to visit her and find out how the operation went, I learned from the nurse, because... the doctor was no longer there. That the operation was unsuccessful, the pupil did not dilate and it was not possible to install a new lens. Sorry if I explain incorrectly, everything is from the words of the nurse. They offered the option of leaving it for another week and installing the ordered lens (so that it wouldn’t disappear.) on the second eye, which, in principle, sees.
And it’s not clear what to think, and what’s the best thing to do here, because... It remains unclear to me whether the left eye will see at least as before, or is it a loss of vision in one eye? How often does this even happen? I doubt that my grandmother will even decide to install a lens in her right eye, but if she does make such a decision, is there a chance for a successful outcome? If you need clarification, ask, I’ll try to figure it out.
I understand that it is difficult to answer such questions in absentia, especially without any accurate data, but help me navigate and help me make the right decision, Thank you in advance.
Today there was a meeting with the doctor.. His explanation is somewhat different from what the nurse said yesterday..
The doctor said that the grandmother had stage 4 cataracts on her left eye, and the ultrasound machine was almost broken while the operation was being performed - the lens was not crushed in any way, and a whole bottle of something was used up, as I understood it was about a drug that expands the icon. And after the lens was removed, it became clear that there was a lot of “garbage” in the eye that had accumulated throughout her life and which she simply had not seen before (why is that so?). and she decided not to put a lens on this “bad” eye, guided by saving our money. The original lens was removed, but a new lens was not installed. And now she constantly sees “squares”, “flies” and “crows” and large light spots. And we were told that this is the case now and will always be, because... This can only be corrected by a complete replacement of the vitreous, a complex operation that she is unlikely to undergo and which is performed only in the federation. But besides this garbage, she also sees something with this eye, which I personally did not expect. the fact that the pupil did not open was mentioned in passing.. After this result, the grandmother, of course, just wanted to run away from there, but the doctor began to explain that the second eye should be done while there is such an opportunity and then it might be too late, and in the end it was said that she would soon go blind if the operation is not performed, and this completely scared her. She suggested installing the ordered lens on the second eye, which is still in satisfactory condition and sees the top line.
There are a lot of things that confuse me. -Why was the decision made to operate this eye, since it was in such poor condition? - Why didn’t she see this garbage before before the operation at all, the eye saw it, albeit poorly - Is it possible to leave the eye like this without a lens at all?
Now it’s not clear what to do here, on the one hand, I think this is my grandmother’s last chance to somehow improve her vision, because if she returns home, it’s unlikely that she will undergo any kind of eye surgery, but on the other hand, after what happened, it’s clear that the stakes are too high and you could be left completely without vision if something similar happened.
Maybe someone has thoughts about what is happening here. Thank you..
source
Rare complications
There are complications that occur rarely in patients. Some of them can be corrected, others cannot be treated. In extreme cases, repeat surgery may be necessary to correct the person's vision function.
Lens rupture
The lens is a capsule containing a clear liquid. Particles spread throughout the internal structure of the eyes can damage these elements. For example, the vitreous body. This provokes an increase in intraocular pressure, the walls of the eye chambers begin to expand, gradually squeezing the retina and optic nerve. Their function decreases, and retinal detachment or optic nerve atrophy may occur.
Intraocular lens displacement
When cataract surgery is performed, an artificial model is implanted in place of the lens. It is called an intraocular lens. Around the lens are ligaments into which the lens must fit.
If the installation was performed incorrectly, it gradually shifts towards the retina. This leads to swelling, inflammation, and mechanical damage to the vitreous and retina.
Neurological disorders
The tissues of the eyes are not only well supplied with blood, but also innervated. If the doctor damages any nerve during the procedure, neurological disorders will occur. This may be twitching of the eye, the formation of nystagmus (involuntary eye movements). You need to contact a neurologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Out of sight!
An outstanding ophthalmologist, who has performed over 11 thousand cataract operations in different countries of the world, Professor Mikhail Konovalov, agreed to clarify the situation, highlighting misconceptions and fears .
Risk area
– Answer honestly: are there many unsuccessful cataract operations? Ivan S., Novosibirsk
– With a good diagnosis and a standard situation, when the problem is limited only to clouding of the lens, failures, according to the best ophthalmological clinics in the world, are about 4-5%. Moreover, failure is often expressed in slightly worse visual acuity than expected, and not at all in the absence of vision.
Risk factors include high intraocular or blood pressure and concomitant diseases, such as diabetes. If there is a serious failure, it is sometimes very difficult to repeat the operation, but this is a common feature of eye surgery. So choose your clinic and surgeon very carefully.
What is the reason?
– The doctor said that I have cataracts, but for my age my vision is quite tolerable... What kind of disease is this? S. Sergeeva, Novosibirsk region.
– A cataract is any clouding of the lens of the eye, even one that does not reduce visual acuity at the moment. And it can occur at any age. There are congenital cataracts, caused by disturbances in intrauterine development of the fetus. Or complicated - it usually develops in middle-aged or young patients against the background of systemic diseases of the body or under the influence of various environmental factors, such as increased doses of radiation. Traumatic cataracts can occur as a result of injury or contusion to the eye. But the most common cataract is senile (age-related), which sooner or later affects more than half of the world's population. Over the years, the lens begins to lose transparency. There is an opinion that this is an inevitable consequence of the aging of the body. And yet, it is not always possible to say exactly why cataracts developed. It is known that changes in the structure of the lens occur against the background of a shift in general metabolic processes. Ultraviolet radiation is also a damaging factor – cataracts are more common among southerners than among northerners. Therefore, it is recommended for everyone to wear sunglasses in summer.
How to minimize the risk of complications
To reduce postoperative complications, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- staying at rest in a dark room so that negative environmental factors do not affect the eyeballs;
- use of sunglasses outdoors so that bright sun rays do not negatively affect the retina of the eyes in the postoperative period;
- postoperative antibiotic therapy, which eliminates the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- eating food rich in vitamins, nutrients, microelements necessary for normal metabolism and regeneration of damaged surfaces;
- lack of exercise in the first month after surgery, then exercises are prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor;
- the use of moisturizing drops that eliminate the risk of drying out the cornea.
Cataract removal is an operation that damages a small amount of tissue. Despite this, the patient may develop many complications, especially if he does not adhere to the doctor's recommendations. If a complication appears, you need to immediately contact a specialist so as not to lose vision function.
Preparation for implantation of intraocular lenses
At the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, before implanting an intraocular lens, an ophthalmologist draws up an individual preoperative examination plan. It includes laboratory tests, as well as instrumental diagnostic methods that allow you to assess the general condition of the whole organism. Typically, the examination plan includes:
- Blood test for hemoglobin level;
- Blood clotting test;
- Blood sugar test;
- Blood chemistry;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Extensive ophthalmological examination.
Laboratory tests must be ready no later than two weeks before surgery. They are taken in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach. And also, no earlier than 14 days before the start of the operation, it is necessary to do an ECG. If you have a history of diabetes, it is recommended that you visit an endocrinologist before IOL implantation. You can undergo preoperative preparation, including a diagnostic examination and laboratory tests, at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency in one day, which will significantly save your time. However, it should be borne in mind that the list can be changed based on the individual indications of each patient.
A few days before the operation, the patient is examined by ophthalmologists. The day before, it is recommended to stop taking medications that affect blood clotting.
Rehabilitation after implantation of intraocular lenses
The next day after the operation, vision is completely restored. In just 10 days the patient can start working.
However, there are general rules of conduct after surgery:
- Physical activity is not recommended for a week after surgery;
- You should not visit saunas or swimming pools to eliminate the risk of infection.
Your treating specialist will prescribe all the necessary medications to quickly recover your eye after surgery. Taking any other medications, including those from a home medicine cabinet, must be agreed upon with an ophthalmologist. After completing the rehabilitation course, you must come to see a doctor in 2 weeks for an in-person examination.