Congenital farsightedness is a physiological phenomenon that is associated with the size of the child’s eyeball. 90% of children are born with a slight degree of hypermetropia. As the body grows, the eye also enlarges, and over time, vision returns to normal. But sometimes pathological farsightedness can develop. How to recognize its symptoms?
Farsightedness is a refractive error in which the resulting image is formed in the area behind the retina. This leads to the fact that objects located nearby, at a distance of approximately 20-40 cm, are visible blurry and
In this article
- Physiological cause of congenital farsightedness
- The magnitude of childhood farsightedness by age
- Farsightedness in children under 3 years of age
- Hypermetropia in a child aged 6 years
- Degrees of farsightedness in children
- Symptoms of farsightedness in children
- What consequences can cause farsightedness?
- Treatment methods for farsightedness in children
blurry, but at longer distances the vision is clear and precise.
How to treat farsightedness in children?
In this article
- How to treat farsightedness in children?
- Farsightedness in children - characteristics of the disease
- Causes of farsightedness in children - what causes the pathology?
- How do physiological farsightedness differ from congenital farsightedness?
- Diagnosis of childhood farsightedness
- How are glasses and lenses selected to correct childhood hypermetropia?
- Does eye gymnastics help with childhood farsightedness?
According to ophthalmologists around the world, visual pathologies are “getting younger.” If just a few 10 years ago, visual impairment was predominantly characteristic of older or elderly people, today refractive errors are increasingly being diagnosed in children, including very young children - up to 6-7 years of age. There are many factors that contribute to this trend: poor environment, poor diet, use of electronic devices, and so on. Be that as it may, doctors are sounding the alarm and calling on parents to more carefully monitor the state of their children’s vision.
In childhood, refractive errors cannot be treated by any means. Nowadays, the most effective and popular method of correcting vision pathologies is laser procedures. However, they are contraindicated for children. A person can only sign up for such an operation independently upon reaching 18 years of age. Treatment of childhood farsightedness, myopia, and astigmatism should be carried out using other methods. There are quite a lot of them, but not all of them provide complete relief from the disease.
First of all, treatment of farsightedness in children is aimed at stopping the development of the pathology. Subsequently, the refractive error may disappear on its own. It depends on the individual characteristics of the body and many other factors. Let's consider all the means available to ophthalmologists to help a child with farsightedness preserve their vision.
Preventive measures
Ophthalmologists urge parents to follow preventive measures and do gymnastic exercises from the first days of their baby’s life. Let's talk about some of them. Firstly, you should teach your child to blink (this way the cornea is not susceptible to drying out), be sure to monitor his posture and teach him to look from near objects to distant objects and vice versa as often as possible.
If the child is under 7 years old, then try to limit watching TV, playing on the computer and gadgets, or other activities to half an hour a day. A student can perform the same series of actions and activities, but for an hour. It is best to watch TV two to five meters from the screen or monitor and 40 cm from the computer. In this case, it is recommended to sit directly in front of the equipment, and not to the side. Make sure that the lighting in the workroom is natural, and that light from other sources is not directed into the eyes - it should fall on the object of study, and not on the face (it should remain in the shadow).
And, perhaps, the most important rule is not to forget about gymnastic exercises for the eyes (they serve as an excellent prevention of any diseases, including farsightedness and myopia). It will be useful at any age and under any set of circumstances. Even if both you and your child are absolutely healthy.
Gymnastics for the eyes
We will also tell you about some gymnastic exercises that can prevent the development of the disease, and then your child will not have to wear glasses for farsightedness. They need to be performed every half hour if there is any work or play going on:
- train the accommodative function of the eyes by placing a colored mark at eye level (preferably on a window). The child should look at the point for several seconds, and then switch his gaze to objects located outside the window, that is, at a far distance.
- To reduce visual fatigue, you should massage your closed eyes for 10 seconds or look to the sides, up and down, without changing the position of your head.
- It is also recommended to wash your face alternately with cold and hot water, sprinkling your eyes.
In childhood, vision plays a key role as it affects the overall development of the body and health in the future. Therefore, it is important to visit an ophthalmologist from the first day of life and, in case of any violations, immediately resort to solutions to the problem. And also follow all recommendations and do not refuse to wear glasses or contact lenses if a specialist has identified any pathologies. In any case, only a competent specialist can answer the question of whether children with farsightedness need to wear glasses after examination and diagnostic procedures.
Farsightedness in children - characteristics of the disease
First, we’ll find out what is meant by farsightedness, after which we’ll look at issues related to the development of this disease in children. Farsightedness (hyperopia) is a refractive error that affects near vision. A farsighted person sees well into the distance, but objects that are close to him cannot be seen clearly. The higher the degree of hypermetropia, the shorter the distance from which it is clearly visible becomes. In severe forms of the disease, the ability to see clearly is lost, which manifests itself at any distance. It is important to prevent this from happening. A high degree of farsightedness, that is, with a very strong deviation of vision from the norm, correcting the pathology is problematic, especially in childhood, when surgical and laser operations are contraindicated.
Farsightedness - what is it?
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is one of the most common visual defects that occurs in children and adults, along with myopia and astigmatism. The cause of this refractive error is often a weakness of the refractive apparatus of the eye caused by insufficient curvature of the cornea. In this case, the focusing of light rays occurs not in the center of the retina (macula), but behind it. Therefore, nearby objects appear fuzzy and blurry.
Farsightedness can also develop due to a shortened eyeball (20-22 mm instead of 23.5 mm). At the same time, the distance between the center of the cornea and the macula zone of the retina is reduced, which leads to focusing failure. A child with farsightedness experiences discomfort when working with objects at close range, for example, while writing, reading or working at a computer monitor. The letters merge, appear fuzzy and blurry. The higher the degree of the disease, the worse the person will see up close. The degree of progression of the pathology is determined by diopters (D).
Causes of farsightedness in children - what causes the pathology?
In adulthood, hypermetropia can occur after eye injury, due to complications caused by operations on the organs of vision. Sometimes farsightedness is caused by eye diseases of an infectious nature, as well as tumors in the eye and orbital areas. These factors can cause farsightedness in children, but this happens rarely. Hypermetropia in childhood is mainly due to a genetic factor.
Actually, there are two main causes of farsightedness in childhood: improper eye shape and damage to the eyeball system, which is responsible for refracting light rays. Sometimes the occurrence of hypermetropia is a consequence of both of these reasons.
Symptoms of the disease
The main problem that arises when it is necessary to timely identify children's farsightedness is the absence of complaints from the patient himself - only by the age of 5-6 years will the child be able to complain of visual disturbances.
Before this age, parents can suspect trouble only on the basis of indirect results of monitoring their child - the child’s rapid fatigue with increasing visual load, irritability and nervousness, and behavioral characteristics.
With young children, you need to pay attention not only to how the child plays, but also to what toys he prefers.
It is also important to remember that the use of bright and colorful pictures in children's books, large and colorful toys for young children is not an attempt by manufacturers of children's goods to get maximum profit, but also the conditions necessary for the normal development of the eye and the formation of vision.
A large drawing and a toy are much easier to see, and large letters in children's books will make learning the alphabet an exciting process, and not a source of eternal irritation for the baby.
Abnormal eye structure due to farsightedness
Irregular eye shape refers to an anteroposterior axis or diameter that is too short. In the absence of farsightedness, the normal axis length is 23-24 mm. For farsighted people it can be much shorter. It is not known exactly why such an anomaly develops. This can happen in the womb. Poor nutrition, poor environment, and stress experienced by a pregnant woman affect the condition of the fetus. Difficult childbirth, accompanied by injuries, can also contribute to the further development of farsightedness.
Causes of farsightedness
Hypermetropia is associated with weakness of the refractive apparatus or flattening of the eyeball, and is often combined with other defects of the organ of vision, which can result from the following risk factors:
- diabetes;
- age-related changes in eye structures;
- genetic predisposition;
- injuries;
- eye fatigue;
- excessive physical activity;
- poor nutrition;
- increased intraocular pressure.
Congenital form of eye disease
The disease is associated with defects in the structure of the organ of vision and is often hereditary. The development of the refractive system of the eyes is influenced by the mother’s lifestyle in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. Risk factors are:
- poor nutrition;
- bad ecology;
- stress;
- infectious diseases;
- smoking, alcohol abuse.
Acquired hypermetropia
Farsightedness develops when the refractive system (lens, cornea) is damaged or the anterior-posterior axis of the eyeball is reduced, resulting in the following reasons:
- tumors near the eye socket;
- surgical interventions;
- eye injuries;
- removal of the lens for cataracts and its damage;
- taking medications.
Farsightedness in children
Newborns are characterized by physiological hyperopia of both eyes, which is associated with the small size of the eyeball, weak curvature of the cornea and low refraction of the lens. A child’s vision in the first months of life is plus 4-5 diopters. Hypermetropia in children noticeably weakens by the age of 8 and disappears by 12-14 years.
Pathology is considered vision at 3-4 years, as at birth.
The following reasons lead to this:
- Anomalies of the eyeball - underdevelopment, irregular shape.
- Disturbances in the development of the refractive system - displacement or small size of the lens, its absence, flat cornea.
Age-related hypermetropia
The pathology is associated with disturbances in the structure of the lens and weakness of the ciliary muscle, which worsens refraction. The process begins at 25 years of age, vision decreases by 40-50 years. The ability to accommodate completely disappears by the age of 60-65. Presbyopia is a natural condition caused by age-related changes in the tissues and muscles of the eye, and occurs in 30% of people.
Problems in the structure of the optical system of the eye
When we talk about disturbances in the functioning of the refractive system of the organs of vision, first of all, we mean such eye structures as the cornea and lens. The first has a constant refractive power of 40 diopters, but the lens changes its curvature, so its refractive power can range from 19 to 33 diopters. This is typical for a healthy person. With farsightedness, the cornea is flat or the lens is not convex enough. The rays that pass through them are refracted incorrectly, throwing them beyond the plane of the retina. The picture the brain receives blurs up close. Distance vision is preserved. However, the progression of hypermetropia will subsequently lead to a deterioration in visual functions, no matter from what distance a person wants to view an object or object.
Diagnosis of the disease
If a child quickly gets tired when working with objects at close range, but does not have any complaints about blurred vision, he should consult an ophthalmologist. Comprehensive diagnostics of the visual system will reveal farsightedness even at the earliest stage. To do this, the doctor will examine the fundus of the eye, measure the size and curvature of the child’s cornea, and also check visual acuity. In addition, additional examination methods are carried out, such as autorefractometry, skiascopy, visometry, assessment of eye movements and testing binocular vision. As a result, the specialist will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis and select the optimal method of vision correction. Buying glasses yourself is strictly prohibited. This can lead to the progression of the pathology and serious disturbances in the functioning of the visual system.
Why is farsightedness dangerous in childhood?
The problem with hypermetropia in children is the difficulty of identifying it at an early stage. This is due to the natural state of the visual organs after birth. They are still small, so every child is characterized by some degree of hypermetropia. The norm for farsightedness in children immediately after birth is about +4 diopters. Its degree can be even higher. This indicator of farsightedness persists in a child up to 5-6 years of age, sometimes up to 7 years of age. It is very difficult to distinguish this condition, which is natural, from a pathological process. This can only be done during the examination.
Diagnostic measures
Get a complete vision examination at the Lege Artis Eye Clinic
It's time to correct your vision!
Make an appointment by phone:
8(804) 333-02-14 Free call
Diagnosis of hypermetropia in children is carried out by an ophthalmologist. Visual acuity testing is carried out using different methods, depending on the age of the child. Also, before the study begins, drops are instilled into the eye to dilate the pupil. This leads to relaxation of the ciliary muscle and allows you to correctly measure the light refractive ability of the eye. For timely detection of farsightedness, it is recommended to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist at least once a year.
Diagnosis consists of collecting an anamnesis, parents provide complete information about the child’s behavior and present complaints: a child with problems with visual perception quickly gets tired, becomes withdrawn, has a predominant bad mood, school-age children are characterized by slow reading, but bright pictures at a distance (billboards, posters) they look at with great interest.
To identify farsightedness, different diagnostic methods are used:
- visometry - tables with pictures are used for children, tables with letters are used for middle school children;
- determination of violations of the refractive power of the eye is carried out using autorefractometry, necessarily in conditions of cycloplegia: drug dilation of the pupil and switching off accommodation;
- skiascopy and retinoscopy.
How do physiological farsightedness differ from congenital farsightedness?
So, the norm for farsightedness in children under 5-6 years of age is no more than +4 diopters. After 6 years it decreases noticeably. Between the ages of 8 and 10 years, eyeball growth is at its fastest. During this time, vision usually returns to normal, although in some cases the eyes may change their shape as a result of body growth up to 18-20 years.
Farsightedness is observed in all children under 6 years of age. It can be distinguished from congenital hypermetropia, which already has a pathological basis, during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
Most often it is detected during an examination, which is carried out at school in the first grade. Children of preschool age are not always examined annually, so congenital farsightedness can progress, thus “hiding behind” the physiological form of this refractive defect. Parents who themselves suffer from it should check their child’s vision more often in order to notice the development of the disease in time.
Indications for the use of corrective optics. When does a child need glasses?
glasses for a child, it is important to undergo an examination. Only a specialist can tell what stage the disease is at, whether it is progressing and how to correct vision. As mentioned above, at the age of up to 7 years, farsightedness can be corrected independently, naturally, but again, such a conclusion can only be made after examination by a specialist. So, in what case does a child need glasses for farsightedness?
Ophthalmologists talk about the following indications:
- when the disease is greater than the age norm;
- visual acuity begins to decrease;
- there is convergent strabismus or optical strabismus. Experts call the latter anisotropy;
- if the child was diagnosed with astigmatism with indicators: 0.75-1.5 diopters;
- if the child complains of asthenopia, so-called visual fatigue.
How does farsightedness manifest in children?
A sign of any refractive error is blurred vision. With farsightedness, its sharpness decreases when a person looks at objects close up. However, a preschool child does not understand that blurry pictures in a book are a visual pathology. He does not complain about his condition, but the disease develops further. Parents can notice its first symptoms by observing their child. If he moves a book or magazine away from his face, gets tired quickly, constantly rubs his eyes with his hands, he should make an appointment with a doctor.
Children over 7 years old who already go to school, read and write, can themselves pay attention to the deterioration of their vision. If they come with complaints of feeling unwell, dizziness, headaches, eye fatigue, you should not ignore them. Most likely, the child has farsightedness.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the degree of farsightedness; the higher it is, the more severe the symptoms:
- With a weak degree, headaches, dizziness occur, and the eyes quickly get tired.
- In moderate cases, the child is capricious, sleeps poorly, and is bothered by inflammatory eye diseases such as blepharitis or conjunctivitis. Visual acuity at close range is reduced, although at a long distance he sees everything clearly.
- With a high degree, visual acuity is lost near and far.
Children cannot concentrate on one job for a long time, they are irritable, and become withdrawn due to vision problems. Sometimes they feel a burning sensation and a feeling of sand in their eyes.
Inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane appear due to the fact that the child constantly rubs his eyes due to fatigue; he can cause an infection.
Diagnosis of childhood farsightedness
To determine whether a child has hypermetropia or not, you can use a duochrome test. It is available on the Internet and is a table with two fields: red and green. Each half depicts optotypes (symbols). You need to read the table from a distance of one meter, first with one and then with the other eye. If a child clearly sees the symbols on the green half of the picture, but the letters on the red background are blurred, he is likely developing hypermetropia. The degree of farsightedness cannot be determined at home. To do this, you need to visit an ophthalmologist's office. He will conduct an examination, determine the nature of the pathology, its causes, type, degree of it in the child and other factors, on the basis of which he will prescribe treatment.
Treatment
Is it possible to cure farsightedness in a child? Yes, if you consult a doctor in time. At an early age of up to 4 years, it is difficult to notice pathology, since the child cannot describe his feelings. But already at 5-6 years old one can suspect problems with vision.
Treatment of infants
Even if a baby has farsightedness of 2.5-3 diopters, the baby does not need treatment. All treatment procedures are possible once he reaches one year of age.
Treatment at 1-3 years
Farsightedness in children 3 years old goes away on its own closer to 4-6 years, but if no improvement is observed, then you need to move on to treatment. Otherwise, by the age of 10, the child’s visual acuity will significantly decrease and he will have to constantly wear glasses or contacts.
Cardinal methods are not used. If the degree of farsightedness at 1-3 years is high, then hardware techniques are used. These include:
- vacuum massage;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound;
- electrical stimulation;
- laser therapy.
Other procedures can be used to improve metabolic processes.
Hardware techniques are absolutely painless. They are held in a playful way, so children can easily tolerate them. Hardware treatment can be performed no more than 3-5 times a year.
Glasses are not prescribed at this age. Not only will they not bring results, but they can cause harm.
To restore visual acuity without medical procedures, you need to provide your child with vitamins. Be sure to include fresh fruits (bananas, peaches, apricots, prunes), vegetables (carrots, tomatoes, cabbage, peas), blueberries, rose hips, dried fruits and walnuts in your diet. The child needs vitamins A and C, as well as potassium.
It is useful to give your baby medications in the form of dietary supplements. They improve metabolism and accelerate the development of the eye organs, which reduces pathology.
Therapeutic methods for children aged 4-6 years
Treatment of farsightedness in children of this age group necessarily begins with vision correction. A child, even with a mild degree of hypermetropia, needs to wear plus glasses, about +1D. They should only be worn while reading, playing on the computer or watching TV. You shouldn't wear glasses all the time.
Together with correction, hardware treatment and exercise therapy for the eyes are used. How to treat farsightedness in children with exercise?
Gymnastics for the eyes looks like this:
- You need to take a sitting position. First look forward, then turn your head to the right and return to the starting position. At the same time, move your gaze following the movements of your head. Similarly, you need to turn your head to the left. Repeat 5-10 times in each direction.
- In a sitting position, you need to extend your arm at a distance of 30 cm from your eyes and put out your index finger. First you need to look at it for 30 seconds, and then focus your gaze on a distant object for 20-30 seconds. Repeat this up to 10 times.
- You need to take a sitting position, put your right hand at eye level, your palm should be at a distance of 50 cm from your face. Then make circular movements with your fingers clockwise, then you need to change your hand and rotate your fingers clockwise. Should be repeated 7 times.
It is useful to alternate between reading and drawing, using each eye alternately. Read more about vision correction in children →
Treatment at 7-10 years
Farsightedness in children over 6 years of age is manifested by the fact that the weak (far-sighted) eye initially strains to see normally, but this only leads to spasms of the eye muscle due to prolonged overstrain. From the age of seven, the attending physician prescribes glasses with collective lenses. They also use hardware techniques, vitamin therapy and exercise therapy.
In rare cases, when the degree of hypermetropia is high and strabismus and other complications develop, microsurgery is indicated. During the operation, the lens is removed and an artificial one is placed in its place. After surgery, the child sees well at any distance. Read more about eye surgery →
How is farsightedness treated in children?
Treatment of childhood farsightedness is carried out using three methods: wearing optics (spectacles and contact lenses), hardware therapy, and performing eye exercises. As already noted, laser correction of farsightedness is not performed in minor patients. The eyes grow, the cornea changes its shape, and the stage of the refractive error also changes. High farsightedness can progress to moderate and even weak. It is necessary that the eyeballs take their natural shape. For this reason, you should not even wear lenses a few days before surgery, when it is prescribed for adults. The impossibility of prescribing such a procedure is not critical. It is possible to cure childhood farsightedness or stop its development using other methods.
Is it possible to warn?
Are there methods to prevent the disease? In order to prevent the occurrence of farsightedness or detect the disease in time and begin treatment, it is necessary:
- Regularly visit an ophthalmologist for preventive examinations.
- Monitor the variety of your child’s diet (include foods rich in vitamins and microelements).
- Properly organize the place where the child will study (maintain the correct height of the chair and desk, monitor the lighting).
- Limit your child's time at the computer or TV.
- Take your baby for walks in the fresh air more often.
Farsightedness that appears at a young age (up to a year), as a rule, does not cause serious discomfort to the child, and by the age of 4 it can go away on its own.
Things are worse if the child has already started school, and signs of the disease are still making themselves felt.
In this case, treatment is necessary; the choice of one or another method is made by the doctor after diagnosis.
An ophthalmologist talks about farsightedness in children in this video:
How are glasses and lenses selected to correct childhood hypermetropia?
Correction of the first degree of farsightedness in children is not required. The accommodative apparatus copes with visual acuity up to +3 diopters. It compensates for the refractive error. Hyperopia of 3 to 6 diopters is corrected by optics with an optical power 1 diopter less than the actual visual deviation. This is done to stimulate the accommodative abilities of the eyeball. Farsightedness in a child over 6 diopters is considered severe.
It is very difficult to choose glasses, since the patient has poor vision at long distances. High degrees of hypermetropia are better treated with contact lenses. They do not cause discomfort and do not take long to get used to. Treatment of farsightedness in children 7 years of age and older is carried out using contact lenses. At this age, the child can handle them himself. Until the age of 6-7 you have to wear glasses.
Treatment methods for hypermetropia in children
Farsightedness is treated conservatively in children under 18 years of age. If there is no positive effect after adulthood, microsurgery or laser vision correction is used.
Starting from a very early age - from several months of life - optical means for vision correction - glasses or contact lenses - are used. Spectacle correction is the most common due to its availability and low cost. Pleoptic hardware treatment is used to develop visual acuity. You can get high positive results and remove glasses in the future only if you choose the right lenses. To do this, a diagnosis is carried out, after which the doctor writes a prescription for the necessary glasses. Parents can choose the frame themselves; it is advisable to give preference to materials such as carbon or plastic. These frames are durable, reliable and light, and do not cause discomfort. To ensure that your child wears glasses without whims, it is better to choose frames in the child’s favorite color scheme.
Some parents and their doctor select contact lenses to correct farsightedness, as they have their advantages - first of all, the lenses do not slip or get dirty, and do not interfere with the child’s participation in active sports.
Does eye gymnastics help with childhood farsightedness?
Eye exercises allow you to restore visual acuity after eye strain, that is, while studying. Daily exercises for farsightedness prevent its further progression. It is impossible to cure the pathology by doing gymnastics, but exercises help stop its development. There are many types of them. The specific complex should be advised by the attending physician. With high hypermetropia in children, exercises are contraindicated.
Symptoms, signs and diagnosis of farsightedness
non-physiological, the child has difficulty distinguishing between nearby objects, when reading he moves the book far from his eyes, and so on, the need to do this regularly irritates many patients, which they mention in a conversation with the doctor, that is, an increase in the refractive power of the lens . Visual discomfort in patients with farsightedness can manifest itself:
- rapid fatigue;
- burning in the eyes;
- pain in the eyes;
- pain in the eyes;
- increased tearfulness;
- photophobia ( all of the above symptoms worsen in bright light
); - headaches.
the higher it is, the faster accommodation “gets tired” and the more pronounced the clinical manifestations of the disease. For farsightedness, the doctor may prescribe:
- measurement of visual acuity;
- determination of the degree of hypermetropia;
- study of the refractive systems of the eye.
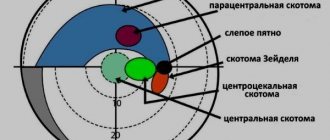
Determining the degree of hypermetropia
because he sees them oddly that is, lenses , that is, has he become better able to see the letters on the table? Each subsequent lens used in the diagnostic process must have a refractive power of 0.25 diopters more than the previous one . Depending on the violation of the refractive system of the eye, they are distinguished:
- Mild hypermetropia
– up to 2 diopters. - Moderate hypermetropia
– from 2 to 4 diopters. - High degree of hypermetropia
- more than 4 diopters.
Types of farsightedness
intensification , which is observed with high degree hyperopia. For farsightedness, the following is determined:
- Obvious hypermetropia.
This is the severity of hypermetropia, determined when accommodation is turned on (
preserved
), when the lens of the eye functions normally. Obvious hypermetropia is determined during a visual acuity study during the selection of corrective lenses. - Complete hypermetropia.
This term denotes the severity of hypermetropia, determined when the accommodation apparatus is turned off.
During the study, special drops ( atropine
) are used. Atropine causes persistent relaxation of the ciliary muscle, as a result of which the ligaments of the lens become tense and it is fixed in the most flattened state, when its refractive power is minimal. - Hidden hypermetropia.
It is the difference between complete and obvious hypermetropia, expressed in diopters. Hidden hyperopia reflects the extent to which the compensatory capabilities of the lens are involved in a particular patient.
Study of the refractive systems of the eye
In the diagnosis of hypermetropia, the following can be used:
- Skiascopy (
shadow test ).
The essence of this study is as follows. The doctor sits opposite the patient and, at a distance of 1 meter from the eye being examined, installs a special mirror that directs a beam of light directly to the center of the patient’s pupil. The light is reflected from the retina of the eye being examined and is perceived by the doctor's eye. If during the examination the doctor begins to rotate the mirror around a vertical or horizontal axis, a shadow may appear on the retina, the nature of the movement of which will depend on the state of the refractive system of the eye. With hypermetropia, this shadow will appear on the side towards which the mirror will shift. When a given shadow is identified, the doctor places lenses with a certain refractive power in front of the mirror until the shadow disappears. Depending on the refractive power of the lens used, the degree of hypermetropia is determined. - Refractometry.
To conduct this study, a special device is used - a refractometer, consisting of a light source, an optical system and a measuring scale. During the examination, the doctor directs a beam of light into the patient's pupil, causing horizontal and vertical stripes to appear on the retina. Normally they intersect with each other, but with farsightedness they diverge. In the latter case, the doctor begins to rotate a special handle, as a result of which the refractive power of the device changes, which leads to a shift in the lines on the patient’s retina. At the moment when these lines intersect, the refractive power of the lens required to achieve this result is estimated, which determines the degree of farsightedness. - Computer keratotopography.
This method is designed to study the shape, curvature and refractive power of the cornea.
The study is carried out using modern computer technologies, without causing any discomfort to the patient and without taking much time ( on average, the procedure lasts from 3 to 5 minutes
).
Diagnostics
If parents notice signs of hypermetropia in a 2-3 year old child, then they should not self-diagnose. If unpleasant symptoms occur, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist who will conduct the necessary tests.
During the examination, a specialist may use special drops that dilate the pupil of the eye. Thanks to this, the lens relaxes, which allows the specialist to examine the real refraction of the eye.
In some situations, you have to deal with hidden visual impairments. In this case, the condition of this organ deteriorates significantly. Parents should sound the alarm if the child exhibits very severe irritability, headaches and a general deterioration in condition that, at first glance, has no apparent reason.
In such situations, you need to undergo a full examination. If we talk about diagnostic methods, then first of all the specialist asks the child to read the signs indicated on special tables, while closing each eye in turn. This will help determine the degree of farsightedness that the child suffers from.
Then, using a special computer, the optics of the eyes are checked. Today this is the most accurate method for determining the degree of hypermetropia. At the end of the test, the equipment produces a result that will indicate the number of diopters for each baby’s eye. Also, with the help of modern equipment, optical power can be determined. If necessary, a special additional examination is carried out, for example, ultrasound (to determine the condition of the fundus).
If we talk about the treatment of hypermetropia in both eyes in a child or when only one visual organ is affected, then it always depends on the degree of the child’s general condition, as well as on individual characteristics.