When an ophthalmologist tells a patient that he has false myopia, many do not understand what they are talking about. In this article we will talk in detail about pseudomyopia, its causes and treatment options.
False myopia is commonly called a functional visual disorder in which the muscle responsible for the normal functioning of the accommodative apparatus spasms.
Unlike true myopia, false myopia is reversible. It is important to notice the symptoms as early as possible and contact an ophthalmologist before the process of vision deterioration reaches an irreversible stage.
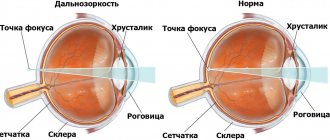
Visual acuity near, far, and at an average distance depends on how well the eye's accommodation mechanism works. This is the name given to the ability of the eye's natural optics to adjust to different distances, providing clear vision. This is possible due to the elasticity of the eye lens and the work of the ciliary muscle, due to which it changes its curvature, thereby ensuring correct focusing of the image. If for some reason this muscle is in a state of spasm, then the lens does not change curvature, focusing is impaired and the clarity of vision decreases. This condition is called a spasm of accommodation. This is what is commonly called false myopia.
Here are the symptoms that may indicate accommodative spasm:
- eyes get tired quickly when working at close range;
- unpleasant symptoms: dryness, burning, redness, pain;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision;
- tearfulness;
- weakness, headache.
What is false myopia?
the content of the article
- What is false myopia?
- Symptoms of false myopia in children
- Causes of false myopia in school-age children
- Treatment of false myopia in children
- Prevention of accommodation spasm
- Complications of false myopia
False myopia is a spasm of accommodation. Many people have experienced the loss of the ability to clearly see distant objects for some time. Usually this condition appears after prolonged visual work. This is called false myopia. Accommodation is the ability of the eye to refract light rays. This is necessary so that a person can clearly see objects at any distance.
The term "accommodation" is translated as "adjustment". That is, the eye literally “adjusts” to certain conditions in order to provide clear vision. This occurs due to changes in the curvature of the lens, which is influenced by the ciliary muscle. It is shaped like a ring and is located around the lens. If a person looks into the distance, then the ciliary muscle is relaxed. When the eye focuses on an object located nearby, it tenses, making the lens more convex.
The cause of false myopia is a spasm of the ciliary muscle of the eye. It continues to remain tense even when there is no need to focus on a nearby object. Because of this, visual acuity decreases. A person has difficulty seeing objects that are located at a distance from the visual organs. The symptoms of this disorder are similar to those of myopia. The difference between these conditions is that false myopia is a reversible process.
Vitamins for false myopia
The patient can take vitamins along with eye drops. They must contain carotene, vitamin C, and retinol. The drug “SuperOptic” is in high demand, containing antioxidant compounds, B vitamins, selenium, copper, manganese, omega-3 fatty acids and other compounds important for the full functioning of the visual organs.
If a person already has false myopia, for prevention purposes he should take eye vitamins prescribed by a doctor every six months.
False myopia in school-age children
False myopia often occurs in schoolchildren. This usually occurs under increased visual stress: after prolonged work at the computer, reading a book in low light. Spasm of the ciliary muscle is associated with the focusing of the lens on objects that are located close to the eyes. After prolonged tension, the muscle is not always able to relax quickly. While the ciliary muscle is tense, the child experiences difficulty with distance vision. False myopia develops not only in school-age children. This condition is common among adults. Especially those who spend a lot of time at the computer. But most often, accommodation spasm occurs in schoolchildren. About every sixth student between the ages of 10 and 16 experiences false myopia. The main reason for the occurrence of this condition in children is high visual stress during the learning period and a lack of vitamins in the body.
Classification of pseudomyopia
Pseudomyopia has the following varieties:
- Physiological. This is the most common type of false myopia, resulting from prolonged visual strain. In this case, the person focused his eyes on the computer or TV monitor for a long time. At the same time, the ciliary muscle contracts and does not relax, and the effect of myopia occurs.
- Artificial. Occurs as a side effect during the use of one or another group of medications. It does not require treatment because it goes away immediately after stopping the medication.
- Pathological false myopia occurs as a result of a violation of the mechanism of accommodation due to pathology.
- Mixed pseudomyopia is understood as a temporary decrease in vision resulting from the action of several pathogenic factors.
Symptoms of false myopia in children
It is very important for parents to promptly pay attention to their child’s complaints. False myopia is a reversible process, but its danger lies in the fact that if left untreated, it can turn into true myopia. The following symptoms allow you to diagnose a spasm of accommodation:
- frequent headaches;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- pressure in the eyeballs;
- decreased concentration;
- burning sensation in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- lacrimation.
Preschool children and primary school students cannot always describe their condition. With a spasm of accommodation, the child often becomes capricious, irritable, and refuses to do homework or read books. Often in this state, children begin to rub their eyes, which causes them to become red and watery. The child loses interest in any visual work: reading, drawing, etc. Symptoms of false myopia should be an alarming signal for parents. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the spasm of accommodation will occur more often. At first it may last for several hours after long visual work. Then - a few days. Ultimately, this can lead to the development of myopia.
Causes of false myopia in school-age children
The main cause of accommodation spasm is increased visual stress. At school age it is almost impossible to avoid them. For many children, the load on the visual system during learning becomes colossal. Before going to school, they rarely had to deal with such volumes of work. But stress on the visual analyzer is not the only cause of false myopia in children. Spasm of accommodation also occurs for other reasons. Among them:
- violations of the daily routine: insufficient sleep, lack of walks in the fresh air;
- insufficient lighting of the workplace or incorrect posture during lessons;
- excessive passion for computer games, watching TV at close range;
- insufficient distance from the eyes to a notebook or book - less than 30 cm;
- the size of the chair or desk does not match the child’s height;
- lack of vitamins and minerals that are beneficial for visual health;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine;
- violation of the tone of blood vessels that supply the brain;
- suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- metabolic disorders, obesity.
Parents cannot always monitor how their child does homework. Often children who are deprived of parental control do not maintain the required distance from their eyes to the textbook, watch TV for a long time or play on the computer. Therefore, adults need to make an appointment for their child to see an ophthalmologist at least once a year. Prevention of vision and timely diagnosis of disorders will allow the doctor to prescribe treatment and prevent serious pathologies.
How is a spasm of accommodation diagnosed?
In order to diagnose false myopia in school-age children, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist. The doctor will collect anamnesis during a conversation with the child or his parents. A mandatory procedure performed by an ophthalmologist for symptoms of accommodative spasm is computer refractometry. This research method allows you to examine the refractive power of the eye.
When examining children, the ophthalmologist will also conduct a vision test. Usually the Sivtsev table is used for this. This allows you to determine how many diopters the child’s vision has fallen. During the examination, the doctor also measures intraocular pressure and conducts a shadow test. If in doubt, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the eye or an MRI. These procedures will help identify abnormalities in the structure of the visual apparatus.
Diagnostics
False myopia is diagnosed only instrumentally
, since a survey and medical history do not help differentiate it from the true form of pathology. To do this, methods are used aimed at searching for anomalies that cause a decrease in visual acuity:
- ophthalmoscopy - visual examination of the fundus using a special instrument;
- refractometry - study of the refraction of light inside the eyes with a wide and narrow pupil;
- tonometry - measurement of intraocular pressure;
- perimetry - instrumental determination of the boundaries of visual fields;
- visometry - measurement of visual acuity using specially designed tables.
If, during the examination of the functioning of the visual organs, the doctor does not detect any pathology, but there are signs of myopia, a diagnosis of false myopia is made.
Treatment of false myopia in children
In case of spasm of accommodation, the doctor selects therapy individually, based on the characteristics of the child’s body and the frequency of occurrence of false myopia. Treatment of this condition is a complex of measures. It is almost impossible to relieve a child from accommodative spasm with one medication. The main goal of treatment is to eliminate spasm of the ciliary muscle of the eye and relax it. For false myopia, children are often prescribed drops such as:
- "Atropine";
- "Irifrin";
- "Mydriacyl";
- "Tropicamide";
- "Cyclomed".
Treatment with drops is carried out in courses. Their duration depends on how often the child experiences a spasm of accommodation. The average course duration lasts from 1 to 4 weeks.
Drops with a moisturizing effect are often used to treat false myopia. They will help relieve the child of the symptoms that accompany this condition: relieve redness and dryness of the cornea.
Treatment for spasm of accommodation often includes:
- gymnastics for the eyes;
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- diet.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving spasm of the ciliary muscle. The treatment regimen is determined by an ophthalmologist. His instructions must be followed strictly.
In addition to drug treatment, surgery and exercises, physical therapy is prescribed. It is used, as a rule, in the complex drug treatment of myopia. To improve the effectiveness of therapeutic measures, massage the back and collar area.
You should include in your diet more foods containing vitamins C, A, E. They are found in fruits, carrots, some animal products, nuts, and vegetable oil. Seafood should also be included in your diet.
Medicines
To treat false myopia, mydriatics are used - drugs that relax the ciliary muscle. Most often, the ophthalmologist uses Midriacil. At the same time, vitamin complexes are used, which have a beneficial effect on the visual apparatus and prevent deterioration in the visibility of objects.
Sometimes vitamin preparations are dropped into the eyes. They restore normal functioning of the ciliary muscle and improve blood supply to the lens.
Surgery
Most often, patients with false myopia are treated with laser vision correction. The laser beam stimulates the visual function of the eye and restores the functioning of the ciliary muscle. The operation does not allow an increase in the degree of myopia.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes sclera-strengthening operations for patients. During retroscleroplasty, elements of the patient’s blood or a synthetic gel developed for plastic surgery are injected into the eye. With scleroplasty, the eyeball is strengthened by introducing a graft into it.
Prevention of accommodation spasm
There is a set of rules that must be followed in order to prevent the development of false myopia. They allow you to normalize the functioning of the ciliary muscle of the eye and avoid a decrease in visual acuity due to the progression of myopia. Prevention of accommodation spasm includes:
- strict adherence to the daily routine - night sleep should be at least 8 hours;
- proper nutrition, which must include taking vitamins;
- performing regular physical activity, playing sports;
- maintaining a distance of more than 30 cm between the eyes and a textbook, notebook or monitor;
- ensuring the correct level of lighting during visual work.
It is necessary to give your eyes a rest. Children should take breaks from visual work at least once an hour. Ophthalmologists also recommend performing exercises that help relax the ciliary muscle. The simplest exercise is squinting. You need to close your eyes for 5 seconds, then open your eyes as wide as possible. The exercise should be repeated 10 times in a row.
Exercises
Gymnastics to prevent accommodation spasms are very effective. Performing a set of exercises daily not only fights spasm, but also prevents its occurrence in the future. Exercises are very beneficial for children because they help keep the eye muscles in good condition.
It is recommended to glue a small black dot with a diameter of no more than 5 mm to the window. At the beginning of the exercise, the gaze is focused on this point, and after half a minute the gaze is moved into the distance. Repeat these steps several times. This exercise relieves accommodation spasm well and prevents the development of myopia.
Procedures using computer programs are widely used. They have a positive effect on eye tissues and prevent myopia from turning into true myopia.
Complications of false myopia
If you do not take the necessary measures to prevent accommodative spasm and do not adhere to the treatment prescribed by the doctor, the child may develop true myopia. Often, when refractive error becomes a consequence of false myopia, doctors diagnose moderate or high myopia - more than 3D.
In some children, vegetative-vascular dystonia occurs due to accommodation spasm. Disturbances in the functioning of the ciliary muscle of the eye often lead to the fact that the child’s pupils can dilate or contract involuntarily. Vegetative-vascular dystonia often manifests itself in school-age children. False myopia contributes to the development of this pathology.
Spasm of accommodation can lead to asthenopia. This is a pathological condition, which consists of rapid eye fatigue and discomfort during visual work. Some children experience pain in the eyes and watery eyes. Many schoolchildren complain of frequent headaches and double vision.
How to stop progressive myopia?
Progressive myopia in adults is corrected by laser therapy. The rays are absolutely safe for the body and the organs of vision in particular. They affect the cornea, changing its shape. As a result, the shell becomes flatter and its optical power decreases. Thanks to this, the image falls directly on the retina, and the patient clearly sees distant objects.
Surgery
If myopia progresses in an adult and has reached a high degree, surgery is performed.
The surgery is called myopic keratomileusis. The essence of the manipulation is to excise the upper layers of the cornea, remove the optical disc and return the excised layers of the cornea to their place. This allows you to preserve the functions and structure of the stratum corneum.
Taking vitamins
For false myopia, the following vitamins are useful:
- A;
- IN 1;
- AT 2;
- AT 6;
- AT 12;
- WITH.
Of the microelements, calcium and zinc are especially important. Ready-made vitamins for adults, which are prescribed for myopia - Blueberry Forte, Vitalux Plus, Vitrum Vision.