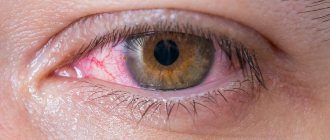
Fungi and spores are constantly present on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
They belong to normal microflora.
There are pathogenic fungal formations that cause inflammation of the eyes.
Typically, this disease occurs in a chronic form; no purulent discharge is observed . Instead, films and nodular infiltrates may appear. To determine the disease, it is necessary to conduct microscopy after taking a smear. Treatment is carried out with fungicidal agents over a long period of time in order to completely eliminate the microorganism from the surface of the eyes.
Causes
Most fungal growths on the surface of the eye do not cause an inflammatory reaction . They belong to normal microflora. About 50 species are pathogenic, producing clear clinical symptoms. Most common:
- parasitic fungi;
- yeast-like fungi.
Fungi, which belong to normal microflora, can cause inflammatory reactions in the following cases:
- chemotherapy treatment of malignant neoplasms;
- radiation burns;
- diabetes mellitus and its complications;
- fungal infection of the skin;
- use of certain categories of medications (glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics);
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiency;
- wearing contact lenses without applying hygiene rules.
If a pathogenic fungus gets on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes, a lesion does not always form; this requires exposure to negative factors:
- strong wind;
- low temperatures;
- unsanitary living conditions;
- use of antibiotics;
- decreased immune function.
Fungal infection of the eyes is similar to other types of conjunctivitis. To restore the body, the doctor must determine the root cause. Only after this do they begin treatment.
Why does ophthalmomycosis occur?
Fungal infection is possible through inhalation of dust containing spores of mycotic organisms.
Fungal conjunctivitis occurs when the following microorganisms enter the eye structures:
- aspergellus;
- candida;
- sporotrichum;
- actinomycete;
- coccidioides;
- penicillium;
- Rhinosporidium.
The main causes of infection are the following:
If you use contact lenses incorrectly, the disease will not be long in coming.
- decreased immunity;
- eye injuries, especially with the formation of a wound (burns, wounds);
- lack of personal hygiene;
- improper care and installation of contact lenses;
- contact with infected animals;
- professional activities related to storing grain, baking bread;
- using household items of a sick person that have not been disinfected;
- skin fungal diseases;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- consumption of unwashed vegetables and fruits, contaminated water;
- eating moldy foods;
- fungal infection of residential premises.
Risk group
Are the following categories of patients at risk:
- HIV-infected;
- persons with congenital immunodeficiency;
- people who use antibiotics for a long time;
- patients living in unsanitary conditions;
- patients with systemic disease caused by fungal infection.
People from the above list should periodically contact an ophthalmologist and other doctors to check their body. If fungal infections are detected early, the disease is easier to cure.
Classification
Depending on the manifestation of clinical symptoms, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- catarrhal - the symptoms do not appear clearly, slight redness and inflammation are formed, there is no discharge from the eyes;
- purulent - formed when a bacterial infection spreads, which leads to the release of a purulent infiltrate from the inner corners of the eyes;
- membranous, nodular – characterized by the presence of foreign formations on the surface structures of the eyes;
- complicated by keratoconjunctivitis - the transition of a fungal infection to the cornea, which causes damage, inflammation, swelling, and minor hemorrhages.
Depending on the spread to various structures of the eyeball and surrounding skin surfaces:
- keratitis – inflammation of the cornea;
- blepharitis - inflammation of the eyelid;
- conjunctivitis – inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Depending on the presence of various formations, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- granulomatous - penetration of fungi into the meibomian glands, which causes the formation of yellow grains;
- exudative – the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, as a result of which purulent exudate is released from the inner corners of the eyes.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor classifies the fungal infection, since the methods of therapy depend on it.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by the following manifestations of clinical symptoms:
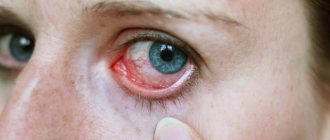
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- the appearance of grains in the granulomatous form, which can subsequently open, forming fistulas (holes);
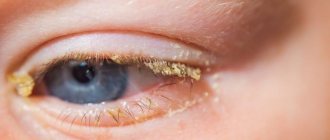
- the formation of green and yellow pus in the exudative form;
- with certain forms of fungal infections, erosions and ulcers can form on the conjunctiva, cornea, and they become covered with a green coating on top;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes, into which fungi and bacteria penetrate, causing suppuration;
- covering the mucous membrane of the eyes with gray or yellow films that can be removed by a doctor;
- keratitis – inflammation of the cornea;
- increased production of tear fluid, which is replaced by dry eyes, which leads to damage and microtrauma on the surface of the cornea.
Unlike other types of conjunctivitis, the fungal form has minor clinical symptoms . This continues until complications arise. If there is no treatment or the patient has an immunodeficiency, this leads to deformation of the eyelids, as a result of which the patient is unable to close the eyes completely.
Diagnostics
Since the various forms of conjunctivitis are similar to each other, the doctor needs to use 2-3 diagnostic methods to determine the root cause:
- Collecting data from the patient's words . A person is worried about redness of the eyes, a feeling of a foreign body, and films may appear on the mucous membrane.
- General examination of the patient . The doctor detects inflammation of the conjunctiva. In rare cases, purulent discharge is formed, so the disease can be confused with a bacterial form.
- Bacteriological culture . A swab is taken from the patient's eyes and sent to the laboratory. It is sown on a nutrient medium. After 5-7 days, bacterial flora develops, which causes the disease or complicates fungal conjunctivitis. Additionally, an antibiotic to which the bacteria are sensitive is determined.
- Microscopy . A swab is taken from the patient's eyes, applied to a glass slide, and examined under a microscope. The laboratory technician will see many mushrooms made from spores.
Only after a complete diagnosis does the doctor prescribe treatment.
Why does conjunctivitis occur in children and how is it treated?
In ophthalmological practice, inflammatory lesions of the conjunctiva are a fairly common phenomenon, especially in childhood. This disease is called conjunctivitis. It is caused by various reasons, on which treatment depends. Let's consider the main factors that provoke the occurrence of conjunctivitis and the symptoms of this disease.
Clinical picture of conjunctivitis in children
The connective mucous membrane lining the eyelids on the inside and connecting them to the eyeball is called the conjunctiva. This thin transparent tissue performs two important functions - protective and secretory. The conjunctiva protects the eyes from external factors - dust, germs, bacteria, fungi, viruses. In addition, the mucous membrane ensures constant wetting of the eyeball. If foreign bodies enter the connective membrane, irritation begins, activating the protective and secretory functions of the conjunctiva. The person experiences lacrimation, blinks reflexively, and the foreign body is eliminated. When an infection, fungus or other pathogenic microorganism gets on the mucous membrane, inflammation begins, called conjunctivitis.
Why does conjunctivitis occur in childhood? Children often rub their eyes with their hands when playing outside or in kindergarten with sand, dirty and dusty toys, so the risk of getting irritating substances on the conjunctiva is quite high. At the same time, the child’s immunity is still weak. The body cannot neutralize pathogenic microbes, and therefore conjunctivitis can be a consequence of even a common cold. The disease progresses in the same way as in adults. There are no big differences in the methods of combating conjunctivitis in childhood and adulthood.
Causes of conjunctivitis
The catalyst for the inflammatory process on the mucous membrane can be:
• Infections. These include pathogenic bacteria, for example, streptococci, gonococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and opportunistic fungi and bacteria that are always present in the external environment. Bacterial infections are severe and long-lasting compared to other types of conjunctivitis. On average, infections are treated for 10-14 days.
• Viruses, including herpes and adenoviruses. Typically, viral conjunctivitis lasts no more than 7-10 days, but the disease can become more complicated if it is accompanied by a bacterial infection.
• Fungi. Children with immunodeficiencies are susceptible to fungal conjunctivitis. Such inflammation of the mucous membrane takes a long time to be treated.
• Chlamydia are microorganisms that differ in nature from bacteria and viruses and occupy an intermediate state between them.
• Allergies. Intolerance to certain foods or allergies to pollen, fluff, or animal hair can cause inflammation of the conjunctiva.
• Eye injuries and poor hygiene. A child can inflict a minor eye injury on his own without noticing it. He will rub his eyes with his hands and accidentally cause an infection.
• Long-term course of inflammatory diseases of the eyes, ears, nose: rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis.
These are the main causes of conjunctivitis. Sometimes the baby is already born with incipient inflammation on the mucous membrane. This happens if a woman becomes ill with any infectious disease during pregnancy. The infection can enter the child's body through the blood.
Signs of conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis is not a disease that occurs exclusively in childhood. It can occur at any age. Even the fetus in the womb is not protected from this disease. This disease is often diagnosed in infants. However, most often the first signs of conjunctivitis are detected in children of 3 years old, when the child goes to kindergarten. The number of contacts increases, and keeping track of the baby is much more difficult.
Conjunctivitis does not appear immediately. The incubation period for viral forms of inflammation of the conjunctiva is 5-7 days. Bacterial conjunctivitis appears after 6-10 days. Inflammation caused by an allergy is noticeable almost immediately, once the pathogen is on the connective membrane.
The symptoms of the disease differ in the different forms in which conjunctivitis occurs, that is, it depends on the reasons that caused it. There are general signs, nonspecific, characteristic of any type of inflammation of the connective membrane of the eye:
• swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
• redness of the conjunctiva, edges of the eyelids and other structures of the eyeball;
• photophobia;
• lacrimation.
Signs of any conjunctivitis, except photophobia, are visible to the naked eye. But all these symptoms give a superficial idea of the disease. To accurately establish its nature, you need to know other signs characteristic of various forms of conjunctivitis. The bacterial type of inflammation is always accompanied by the release of yellow-brown pus of varying consistency. Pus accumulates on the edges of the eyelashes or in the corners of the eyes. Especially a lot of purulent discharge is observed in the mornings. Due to the pus, the baby's eyelids stick together, so it is difficult for him to open his eyes without the help of his hands.
Viral conjunctivitis is sometimes accompanied by headache, as it is often combined with rhinitis. Also, the viral form of the disease is characterized by fever, cough, and runny nose. With allergic conjunctivitis, the patient is bothered by a burning sensation and almost unbearable itching in the eyes, which is why the child rubs his eyes with his hands, the eyelids turn red and begin to hurt.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis begins with photophobia. Unfortunately, this symptom is difficult to detect in very young patients who cannot complain of pain in the eyes in bright light or explain their condition. Two or three times after chlamydia enters the conjunctiva, the eyelids and mucous membrane swell. Pus accumulates in the fold of the lower eyelid.
A person without medical education will not be able to accurately diagnose the disease and determine the form of conjunctivitis. The symptoms of chlamydial and bacterial inflammation of the mucous membrane are similar. In addition, fever is not a specific sign of this disease. Before the age of 7 years, the temperature usually rises with any inflammation. A child over 7 years old can experience the disease without this symptom. Thus, you will not be able to understand on your own how and how to treat conjunctivitis in a child. If one or two of the above signs of illness are observed, it is necessary to show the patient to a doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children
So, there are many different forms of conjunctivitis. Treatment depends on the causes of the disease. In general, this disease is not very dangerous. But this does not mean that conjunctivitis in a child goes away on its own, without treatment. It becomes dangerous if there is no treatment and another infectious or viral disease is added to conjunctivitis. This can lead to conjunctivitis protracting and causing complications, which causes vision deterioration. In this regard, the child must be shown to a doctor, and not try to cure him on his own at home. After a diagnosis is made and the necessary medications are prescribed, the baby can be treated at home. It is only important to follow all the instructions of the attending physician.
For bacterial conjunctivitis, the patient is prescribed antibiotics in the form of eye drops or ointments. You need to wash your eyes with special solutions every 2-3 hours to prevent the formation of a purulent crust. It is best to instill drops during the day and apply ointment to the eyes at night. It has a calming effect, relieves pain and itching, helps the baby sleep and prevents the pus from drying out and the eyelids sticking together.
Viral conjunctivitis does not require specific treatment. It is necessary to regularly wash your eyes with solutions. Within a few days, the baby’s body must cope with the virus. With viral conjunctivitis, it is important to prevent infections from entering the organs of vision. Make sure your child doesn't scratch his eyes and wash his hands frequently.
When treating allergic conjunctivitis, it is first necessary to protect the patient from the irritant. To do this, of course, it is necessary to establish what exactly is the irritating substance. Also, with this form of inflammation, antiallergic and antihistamine drops are prescribed. They are used in courses, usually lasting 2-4 weeks.
It is not recommended to treat conjunctivitis in children at home with folk remedies. In adulthood, the body copes with this disease quite quickly. Cure conjunctivitis at home yourself, if the disease is of an allergic nature or viral origin, is quite simple and quick. The therapy uses compresses made from herbs and decoctions. It is better not to use folk remedies for treating children without examination by a doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children under one year of age
In infants, the nasolacrimal ducts are not fully opened. Because of this, conjunctivitis in newborns takes on a nonspecific form - dacryocystitis. With this disease, tears do not flow out, which leads to the formation of swelling. The nasolacrimal ducts will open on their own a few months after birth. If conjunctivitis occurs before the tear ducts are fully opened, conventional treatment with drops and ointments will not be enough. Parents will have to give a light massage to the child, pressing on the inner corners of the eyes. Massage helps reduce itching, burning and pain. Otherwise, the little patient will cry constantly.
Conjunctivitis resolves quickly with timely treatment. If the disease is neglected, there is a risk of developing dry eye syndrome, blepharitis, keratitis, cataract, and scarring of the soft tissues of the eye. These pathologies require long-term treatment, otherwise the process of deterioration of visual functions may begin.
Come for a diagnosis at the Kazakh Research Institute of Eye Diseases at the address: Almaty, Tole bi street, 95a (corner of Baitursynov street). Telephone; +7 (727) 279 54 36
Treatment
Complex therapy is used to prevent the formation of complications. Fungal infections are quite difficult to remove, so treatment lasts for 1-2 months . Additionally, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests to determine the trend toward recovery.
Local antimycotic drugs
Medicines against fungi in tablet form have a strong effect on the liver. Therefore, doctors most often prescribe local drugs:
- eye instillation solutions (Nystatin, Natamycin);
- ointments under the eyelids applied before bed (Nystatin).
Solutions are used throughout the day. Ointments are necessary to suppress the growth of pathogenic microflora at night.
Systemic antimycotic drugs
If the fungal infection is extensive, the doctor prescribes a systemic remedy . For this purpose, Fluconazole and Intraconazole are used. If the patient suffers from immunodeficiency, the drugs are administered intravenously.
If a person experiences liver damage during long-term therapy, doctors prescribe hepatoprotectors.
Antibacterial drops
Antibacterial drops are often used during treatment. They do not affect the state of the circulatory system. Thanks to the drops, you can keep the entire microflora of the body normal.
An excellent remedy would be “Albucid”. This drug inhibits the growth of bacteria, including various fungi, gonococci, etc. Sold in 20-30 percent concentration. These drops should be used no more than six times a day. You need to instill about 3 drops. Among the disadvantages, burning sensation during use should be noted.
Tobrex eye drops are also a good remedy that allows you to cope with a large number of symptoms. Fungal conjunctivitis is most often treated with this drug. If the disease is in an acute stage, then drops should be used every four hours. Among the disadvantages of the drug, it is necessary to note a possible allergy to it in the form of swelling and redness.
Complications
If left untreated, the disease is complicated by the following cases:
- spread of fungal infection into the eyeball or other tissues;
- damage to the eyelids, as a result of which their inversion occurs, a person cannot completely close his eyes;
- inflammation of the cornea;
- inflammation of the tear ducts;
- inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
In order to prevent complications in a timely manner, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor and carry out treatment.
Spelling the word "conjunctivitis"
The difficulty in choosing the spelling of this word with “ь” or “ъ” is determined by the fact that in Russian this borrowed word has a different morphemic composition than in the source language.
The name of this disease is formed in a suffixal manner from the cognate word “conjunctiva”:
conjunctiva - conjunctivitis.
To understand why in Russian this word should be written with a hard dividing sign at the root, and not with a soft sign, as is found everywhere, let’s say, in educational articles, let’s turn to the Latin language, from which the lexemes in question are borrowed.
At the beginning of these foreign language terms there is the original Latin prefix con-, which is not distinguished in the morphemic composition of these words in the Russian language, and the etymological root begins with the letter “yu”, which corresponds to the conditions for writing a hard sign in the Russian language:
The letter “ъ” is written in a word at the junction of a Russian prefix ending with a consonant, before the root of a word starting with the letters “e”, “e”, “yu”, “ya”, as well as after the Latin prefixes ab-, ad-, diz -, in-, -inter-, con-, ob-, sub-, etc.
Let us immediately note that in the Russian language, in borrowed lexemes, the indicated Latin prefixes are distinguished with difficulty or are not distinguished at all, but merged with the root of the words, as happened with the medical terms under consideration.
If there is difficulty in writing the word “conjunctivitis,” turn to any dictionary.
In the dictionary word “conjunctivitis” the separator “ъ” is correctly written.
Foreign words and derived lexemes with the initial element con- are written in a similar way:
- conjecture (guess, text correction);
- conjugation (bringing together chromosomes);
- conjuncture (current situation);
- opportunistic
- opportunist
- conjunctive (subjunctive mood of the verb).
Prevention
To prevent the development of fungal conjunctivitis, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- daily hygiene of hands, face, eyes;
- wearing contact lenses according to the rules;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases;
- immunodeficiency therapy;
- annual preventive examination by an ophthalmologist.
Fungal conjunctivitis is a disease that is difficult to treat, especially with complications. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor if eye inflammation occurs and fully adhere to the treatment rules.
Folk remedies
According to ophthalmologists, fungal eye disease cannot be cured with folk remedies alone, but with their help it is possible to reduce the intensity of the symptoms of conjunctivitis. Effective medications that are recommended to supplement basic therapy include:
- Drops with aloe juice for fungal conjunctivitis. Freshly squeezed liquid is diluted with boiled water 2:1 and instilled into the affected eye 2-4 times a day. The product helps eliminate swelling and pain.
- Lotions made from chamomile infusion. To prepare the decoction, 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the flowers and leave for 30 minutes. The liquid is filtered off and cotton swabs are soaked in it, which are immediately applied to the eyelids. This remedy is useful for both fungal and allergic conjunctivitis; in addition, it has antiviral properties, cleanses the tear ducts, relieves redness and swelling.