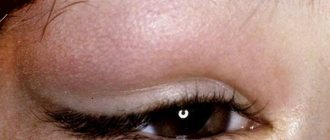
Filamentous keratitis is an ophthalmological disease characterized by damage to the cornea. It appears against the background of a sharp decrease in the function of the lacrimal glands (dry eye syndrome). The pathology is accompanied by the appearance of single or multiple growths in the form of threads on the cornea.
Hypofunction of the lacrimal glands causes inflammatory-dystrophic changes, the transparency of the cornea decreases, and vision deteriorates. The disease is quite common, it is diagnosed in 5% of the world's population. Women aged 45-60 years are most often affected. Let's look at the symptoms and treatment of filamentous keratitis.
Causes
There are primary (typical, idiopathic) filamentous keratitis and secondary (atypical). The exact causes of the primary form still remain unclear. It begins with a decrease in the amount of tear fluid secreted and a change in its composition.
It was found that filamentous keratitis appears due to disruption of the endocrine system. It is often detected in people with Sjogren's syndrome, which is characterized by autoimmune damage to the exocrine glands, including the salivary and lacrimal glands, with the simultaneous development of immune-inflammatory pathologies (neuritis, myalgia, arthralgia, etc.). The primary form can be provoked by:
- Other autoimmune diseases (diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus);
- Scleroderma;
- Cirrhosis;
- Hepatitis;
- Hemolytic anemia;
- Skin diseases;
- Weak immunity;
- Age-related changes;
- Hormonal imbalance before and after menopause;
- Avitaminosis.
Secondary filamentous keratitis is based on changes in the normal process of tear fluid entering the conjunctival cavities.
The causes may be: conjunctivitis after trachoma, diphtheria, scarring after an eye burn, or improperly performed ophthalmic surgery.
The cornea can also be damaged as a result of external factors:
- Microtrauma of the eyes;
- Long stay in a room with air conditioning or fan heater;
- Watching TV for a long time, working at the computer;
- Exposure to toxic substances, dust, cigarette smoke;
- Use of low quality cosmetics;
- The use of certain medications (GCS, antidepressants, oral contraceptives, blood pressure lowering agents);
- Use of contact lenses;
- Contact of pathogenic microflora from the environment with the eyes;
- Unsuitable climate (dry air, dust, sand, strong wind).
The peculiarity of the disease is its protracted course. The periods of remission are short-lived, they depend on the activity of the concomitant pathological process. Ophthalmologists classify the disease as a manifestation of severe dry eye syndrome, severe corneal-conjunctival xerosis (drying of the mucous membranes).
Classification of keratitis
Researchers have based the classification of keratitis on various factors: origin, location, causes of development, forms of progression, degree of damage.
So, according to where the disease “came” from - from within the body or from the external environment, keratitis is divided into:
- endogenous. When the disease was caused by the body’s own specific bacteria, lack of vitamins, general diseases and allergies;
- exogenous. Developed as a result of injuries, foreign bodies, burns, etc.;
- unknown etiology.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the disease can be:
- superficial. The lesion extends no more than one-third of the thickness of the corneal layer;
- deep. When the inner, deeper layers of the cornea are affected.
The division of keratitis into:
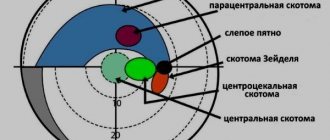
- peripheral. Do not enter the iris and pupil;
- paracentral. Located in the area of projection of the iris;
- central. Located on the projection of the pupil zone.
Symptoms
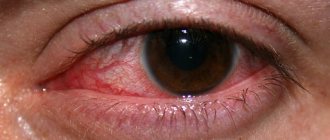
Filar keratitis often affects both eyes. It begins with redness and swelling of blood vessels. A viscous mucus is formed, resembling thin threads. If they are removed, small ulcers form on the cornea. Symptoms of filamentous keratitis are characterized by:
- Pain, dry eyes;
- Redness of the conjunctiva;
- Itching;
- Feeling of squeezing of the eyes;
- Light intolerance;
- Contraction of the eye muscles;
- Discomfort, pain when blinking;
- Foreign body sensation;
- Absence or decrease in tears when crying.
Subsequently, the epithelium begins to peel off. Horny areas form on the cornea, but its sensitivity does not change. The further course is characterized by degeneration of an increasing number of cells, and eye function is impaired.
One of the signs of filamentous keratitis is clouding of the cornea. It is caused by edema, the appearance of infiltrates, single and multiple. Infiltrates can be located on the surface or in the deep layers of the cornea. Superficial ones can disappear without causing clouding.
At the site of infiltrates, ulcers with a clean or purulent bottom may form. If the edges of the formation heal, its bottom will clear. After the epithelium heals, this place will be filled with connective tissue. If the development is unfavorable, the cornea will collapse and a cataract will appear. If it fuses with the iris, the patient will develop secondary glaucoma. Sometimes the cornea becomes flattened after ulcers.
Filamentous keratitis is accompanied by changes in the functioning of the glands (salivary, sweat), dryness of the nasopharynx, and difficulty swallowing. The skin becomes dry and peels. Systemic manifestations include: bowel disorders, polyarthritis, muscle weakness. Teeth become loose and fall out.
The essence of pathology
Normally, tear fluid forms a three-layer film that evenly covers the cornea of the eye. The outer layer of this film is formed by lipid cells that are secreted by the meibomian glands. This layer reduces friction between the eyelid and cornea when blinking and reduces the evaporation of fluid from the surface of the eye.
The middle layer is an aqueous solution of electrolytes and organic compounds. This solution saturates the cornea with nutrients and oxygen. In addition, it performs a protective function due to its complex chemical composition containing immunological, metabolic, and anti-inflammatory components. Mechanical protection is provided by simply washing out foreign bodies from the eye.
Biomicroscopic picture of filamentous keratitis
The mucin layer consists of cells of a protein nature, a product of conjunctival goblet cells and lacrimal acinar cells. This layer is a physical barrier that prevents foreign objects from reaching the surface of the cornea.
In addition, mucin performs a signaling function. When the cornea is damaged, these cells transmit a signal to increase epithelial division.
The tear film is unstable and ruptures. This stimulates the blink reflex, which helps restore its integrity.
A general weakening of the immune system and exhaustion of the body change the physiological composition of the precorneal tear film, which leads to deterioration of its characteristics, frequent ruptures, dryness of the surface of the cornea and conjunctiva, and the development of dry eye syndrome.
Diagnostics
If you suspect filamentous keratitis, it is better to consult an ophthalmologist. Consultations with a rheumatologist are necessary; women should additionally visit a gynecologist-endocrinologist. Experts will help you find out the causes of the disease.
The diagnosis is made by typical changes in the eyes, noticeable during biomicroscopy. Growths in the form of threads form in the cornea, foci of infiltrates, opacities, and keratinized areas appear. During diagnosis, microscopy of the cornea is performed to determine changes.
An installation test is performed to detect epithelial defects. Microscopic, cytological analysis of scrapings allows us to identify altered epithelial cells. Diagnostics also includes studies of tear fluid, the Norn test is performed (the stability of the tear film is analyzed), Schirmer's test (the amount of tear fluid is assessed).
They also do tests for lactoferrin (a multifunctional protein) and protein content. The osmolarity of the tear fluid is assessed, the number of Ap4A molecules (natural components of tears) is determined. The tests performed allow us to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
Treatment
Treatment of filamentous keratitis involves the use of a combined regimen. The effectiveness of measures will be higher if the disease is detected early. It is necessary to determine the causes of the disease and act on them.
Therapy of concomitant pathology will affect the condition of the eyes, causing stable remission.
The ophthalmologist will prescribe medications intended for the following purposes:
- Moistening the eyes;
- Stimulating the production of tear fluid;
- Retention of tear fluid in the conjunctival sacs;
- Eliminate inflammation;
- Cell nutrition.
Eye hydration can be ensured using solutions and gels with varying degrees of viscosity:
- Low (“Vizimed”, “Optiv”, “Vizin”);
- Medium (“Lakrisin”, “Ophtolik”, “Systein-ultra”);
- High (“Vizmed-gel”, “Systein-Gel”, “Oftagel”).
Medicines will replace tear fluid, some will enhance the process of epithelial restoration. They are used 4 times a day.
To eliminate inflammation, you need drops with corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone). Drip the solution 2 times a day. in the 1st week and 1 r./d. in the 2nd week Wash your eyes with sodium chloride solution (2-3 times a day).
Use antimicrobial agents, such as Syntomycin emulsion, if necessary. It is necessary to apply a compress. Apply the drug to a napkin and apply it to your eyes. Carry out the procedure 2 times a day. (1 week).
To nourish the cells, solutions with vitamins (ascorbic acid, riboflavin) are prescribed. Taurine drops are also used, which improve metabolism in tissues. They are buried 3-5 times a day. To eliminate cloudiness in the eyes with filamentous keratitis, electrophoresis with a solution of “potassium iodide” (2-3%) is used.
Immunosuppressive therapy is required to suppress unwanted reactions from the immune system. Cyclosporine helps a lot. It is an immunosuppressive drug and should be used 2 times a day. (1 month).
Electrophoresis with atropine and wearing soft contact lenses, which stop the development of pathology, give a good effect for filamentous keratitis. During the treatment period, it would be a good idea to stick to a salt-free, low-carbohydrate diet. You need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
If the disease progresses despite treatment, and vision becomes worse and worse, surgery is prescribed. It consists of removing filamentous formations, shading the place of their attachment with silver nitrate and zinc sulfite. The goal of other interventions is to correct the amount of fluid in the conjunctival cavities. In some patients, according to indications, punctal plastic surgery is performed, and the lacrimal canaliculi are sealed with implants made of collagen and silicone.
Treatment of keratitis in adult patients
Treatment of the disease can be either conservative or surgical. The doctor determines how to treat keratitis. He may prescribe antibiotics, antihistamines, and antiviral drugs for oral administration. Locally - antibacterial, antiseptic, moisturizing drops, anti-inflammatory ointments and gels, agents that defeat the herpes virus. In addition, the specialist will select medications that promote regeneration.
If the process has gone too far, surgery may be indicated, which may involve excision of the affected area of the cornea, replacing it with a graft, and removing superficial scars and scars.
Prevention of keratitis of any etiology consists of maintaining immunity, timely treatment of general and eye diseases, eye hygiene and timely examinations by an ophthalmologist.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine recipes are used in addition to the main treatment. A plant called “eyebright” helps a lot with eye diseases. It helps eliminate inflammation in the eyes, lacrimal glands, and relieves fatigue after hard work.
To prepare a medicinal decoction, use eyebright flowers. For 1 tbsp. You will need 1 teaspoon of water. l. raw materials. Fill it with water, bring to a boil, leave for 2 hours. Take 1⁄2 tbsp of the product. 3 rubles/day During the day, rinse your eyes with warm infusion several times.
To treat filamentous keratitis, compresses are necessary; they will speed up the healing process. Do the procedure half an hour before bedtime. Moisten gauze, cotton swab or soft cloth with warm infusion of eyebright and apply to eyes. Leave the compress on for 15 minutes.
If your eyes hurt, clay lotions will help. Place it on gauze, the layer should not be thicker than 2 cm. The compress is applied to the eyes, forehead, and back of the head. Pre-wipe these areas with a damp cloth. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes.
Traditional medicine recipes include steam baths:
- Based on dill seeds. Grind the raw materials, boil in 1 liter of water. Lean over the container with the broth and cover yourself with a towel. Stay like this for 10-15 minutes. The procedure is best done before bedtime;
- From a collection of herbs. You will need: eyebright, valerian (root), chamomile (flowers), elderberry (flowers) in equal parts. Boil the mixture a little, then carry out the procedure for 10-15 minutes.
A compress of sweet clover (flowers) will help relieve inflammation. At 1⁄2 tbsp. water will require 20 g of raw materials. Boil the broth for 15 minutes, strain, moisten the cloth, apply to the eyes for 15 minutes. Make compresses with sweet clover 2-3 times a day.
Sea buckthorn oil can help with filamentous keratitis. It will effectively eliminate pain and light intolerance. Instill the product in the first 2-3 days, 1-2 drops. with an interval of 1 hour, on subsequent days - with an interval of 3 hours.
Use aloe juice for treatment. Cut 2 leaves from a plant that is at least 3 years old, wrap in foil, and place in the refrigerator. In 7-10 days. squeeze out the juice, filter. Pour it into a small glass bottle, add a grain of mumiyo, and shake. Instill the product 1 rub/day. 1 drop each Starting from the 2nd month, use only aloe juice without mumiyo.
Forecast, prevention
Filar keratitis is quite difficult to treat, since it is caused by systemic pathologies. Pathological changes in the cornea cause vision to gradually deteriorate until it is completely lost. Sometimes the disease leads to perforation (perforation), softening of the cornea, and in some cases the membranes of the eyeballs fall out. Other complications:
- Keratoiritis (inflammation of the cornea, iris);
- Keratoiridocyclitis (inflammation of the cornea, iris, ciliary body);
- Keratoscleritis (inflammation of the cornea, sclera);
- Optic nerve atrophy;
- Glaucoma;
- Belmo.
There is a risk of developing life-threatening conditions: sepsis, phlegmon, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus.
There is no specially designed prevention. If you are diagnosed with Sjögren's syndrome, see your ophthalmologist regularly. He can recommend preventive measures.
Protect your eyes from injury. To perform work that is known to be hazardous to the eyes, wear special glasses. Avoid exposure to other negative factors. When using contact lenses, follow the rules of hygiene.
Pay attention to strengthening your immune system. Temper yourself, lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well. For inflammatory and other eye ailments, try to get treatment as quickly as possible.
General information
Keratitis is an inflammatory process of the cornea.
This disease most often affects the anterior part of the eyeball and ultimately causes visual impairment in humans. If a person develops keratitis, the symptoms of this disease arise as a result of infections. It can be an infection of viral, microbial, fungal origin. In addition, this disease is often a consequence of thermal, mechanical, chemical damage, as well as a result of disruption of the innervation of the cornea. Keratitis can also develop in people suffering from metabolic disorders, allergic manifestations, and hypersecretion of the meibomian glands . However, in some cases there is an unclear etiology.