In ophthalmology, congenital myopia
It is considered one of the most difficult diseases to treat. Its main cause is a violation of the development of the visual organs at the stage of intrauterine fetal formation. In some children, such deviations occur in a latent form and begin to progress only when the load on the optical apparatus is incorrectly distributed. Some children are faced with a progressive form of myopia, which rapidly develops, despite the correct dosage of visual stress.
Congenital myopia is detected in children in the first year of life
when most treatments cannot be used. However, this does not become an obstacle to complex therapy aimed at stabilizing the eye and returning visual acuity.
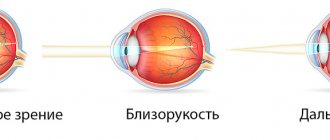
Degrees and types of myopia
Hereditary forms of myopia are classified in the same way as acquired visual defects. They can have a progressive or non-progressive form, a high level of loss of visual acuity immediately after the birth of the child, sometimes deterioration occurs over several months.
It is important to know! Unlike a disease, the cause of which was not a congenital predisposition, but acquired changes, the described type of pathology always develops more rapidly and has a lot of complications.
Congenital myopia is characterized by three degrees of the disease
, which reflect the severity of vision loss:
- weak, with vision loss down to -3 diopters;
- average - from -3 to -6 diopters;
- strong - over -6 diopters.
Due to the violation of the refraction of the light flux inside the eyes, congenital myopia is divided into three types:
- refractive - the occurrence of myopia is caused by improper refractive power of the cornea, vitreous body or lens (lens);
- axial - the development of pathology is provoked by the incorrect structure of the eyeball, in which it lengthens in the anteroposterior direction;
- combined, or mixed - pathology in which there are signs of refractive and axial anomalies.
Also, congenital myopia can be complicated or uncomplicated
. Over time, visual imperfections are complemented by strabismus, amblyopia, and other anomalies characteristic of childhood.
Prevention of myopia
Any disease, including myopia, is easier to prevent than to cure. Therefore, it is important to prevent myopia from an early age.
Maintain a distance of at least 30 cm between the eyes and the monitor, book, tablet, etc. This will reduce the effort required to focus vision and prevent the development of both temporary and permanent myopia.
The eyes need to be given rest. The longer your vision is strained, the higher the risk of developing myopia. Therefore, you definitely need to take a break after 40 minutes of visual work.
You should not read while lying on your back or side, or in a moving object (in a car, train, subway, etc.). The accommodation apparatus will have to reconfigure itself every second in order to capture the image, which will inevitably lead to its overstrain. If you read while lying down, then one eye will always be further away from the object than the other, which also causes visual strain.
It is important to always keep your back straight. Correct posture will allow you to look at the object of vision from the required angle.
Due attention must be paid to adequate lighting. This will relieve your eyes from overstrain. Sunlight is optimal for the human eye. But since it is not always possible to achieve such lighting when working, it is important to use artificial light. Be sure to install a desk lamp when working in the evening hours.
It is important to protect your eyesight from the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation.
Proper nutrition is an equally important factor for the prevention of myopia. Daily intake of minerals and vitamins will allow the organ of vision to function better and avoid overwork.
Vitamins for eyes for myopia
In order to avoid the development of myopia, it is important to consume vitamins that help preserve vision. If this is not possible, then you should use special complexes that your doctor can recommend.
Thiamine or vitamin B1. It affects the functioning of the nervous system as a whole, and its deficiency will lead to the eyes quickly getting tired and binocular vision to deteriorate, which increases the risk of developing myopia.
Riboflavin or vitamin B2. Its lack negatively affects the elasticity of blood vessels and provokes their ruptures, including those located in the eyeballs. Increased fatigue and tension of the accommodative muscle are manifestations of insufficient intake of riboflavin in the body.
Niacin or vitamin B3. With its lack, the blood supply to the optic nerve deteriorates.
Priridoxin or vitamin B6. Its deficiency causes inflammation of the optic nerve and provokes conjunctivitis.
Cyanocobolamine or vitamin B12. Without it, your eyes water and get tired faster.
For the prevention and treatment of myopia, it is important to supply all vitamins, and especially those belonging to group B.
Reasons for development
According to ophthalmologists, congenital myopia can be acquired through genetic inheritance by a child from one or both parents. The anomaly is formed at the stage of embryonic development. The most common type of defect is elongation of the eyeball. At an early stage of growth, the shape of the eye may stabilize and approach spherical, but in most cases it remains elongated. If there are traumatic factors in the baby’s life, myopia will progress. These include:
- premature birth of a baby or his birth with signs of hypoxia;
- insufficient or excessively bright lighting in the room where the baby spends most of the day;
- Incorrect placement of toys and mobile devices - objects placed low and close to the child’s face cause him to strain his eyes excessively;
- non-compliance with recommendations on hygiene of the child’s face and visual organs on the first day;
- previous intrauterine or postpartum infections.
If a child was injured during childbirth, or an increase in intracranial or intraocular pressure was recorded in the first months after birth, there is a high risk of rapid progression of congenital myopia. Introducing too early to playing with the phone, watching TV, books with small drawings, etc. is also not good for the baby.
Symptoms
While an adult and even a teenager can tell a doctor that they have vision problems, this is not possible for a child with congenital myopia. And the point here is not so much a lack of communication skills and a small vocabulary, but rather the fact that the little patient simply does not understand that he does not see well enough. For him, a blurry picture in the distance may seem normal. That is why, in order to identify pathology in the early stages, it is important to carefully look at the child’s behavior.
The following are indications that your child may be nearsighted:
- characteristic myopic squinting when making visual contact with objects more than 1 meter away;
- excessively frequent blinking with redness of the eyelids or profuse lacrimation, which, meanwhile, excludes an allergic reaction;
- bringing the eyes to the nose when trying to see something 1 m or more away;
- the baby gets tired quickly when playing or walking.
Children with a congenital form of myopia, as a rule, within an hour after active games with bright toys begin to rub their eyes, be capricious, and put their heads against their parents. This indirectly indicates that the child is suffering from discomfort in the eyes and, probably, headaches due to unconscious tension in the visual apparatus. If the parents managed to identify at least one sign from the above, they need to make an appointment for the little patient to be examined by an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Correction of presbyopia for myopia
There are two standard ways to correct presbyopia and myopia - glasses and contact lenses. When selecting conventional monofocal lenses, the degree of myopia is taken into account. In order to determine the optical power of the lenses that the patient will need, the degree of myopia is subtracted from the value corresponding to the age of the presbyopic lens. What does it mean?
For presbyopia, lenses with positive diopters are prescribed. If a person has always had good vision, then he will need presbyopic lenses with a power of +0.75-+1 diopters. After about five years, the optical power will have to be increased by 0.5 diopters. At about 60 years of age, you will already have the necessary ophthalmic products with an indicator of +3 diopters. After age 65, there is usually no need to adjust the power of your optics.
If myopia is present, the doctor will subtract the optical power of presbyopic lenses. However, clarification is always required. It is possible to understand exactly which diopters are suitable for the patient only after trying them on. For moderate and high myopia, you will need two pairs of glasses, which will have to be worn alternately. For convenience, it is better to choose multifocal contact lenses or bifocal glasses with several optical centers for vision at all distances.
Early diagnosis
Unfortunately, congenital myopia is not detected immediately after birth, even if the baby already has serious problems. In modern clinics, there are special hardware technologies that make it possible to diagnose vision in children from 3 months. If you do not do this, even before the age of one, the child will face complications:
- squint;
- lazy eye syndrome (amblyopia);
- retinal detachment or rupture;
- optic disc atrophy.
Such diseases are much more difficult to correct, and sometimes doom the child to a complete loss of visual connection with the outside world. That is why it is important for parents and pediatricians to pay attention to the baby’s ability to perceive surrounding objects with his eyes.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the child is examined using skiascopy, ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound or tomography of the eyes. Children with a hereditary predisposition to myopia are advised to undergo annual fundus examinations.
Important! At the Vision Restoration Center, we use the PlusOptix device to determine the degree of vision impairment of a child. It determines the refraction of the eye from a distance at the moment when one of the parents is holding the child in his arms.
Correction methods
In general, treatment of congenital myopia is a set of measures aimed at stopping the development of the disease and preventing complications. If diagnosed myopia progresses slowly (no more than 0.5 diopters per year), dynamic observation and a set of preventive measures are indicated:
- taking vitamins and microelements with components beneficial for vision, enriching the diet with products necessary for the eyes, but with the condition that the little patient is not allergic to them;
- balanced load on the eyes - you should not burden your child’s vision with numerous bright details; it is better to leave a few favorite medium-sized toys in his crib, and cover the walls with moderately bright, preferably plain, wallpaper;
- maintaining visual hygiene - avoid keeping the child in a dark room for a long time with limited light (a night light, for example) or in conditions of excessive brightness (in direct sunlight);
- performing simple eye gymnastics, which parents will have to do together with the child or resort to various tricks so that the baby performs the necessary actions.
Children with severe vision loss need optical correction. You can use glasses or contact glasses made to individual specifications. Constant wearing of glasses is indicated only if there is a significant decrease in visual acuity on the recommendation of a pediatric ophthalmologist. Children with mild myopia can use them to watch TV, read and while doing schoolwork.
Physiotherapy helps to improve the condition of the eyes and achieve stabilization, and in cases of low myopia, to restore vision. Modern ophthalmology has a variety of devices created specifically for children that can restore the natural accommodation of the eye, improve the hydrodynamics of the eyeball and microcirculation in it, and normalize the functioning of the intraocular muscles. Such procedures include:
- electrical stimulation;
- vacuum eye massage;
- infrared therapy;
- electrophoresis of the collar zone with medications;
- acupuncture.
To achieve noticeable improvement, you will have to undergo a course of 10-15 physical procedures.
If conservative methods do not help stop the progression of myopia, surgical methods are used: for example, scleroplasty. Scleroplasty does not improve vision, but it helps strengthen the walls of the eyeball and protect the retina from possible stretching to avoid further progression of myopia.
Important! The use of laser operations to correct vision for myopia in children is possible only after patients reach 18 years of age.
Methods for treating age-related myopia
If you suspect the development of poor distance vision, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Examination, an important stage of therapy
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, much less turn to traditional healers.
Important: Myopia is related to a person’s psychological state, but not so much as to refuse the help of professional doctors.
Today, this pathology is treated in the following ways:
- laser surgery,
- eye microsurgery,
- optical correction,
- exercises for the eyes.
Laser surgery for age-related myopia
With this type of correction, the disorder can be eliminated forever.
However, after 40 years, there is a risk that after surgery the myopic disorder of the visual system will turn into hypermetropia, i.e. farsightedness.
Laser correction eliminates the need to wear glasses
Despite this, many ophthalmologists advise patients to undergo laser correction even in old age.
If there are no contraindications in the form of corneal damage or inflammatory processes, then the result in most cases justifies positive expectations. Read more about laser correction here.
Features of microsurgical manipulations on the eyes
It happens that patients over 40 years old cannot undergo laser correction for certain reasons.
In such a situation, the ophthalmologist may suggest a surgical treatment method.
Ophthalmic surgeons perform surgery
Fact: Microsurgery typically involves inserting a phakic lens or completely replacing the natural lens with an intraocular lens.
This method of therapy is more traumatic, so the patient must be extremely careful in the postoperative period. The slightest damage to the mucous membrane or infection can trigger a relapse.
Details of the treatment of patients after 40 years of age are in this material.
The essence of optical correction
Optical correction of visual acuity is considered classic and has virtually no contraindications.
In this case, the patient is prescribed to wear glasses or contact lenses.
Individual selection of optical correction
The diopter value and glass characteristics are selected individually.
Important: However, there is one nuance: you cannot give 100% correction, otherwise the eye muscles will atrophy and the disease progresses even faster.
The best option is a correction of up to 95%.
Forecast
Unfortunately, congenital myopia cannot always be completely eliminated. If treatment for myopia is not started in time in childhood and amblyopia develops, then even after reaching the age of 18 and undergoing laser vision correction, it is impossible to completely eliminate the consequences of the vision anomaly inherited from the parents. However, prognoses depend entirely on how quickly the pathology was detected. If the pediatrician and parents noticed deviations in the child’s behavior indicating myopia in the first 3 months and began full treatment, the chances of a successful outcome become very high.
The only exceptions are cases of malignant, rapidly developing myopia. It is difficult to contain, it cannot be corrected by a limited range of means and methods approved for use in children.
The only way to avoid serious vision problems in a child
— even before pregnancy, discuss with a neonatologist measures to prevent eye abnormalities in the baby. They are especially important if one or both parents are nearsighted.
How is presbyopia diagnosed?
When a patient aged 40 years or older comes to see an ophthalmologist with complaints of headache, fatigue and poor near vision, he is prescribed a series of procedures for an objective diagnosis. Such studies include:
- checking visual acuity with an additional refraction test;
- skiascopy or computer refractometry to determine refraction;
- ophthalmoscopy and biomicroscopy to study all structures of the eye, including the fundus;
- tonometry and gonioscopy to exclude glaucoma accompanying presbyopia.
After the examination, the doctor decides on prescribing means for presbyopia correction. Their choice depends on the presence or absence of other vision pathologies and many other factors. First, it’s worth finding out how presbyopia manifests itself in myopia and farsightedness, and what a patient with several vision pathologies should do.