The combination of cataracts with myopia or farsightedness is a fairly common occurrence in the daily practice of ophthalmologists. Cataract itself is considered a very serious pathology that requires a special approach and cannot be corrected by conservative therapy. If myopia and hypermetropia are added to it (these terms are used to denote myopia and farsightedness), the situation can only be corrected with the help of a specialist who knows the methods of modern high-tech treatment of eye diseases.
What are myopia and hypermetropia?
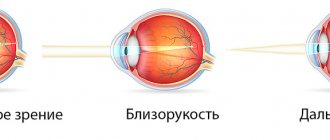
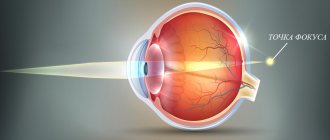
Myopia or myopia is a pathology in which the eyeball is increased in length and because of this the retina is located behind the focal plane. The image is formed in front of the retina and up close objects appear blurry.
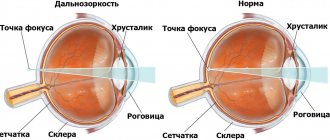
Hypermetropia, or farsightedness, is an eye disorder in which objects near you appear blurry and unclear, but distant objects appear clear.
What are the advantages of contact lenses?
contact lenses. Optics does not treat refractive errors, but only allows a person to see well if there is a vision pathology. Also, glasses and contacts help stop the progression of eye disease. When wearing them, your vision will not deteriorate further.
Contact optics have many advantages over glasses. They provide higher image quality and do not limit the field of view. In addition, unlike glasses, the lenses do not fall off the face, do not fog up, they will never break or injure the face and eyes. You can wear them in any weather. The lenses will not be a hindrance in bad weather conditions. Rain, snow, cold do not affect the quality of correction. Contact optics make it easier to lead an active lifestyle. Athletes and tourists prefer to wear it.
All these advantages of contact correction products are undeniable. However, people choose this method of correcting visual pathologies not only because of the described advantages. In some cases, wearing glasses is contraindicated or useless.
Differences between the two pathologies
The difference between myopia and hyperopia is that with farsightedness, a person cannot clearly see near objects, work with small objects or read, but he can clearly see objects that are in the distance. But with myopia, on the contrary, distant objects are seen blurry, but near ones are very clear.
Also, myopia and farsightedness differ in that myopia can be inherited and manifests itself during the formation of the body, i.e. in childhood, and hyperopia, in turn, can begin to develop in adulthood, usually after 40-45 years. Unfortunately, this is an inevitable process for everyone.
Causes
Myopia is a common phenomenon; according to statistics, there are more than 1 billion people on the planet who suffer from this vision disorder. The reasons for the development of myopia may be the following:
- Strong refraction of light rays , while the size of the eyeball corresponds to the standard, but due to strong refraction, the light rays converge into focus not on the retina, but in front of it.
- Irregular shape of the eyeball - the length of the anteroposterior axis of the eye exceeds the norm, because of this light rays do not reach the retina. As a result, the back wall of the eye also stretches and changes in the fundus occur, for example, retinal detachment, myopic cone, etc.
- Heredity. Experts believe that the predisposition to myopia is transmitted at the genetic level, just as hair color, nose shape, face shape are transmitted and the size of the eye or the refractive properties of the lens. If only one person has myopia, then the likelihood of this eye disorder occurring in the child is reduced by approximately 30%. Those at risk include those who have both parents with myopia.
- Weakening of the scleral tissue can lead to an increase in the size of the eyeball, which leads to myopia.
The reasons leading to the development of farsightedness include:
- Eyeball with reduced length.
- Weak refractive power of light rays, due to which focusing does not occur on the retina itself.
↑ Mechanism of action of lenses
Let's get down to explaining the functioning of a device that occupies a fairly important place in the lives of many people. As you know, glasses correct the process of visual perception in people with impaired vision. Glasses use different types of lenses. It is they – lenses – that are the device that changes the trajectory of light rays – i.e. refracting them.
I don’t want to get too ahead of myself, but it should be recalled that in the Chapter devoted to the mechanics of elementary particles, we paid much attention to the reasons and mechanism for changing the trajectory of moving particles. And the main reasons for the change in trajectory, if you remember, were named as the Fields of Attraction and Repulsion. So in this article we will only try to concretely apply the processes we have already revealed.
In addition to glasses, there are many other types of optical instruments where people have found use for lenses - magnifying glasses, binoculars, telescopes, microscopes. These are the most basic ones.
Our eyes
- This is also a type of optical instrument. And as befits such devices, they incorporate lenses - crystals. Inside the eye, or more precisely, inside the ciliary body, there are muscles that control the shape of the lens - increasing or decreasing its curvature. These muscles are called accommodative, since changing the shape of the lens is an act of accommodation (adaptation). These muscles are connected to the lens via the ligaments of Zinn. When the muscle is relaxed, the distance between it and the lens increases, and the ligaments become tense - the curvature of the lens decreases. Those. the crystalline lens (lens) becomes more elongated and flatter. The muscles relax - its distance to the lens decreases, and as a result, the tension of the ligaments of Zinn weakens. As a result, the curvature of the lens increases, since the relaxed ligaments do not stretch it.
Conventional lenses made of glass can be made of any shape - both convex (converging) and concave (diffusing). Converging lenses convert a parallel beam of light rays into a converging one. Scattering beams, on the contrary, transform a parallel beam into a divergent one. The lens is an example of a converging lens. The degree of convexity or concavity can be any, including very small, tending to zero. But at the same time it will still exist.
Optical instruments use lenses of all kinds - convex, concave, convex-concave, biconvex and biconcave. In this case, the amount of curvature of both surfaces of the lens can be any - it all depends on the specific tasks that are sought to be achieved with the help of this device.
Why do we need different curvatures – both of the lens and of glass lenses? And how does this affect the characteristics of the image obtained “at the output” of the lens (i.e., the image that passed through it)?
To answer these and other questions, we will need to recall I. Newton’s experiments with glass prisms, with the help of which he decomposed white light into a spectrum. Why do we need this?
The thing is that when light (visible photons) passes through a lens, the same thing happens to them as when they pass through a prism. Photons (like any other energy units of the Universe) are deflected under the influence of the total Attractive Field of the lens substance. The same as they were deviated in I. Newton’s experiments under the influence of the total Attractive Field of the prism’s substance. Accordingly, it is not difficult to conclude that the total Attractive Field from those parts of the lens (or prism) where the thickness of the substance is greater will also be greater. This is the whole “trick”. There is more substance (glass) at the base of the prism. Therefore, in I. Newton’s experiment, it is in the direction of the base of the prism that photons are displaced (refracted), and not towards the top. We can observe the same process in a lens - where there is more substance - light rays are deflected (refracted) there.
If the lens is convex, then along its axis (towards the center) there will be more substance than at the edges.
The thickening along the lens axis may be negligible. However, even if this is so, it is still there. And the attraction from the central part of the lens will be, although not much, greater than from the edges.
If the lens is concave, then the thickness of the substance at the edges will be greater than in the area of the lens axis.
And in this case, the attraction from the material of the edges is greater than the attraction of the central region of the lens.
This is why a convex (converging) lens deflects photons (and any other particles) closer to the center of its axis. And the concave (scattering) one is closer to the edges. Therefore, the image “passed” through a convex lens decreases in size. And the rays after such a lens converge at one point earlier than if they had not passed through it.
The image “passed” through the concave lens, on the contrary, expands and increases, since the photons of light rays are attracted by the edges and deflected in their direction.
Are two pathologies possible at the same time?
Two pathologies are possible at the same time, but there are different options. This happens quite often and each deviation has its own correction methods.
Can myopia turn into hypermetropia?
As we age, the body experiences changes related to vision and dysfunction of the visual organs is called presbyopia. It occurs in people over 40 years of age and does not depend on the size of the eyeball or refractive power. Due to the aging of the body, the elasticity of the lens decreases, the ciliary muscles weaken, so presbyopia can occur even in those who suffer from myopia. In addition, if you have myopia up to 3-4 diopters, it may happen that the “minus” is compensated by the “plus” and there is a possibility of improved near vision.
If the degree of myopia is high, then two pairs of glasses will be needed. Some will be designed for close-up work, others for distant objects.
REFERENCE. Symptoms of presbyopia - the eyes quickly get tired when working close, text may blur before the eyes, the brightness of images is lost and there is a constant lack of light.
Age-related farsightedness cannot be avoided, because the lens will no longer be able to return to its original properties. Therefore, you will have to use vision correction devices or replace the lens through surgery.
Are multifocal lenses suitable for myopia and presbyopia?
Such ophthalmic products are equipped with 2-3 or more optical zones. They correct not only myopia and age-related farsightedness. Also, these correction tools provide clear vision at an average distance. At the same time, the transition from close to far distance is not felt. The lenses adapt to the brain's functioning, providing high-quality images wherever a person's gaze is directed.
Popular models of contact optics with multifocal design:
- 1-Day ACUVUE Moist Multifocal - one-day lenses with a high level of moisture content - 58%.
- Clariti 1 day Multifocal is a one-day ophthalmic product that can be worn flexibly, that is, left on the eyes overnight.
- Dailies Total 1 Multifocal are disposable multifocal lenses made of water-gradient material. They allow oxygen to pass through perfectly and are perfectly hydrated.
Before purchasing any lenses, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
Treatment methods
For vision correction with a combination of two pathologies, there are specific features. When prescribing therapy, the doctor takes into account not only the presence of myopia and farsightedness, but also their combination and gives individual recommendations.
Gymnastics for the eyes
A person’s eyes are stressed and tired every day, so even people with perfect vision need to give their eyes rest. Doctors always advise doing exercises that will not take much time but will bring a lot of benefits.
What exercises to do for myopia?
- Frequent blinking, you need to close your eyes tightly for a couple of seconds and then blink quickly for about a minute;
- Drawing lines down and up with the eyes and rotating in a circle. Here it is important to work only with your eyes, it is advisable not to shake your head;
- Tilt your head back and look at the ceiling, then look down at the floor.
For myopia, it is recommended to do not only eye exercises, but also general physical exercises that will help improve blood circulation.
What exercises for hypermetropia?
- Sit upright and begin to slowly turn your head in different directions;
- Take a pen or pencil and hold it 30 cm away from your face, look at the tip for 10-15 seconds, and then look at the object behind the pencil or pen.
After exercise, it is advisable to massage your neck and head.
Another popular exercise is palming. To perform it, you need to cover your face with your hands and relax, feel the silence, and abstract yourself from extraneous sounds. After a few minutes, open your eyes and blink quickly for a couple of seconds.
Why does farsightedness turn into nearsightedness?
The transition from farsightedness to nearsightedness is possible in severe forms of hypermetropia, when vision is impaired at all distances. This happens because farsighted people have to readjust their gaze when they look at different objects and strain their eyes a lot. Thus, a person often experiences visual fatigue, which leads to myopia.
Does it happen that myopia turns into farsightedness? Such a phenomenon is excluded. But, of course, presbyopia (age-related farsightedness), which manifests itself after 45-50 years, cannot be avoided by anyone. This state of the visual system is a natural physiological process, as it is associated with aging of the lens and a decrease in its elasticity. At the same time, presbyopia will not harm people with a weak degree of myopia, since they may experience a slight compensation of minus diopters. But if a person has moderate or high myopia, then in the future he will most likely have to use bifocal glasses or switch to special multifocal lenses.
Now you know that farsightedness can turn into nearsightedness if you do not monitor the health of your eyes. This phenomenon can only be avoided if you wear glasses or contacts, perform special exercises and give your eyes more rest. It is also worth visiting an ophthalmologist, because only he can notice the first signs of visual impairment and prescribe treatment.
Prevention
People who suffer from myopia or hypermetropia should maintain eye hygiene and have their vision checked regularly. During the day, your eyes get very tired and you need to give them a rest and do gymnastics.
Advice! If you have myopia, doctors advise paying attention to strengthening your body, watching your diet, and playing sports; swimming, running, tennis, and badminton are especially good.
While working, make sure there is good lighting so as not to create unnecessary strain on your eyes; do not read while lying down or in transport. When working for a long time, you need to take a break every 30-40 minutes