The development of farsightedness in patients of different ages is a serious problem in modern ophthalmology. Despite the fact that today there are many correction methods, stopping the progressive pathology is not so easy. What methods can slow down its development and keep vision bright and contrasting?
It is quite difficult to provide accurate statistics regarding how many people in the world suffer from farsightedness.
In this article
- Causes of farsightedness
- At what age is presbyopia diagnosed?
- How to get rid of age-related farsightedness with glasses?
- How to combat age-related farsightedness with lenses?
- How to combat age-related farsightedness with medication?
- How to stop farsightedness using folk methods?
- Is it possible to prevent age-related farsightedness with surgery?
- How to prevent the development of age-related farsightedness?
The fact is that not all people regularly visit an ophthalmologist after noticing certain changes. But, despite this, the specialists still managed to calculate the average number of patients. According to most ophthalmologists, symptoms of farsightedness exist today in more than 30% of the world's population. Unfortunately, not many people go to see a doctor asking how to stop the development of farsightedness. Most of them do not attach due importance to this diagnosis. No eye problems should be overlooked.
What is farsightedness and why is it dangerous?
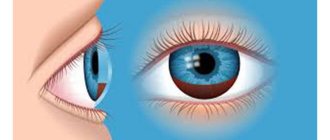
Farsightedness is one of the most common refractive errors. The human eye has two light-refracting media: the cornea and the lens. Normally, the rays are refracted, fall on the retina, where they are focused, transformed, and only then transmitted in the form of signals to the brain.
However, when the cornea is not convex enough, or the lens does not perform its functions, or the path of the beam is too reduced, the image is focused behind the retina. This causes a blurry image on the retina. A low-quality signal is transmitted to the brain, the person sees a blurry picture.
With this disorder, the patient sees poorly at close range, he cannot read small print or distinguish small objects. To move the focus away, the book is placed as far away from the eyes as possible, extending the arm forward. This type of refractive error is called farsightedness or hyperopia.
However, with a high degree of illness, objects that are located in the distance are poorly distinguished. Complications of farsightedness in adults are rare. Most often they develop in children if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner.
Complications include:
- Strabismus - the axes of the eyeballs are not aligned with each other, the eyes are directed in different directions. Strabismus can make it difficult to judge the distance to an object or the relationship of different objects to each other, or to perceive depth. As a result of strabismus, one eye may become weakened, which gradually leads to the development of amblyopia.
- Amblyopia - with this pathology, one eye dominates the other. It develops, as a rule, as a result of strabismus, cataracts or other ophthalmological diseases. If a child primarily uses only one eye to focus, there is a risk that the other eye will gradually weaken. If left untreated, a person may lose vision in the weakened eye.
Main characteristics
How to treat farsightedness
Hypermetropia (farsightedness) is one of the types of clinical refraction of the organ of vision, in which light rays entering the eye, which is in a state of resting accommodation, are focused behind the retina. The action of accommodation mitigates partially or even completely the negative effect of hypermetropia on the visual system.
What affects the symptoms of the disease?
However, the completeness of compensation for this influence, and, consequently, the symptoms, very significantly depend on the patient’s age, the degree of farsightedness, the presence of astigmatism, the eye’s ability to accommodate and vergence, and the characteristics of visual work.
The degree of hypermetropia is determined by the strength of the lens that must be placed in front of the eye to accurately focus light rays on the retina. Farsightedness is often accompanied by astigmatism. The greatest degree of hypermetropia occurs in people with aphakia.
When farsightedness does not need to be treated
Moderate hyperopia in early childhood is the norm. Its presence is associated with the anatomical features of the child’s eyes, which have a slightly shortened size of the eyeball.
The child corrects his physiological farsightedness by contracting the eye muscles, thanks to which he sees clearly at various distances. As the body grows and the optical system develops, hypermetropia goes away—no treatment for the pathology is required.
Children with physiological hypermetropia up to 2 diopters do not need to correct their vision with glasses. If the disease is more severe, the child requires correction, as there is a risk of complications developing.
Young people with farsightedness also do not always require correction, since their disease is compensated by the lens, which changes its curvature.
Types and degrees of farsightedness in adults
The classification of the disease allows us to divide hypermetropia into different types.
According to one classification, based on the mechanism of development of the disease, axial and refractive hyperopia are distinguished. The first is associated with the shortened anteroposterior axis of the eyeball, and the second is caused by a decrease in refractive power.
According to another classification, there is obvious as well as hidden farsightedness. The latter is discussed in the case when the existing anomaly in the refractive power of the organ of vision is compensated due to the voltage of accommodation. And if self-correction of hypermetropia is impossible, the need for optics arises, the disease is regarded as obvious. It is worth noting that with age, the latent form, as a rule, transforms, becoming explicit.
Generally speaking, the classification of such types of farsightedness as natural, congenital, and senile is based on age. The first can be observed in children as a physiological phenomenon; the second represents congenital weakness of refraction; the third develops in old age and is called age-related hypermetropia.
There are also three degrees of farsightedness, determined by the number of diopters:
- weak degree - less than 2.0 diopters;
- average degree - less than 4.0 diopters;
- high degree - more than 4.0 diopters.
Low degree of farsightedness is characterized by the fact that the eyes cope with their task with the help of accommodation. If there is moderate, much less high, farsightedness, then farsightedness is corrected for both close and long distances.
At a young age, farsightedness takes on a hidden form due to the greater accommodative capabilities of the eyes, but their overstrain can lead to headaches and nausea. If alarming symptoms occur, you should visit an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination.
Symptoms
At a young age, the accommodation reserve often helps to ensure a clear image on the retina without the development of asthenopia. However, its deficiency, which develops as a result of visual fatigue or as a consequence of age-related changes in the body, with medium and high degrees of farsightedness can provoke the occurrence of the following symptoms and conditions:
- Blurred vision.
- Asthenopia.
- Violation of accommodation and binocular vision.
- Amblyopia.
- Strabismus.
More often, these symptoms appear in patients with esophoria and insufficient negative fusion reserves. Presbyopia that develops with age can lead to the transition of latent hyperopia to manifest hyperopia, which is accompanied by blurred images, especially near.
The first symptoms of farsightedness
Farsightedness is an insidious disease. The first symptoms appear in childhood and seem far from eye diseases. Children study poorly, get tired quickly, cannot concentrate on doing work, are capricious, and sleep poorly.
Fatigue of the visual apparatus of the eye with farsightedness is primarily manifested by asthenic complaints. Early diagnosis and prescription of optical correction (glasses, contact lenses) can reduce the occurrence of complications of hyperopia such as strabismus and amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome).
The progression of farsightedness can lead to disturbances in the outflow of intraocular fluid and, as a result, an increase in intraocular pressure and the development of glaucoma.
If your child is doing poorly at school, is capricious, or experiences fatigue from visual stress, check to see if he has farsightedness. To do this, you need to urgently contact an ophthalmologist.
Farsightedness is rarely detected during routine vision testing. Only a complete ophthalmological examination with testing of visual acuity, both at a distance and near, can reveal farsightedness and the degree of its development.
Why does hypermetropia occur in adults?
The development of farsightedness, just like myopia, is associated with a discrepancy between the refractive power and the anteroposterior size of the visual organ. However, there are differences. With hypermetropia, such a discrepancy is a consequence of the relative weakness of the ocular refractive apparatus, or arises as a result of a shortened anteroposterior axis of the optic apple.
It must be said that in some patients the shortened axis is combined with insufficient optical power, which, of course, is not at all a favorable sign. However, both mechanisms lead to the fact that the rays, after being refracted, are focused at a point located behind the retina, this is the essence of the disease.
There are a number of factors influencing the development of the disease: genetic; aging of the body; various brain injuries; disorders of the central nervous system; weakness of the eye muscles; unfavorable environmental situation; working with small objects; frequent stress, apathy, depression; poor eye hygiene; bad habits, unhealthy diet.
The development of pathology is sometimes influenced by several of the above factors. Therefore, the therapeutic course must be comprehensive.
How does the disease manifest itself?
As a rule, farsightedness causes systematic muscle overstrain, which is why the main symptoms that define the disease appear: visual fatigue and headaches.
With pathology, the eyes become very tired when reading, and there is a burning sensation in the eyes. When working for a long time and looking at close objects, lacrimation and tingling may occur. Symptoms indicating farsightedness may include intolerance to bright lighting and the appearance of unpleasant sensations.
There is visual discomfort, which is accompanied by the feeling that letters and even lines merge with each other and become blurry. You always want to move the object you are looking at away from your eyes.
In addition, with moderate or high degrees of hypermetropia, patients very often exhibit changes in the fundus, expressed in the form of the development of hyperemia and unclear boundaries of the optic nerve head.
Effective Treatments
Faced with refractive error, people begin to become actively interested in how to treat farsightedness and forget about poor vision forever, since poor vision brings a lot of inconvenience.
The fact is that the ophthalmologist will not immediately give a definite answer. To make a prognosis, it is necessary to fully examine the patient. In this case, the following matters: age; individual characteristics of the body; causes of the disease.
The treatment method is selected strictly taking into account the patient’s age. Children, adults and the elderly are treated differently. Therapy is prescribed only after diagnosis. The therapeutic course and specific type of correction are selected individually exclusively by an ophthalmologist.
The main task of treating farsightedness is to change the optical power of the eyes so that the visible image is focused not behind the retina, but on it. There are conservative treatment and surgical vision correction.
Farsightedness in humans is corrected with glasses. Glasses are used while reading, watching TV, working on a computer or other activities in which the gaze is focused at close distances.
An alternative to glasses may be contact lenses made from organic or mineral materials. Lenses are very convenient during outdoor activities and sports, but they are contraindicated for small children.
Conservative treatment includes hardware methods for improving vision. These include ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, vacuum massage, glasses - massagers, a set of physiotherapeutic procedures. The methods give good results and avoid surgical correction.
Vitamins during illness are also of no small importance, as they help maintain the tone of the eye muscles.
When watching TV, doctors recommend wearing perforation glasses, which help reduce the stress of accommodation.
Surgical correction involves laser vision correction. Using a medical laser, you can change the abnormal shape of the cornea, which most often causes the disease. The beam removes a layer of eye tissue, which leads to a change in the curvature of light refraction.
Laser correction is one of the most convenient and effective methods of treating eye diseases associated with impaired visual acuity. It allows you to treat myopia or farsightedness at the same time. The operation lasts several minutes under local anesthesia, after which the patient goes home the same day.
But there is a risk of complications leading to repeated vision correction. If the patient has age-related farsightedness with severe accommodation disturbances, then laser treatment is not used. If the disease has reached its most severe stage, treatment may include implantation of a phakic or multifocal lens.
Is it possible to wear someone else's glasses?
To avoid permanent loss of vision, do not wear someone else's glasses. It often happens that one of the spouses does not find time to undergo examination by a doctor and begins to wear optical products of his husband or wife. As a result, his vision begins to quickly shrink, because his eyes must adapt to “foreign diopters.”
Important! If your vision deteriorates, you don’t need to rush to the “Optics” store; you don’t know what kind of glasses to buy there.
Most likely, you will be praised for the most expensive lenses. But you need optics with the right, not expensive, diopters.
During the examination, in addition to prescribing the correct diopters, the doctor can recognize the onset of the disease. Based on the severity of the problem, he may refer you for laser vision correction.
In addition to laser therapy, doctors have many other treatment methods.
Gymnastics for farsightedness
Special exercises for the eyes help relieve fatigue after visual stress, and when performed regularly and conscientiously, they improve vision and help normalize the functioning of the visual organs. They need to be performed daily, this is the only way to get rid of the disease.
A set of exercises to improve vision:
- Close your eyes. Gently massage them with circular movements of your fingertips. This will relax the eye muscles and improve blood circulation.
- Close your eyes for 3 seconds, then open them for the same amount of time. Repeat 15 times.
- Blink quickly for 1-2 minutes.
- Make circular rotations with your eyes left and right for 10 seconds in each direction. Repeat 5 times.
- Move your eyes up - down - left - right for 1 minute.
- Take a comfortable position while standing or sitting. Look in front of you, slowly turn your head to the right, looking behind your head. Return to the starting position and repeat the exercises on the other side. Repeat 10 times for each side.
- Look straight ahead. Extend your right hand forward, look at your index finger. Slowly turn your hand to the right, watch your finger, your head does not turn. Repeat the exercise with your left hand. For each side, do 10 repetitions.
- Bring your eyes to the bridge of your nose for 2 seconds, and then return to their original position. Repeat 5 times.
- Place your index finger at eye level, at a distance of 15 cm, make circular movements with your finger clockwise and follow it with your eyes. Repeat the exercise, only counterclockwise. Repeat 10 times for each side.
- This exercise is best done in front of a window. Extend your index finger in front of you at a distance of 30 cm. Look at your finger for 3 seconds, then look at a distant object outside the window. Repeat 20 times.
If any of the exercises cause severe discomfort or dizziness, skip them.
Performing vision exercises every day helps improve vision. The main thing is to do it correctly. Don't expect quick results. On average, the effect of gymnastics becomes noticeable after a month.
Treatment of farsightedness with folk remedies
Along with the listed methods of treating the disease, it is also possible to treat farsightedness with folk remedies. Infusions and decoctions will help correct farsightedness.
- Chinese lemongrass. Pour the fruits of the plant with 70-degree alcohol in a ratio of 1:3, leave for seven days. Drink about 1/5 glass before meals. The course of treatment is from 25 to 31 days.
- Eyebright. Pour a glass of boiling water over a tablespoon of herbs, leave for three hours to infuse, then filter. It is recommended to drink half a glass after each meal.
- Blueberry. Farsightedness can be treated with blueberries, or more precisely, with the leaves of this plant. Take two teaspoons of dried leaves, pour them into a glass of boiling water, and leave for an hour. Then filter the broth. Take half a glass twice a day.
- Wheatgrass. It is also a fairly effective method of treatment. You will need wheatgrass rhizomes, thoroughly crushed and dried. Fill them with water at the rate of one liter per four teaspoons, boil until only a quarter of the original volume remains. Then filter the broth and consume a tablespoon four times a day.
- Motherwort. Grind and dry the herb, then brew for forty minutes in a glass of hot water at a rate of 250 milliliters per tablespoon. You should take a tablespoon twice a day, preferably in the afternoon. Motherwort effectively improves vision.
- Swamp calamus. Calamus root is crushed, prepare an infusion from it in the proportion of 2 tablespoons per glass of vodka. The mixture must be infused for at least eight days. Take the tincture three times a day before meals, 20 drops.
- Fruit and vegetable cocktail. For this product you will need: a liter of water; orange, 1 pc.; lemon, 2 pcs.; grapefruit, 3 pcs. Squeeze the juice from the fruit, stir it and add water. Take half a glass twice a day before meals. Of course, citrus fruits can treat farsightedness only if you do not suffer from an allergy to them. It is advisable to store the juice in the refrigerator so that it does not lose its medicinal properties.
In addition to citrus fruits, try to include blueberries, lingonberries, cherries, carrot, beet and cucumber juices in your diet. All this will have the most beneficial effect on eye health.
In addition, you will need a lot of vitamin C, which is found in onions, rowan berries, rose hips, and dill. Please note that dietary nutrition must be balanced.
Whether it is childhood or age-related farsightedness, it is necessary to consume fresh carrots, beets, celery, cucumbers, chicory, parsley, garlic, dill, spinach or their juices. It is recommended to use fresh blueberries or blueberry jam, 2-3 tbsp. l. 3-4 times a day. Blueberries reduce eye fatigue. Fresh cherries are also useful.
The most beneficial foods for the eyes are blueberries and carrots. It is recommended to eat a handful of blueberries or grated carrots every morning. Add fat-containing products to them, such as sour cream and cottage cheese. Fats help vitamins be better absorbed. Before taking vitamin complexes, it is important to consult your doctor.
Diet
The eyes really need microelements and vitamins, which are contained in blueberries and cherries, carrot and lingonberry juices. Cucumber and beetroot juices have a beneficial effect on the eyes.
It is recommended to use the juices of hot and spicy plants - garlic, onion, celery and dill. The body must take in enough vitamin C daily, which is rich in green onions, dill, citrus fruits, rose hips, black currants and red rowan.
To sum up the diet, it can be noted that you need to get a balanced diet consisting of vegetables, herbs and fruits. These products contain anti-aging antioxidants.
Include in your diet vegetable oils (especially olive and corn), nuts and sea fish, rich in phosphorus, iodine and other beneficial microelements. They also contain beneficial polyunsaturated acids that strengthen blood vessels.
Prevention of farsightedness in adults
Preventing the disease is much easier than treating it. In the case of farsightedness, correct behavior will delay wearing glasses and preserve good vision for a long time. In some cases, it will help slow down the aging process of the eye. Prevention of farsightedness should include a number of components.
Proper workplace lighting. Combining natural and artificial lighting is harmful to vision.
Loads on the eyes should be dosed, alternated with rest and a change of activity - active movement, eye gymnastics.
Perform special eye exercises every 60 minutes.
Timely visit to the doctor, detection of farsightedness at an early stage and proper correction.
General strengthening measures for the eyes and the body as a whole. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition - all this can be regarded as the prevention of farsightedness.
How to get rid of age-related farsightedness with glasses?
One of the common methods of combating age-related farsightedness is wearing glasses. In such cases, both bifocal and progressive optical products can be used.
Bifocals are considered by ophthalmologists to be an outdated version, since the prevention of presbyopia with their help has not shown proper results.
More modern, progressive glasses do not cure farsightedness, but slow down its development. They have a number of advantages. For example, there is no obvious boundary between lenses, which ensures smooth focusing. However, they have a rather narrow field of view, which can cause peripheral vision to be distorted.