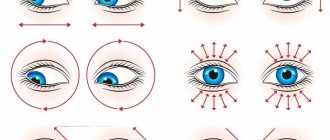
Farsightedness, or hypermetropia, is a widespread type of refractive error (improper refraction of light in the optical system of the eye), in which the focal point of the clearest image is not on the retina, but deeper, behind it. At the same time, nearby objects are seen as blurry and unsharp, while distant objects can be perceived quite clearly.
Like other types of refractive error - myopia and astigmatism - farsightedness can either be passively corrected by optical devices (glasses, contact lenses) or radically eliminated (ophthalmic surgery, excimer laser correction of the shape of the corneal layer).
It should be noted that the acceleration of the pace of life and the widespread introduction of high technologies, including medical ones, sometimes encourage patients to insist on a more risky, expensive, complex or simply “fashionable” method of treatment - in the expectation that the result will be achieved instantly and without any own efforts. Whatever criticism such an attitude may be subjected to, it is quite natural, expected and typical of human psychology. A sadder trend is that under the pretext of being busy (which often masks basic laziness and inertia), people often refuse absolutely safe, but sometimes more effective methods of treating ophthalmological diseases, not to mention preventing the latter. It is precisely these therapeutic and preventive properties that eye gymnastics has - special systems of exercises developed by ophthalmologists for a wide variety of options, stages of development and degrees of severity of visual pathology. Such complexes, as a rule, are extremely simple, take very little time and require only one thing: patience. When performed regularly every day, they can not only eliminate heaviness, fatigue, pain in the eyes, prevent the progression of an existing anomaly or the formation of a new one, but also completely restore vision. Note: restore without glasses, lasers or any intervention.
A little about pathology
In a normal state of the eye, the image is focused on the retina, but with farsightedness or hypermetropia - behind it. Therefore, objects that are close appear blurry, while distant ones appear clear. This effect appears due to the direction of the light rays. From distant objects they fall into the eyes of the beholder in parallel streams, which, when focusing, are refracted correctly. Near objects reflect diverging streams of light, which is why the eyes of a person with farsightedness see them blurred.
The causes of farsightedness may be the following:
- Along the longitudinal axis, the eyeball is shorter than normal.
- The eye system has deformed focusing contours, or there is a displacement in the elements, which provokes a disruption in functioning.
When these causes are combined, the disease becomes complicated and can only be treated surgically.
Dr. Bates complex for farsightedness
The famous ophthalmologist William Bates developed a set of exercises for people with farsightedness. The doctor believed that the cause of the disorder was excessive eye strain when looking at objects up close. All the exercises in this complex will help you relax and relieve tension from your eyes.
Bates complex for hypermetropia:
- Reading a special table or book with small symbols at a distance of 30 cm from the eyes. It is advisable to change the lighting, because in dim light conditions the eyes relax. You need to work with the text for 10-15 minutes, without effort or tension. While reading, you should remove your glasses and contact lenses. The additional optical system can only be used initially, when the font cannot yet be seen. If you feel discomfort during the process, you need to stop and do a relaxation exercise (palming).
- Look at the empty space between lines when reading books.
- Go out into the fresh air or open a window. Look at homogeneous objects (grass, sky), then at the manual test chart.
- Watch flying birds, watch special films, follow moving objects.
Bates turns
Stand in front of a window with vertical bars, legs apart (30 cm or more if you are tall). Lower your arms, keep your back straight. Smoothly and continuously turn the body and head 180° in different directions.
The gaze must also move, then objects will appear blurry. Distant objects visually begin to move in the direction of body movement, and near ones - in the opposite direction. This phenomenon indicates that the eyes have relaxed. The vertical bars will begin to move in the opposite direction, and the objects behind the glass will begin to move in the direction of the turn.
During the process, you cannot focus your gaze on external movements. It is advisable to free your head from thoughts and relax as much as possible. Usually it is comfortable to make 16 turns per minute.
Exercise with Sivtsev's table
This exercise requires a Sivtsev test chart. You need to hang it in a dark place and set up dim lighting. The patient should be able to distinguish text from a distance of 5 m. This exercise requires little effort.
Stand 5 m from the table, take a manual format table and put good lighting on it. The patient must first read the large chart, then follow the white stripes on the manual chart. You need to blink during the process. Repeat several times.
Bates believed that by systematically performing this exercise, vision could be restored in case of farsightedness. The exercise will be useful for patients with presbyopia (age-related farsightedness).
Exercise with Debko table
To complete this exercise you need a Debko table. You should perform slight turns of your head, visually moving the tip of your nose and your gaze along the lines on the table. You need to continue the exercise until the lines begin to slide in the opposite direction. After this, you need to repeat the exercise for the bottom of the table.
Having finished with the table, you need to close your eyes, turn your head and move your gaze along imaginary lines. Next action: open your eyes and draw lines with your gaze on the white surface of the table. This exercise will help you distinguish text at any distance.
Gymnastics for eyes with farsightedness
Exercises for farsightedness can only be beneficial with the recommendation of an ophthalmologist and for initial farsightedness. They may not be effective at all stages. Complex forms are treated with surgery, and gymnastics at the primary stage of farsightedness helps slow the development of the pathology.
Exercise may also be indicated for the prevention of disease at an early age and for visual fatigue. With initial or moderate farsightedness, they can help restore quality of vision.
Exercises to restore vision in case of farsightedness provide the following results:
- improvement of blood circulation in the cervical region;
- stabilization of blood supply to the eye muscles;
- improvement of the condition and functioning of the eye muscles;
- maintaining normal functioning of the lens.
Specific gymnastics are selected taking into account the degree of the problem and the desired result. It must be prescribed by a doctor.
The effectiveness of visual gymnastics
Visual gymnastics is considered one of the elements of therapy for eye diseases, although not all ophthalmologists recognize its effectiveness. This is due to the characteristics of the body of different patients, their visual pathologies. Before starting classes, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist. Treatment for myopia at home is described here.
Gymnastics does not provide complete relief from vision diseases, but it is considered one of the elements of treatment. The method is aimed at training the eye muscles, relieving discomfort, activating blood circulation, and preventing complications. Monotherapy in this case is absolutely useless; benefits are observed only if complex treatment is carried out. There are exercises not only for farsightedness, but also for nearsightedness.
Regularity of exercises plays an important role; daily exercises are considered a prerequisite.
Eye exercises to prevent farsightedness
If you perform exercises for preventive purposes, you can prevent farsightedness and other vision-related problems and relieve eye strain.
For prevention, the following simple complex can be performed. It is important to do it exactly in the suggested sequence. You can repeat these exercises every hour:
- Close your eyes, but do not squint your eyelids too much, but relax. Cover them with your palms, creating complete darkness. There is no need to press your hands tightly. Stay in this position for a couple of minutes. Then move your eyes, but still don't open them. In this case, you need to hold your gaze at different points on each side for several seconds. Do at least ten such manipulations.
- Focus your gaze on the tip of your nose and imagine that it is a pencil. Moving your head without taking your eyes off, write your name in cursive in the air. This must be repeated at least three times.
- Place your hands in front of you, spread your fingers and look at the gaps between them, without paying attention to the fingers themselves. If you do everything correctly, then what is visible between the fingers will be perceived clearly, but the clarity of the fingers will be blurred. After half a minute, focus your gaze on your fingers, ignoring any gaps. Repeat the exercise at least five times.
This complex, when performed regularly, can reduce the risk of farsightedness if there is a predisposition to it.
What are the easiest exercise options?
First of all, it is necessary to talk about step gymnastics. These exercises help with farsightedness quite well. They need to be done like this:
- take a position near the window at a distance of 1 meter;
- extend one of your arms forward, raising your palm up and turning it towards you;
- carefully examine the details (folds of skin, fingerprint pattern, etc.);
- look at the window frame, examine all the small cracks and irregularities;
- look outside, at any object located about 50 meters away;
- turn your gaze to another object that is already a hundred meters away;
- look at the sky;
- repeat the procedure in reverse order.
If you repeat this exercise hourly, or at least at every opportunity, the effect will appear quite quickly. This gymnastics is perfect for children over five years old.
Exercise with numbers. Warm palms are placed on closed eyes. Next, you need to use your pupils to draw numbers from one to ten one by one. The duration of the gymnastics is approximately two minutes. It is useful for people who put too much strain on their eyes. Suitable for both adult patients and children. This exercise allows you to activate blood flow, which helps improve the situation with farsightedness and the following pathologies:
- glaucoma;
- cataract.
Another version of the exercise is called the “visual arc”. It is also beneficial for both children and adults equally. You should do the following:
- sit on a chair facing the window;
- the gaze is directed to the knees for a time sufficient to consider all the details;
- then slowly turn their eyes to objects on the street;
- after that, pay attention to the frame;
- gradually lowering their gaze downward, they examine everything that comes into their field of vision.
It is best to do three repetitions. At the end, the eyes are closed tightly three times and sharply opened as wide as possible.
Palming. This exercise is done while sitting comfortably in a chair:
- close your eyes with your palms;
- relax and think about the positive;
- you need to feel the warmth coming from your hands;
- duration is five minutes;
- You need to do it three times a day.
The following technique trains the eye muscles well. It is necessary to alternately focus on the window and on objects that are as far away as possible behind the glass.
Vision training for farsightedness
The following exercises are indicated for the development of age-related farsightedness. The disease often makes itself felt after forty years.
Performing exercises several times a day can support conservative therapy and enhance its effectiveness.
Eye gymnastics for age-related farsightedness is performed in the following sequence:
- First, move your eyes alternately in four directions. Do 5-10 times in each direction.
- On the glass in the window you need to stick a black mark measuring one centimeter by centimeter. Move one and a half meters away from the window. Focus first on the mark, then out the window behind it, while your eyes should be relaxed. After 30 seconds, focus on the mark again. After each repetition, blink frequently, squinting your eyes tightly and losing focus. Repeat at least three times.
- Stand in front of the wall clock at a distance of about 1.5 meters from it. For a few seconds, focus and hold your gaze on the marks in the direction of the arrow. Fix your gaze in the following sequence: 12, 3, 6, 9. After making three circles, repeat the same in a counterclockwise direction. You also need to make three cereals.
- Using eye movements, imitate the ligature of a bow in front of them. Then change the shapes in the following sequence: bow, figure eight, pentagonal star, square, triangle. The gaze needs to move smoothly. One approach with completing the entire list of figures is enough.
Other exercises for farsightedness at home
In order for vision to return to normal under severe stress, for example, after working for a long time at the computer, watching TV, reading, etc., eye gymnastics is necessary. With the help of a simple set of exercises, which can be performed not only at home, but also at school or work, the visual muscles will relax. This will allow a person to get rid of burning and dry eyes.
This complex includes:
- Frequent blinking for 1 minute (without effort);
- Perform rotational movements of the eyes clockwise and counterclockwise 10 times in each direction;
- Alternate eye movements left and right without turning the head 10 times.
In addition, experts recommend yoga to improve overall health. Among a large number of asanas, there is a special gymnastics that tells how to eliminate farsightedness and prevent its progression. Its regular implementation improves muscle elasticity and activates blood supply to the eye tissues, improving the flow of oxygen and other important components for the proper functioning of the visual apparatus.
Also, patients with farsightedness can resort to the help of such a method as solarization - a method of restoring vision with sunlight. Correct execution of this gymnastics reduces inflammation in the entire system of visual organs, activates the adaptive ability of the eyes during a sharp change in lighting brightness, and helps slow down destructive pathological processes in presbyopia.
Bates method
Vision exercises for farsightedness according to the method of Dr. W. Bates are aimed at eliminating the visual focusing disorder that often accompanies simple and moderate forms of farsightedness. Gymnastics helps enhance the effectiveness of drug treatment and relieves severe eye strain.
- You will need a book with fine print. You need to read it for 15 minutes without glasses, trying not to strain. You can do this slowly. If at first it is difficult and your eyes hurt, you can wear glasses, but gradually you should try not to use them for reading.
- When reading a book with small print, you sometimes need to move your gaze from the line to the space between the lines. Do this several times on one page.
- While reading a book, take your mind off it and walk around the room or open space, looking at objects close and distant from you.
- Bird watching is helpful for hypermetropia. In flight, they are constantly moving, and by watching them, we contract and relax the eye muscles in the rhythm necessary for treatment. When you finish observing, relax your eyes for a while; you can lie down and close them.
Restoring vision according to Zhdanov
Personal awareness plays a big role in implementation; it is necessary to remember about prevention. It is important to follow the 3 rules of hygiene - rest, palming, avoiding glasses. The set of exercises includes moving the eyes in different directions (“figure eight”, clockwise and back, horizontally and vertically, drawing squares). All actions should be repeated 7-10 times, the head should remain motionless, light blinking will help relieve tension at the final stage.
Exercises according to the Zhdanov system
Professor Zhdanov has developed training systems for various eye diseases. They are based on traditional ideas regarding the functioning of the organs of vision. Gymnastics for farsightedness in adults is aimed at working the extraocular muscles. Before performing the workout, you must adhere to the following rules:
- If you have glasses or contacts, remove them.
- In case of retinal pathologies, accuracy and attentiveness are especially important.
- Each exercise must be repeated at least three times.
Now let's look at the exercises themselves:
- "First finger of the hand." The fingers of one hand need to be gathered into a fist. Raise your thumb up and stretch your hand forward, blink 2-3 times, look into the distance, then focus your eye on the finger for 5 seconds. Gradually lower your hand down. Number of repetitions – 5-10.
- "Move your finger." Clench the fingers of your right hand into a fist, and extend your index finger forward. Raise your hand to your face so that your index finger is at the level of your eyeball. Look into the distance. Start moving your index finger quickly from side to side, trying not to focus your attention on it. Not my height, move your hand to the left 20 cm, return to the starting position and move your fist 20 cm to the right. During all this, follow the index finger with your eyes. Repeat the exercise for two minutes.
To improve blood circulation during the treatment of farsightedness, Zhdanov advises performing a general strengthening complex, which includes the exercises suggested below. They must be repeated at least five times and done twice a day.
- Turns the head to the sides.
- Tilt your head up and down.
- Tilt your head to the right, then return to the starting position and tilt your head to the left.
- Raising and lowering the shoulders.
- Shoulders should be pulled forward, then back. The back and chest need to be rounded alternately.
- Stand straight, keep your feet together. Rotate your shoulders forward so that your legs do not move from their original position.
- In the same position, rotate your shoulder back.
- The starting position is standing. Lock your hands. Twist your body to the right and back. Hold this position for five seconds, then return to the starting position. Perform twisting to the left and back.
- Side bends.
Bates technique
Before therapeutic exercises, preparation is carried out; the patient must remove lenses or glasses, relax the facial muscles, and blink.
Exercises:
- moving the gaze with fixation for a second down and up;
- alternately moving the gaze left and right;
- moving your eyes up to the right, smoothly moving your gaze to the lower left corner;
- moving the eyes left up, diagonally right down;
- moving the eyes around the perimeter of the drawn rectangle in two directions alternately;
- moving your gaze in both directions around the dial, stopping at positions 12, 3, 6 and 9;
- placing the hand in front of you with fixation of the gaze at a point in the area of the thumb, bringing the hand to the face in the nose area, sharply redirecting the eyes to an object located in the distance;
- drawing an imaginary figure in the contours of a snake in 2 opposite directions;
- closing your eyes with force.
At the final stage, gymnastics of the neck and shoulder girdle is performed in the form of compressions, rotations, and relaxations. When performing gymnastics, the organs of vision are involved, the head must be in a fixed state. The exercises must be repeated 20 times, each ending with blinking. Find out what to do if your computer hurts your eyes by following this link.
The treatment system shows effectiveness in the initial stages of development of eye diseases; its systematic use gives results.
Exercises for farsightedness in children
In childhood, a high degree of hypermetropia is usually the result of congenital pathologies that are eliminated surgically. Here it is also necessary to take into account that the child’s eye and all its structures are actively developing, and over time, farsightedness may disappear completely or be reduced to a minimum. Regular eye training for childhood farsightedness gives results with low and moderate severity of the disease. Gymnastics is aimed at training the accommodative apparatus, it stimulates its development and improves functionality. Young children may find it difficult to concentrate on gymnastics, so a different form is preferable for them.
The following set of exercises can be used for children:
- A light massage is performed on the baby's eyeballs using the fingertips. The eyelids should be closed. Do it for five seconds. There are only five repetitions, resting 30 seconds between them.
- Lay your baby horizontally on his back. Attract his attention with his favorite toy. When the child focuses his gaze on the object, smoothly bring the toy closer to his eyes, moving it like a snake. The number of repetitions at first is no more than two, then it is increased to five. This gymnastics involves the ciliary muscle and trains the mechanism of accommodation.
- This exercise is suitable for children who can already walk and perform simple tasks, aged 2-5 years. The child should focus his attention on the bright ball. Then throw the toy forward. The baby must follow it with his eyes, then find it and bring it back. The second option is to put the child on the floor and sit opposite him at a distance of 2-3 meters. You need to roll the ball towards each other. Let the child carefully watch his movement. This charging should be carried out within five minutes. It helps stimulate visual accommodation.
- The exercise is suitable for a child who is learning to imitate the movements of those around him. Attract his attention with simple grimaces so that he fixes his gaze on your face. The essence of the lesson is repetition of actions. Alternately you need to close and open your eyes.
- This activity can be done with a child who already can read. Take a bright book with large letters that is appropriate for the baby’s age, and invite him to read a couple of lines from a comfortable distance. Then bring the book 15 cm closer to him and ask him to do the same. You need to do this for five minutes every day. Gradually bring the book closer to a standard distance.
Older children will be interested in sports games with a shuttlecock or ball. They can be useful in complex treatment, influencing the accommodative mechanism of the eye and the visual system as a whole.
Eye exercises for farsightedness can in many cases help restore vision. But, as a rule, they give results as part of complex therapy. In any case, it is important to adhere to the measures prescribed by the doctor.
Training techniques
Exercises with a pencil
Exercises with a pen or pencil:
- take a pencil, extend your arm, blink several times, look at objects located in the distance;
- direct your gaze to the pencil, move your hand 15 cm from your eyes (without looking away), slowly return your hand to the starting position, blink, do 5-10 repetitions;
- bring the pencil to your face, tilting it to the left and right, move the pencil 20 cm to the left, return to its original position, repeat, moving it to the right (during all actions, the gaze should be directed into the distance, the pencil is located at eye level, repeat for 3 minutes.
Palming
Palming can be translated as “palming”, from the English palm - palm. The technique is aimed at relaxing and strengthening the eye muscles. You can find out what to do if your vision decreases in the article.
- Close your eyes tightly with your palms for a while; correct execution is ensured by observing the following conditions:
- isolation of the eyes from the light source (eyes tightly closed);
- before starting gymnastics, you need to rub your palms together;
- Relaxing the eyes will provide a positive attitude towards performing gymnastics.
Gymnastics:
- direction of the eyes down and up, diagonally, to the sides (left up, right down, vice versa), several repetitions are performed, at the final stage you need to blink;
- drawing a rectangle, a circle clockwise and counterclockwise with one's gaze, blinking;
- drawing a zigzag with the eyes from left to right and vice versa;
- crossing your palms in the form of an inverted “V”, applying it to the eye area (without strong pressure).
Gymnastics should be accompanied by pleasant sensations; it is recommended to repeat a set of exercises daily in the morning and evening. Palming is performed when the eyes are tired from work.
Solarization
The exercises are performed with eyes closed and require a light source: candle, lamp, sun. It is necessary to move your head alternately in different directions (or your hand in front of your eyes), which will ensure alternation of light and shadow.
Gymnastics:
- stand close to a candle or window with your feet shoulder-width apart and peer into the distance;
- smooth alternating turns of the body to the right and left; with maximum rotation, the heel of the opposite leg is allowed to lift off the floor;
- When making turns, the window or candle must be kept in sight (focus on the moments when the light source “floats” past from the side), repeat 30-50 rubles.
It is necessary to avoid straining the visual organs - they should always be relaxed. There is no need for a detailed examination of the light source.
Vision diseases
The formation of human visual organs begins in the prenatal period, and the most intensive period of their development is considered to be the age from 1 to 5 years. Initially, the state of the visual organs in most cases is excellent, but over time, due to nervous stress, fatigue, irritability, exposure to environmental conditions and the characteristics of a person’s lifestyle, it, as well as the state of the entire nervous system, unfortunately becomes not much better. In addition, the hereditary factor also plays a role. Thus, if some people’s vision may deteriorate slightly, and they do not experience any particular, so to speak, inconvenience, then others may begin to develop all sorts of diseases.
Of course, there are many diseases of the organs of vision, but among them there are those that are considered the most common and which affect the largest number of people. Below we invite you to familiarize yourself with a brief description of common visual ailments, as well as a description of the reasons that provoke their development.
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Myopia is a vision defect in which the formation of images does not occur on the retina, as it should occur, but in front of it. The result of this state of affairs is that a person sees objects located close to him perfectly, but he sees those located far away extremely poorly. In the vast majority of cases, myopia develops in adolescence, and if the development of this disease is not stopped in time, it will progress, as a result of which it can even lead to complete loss of vision.
The main reasons for the development of myopia are:
- change in the shape of the cornea;
- spasm of accommodation (we talked about what accommodation is in the last lesson);
- displacement of the lens as a result of any injury;
- sclerosis of the lens (typical for older people).
Hypermetropia (farsightedness)
Hyperopia is a visual defect opposite to myopia, which is characterized by the formation of an image behind the retina, i.e. a person distinguishes objects located far from him well, but sees those that are close much worse. Quite often this disease is accompanied by headache.
The main reasons for the development of hypermetropia are:
- reduced size of the eyeball;
- lens dysfunction - a decrease in its ability to change its curvature (typical for older people).
Strabismus (squint)
Strabismus is a violation of the parallelism of the visual axes of each eye. The main sign of strabismus is that the corneas are located asymmetrically with respect to the edges and corners of the eyelids. Strabismus can be not only acquired, but also hereditary [The Vision Therapy Center, 2020].
The main reasons for the development of strabismus are:
- various eye and/or head injuries;
- mental trauma;
- stress;
- paralysis;
- fright;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- infectious diseases;
- somatic diseases;
- sudden deterioration of vision in one eye;
- abnormalities in the development and/or attachment of the extraocular muscles;
- myopia;
- hypermetropia;
- astigmatism.
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a vision defect in which there is an abnormality in the shape of the eye, cornea or lens. Due to astigmatism, a person ceases to see clearly. If this disease is not treated in time, vision may sharply decline, and strabismus may also develop. The interesting thing is that in some cases, astigmatism is congenital, and people do not experience any particular inconvenience because of it [News Medical, 2018].
The main reasons for the development of astigmatism are:
- eye and/or head injuries;
- corneal diseases;
- consequences of surgery in the eyeball.
Nystagmus (eye trembling)
Nystagmus is a visual defect manifested in spontaneous vibrations of the eyeballs.
The main reasons for the development of nystagmus are:
- damage to the cerebellum, medulla oblongata or pituitary gland;
- acquired or congenital visual impairment;
- drug poisoning.
Amblyopia
Amblyopia is a defect characterized by decreased vision that cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
The main reasons for the development of amblyopia are:
- genetic predisposition;
- strabismus
Cataract
Cataract is a vision defect, the distinctive feature of which is clouding of the lens of the eye, the result of which is that a person sees everything blurry and as if in a haze.
The main reasons for the development of cataracts are:
- natural aging of the eye;
- diabetes;
- any eye and/or head injuries;
- any radiation harmful to the eyes.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a disease associated with periodic or constant increases in intraocular pressure, resulting in optic nerve atrophy and deterioration of visual acuity.
The main reasons for the development of glaucoma are:
- increased intraocular pressure;
- natural aging;
- chronic eye diseases;
- eye injuries;
- heredity;
- long-term use of antidepressants, antihistamines, psychotropic and some other substances and medications.
Computer vision syndrome (computer vision syndrome)
Computer vision syndrome is a special disease characterized by dry eyes, double vision and pain in the eyes, as well as increased sensitivity to light.
The main reasons for the development of computer vision syndrome are:
- negative effects of radiation from a computer;
- negative effects of radiation from TV;
- neglect of lighting standards while reading, writing and working.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an eye disease characterized by inflammation of the membrane that covers the eyeball, as well as the eyelids on the side of the eyes. Accompanied by profuse lacrimation, irritation and redness of the eyes, in some cases – discharge of pus, sticking, itching and swelling of the eyelids.
The main reasons for the development of conjunctivitis are:
- various eye injuries;
- chemical effects on the eyes;
- infection in the eyes.
The list of diseases considered is not exhaustive - in fact, there are many more diseases directly related to vision. But, as we have already said, we considered the most common ones, so let’s not continue this list (if you have a desire, the Internet and specialized literature can help you), but let’s talk about how you can stop the development of the eye diseases we presented and what means of their prevention exist.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of vision diseases
Currently, the following methods are used for the treatment and prevention of vision diseases:
- spectacle correction;
- contact lenses;
- treatment with medications;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic exercises (eye exercises);
- surgical intervention.
Below we will bring to your attention several exercises for the treatment and prevention of the above-mentioned diseases, and in cases of diseases that cannot be treated with exercises, we will make appropriate reservations.
We also note that the basis of these exercises are the developments of such well-known specialists in working with vision problems as M. S. Norbekov, W. Bates, M. D. Corbett, R. S. Agarwal, M. Windolf and others. Our attention, as the title of the lesson suggests, will be focused exclusively on therapeutic exercises - eye exercises.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of myopia
Ophthalmologists divide myopia into three types:
- slight myopia;
- average myopia;
- high myopia.
Despite this, this vision defect is quite treatable, but the success of this measure depends on how diligent the person himself is in his studies in performing exercises to treat myopia.
Exercises of this type are considered special because... they serve not only for the treatment and prevention of myopia, but also perfectly contribute to the preservation and improvement of vision in general [Portnov A., 2018]. But keep in mind that the more advanced the disease itself, the longer it will take to restore vision.
To treat and prevent myopia, perform the following exercises:
- Blink your eyes very quickly for 5-6 seconds, then take a short break (10-15 seconds) and repeat the exercise. A total of 2 to 4 repetitions should be performed.
- Close your eyes tightly for 4-5 seconds, then open your eyes for 4-5 seconds. A total of 5 to 8 repetitions should be performed.
- Extend your hand in front of you and focus your gaze on the tips of its fingers (note: the hand should be located exactly in the middle of the face). Then slowly move your hand closer, continuing to look at your fingertips, until the image begins to double. A total of 5 to 8 repetitions should be performed.
- Press on your eyelids with three fingers for 2-3 seconds, and then stop pressing. A total of 4 to 6 repetitions should be performed.
- Slowly move your gaze from bottom to top, and then vice versa, trying to keep your head still. A total of 6 to 10 repetitions should be performed.
- Perform circular movements with your eyes from right to left, and then vice versa, trying to keep your head still. A total of 3 to 6 repetitions should be performed.
- Move your half-bent arm to the right side, following with your eyes the movement of your fingers. Then begin to slowly move your hand to the left, continuing to follow your fingers with your eyes. A total of 8 to 10 repetitions should be performed.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of hypermetropia
Exercises from this group allow you to correct vision, normalizing the perception of objects located both far and near. They are also convenient because they can be performed anywhere, i.e. both at home, and at work, and while walking, etc. But there is one condition: they must be performed several hours before meals and at least twice a day. During the process, you should not strain your eyes, and you should make all movements smoothly.
To treat and prevent farsightedness, perform the following exercises*:
- Sit down and extend your arm forward, bending it slightly. The distance from your fingertips to your eyes should be approximately 40-50 cm. Now slowly move your finger in a circle in the air, focusing your gaze on your finger. A total of 8 to 12 repetitions should be performed, changing hands each time.
- Sit and look in front of you, extending your arm parallel to your eyes (the distance from your fingertips to your eyes should be approximately 30 cm). Now concentrate your gaze on the farthest point that you see in front of you, and then move your gaze to your fingertips. A total of 5 to 10 repetitions should be performed.
- Sit down and look in front of you, turning your head to the side. As your head turns, your gaze should also move. After this, turn your head straight and repeat the exercise in the other direction. A total of 7 to 10 repetitions should be performed.
- Move your eyes from left to right (and vice versa), from top to bottom (and vice versa), and clockwise (and vice versa). In total, you should perform 10-20 movements in each direction.
- Focus your gaze alternately on near and far objects
*If only one eye is farsighted, then exercises should be performed while covering the healthy eye with your hand.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of strabismus
The main goal of this type of exercise is to align the visual axes of each eye, but another positive effect from their implementation is general vision correction [Healthline, 2017].
To treat and prevent strabismus, perform the following exercises:
- The exercise is performed with your back to the sun (or light source). Cover your good eye with your hand, leaving the squinting eye open. Tilt your head to the right or left - to the side of the diseased eye - until a ray of sun (or a light source) falls on that eye. In total, you should perform at least 10 repetitions of head tilts
- Tilt your head back and try to focus your gaze on the tip of your nose. In total, you should perform 4-5 repetitions of 20-30 seconds
- Sit with your back straight and your arms extended in front of you. Now, with the index finger of each hand, touch the tip of your nose in turn, while simultaneously watching with your eyes the movement of the fingers. The exercise should be performed rhythmically until the eyes begin to water.
- Place a long, narrow object in front of you, such as a pointer or stick. Then focus your gaze on the tip of this object. After this, begin to make chaotic movements with this object, continuing to focus on its tip. The exercise should be performed until the eyes begin to water.
- Cover your eyes with your hands so that no light enters. Now start drawing with your eyes the outlines of any figures or objects (you can draw a circle, oval, square, cross, etc.)
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of astigmatism
Exercises that relate to the treatment and prevention of astigmatism differ from many other eye exercises in that you will need to use auxiliary objects to perform them.
To treat and prevent astigmatism, perform the following exercises:
- Find a shoebox and attach dominoes in a horizontal position to the lid for a game of dominoes in several rows. Place the box about 30-40 cm away from your eyes and start moving the box first to the left and then to the right. As the box moves to the left, turn your head to the right and vice versa. Please note that you do not need to try to look at the dots on the knuckles - you should move the box so that you feel like you are seeing only solid lines.
- After 3-5 minutes, start moving the box in a vertical plane, i.e. start moving the box from bottom to top and vice versa, while moving your head in the opposite direction to the movement of the box. You can perform the exercise for 6-10 minutes - the time for moving the box in the horizontal and vertical planes should be the same
- Take 3-4 dominoes and take a quick look at them. After this, turn to the side and try to name the numbers you saw on the knuckles. This exercise is also useful because it trains the skill of quickly switching attention and stimulates brain activity. You can perform as many repetitions as you like, but it is advisable to do at least 20 repetitions per set.
- Take a glass of cold water and put it in your mouth until your cheeks swell. Now tilt your head in different directions with your eyes wide open (do 5-10 repetitions in each direction). After this, open warm water in the bathroom and start splashing it into your eyes with your hands, trying not to blink and keep your eyes wide open. The exercise should be performed until the water in the mouth becomes warm (as a rule, up to 20 splashes are enough). At the end of the exercise, pour the water out of your mouth and lightly massage your eyes. When performing this exercise, water helps strengthen the body, stimulate blood circulation, strengthen vision, massage the eyes and tone the nerve endings.
Exercises to treat and prevent nystagmus
Considering that nystagmus is a specific disease, its treatment is not performed with the help of exercises and is usually carried out over a long period of time and in a complex manner, and also either against the background of pathology or against the background of treatment of some underlying disease.
To cure nystagmus, methods such as:
- Optical vision correction – use of glasses or contact lenses (glasses with light filters can be used).
- Pleoptic treatment – stimulation of the retina through light on a monobinoscope, stimulation with contrast-frequency and color tests (computer exercises EYE, “Spider”, “Zebra” and “Crosses”, as well as the “Illusion” device).
- Drug treatment (most often of an auxiliary nature) - the use of vasodilators, as well as multivitamins.
- Surgical treatment - reducing the amplitude of oscillations of the eyeballs, weakening or strengthening of the eye muscles.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of amblyopia
The exercises in this category are quite suitable for performing at home, but a mandatory requirement for obtaining a positive effect from them (improving vision) is correctness and regularity.
To treat and prevent amblyopia, perform the following exercises:
- Stand by the window and cover your good eye with your hand. Hold a piece of paper with text printed on it to your weak eye. Bring the sheet up until it becomes difficult to distinguish the text. After this, slowly move the sheet back until the text becomes legible again. In total, at least 10-15 approaches should be performed for each eye.
- Glue a small black circle with a diameter of 6-8 mm on a 60-70 watt electric light bulb, and a white sheet of paper on the wall. Cover your good eye with one hand and look at the light bulb for 30 seconds. Now turn your gaze to a piece of paper and look at it until you see the image of a circle pasted on the lamp. A total of 5-6 repetitions should be performed for each eye.
- Find a helper and a 100-watt table lamp and put a black paper cap on it with a 5mm diameter hole cut in it. Cover the hole with red film, and sit from the lamp at a distance of about 40 cm. Look at the red dot in the black cap with your weak eye for 3 minutes. An assistant should turn the lamp off and on approximately every 2-3 seconds. The exercise should be performed for at least 3 months and always in a dark room.
- Look at the bridge of your nose or the tip of your nose with both eyes for 30-40 seconds. A total of 6-8 approaches should be performed.
- Sit down and place your hands on your knees. Look straight ahead, then left, then down, trying not to blink. You can perform the exercise only once a day, and it is performed until tears flow from your eyes.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of cataracts
The exercises described below will not help cope with advanced cataracts, but if the disease has not yet begun to progress, then they can help a person not only get rid of this disease, but also strengthen vision in general, and also give a boost of energy for a long time. Each of the exercises, except the last two, should be performed with your eyes closed.
To treat and prevent cataracts, perform the following exercises:
- Rotate your eyes clockwise and counterclockwise. A total of 10 rotations should be performed in each direction.
- Describe an imaginary triangle with your eyes, fixing your gaze on its corners. The direction of eye movement should be changed. A total of 10 movements should be performed in each direction.
- Move your eyes diagonally in the directions "up-left", "down-right", "up-right" and "down-left". A total of 10 movements should be performed in each direction.
- Rotate your eyes around the circle 2 times in each direction, stopping your gaze at the center of the circle every 2 times. A total of 10 rotations should be performed in each direction.
- Describe the figure eight with your eyes. The direction of eye movement can be changed. A total of 10 directions should be performed in each direction.
- Look at the switched on lamp for 2-3 seconds and quickly close your eyes with your palms for 2-3 seconds. A total of 10 repetitions should be performed
- Blink rapidly for 10-15 seconds. A total of 4-5 repetitions should be performed
- Shift your gaze from the tip of your nose to the area between your eyebrows. A total of 15-20 repetitions should be performed.
- Look alternately at the tip of your nose and then into the distance. A total of 15-20 repetitions should be performed.
- “Write” various words with your nose or “draw” any objects, fixing your gaze on the tip of your nose. The exercise should be performed for 2-3 minutes
- Raise your arms bent at the elbows at eye level and spread your fingers. Then slowly and smoothly turn your head in different directions, unfocusing your gaze. You should perform up to 30 repetitions in total.
- Perform “palming”: turn your head towards the sun (or other light source), lightly cover your eyes with your palms, pressing your fingers tightly together (the middles of your palms should be located at the centers of your eyelids), and also closing your eyelids. Then think about something pleasant for you for 15 seconds and begin to gradually release your eyes from your palms, allowing your eyes to get used to the light (no need to raise your eyelids). In total, you should perform up to 10-15 such repetitions.
- Take turns opening your mouth and eyes as wide as possible. A total of 5-10 repetitions should be performed.
- Close your eyes tightly for 3-5 seconds. You should perform up to 6 repetitions in total.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of glaucoma
Exercises from this series are performed primarily not for the treatment of glaucoma, but for its prevention, because They will not help restore intraocular pressure completely, but they will help maintain eye health at the current level.
To treat and prevent glaucoma, perform the following exercises:
- Do a light massage of the eyebrow area, moving your fingers towards the temples. The exercise should be performed for 3-5 minutes
- Stroke the frontal part of the head, moving your fingers from the eyebrows upward. The exercise should be performed for 3-5 minutes
- Massage the temporal part of the head, massaging it with your fingers. The exercise should be performed for 3-5 minutes
- Lightly tap your forehead with your fingertips. The exercise should be performed for 2 minutes
- Do a light massage of your eyelids, pressing lightly on them with your fingers and moving them in a circle. The exercise should be performed for 20-30 seconds
- Close your eyelids as hard as you can, and then open your eyes as much as possible. A total of 8-10 repetitions should be performed.
- Blink quickly. The exercise should be performed for 2-3 minutes
- Stand in front of the window - look at the street for 3-4 seconds, and then fix your gaze on the glass of the window for 3-4 seconds. You should perform up to 10 repetitions in total.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of computer vision syndrome
Before we describe the exercises in this category, we want to present several effective recommendations that will help to significantly reduce the negative impact of long work at the computer on the visual system.
To minimize the damage caused to your eyesight by a computer when working on it, follow the following general recommendations [Reddy SC, Loh KY, 2008, Chowdhary S., 2021, American Optometric Association, 2020]:
- Install a desk lamp at your workplace (regular, not daylight, otherwise your eyes will get more tired) - this will allow you to properly adjust the lighting.
- Try to use a flat monitor for work.
- Set the screen flickering frequency to at least 85 Hz.
- Adjust the brightness of the monitor, depending on the general lighting in the room - the brightness of the monitor and the general lighting should be approximately the same.
- The center of the monitor should be located approximately 5-8 cm below your line of sight in a straight line.
- When using contact lenses while working, be sure to use rewetting drops.
- Use document holders. Any documents should be located above the keyboard and below the monitor.
- Use special anti-glare filters, especially when it is impossible to avoid glare from natural light.
As for exercises, to prevent and treat computer vision syndrome, do the following [Reddy SC, Loh KY, 2008, Chowdhary S., 2021, American Optometric Association, 2020]:
- As soon as you begin to feel increased eye strain, take a break, close your eyes and lightly massage them through your eyelids for 1 minute.
- Every 2 hours, try to relax your eyes, as well as the muscles of your back and neck, for a few minutes.
- From time to time, take a break from the monitor and look “at nothing,” for example, at the street.
- From time to time, make circular rotations with your eyes in different directions (look in each direction 4 times).
- From time to time, close your eyes and look in different directions (look in each direction 8 times).
- From time to time, start blinking quickly for seconds (do 3 sets).
- Take breaks from work approximately every 40 minutes.
Exercises for the treatment and prevention of conjunctivitis
You already know that conjunctivitis is a disease in which inflammation of the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the eye and the eye itself occurs, so simple exercises will not help here - more specific methods should be used to treat this disease.
To begin with, let's say that conjunctivitis comes in different forms. So, they distinguish:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis is an infection of the eyes followed by mucus discharge.
- Viral conjunctivitis is an infection of one eye followed by the release of tears and mucus.
- Allergic conjunctivitis is redness of the eyelids, followed by severe itching and the discharge of viscous pus.
Bacterial and viral conjunctivitis can be easily transmitted from a patient to a healthy person, for which reason it is very important that the patient observes hygiene and quarantine measures [MedicalNewsToday, 2017, Encyclopedia, 2020]:
- The patient should use only personal and clean linen.
- The patient should use only his own hygiene products.
- After contact with eyes, the patient must wash his hands.
- The patient should refrain from visiting public places.
- You should be extremely careful not to get chlorine into your eyes (visiting the pool is strictly contraindicated).
To treat conjunctivitis, medications and folk remedies are used.
Among the medications for the treatment of conjunctivitis, viruscidal, virostatic drugs are usually used ( specific drugs depend on the form of the disease and only a doctor can prescribe them! ), such as:
- Florenal drops;
- Florenal ointment;
- drops "Gludantan";
- drops "Okoslin";
- Oxolin ointment;
- Dibazol injections;
- Cortisone drops;
- Diphenhydramine tablets;
- calcium chloride solution;
- some other drugs.
Folk remedies for the treatment of conjunctivitis are in no way inferior to medications in their diversity [Mayo Clinic, 2021, Harris K., 2020]. Among them are the following:
- compresses and infusion for washing the eyes from aloe vera;
- infusion for washing the eyes from medicinal marshmallow;
- infusion for washing the eyes from the herbs of hops and blueberries;
- infusion for washing the eyes from rose petals;
- an infusion for washing the eyes from black nightshade leaves, marshmallow root and snapdragon herb;
- infusion for washing the eyes from cornflower flowers.
Mustard, green tea, honey, lemon juice and other remedies are also used for conjunctivitis [Organisfacts, 2020]. You can learn more about recipes for preparing compresses and infusions by searching for relevant information on the Internet. The integrated use of medicines and folk remedies will help get rid of conjunctivitis in record time. However, as we have already said, before using any of the methods you need to consult with a specialist.
If we talk about the prevention of this malicious disease, then to prevent its occurrence it is recommended to follow the following recommendations (especially for children):
- After being outside, doing household chores and visiting the toilet, you must wash your hands with soap and water.
- Use all kinds of remedies and vitamins to increase immunity and strengthen the general condition of the body.
- Play sports, spend time actively, sleep enough time and follow a daily routine.
- If possible, avoid overexertion, increased loads and stress.
- When working at a computer, be sure to take short breaks accompanied by eye exercises, and also use special glasses.
- If even minor signs of conjunctivitis (and other eye diseases) appear, be sure to consult a specialist.
Preventative measures will help you keep your eyes healthy and avoid many problems.