In 1998, the American Optometric Association introduced a new term - computer vision syndrome. This is a complex of visual and ocular symptoms caused by computer work. Read more about this common ailment and methods of prevention from Territory Health ophthalmologist Anastasia Petukhova.
According to various sources, on average, about 60% of all computer users complain about vision, every sixth patient who underwent an ophthalmological examination had problems associated with working on a computer, 22 percent of those who use a computer also have accompanying complaints of discomfort and neck pain , back, shoulders, manifestations of carpal tunnel syndrome (carpal tunnel syndrome).
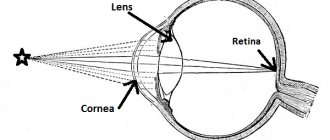
Our brain and eyes react differently to an image on a monitor screen and an image printed on paper. The image on paper has sharp edges, while the characters on the computer screen do not have a sufficient degree of contrast and clarity. Images on a monitor are combinations of tiny points of light (pixels) that are brighter in the center than at the edges. This makes it difficult for our eyes to maintain focus on them, which in turn leads to eye strain and fatigue during and after working on the computer. In addition, the rays of the blue-violet spectrum that monitors generate have a harmful effect on eye tissue.
Etiopathogenesis
The basis for the development of CGS is the mechanism of overstrain of the accommodative apparatus of the eye. Firstly, the differences between images on electronic media and paper are significant. Text on electronic media consists of scattered dots and pixels. In them, the accommodative apparatus of the eye is not able to maintain focus, so it “switches” to the resting point of accommodation. While working at a computer, the accommodative apparatus is forced to “switch” from this point to the image without interruption. This leads to accommodation dysfunction. Secondly, visual overstrain during prolonged work at the computer leads to dysfunction of the ciliary muscle and spasm of accommodation,6 which in turn manifests itself in the clinical manifestations of CVD. It has been proven that after 4 hours of work, computer users show changes in the peripheral part of the visual analyzer in the form of decreased visual acuity, increased refraction, and decreased accommodation indicators7. Also, the organ of vision experiences a greater load when frequently looking from the keyboard to the screen, since these elements of the computer are located at different distances and are not equally illuminated. Another significant mechanism in the development of CGD is a decrease in the number of blinking movements. Studies have shown that among computer users their frequency decreases to 4 per minute (the norm is 18). This leads to disruption of the stability of the precorneal tear film and, as a result, to xerotic changes in the cornea and conjunctiva8. These changes lead to the development of dry eye syndrome (DES). Studies have shown that CVD is the main cause of dry eye syndrome in young patients9.
Factors Causing Computer Vision Syndrome
The position in which you sit at the monitor, the distance from it to the eyes, the lighting of the room and the keyboard, the distance of the keyboard from the eyes, the tilt of the head, the glare of the screen - all this provokes the vision to adapt to work, i.e. strains all eye structures. If at the same time your vision has its own problems - myopia or farsightedness, then it is natural that it is even more difficult for your eyes to be under prolonged stress.
There is an opinion that computer vision syndrome is caused by the radiation characteristics of the monitor. But the point is not so much in the radiation as in the resolution of the screen. Monitor flickering, invisible to the naked eye, causes additional stress and affects the condition of the eyes.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of CVD are divided into: ocular, visual and general.
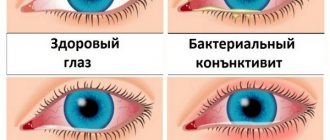
The first group includes: redness of the eyes, pain when moving the eyeballs, pain in the forehead and eye sockets, burning sensation in the eyes; “sand” under the eyelids.
The second group includes: visual impairment; violation of accommodation; double vision; the appearance of rapid fatigue when reading and writing.
The third group includes: headaches, pain in the cervical-collar area, dizziness.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is based on anamnestic data and patient complaints. A history of periodic long hours of work at a computer and the complaints described above indicate CGD.
Also, when examining a patient with CVD, it is necessary to:
- visometry;
- skiascopy;
- determination of the volume of absolute accommodation;
- determination of the reserve of relative accommodation;
- ophthalmoscopy using generally accepted methods;
- determination of tear production and tear film stability (Schirmer and Norn tests);
- rose bengal test;
- Lissamine green test.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out with:
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- dry eye syndrome not associated with computer work;
- blepharitis;
- lagophthalmos;
- presbyopia;
- various types of ametropia.
Prevention and treatment
1. Compliance with occupational hygiene
It is necessary to explain to the patient the rules of working with a computer in an accessible form:
- It is necessary to ensure uniform and sufficient lighting in the room.
- Additional lighting sources should not be directed at the monitor or into the eyes.
- The correct location of the keyboard is 65-70cm from the floor.
- It is necessary to place the monitor 15-20 cm below the horizontal line of sight.
- The distance from the eyes to the monitor is no less than 50 and no more than 70 cm.
- When working, your feet should be firmly on the floor and your knees should be bent at an angle of about 90 degrees.
- The angle between the seat and the back of the chair should be 95-100 degrees.
2. Compliance with the computer work schedule
Periodically it is necessary to relax the accommodative muscles, adjusting the eye to the far point of best vision. During your working day at the computer, you should take 20 second breaks every 20 minutes and look into the distance at a distance of 6 meters.
3. Hygiene procedures
To prevent CVD, people who work with a computer 6-8 hours a day are recommended to carry out a daily course of therapeutic hygiene procedures, including cleansing the edges of the eyelids and self-massage of the eyelids using blepharogel and warm compresses with blepharolosion. In order to prevent the recurrence of clinical manifestations, patients with CVD are recommended to undergo a course of therapeutic eyelid hygiene 2-3 times a year.10
4. Laser stimulation of the ciliary body
This technique is based on transscleral non-contact exposure to the ciliary muscle using infrared laser radiation (1300 nm). The main point of application of MP at the tissue and organ level is the microvasculature. At the same time, the metabolic activity of both epithelial cells and the connective tissue of the ciliary body increases.11
5. Bioresonance therapy
The principle of operation is based on biorhythmic stimulation of the visual analyzer with light, which ensures the normalization of its rhythmic processes and improves the functioning of the eyes.
6. Biomechanical stimulation
It is carried out by influencing human muscles with a mechanical factor, more precisely vibration. As a result, blood supply to the organ of vision improves and its function increases, visual acuity increases and eye accommodation improves.
7. Electrical stimulation of the ciliary muscle of the neuromuscular system, causing motor excitation and muscle contraction and increasing the volume of muscle mass, simultaneously reflexively enhances the entire complex of metabolic and trophic processes aimed at providing energy to working muscles. Thus, electrical stimulation is a pathogenetically substantiated method for diagnosing and treating disorders of the hydrodynamics of the eye, spasm of accommodation, and myopia.12
8. Accommodation training
Working at a computer continues for a long time at close distances and therefore refers to static loads. A set of special exercises improves the nutrition of the ciliary muscle and lens.
9. Drug therapy
It must be carried out after a thorough diagnosis and correction of hygiene and computer work habits. Drug therapy includes the following.
10. Prosthetics of native tear film
In ophthalmological practice, “artificial tears” preparations are common, forming a stable film on the surface of the eyeball that protects the cornea from drying out while reducing blinking movements while working at the computer. Among the polymer bases of “artificial tears” preparations, methylcellulose derivatives, polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sodium hyaluronate, chondroitin sulfate, polyacrylamide, various versions of carbomers, etc. are known.
11. Antioxidant therapy
In ophthalmology, antioxidants such as emoxypine, tocopherol acetate, vitamin C, A, and dicinone are widely used as inhibitors of free radical processes.
Antioxidant therapy with STRIX also showed good results.13 The blueberry extract contained in it, containing vitamin C and anthocyanins, eliminates the oxidative effect of free radicals that are formed in the human body during prolonged work at the computer, which is a priori stressful for the body.14 Beta-carotene , also part of STRIX, is involved in the mechanisms of photoreception of the eye, plays a significant role in maintaining its antioxidant status, reduces lipid peroxidation and normalizes metabolic processes in the cornea.
STRIX Forte is additionally enriched with lutein, which is necessary for the development and maintenance of the normal distribution of retinal pigment epithelial cells. It also colors the macula yellow, creating a natural filtration barrier against short-wave blue radiation. This helps protect the photoreceptors from damage. The point of application of selenium included in STRIX Forte is the arteries and veins of the eyeball. Selenium slows down the process of sclerosis and helps reduce the likelihood of hypoxic-ischemic changes.
STRIX is prescribed according to the following scheme:
Children from 7 years old : monthly course of 1 tablet per day.
Adults: monthly course of 1 tablet 2 times a day.
STRIX Forte is recommended from 14 years of age, 1-2 tablets per day for 1-3 months.
Prices for diagnostic services and consultation with an ophthalmologist
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of glasses for astigmatism with a prescription | 700 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Selection of contact lenses without training | 600 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods for computer syndrome
Crizal Prevencia
Premium class lenses operate in three directions - they maximally protect the organs of vision from UV and blue-violet radiation and transmit useful light. Optimal image clarity and visibility.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist
A person receives 90% of information through the eyes. Decreased visual acuity and various eye diseases lead to loss of this function. Timely contact with a specialist doctor will help to avoid serious problems.
Ophthalmological device "Cascade"
Impact on the visual function of the eyes with light and color stimuli that dynamically move over a certain distance in a closed tube. Particularly effective for accommodation disorders and restoration of binocular vision.
Crizal Eyezen
These lenses can be called an investment in eye health. They are designed to optimize the perception of information from digital gadget screens. The result is excellent focusing, reduced eye fatigue and protection from blue light.
Ophthalmological treatment device "Visotronic M3"
The ophthalmic myotrainer relaxer has a complex effect on the organ of vision and oculomotor muscles. Particularly effective for eye accommodation disorders, as well as during myopia, hypermetropia and computer syndrome.
Computer Syndrome Articles
Blue light and optical coatings that reduce its transmission
Do I need to correct my vision and why is it so important?
Preserving vision and eye health with Crizal Eyezen lenses
Protect your eyes from the sun with UV filter contact lenses
Which spectacle lenses should I choose? Choose your glasses with Crizal Corner