What is accommodation?
Human eyes have the ability to see at different distances. This allows them a natural focusing mechanism.
In this article
- What is accommodation?
- Why is accommodation impaired?
- Symptoms of false myopia
- Diagnosis of spasm of accommodation
- Types of accommodation spasm
- How to distinguish false myopia from true one
- How to relieve spasm of accommodation
- Treatment of false myopia in schoolchildren
- Prevention of false myopia
Using such focusing, we can see a speck on the window glass, adjusting our gaze to a close distance, or we can, looking from the same window, see parked cars, people walking on the street, etc. Accommodation is the ability of the eye to refract light to produce images at different distances.
Accommodation apparatus:
- lens - a natural lens of the human eye, refracts light, transmitting the image to the retina, interacts with the ciliary muscle, providing the function of accommodation;
- accommodative muscle - this muscle is also called ciliary, ciliary, it is responsible for focusing the organs of vision;
- ligament of Zinn - located in the posterior chamber of the eye, formed from thin fibers, holds the lens in the anatomically correct position.
When viewing nearby objects, the ligament of Zinn of the lens relaxes and the ciliary muscle tenses. If you look into the distance, the opposite happens: the accommodative muscle relaxes, and the lens takes on a flatter shape. All processes are controlled by the human nervous system; this happens automatically. We do not need to take any special actions to activate the processes of accommodation.
Causes
Children have to constantly “load” their eyes with reading at school, and then at home when doing their homework. Added to this load is the constant use of gadgets, computers, and watching TV. There are many more factors that can provoke a spasm of accommodation in schoolchildren than the reasons that cause symptoms of false myopia in adults.
- unbalanced diet and lack of vitamins in the body;
- incorrect body position when reading;
- poor circulation in the spine, especially in the cervical region, disorder of the cervical and spinal muscles;
- using a table and chair that is not appropriate for the child’s age;
- increased strain on the eyes in the absence of eye exercises;
- improper organization of the workspace: poor lighting, too large or too small a distance from which the child reads, etc.
These are the most common reasons. False myopia can also be caused by head/eye injuries and neurological diseases.
Actually, the above reasons can become factors provoking a spasm of accommodation in adults. It just occurs more often among schoolchildren. In adulthood, false myopia occurs in those people whose work involves excessive eye strain, for example, office workers, jewelers, and seamstresses.
The main stimulus for the accommodation reflex to appear is the defocusing of the image on the retina under optimal lighting conditions - light rays from a nearby object are not focused on the retina (defocusing on the retina), this defocusing, perceived by the brain, is an impulse to turn on the accommodation mechanism.
A nerve impulse passing along the oculomotor nerve gives a signal to contract the ciliary muscle. The muscle contracts, the tension of the ligaments of Zinn decreases, and as a result the lens changes its curvature. As a result, the focus of the image moves to the retina. If the gaze is moved into the distance, the focus of the image will return to the retina, there will be no defocus signal, there will be no nerve impulse, the ciliary muscle will relax, the tension of the zonules of Zinn will increase, the lens will eventually reduce its curvature and become flat again.
The development of accommodation spasm is promoted by:
- excessive visual stress (TV, computer, doing homework in the evening);
- poor workplace lighting;
- non-compliance with the daily routine (lack of walks in the fresh air, playing sports, insufficient sleep);
- the desk and chair do not match the child’s height;
- failure to maintain the optimal distance to the book (30–35 cm);
- weakness of the neck and back muscles;
- impaired blood supply to the cervical spine;
- poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis;
- insufficient physical activity.
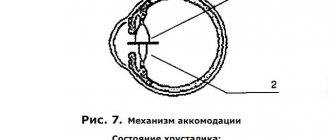
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye.
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
The reasons for the development of the disease may be different. Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs due to injuries and microtraumas. A temporary spasm may occur when the brain is contused or when looking at the sun. If severe damage occurs in the form of a burn, then the disease develops on an ongoing basis.
When neurological pathologies occur, paralysis of accommodation is a sign and can be treated if the root cause is eliminated.
There are the following causes of paralysis of accommodation:
- age-related changes;
- tumors;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- previous injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- intoxication with drugs or chemical elements;
- diabetes;
- constant physical overload.
The development of paralysis of accommodation also occurs naturally with aging. After forty-five years, the lens becomes inelastic and takes on an irregular shape. Eye strain and physical strain also influence the development of pathology. In order to avoid unpleasant manifestations, it is necessary to visit the doctor more often.
Why is accommodation impaired?
Intense visual stress is the main cause of accommodation spasm. The ciliary muscle, which is in a tense state for a long time (for working at close range), spasms and can no longer relax. Therefore, at one point, a person with naturally good vision may stop seeing clearly into the distance.
This problem is common among people who interact with digital devices for a long time (web designers, programmers) or work with information on a computer (managers, accountants, journalists). The likelihood of an accommodation spasm increases for those who do not follow a visual exercise regime, do not pause at work, do not monitor the health of their eyes, forgetting about gymnastics, taking vitamin complexes and the general health of the body. For a long time, false myopia, or spasm of accommodation, can go unnoticed by a person, because it usually affects not two eyes, but one. This disorder causes discomfort, which people usually attribute to fatigue. In order to promptly detect a problem such as a spasm of accommodation, you need to pay close attention to its first symptoms.
Possible complications
Spasm of accommodation, if untreated, can lead to asthenopia. It will be quite difficult to work or study with constant fatigue, headaches and decreased visual acuity. Due to false myopia, true myopia can develop. Myopia and accommodation spasm, although they are different ailments, often cause the same symptoms. It is better to eliminate a symptom such as a spasm than to treat myopia for a long time.
One of the early symptoms of paralysis of accommodation is a decrease in the clarity of perception of objects near
In the initial stage of development, paralysis of accommodation is successfully treated. But in the absence of timely therapy, certain complications may develop.
If initially vision was normal or paralysis appeared against the background of farsightedness, an irreversible weakening of the clinical refraction of the eye may occur. In this condition, the ability to clearly see objects at close range is lost.
Symptoms of false myopia
If you constantly feel discomfort, eye fatigue, headaches become more frequent and there is low productivity while performing usual tasks, undergo a special ophthalmological examination to check whether accommodation is impaired. Before visiting a doctor, you can check your vision yourself. To do this, you need to cover one eye with your hand and look, for example, at the license plate of a car located at an average distance from you. Repeat the same with the other eye closed.
False myopia - symptoms:
- decreased distance visual acuity;
- images seem unclear and blurry;
- constant eye fatigue, pain and burning, headaches;
- low performance.
If there is a spasm of accommodation, you will immediately notice it, since the numbers will seem fuzzy and blurry, they will be double and without contours. False myopia, if it already exists, will not be able to go away without drug treatment, especially with the same increased visual load. Therefore, you will need to consult an ophthalmologist. How do doctors determine false myopia?
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptoms of eye accommodation are often mistaken by people for a sign of fatigue. A person feels that the eyes become tired after hard work, there is slight redness, burning, dryness of the eyes or watery eyes. Subsequently, eye fatigue becomes more pronounced, objects begin to blur, and viewing small details becomes difficult.
The initial stage of accommodation disturbance is asthenopia, characterized by chronic eye fatigue with redness of the whites of the eyes, the edges of the eyelids and unpleasant symptoms - burning, itching, sand in the eyes. Typically, such manifestations disappear after a night's rest.
Symptoms of accommodation spasm are more prolonged and unpleasant. Painful sensations, pain and burning in the eyes intensify, clarity of vision deteriorates, patients note double vision of objects. For young children, indirect signs are moodiness, irritability, the habit of squinting their eyes, and schoolchildren’s academic performance decreases. Without consulting a doctor, a spasm of accommodation can develop into childhood myopia.
A complex form is a pathological spasm of accommodation. Eye symptoms are supplemented by eyelid tremor and nystagmus. The general condition of the body worsens - migraine attacks, trembling fingers, and emotional lability appear.
Symptoms of accommodation paresis manifest themselves differently in nearsighted and farsighted people. With farsightedness, distant vision also deteriorates. Patients with myopia (myopia) often experience severe headaches, severe itching and burning in the eyes.
Diagnosis of spasm of accommodation
At the first stage of the ophthalmological examination, vision is checked using a letter table and special equipment. First, the results are recorded without instilling drops that dilate the pupil, and then studies are carried out with a dilated pupil, the fundus is examined using a slit lamp, intraocular pressure is measured, refraction, volume and accommodation reserves are determined.
Causes of accommodation disturbance:
- disturbance of sleep and rest patterns;
- lack of necessary physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive visual stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- injuries, tumors, vascular disorders.
Accommodation disorders also have physiological causes. Due to the natural aging of the lens, which can no longer perform its accommodative functions, vision deteriorates. In young people, problems with accommodation are more often associated with abnormal eye strain. Spending a long time at a computer in a forced position leads to disruption of the blood supply to the cervical spine and organs of vision, which negatively affects eye health.
Diagnostics
If this condition is identified, measures to eliminate it are prescribed. First, the affected persons undergo a comprehensive examination of the visual analyzer.
Diagnostic measures:
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedist, pediatrician and neurologist is prescribed. The doctor finds out the patient’s daily routine, time spent at the computer during the day, and the presence of pathology in the family.
After conducting all research methods, the ophthalmologist determines the severity of the disease and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Types of accommodation spasm
With a spasm of accommodation, the muscles responsible for focusing are in a tense state even when this is not necessary. In this condition, a person loses his usual visual acuity, so the symptoms are similar to true myopia. Due to the development of digital technologies, the percentage of adults with such visual impairment is increasing, whereas previously this problem was more common among schoolchildren and students.
Depending on the reason that caused such a violation, a spasm of accommodation occurs:
- physiological - occurs as a self-correction for farsightedness and astigmatism;
- artificial - paralysis of the ciliary muscle caused by the effects of drugs;
- pathological - with such a disorder, there is a sharp deterioration in visual acuity due to constant tension of the ciliary muscle after long work at close distances, with small objects;
- mixed - occurs when several types of violations are combined.
Can a spasm of accommodation lead to myopia? A pathological, prolonged spasm of accommodation when the body’s alarm signals are ignored and the lack of adequate treatment can lead to the formation of not false myopia, but true myopia. Without correction, a person will experience constant malaise, irritability, and fatigue. Children in this condition experience a significant decline in academic performance.
Symptoms of spasm
False myopia develops when the ciliary muscle, which is responsible for changing the curvature of the lens when focusing the eye, is overworked. The closer the object is, the more the biconvex lens of the eye bends and the higher the tension of the ciliary muscle.
Characteristic signs of false myopia:
- deterioration of visual perception at long distances;
- rapid fatigue;
- cephalalgia and pain in the eyeballs;
- rolls eyes;
- hyperemia;
- double vision occurs;
- the perception of objects located at close range becomes less clear.
Children's performance at school is deteriorating. In adults, performance decreases.
Spasm and paralysis of accommodation are different concepts. Paralysis is the loss of the ability to clearly see objects located closer to the far point of clear vision. The spasm can lead to paralysis if not treated promptly.
How to distinguish false myopia from true one
Myopia caused by heredity, a special shape of the eye, injury, infection, or when the ciliary muscle is not spasmed is called true. Vision deteriorates due to the fact that, due to diseases and growth characteristics, the eyeball acquires an elongated shape and light rays are focused not on the retina, but in front of it.
How can a spasm of accommodation be distinguished from myopia? With false myopia, a person cannot see into the distance only because the work of the accommodative muscle is impaired. This process is reversible, although the disease is difficult to treat. The ciliary muscle cannot be involved in the processes of accommodation, as it is in constant tension. For this reason, one of the most effective methods of treating this disease is the use of drugs whose action is aimed at relaxing the ciliary muscle.
Treatment
After a comprehensive examination, the doctor tells you how to treat spasm of accommodation in both eyes. Typically, therapy includes medications, hardware methods, health and hygiene measures. It would not be amiss to do special gymnastics for the visual analyzer.
It helps relieve spasm of accommodation of the eye and strengthen the muscles. An integrated approach allows you to restore vision in a few weeks.
Drugs
Medicines are used for spastic contraction of the ciliary body. They help relax the muscles. Such drugs are called mydriatics.
They influence the tone, thereby changing the curvature and refractive power of the lens.
Drops for false myopia:
- Atropine is contraindicated in cases of angle-closure glaucoma, keratoconus and in children under 7 years of age. The medicine is administered intravenously, intramuscularly, parabulbarly and subconjunctivally.
- Tropicamide is used during pregnancy and lactation. When used topically, an overdose may occur.
- Irifrin has many contraindications and side effects. Therefore, the drug is not prescribed in childhood.
Physiotherapy
If medications are not enough to relieve spasm, treatment is supplemented with hardware methods of treatment. This treatment is allowed for children from 2 years of age. If you combine physiotherapy with drugs and vision correction, the result is very effective.
The following methods are used:
- Drug electrophoresis - allows you to administer drugs through the skin and mucous membranes using an electric current.
- Magnetic therapy - the effect is a constant or pulsed magnetic field. This method of treatment activates microcirculatory blood flow and slows down pain impulses.
- Acupuncture is useful for weak neck and back muscles. To carry out the technique, sterile needles are used. They are placed at certain points to relieve spasm of the entire muscular system.
- Electrical stimulation - allows you to restore metabolic processes and blood circulation of the eyeball. The procedure has a positive effect on the optic nerve, visual cortex and subcortical structures.
Eye exercises
Effective gymnastics for false myopia:
- look up, then look down, left and right;
- move your eyes along the trajectory of the number 8 in normal and inverted form;
- close your eyes and open your eyelids wide;
- blink for 1 minute without stopping;
- fix your gaze on the spot formed on the glass, carefully examine the spot, then turn your gaze to the most distant object outside the window;
- place your hands in front of your eyes, fingers spread out, look through them and at the same time slowly move your head to the sides.
How to relieve spasm of accommodation
Treatment of spasm of accommodation should be comprehensive. The effectiveness of therapy depends on how responsible the approach of the person diagnosed with such a problem is. To help the ciliary muscle relax, special eye drops are used to dilate the pupil. The doctor prescribes the drug depending on how long ago the spasm formed. For two weeks and up to one month, you need to apply mydriatic eye drops to your eyes so that the eye muscle relaxes and then can work again, independently relaxing for long distances and straining when looking at close objects.
False myopia - treatment:
- It is recommended to reduce visual load as much as possible;
- daily, in doses prescribed by the ophthalmologist, instill eye drops with medications that dilate the pupil;
- regularly perform eye exercises by choosing the appropriate technique;
- increase physical activity: play tennis, swimming, dancing to improve blood supply to all organs, including the visual system;
- enriching the diet with foods rich in selenium, vitamins A, B, zinc - include leafy greens, seaweed, egg yolk, salmon, spinach in the menu.
After two weeks of drug therapy, visual acuity improved. In most cases, vision increases by two to three diopters. To achieve a sustainable result, it is necessary to control the visual load regime and constantly do exercises aimed at improving accommodation.
Paralysis of accommodation: diagnosis and treatment. Delivery of contact lenses and glasses in Moscow and Russia
Depending on the cause, surgery may be required to correct the paralysis.
Accommodation paralysis defines a pathological condition in which the near and far points of clear vision of objects and images merge into one. This pathology of neurogenic origin is not widespread.
Most often it appears in children aged 7 to 15 years. It is very rarely detected in middle-aged and elderly people. The disease has no gender and develops equally in both women and men.
Paralysis of accommodation is accompanied by a loss of the ability of the ciliary muscle to tension. With the development of this pathology in people with normal refraction and farsightedness, the ability to recognize close-up small print disappears.
The disease has a certain classification. In medical practice, the types of paralysis of accommodation are clearly defined.
According to the nature of the lesion, paralysis of accommodation is divided into:
- Unilateral - paralysis develops in one eye.
- Bilateral – characterized by paresis of accommodation with pathological changes in the lens, size of the eyeball and its muscles.
Ophthalmologists also distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- Peripheral - caused by dysfunction of the ciliary ganglion.
- Central - accompanied by an inadequate reaction of the pupils and is associated with damage to the midbrain.
- Isolated – caused by damage to the central nervous system, has a central and peripheral form.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the presence of accommodation and establish its type, form and stage of development.
Treatment for paralysis of accommodation is carried out in an inpatient or outpatient setting. Throughout the course, a follow-up examination by an ophthalmologist is carried out and, if necessary, additional examination is prescribed. This is necessary for timely correction of the therapeutic course.
To treat paralysis in modern medical practice, two main methods are used:
- Conservative.
- Surgical.
Conservative therapy includes: the use of medications, ophthalmic drops to relax muscles and improve eye mobility; use of lenses with positive diopters; performing special gymnastics for the eyes.
The therapeutic method is selected individually in each case, according to the stage of development of the disease and physiological indicators.
The prognosis for paralysis of accommodation directly depends on the cause of the development of the pathology. If it is caused by intoxication of the body with medications or toxic substances, it is enough to exclude them from entering the body and vision will be restored on its own.
But when paralysis develops against the background of impaired functionality of the ciliary muscle, it can lead to a gradual decrease in visual acuity, which cannot be corrected with contact lenses.
Accommodation is the ability of an organism or organ to adapt to any conditions.
The essence of eye accommodation can be clearly explained. If you press lightly on the eyeball with your finger and after a couple of minutes open your eyes, you will notice that our vision is failing us, and we see everything as if in a fog. After a certain time, we again enter normal visual mode.
The concept of accommodation is usually used to represent disturbances in the refractive power of the optical ocular system, i.e. for a clear identification of observed objects located at different distances from a person.
The disease occurs when the connection between the nerve, muscle and lens is interrupted, resulting in a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses to the brain.
Eye accommodation is a physiological process of changing the refractive power of the eye during visual perception of objects located at different distances from it.
Two components are involved in the process of accommodation: active - contraction of the ciliary muscle and passive, due to the elasticity of the lens.
With spasm of the ciliary muscle, which is observed with uncorrectable hypermetropia and astigmatism, especially often against the background of a general weakening of the body (overwork, intoxication), accommodative asthenopia also develops, but is accompanied by an increase in refraction - a weakening of the degree of hypermetropia, the appearance of false emmetropia and false myopia. The main sign of accommodation spasm is weakening of refraction at the height of cyclopegia.
Paralysis of accommodation occurs when the parasympathetic part of the oculomotor nerve is damaged due to injury, poisoning or drug exposure.
Treatment of false myopia in schoolchildren
How is accommodation spasm in children treated? When treating false myopia in schoolchildren, an integrated approach is also used. Very often this disorder is combined with the development of true myopia. The task of a qualified doctor in this case is primarily to relieve spasm of the ciliary muscle. Ophthalmologists try not to write a new prescription for glasses if the deterioration of vision is associated with symptoms of false myopia. Only after the spasm of the ciliary muscle has been relieved and vision has improved can you get a prescription. Treatment of accommodation spasm in children and adolescents:
- drug therapy - drops are prescribed that dilate the pupil and relax the ciliary muscle;
- physiotherapeutic sessions - to improve blood supply to the visual organs, train accommodation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, electrical stimulation procedures are prescribed;
- exercises on simulators - daily training of the eye muscles, prevents the progression of myopia, relieves spasm of accommodation;
- massages, performing eye exercises.
Particular attention should be paid to the child’s posture. The health of the eyes depends on how he sits at the table while studying, since an incorrect angle of the head, tension in the cervical spine, and poor circulation can trigger the development of new pathologies.
Prognosis and prevention
Lack of timely treatment can lead to:
- persistent impairment of visual acuity, the ability of the eyes to clearly and clearly see surrounding objects into the distance;
- myopia - a persistent, long-term or not eliminated spasm ultimately leads to the development of myopia, a disruption in the process of refraction of light rays in the eye, in which a person has difficulty seeing into the distance.
But, spasm of accommodation is a reversible functional disorder and can be successfully treated. Drug therapy quickly relieves spasm of the ciliary muscle due to its forced relaxation, therefore, to achieve a lasting result, it is necessary to carry out a full range of therapeutic measures and eliminate the causes.
Preventive measures include general improvement of the body, frequent walks, a good night's rest, balanced nutrition, physical education and sports. An important point is compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards for visual work: good illumination of the workplace, correct seating and posture, sufficient distance when working with a monitor or book, regular breaks.
Prevention of false myopia
The complex of preventive measures to prevent the development of false myopia includes the most effective ways to improve the health of the body as a whole. To increase the protective functions of the body, fitness, sports, and hardening are necessary. By strengthening the muscles of the back and neck, you can solve the problem of worsening accommodation and decreased vision due to osteochondrosis. Taking vitamins will help compensate for the lack of substances necessary for eye health, and exercise will strengthen the accommodative muscle.
What is necessary to prevent the spasm of accommodation from recurring:
- taking medications with lutein and blueberry extract for increased visual stress - lutein is contained in the retina of the eye, it is not produced by the body, so you can replenish its reserves by taking capsules with this component or introducing foods rich in lutein into your diet: spinach, parsley, eggs , yellow and green vegetables and fruits;
- the use of computer programs that relieve visual strain;
- massage courses: general and cervical-collar area;
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns, physical activity.
In order not to miss the first symptoms of false myopia, you need to periodically check your visual acuity at home. Also, you should not ignore routine examinations by an ophthalmologist, especially if a spasm of accommodation occurs due to existing myopia.