Eye myopathy is provoked by a genetic factor.
There are no obvious symptoms. Classified into several types.
There are three degrees of the disease. All diagnosis depends on the medical history.
Eye myopathy is a disease manifested in the form of ptosis and a decrease in the level of motor ability of the eyeball. With the disease, there is no place for diplopia and other pupil abnormalities. If the problem is ignored, then after a while there will be atrophy of the muscles that are responsible for facial expressions and movements of the shoulder girdle.
Causes
The main factors influencing the development of the disease are physiological. They manifest themselves in the improper functioning of certain eye muscles and the shape of their chambers. Dysfunction occurs and they no longer retain the keratin they need. Gradually, their tone weakens, the tissues die.
The appearance of the disease is also influenced by factors such as:
- genetics;
- severe strain on the eyes;
- lack of vitamins leading to metabolic disorders;
- ineffective treatment of eye diseases;
- congenital pathologies of the visual organs.
Myopathy of the eye, what is it?
The factor of heredity is also of great importance, that is, if parents suffer from a similar illness, then their child will have a predisposition to its occurrence. In addition, it should be noted:
- lack of required visual hygiene;
- excessive physical activity;
- incorrect technique for correcting vision defects;
- lack of vitamins, minerals or trace elements necessary for proper metabolic metabolism in the body;
- defects in the anatomical structure of the organ of vision.
The latter can be divided into three sub-clauses:
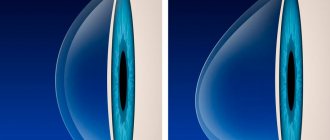
- Non-standard parameters of the eyeball. This is the most common cause of pathology. The norm for this vital element is about 25 cm, but it is not mandatory. And when it is exceeded by 5 mm or more, the shape of the eyeball is ellipsoidal, as a result of which the back wall of the eye stretches and the fundus of the eye changes.
- Imperfect layer of the cornea. The size in this case corresponds to the norm, but the optical system of the organ of vision is subject to excessive refraction. Because of this, incoming rays are refracted at the wrong angle, and the image of an object or person located in the distance is blurred.
- Combined. It combines both types described above.
When treating myopathy, each stage is especially important. After all, all of them: diagnosis, examination and direct measures to get rid of the disease play a very large role in the nature of the result obtained. That is why the patient must be managed by experienced specialists from our clinic, whose professionalism is not in doubt. Prices for the services of our clinic are presented in the price list.
You can make an appointment and ask clarifying questions to our specialists by phone in Moscow (daily from 9:00 to 21:00), using the feedback form on the website.
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna
Disease prevention
There are several preventive recommendations for myopathy:
- First of all, it is important to eliminate bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- a certain dietary food (various cereals, salads with the addition of celery, turnips, milk, liver are shown; remove spicy, fatty, salty foods from the diet);
- Regular sports activities can normalize the patient’s condition;
- get plenty of rest and don’t strain your eyes for too long;
- When working at a computer, the light should be consistently illuminated (for example, darkness, as well as bright light, has an adverse effect on vision);
- When exposed to intense sunlight, use protective glasses to avoid burning the cornea;
- The distance between the book and the eyes should be at least 30 cm, and every hour you should take a break, do some exercises, and blink a little.
If myopathy is detected in time, the outcome will be favorable. To do this, it is necessary to undergo examinations by an ophthalmologist from early childhood. When establishing myopia, correctly prescribed treatment is of great importance.
In this article we will look at what it is - eye myopathy.
This disease is a pathological visual impairment resulting from changes in the refractive functions of the visual system. If the necessary treatment is not provided, the pathological process actively progresses and can lead to severe visual impairment, and in some cases to complete blindness. Therefore, if visual functions are impaired, it is very important to contact a medical institution, where the appropriate diagnosis and required treatment of the disease will be carried out. The disease can occur in only one eye, but myopathy of both eyes is often diagnosed.
Causes
The main cause of the congenital form of the disease with impaired intracellular metabolism is genetic predisposition. The hereditary form of the disease is often called familial myopathy.
The defective gene is transmitted according to an autosomal recessive type; less often, the defective gene is transmitted according to a dominant type of inheritance (through the mother). The hereditary form of the disease can be caused by random gene mutations.
Diseases of this kind can be provoked by pathology of ion channels of muscle membranes or dysfunction of mitochondria (provoked by mutations of the mitochondrial genome).
Impaired absorption of glycogen (glycogenosis) develops in the following cases:
- Insufficient production of enzymes involved in metabolism. The acquired form is provoked by disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands (hypothyroidism, hyperaldosteronism, Cushing and Addison syndrome, acromegaly).
- May be a consequence of chronic intoxication (alcohol and drug intoxication, exposure to heavy metal salts and high levels of ionizing radiation).
- Pulmonary, hepatic and renal pathologies (uremia, renal and liver failure, electrolyte imbalance).
- Heart disease and vitamin D and E deficiency.
Classification of myopathy
Since the disease is genetic, it is divided into the following types:
- Oculopharyngeal view. In addition to decreased vision, the muscle tissue located in the pharynx is affected.
- Ocular view. It occurs in combination with non-muscular degenerative lesions. Occurs at any age, but most often after 40 years.
The disease is classified depending on its degrees:
- weak – up to 3 dioprics;
- medium - from 3 to 6 dioprics;
- pronounced - from 6 dioprics.
Myopathy
Myopathies are a heterogeneous group of muscle tissue diseases. The most severe diseases of this group are hereditary progressive muscular dystrophies (PMD), many of which lead to early disability and death. Hereditary myopathies also include congenital (congenital) muscular dystrophies, structural, metabolic and mitochondrial myopathies, which are typically not as severe as those with PMD. Of the acquired myopathies, inflammatory (polymyositis, dermatomyositis) and endocrine muscle lesions should be noted. A separate group consists of myopathies associated with the pathology of “ion channels” (myotonia, neuromyotonia, myoplegia).
Progressive muscular dystrophies (PMDs) are a heterogeneous group of inherited diseases characterized by progressive muscle weakness of varying severity and skeletal muscle atrophy. They are genetically determined diseases. Characteristically, certain muscles are affected while others nearby are spared. There is currently no definitive treatment for PMD. The main goal of treatment is to maintain muscle strength and prevent the development of contractures and joint deformities.
Congenital muscular dystrophies and structural myopathies Congenital (congenital) myopathies (account for 14% of all myopathies) are a group of genetically determined myopathies characterized by an early onset (usually from birth), a characteristic symptom complex (the “floppy child” syndrome) and a slowly progressive course. The prevalence of congenital muscular dystrophy in Europe is 4.6 cases per 100,000 population. They are observed equally often in both boys and girls. Most congenital myopathies and dystrophies are manifested by the “floppy-baby” syndrome - a term proposed in 1958 by JG Greenfield to designate congenital muscular hypotonia in children, regardless of its origin. Expressed by muscle hypotonia, weak muscle resistance, head incontinence, delayed motor development, increased joint mobility. The first symptoms may be observed in utero (weak fetal movement). Muscle weakness is usually present from birth. Children begin to hold their heads up, roll over, and sit up late. Due to muscle weakness, they cannot sit with a straight back, and kyphoscoliosis (curvature of the spine) develops.
Mitochondrial myopathies and encephalomyopathies are a group of diseases caused by genetic defects of mitochondria (cellular organelles responsible for tissue respiration). The process involves not only muscle tissue of skeletal muscles, but also other organs. Therefore, diseases are characterized by multiorgan involvement. The clinical picture may include the appearance of epileptic seizures, stroke-like episodes, sensorineural hearing loss, cardiac conduction disorders and other symptoms.
Myotonic disorders are a group of hereditary diseases manifested by delayed muscle relaxation (“channelopathies” - pathology of ion channels). The classic sign of myotonia is the “fist” symptom - the patient cannot quickly unclench a tightly clenched fist, straightens his fingers slowly and with great effort, as if in a slow motion movie. Difficulties arise, for example, when trying to quickly get up from a chair or quickly open closed eyes. The face of many patients has a characteristic expression, called “facies myotonica” (hypomimia, “mournful” expression).
Inflammatory myopathies are a heterogeneous group of acquired myopathies, accompanied by inflammatory changes in muscles, muscle weakness and atrophy. The most common are polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. The incidence is 0.2 - 0.8 per 100,000. Women get sick 2 times more often than men. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis manifest themselves as symmetrical muscle weakness and atrophy in the early stages, accompanied by myalgia (in 30-40%). If left untreated, swallowing problems and weakness of the neck, trunk and respiratory muscles may develop. Dermatomyositis develops acutely (within several weeks), polymyositis - from several weeks to several months, occurs in adults after 20 years of age and does not occur in children. Inclusion body myositis begins at age 50 and older. The disease develops gradually, sometimes patients cannot say exactly when the first signs appeared. The main complaint is instability of the knee joints, weakness and atrophy of the thigh muscles are noted, which is characterized by frequent unexpected falls.
Endocrine myopathies are secondary muscle lesions associated with disruption of the hormonal function of the endocrine glands. For example, against the background of acute thyrotoxicosis (sharp loss of body weight, tachycardia, tremor, hyperhidrosis, anxiety, tearfulness), myopathy develops in the form of rapidly increasing muscle weakness, bulbar disorders and amyotrophy (impaired muscle trophism). Myopathy due to hypothyroidism (facial puffiness, edema, dry skin, brittle nails, dull hair prone to loss, bradycardia, drowsiness) is characterized by hypertrophy of skeletal muscles and heart muscles. However, muscle strength is reduced, stiffness is noted, and “cramp syndrome” (cramps of the calf muscles) is characteristic.
Toxic myopathies are diseases of muscle tissue caused by exposure to various toxic substances on the body (drug, alcohol myopathy, etc.). Acute alcoholic myopathy develops against the background of heavy drinking and is manifested by pronounced muscle weakness, myalgia, muscle atrophy, bulbar disorders, and facial lethargy. The chronic form is characterized by a slow development of symptoms (occurs in 80% of men aged 40 to 60 years who have been drinking alcohol for 15–25 years).
Symptoms
So, now it is clear what it is - eye myopathy. To date, the symptoms of this pathological disorder have not been identified. For specialists who study this disease, only one thing is clear: the disease occurs as a result of metabolic disorders in the body that are of hereditary origin. Other assumptions regarding the principle of development of myopathy have not been confirmed. Despite the fact that the pathology is asymptomatic, the main sign of its occurrence is an intense decrease in vision. If such a symptom appears, and there are also cases of this diagnosis in family members, then the likelihood of developing pathology increases significantly.
View gallery
General information
Metabolic myopathy is a large group of hereditary, acquired diseases associated with impaired intracellular metabolism. The exchange of glycogen, lipids, enzymes and ATP is usually disrupted. These disorders are equally likely to appear at any age.
The hereditary form of the disease develops into a chronic pathological process. The danger of the pathology is associated with the likelihood of transient contractures that occur in response to the inability of the muscles to absorb glucose and lipids. Metabolic myopathy develops in approximately 5 out of 10,000 cases.
Diagnostics
As already mentioned, you cannot do without a visit to the doctor. If such a condition occurs, it is very important to determine the cause. It all starts with a survey. The doctor should receive an answer to the following questions:
- how long ago it all started;
- Do any of your relatives have the same problem?
If the appearance of the pathology is genetic, then diagnosis is easy. If not, then the process of determining an accurate diagnosis slows down significantly. First of all, diseases of the nervous system are excluded.
It is quite difficult to establish a diagnosis for large groups of myopathic syndromes that are caused by pathologies of endogenous and exogenous origin. The disease manifests itself in amyloidosis and myoglobinuria.
To determine the presence of the disease, the patient must undergo a series of examinations. These include:
- blood enzyme analysis;
- electromyography;
- muscle tissue biopsy.
It is equally important to undergo the following examinations:
- determination of visual ability using Sivtsev tables;
- establishing visual fields (perimetry);
- fundus ophthalmoscopy;
- determination of intraocular pressure (onometry);
- ultrasound examination of the pathological part of the eye;
- calculation of the optical power of the cornea (ophthalmometry);
- checking the movement of the shadow in the pupil area (skiascopy);
- obtaining data on the production and process of outflow of intraocular fluid (tonography).
Symptoms
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Impaired absorption of glycogen and glucose. With excess glycogen content in muscle cells, patients at rest remain in fairly good health. When activity increases, poor enzyme production interferes with the production of energy from carbohydrates and their derivatives (glucose, glycogen).
- Often, within a few minutes of starting physical activity, symptoms of hypotension begin to appear. If the intensity of the exercise is not reduced, muscle contractures may occur, which can lead to severe tissue damage over time.
- McArdle syndrome is characterized by severe pain and symptoms of proximal muscle wasting. Also, in some cases, muscle thickening and weakness may appear, leading to the formation of contractures over time. The latter is caused by a violation of the ability of muscles to contract. A high level of physical activity provokes the breakdown of muscle tissue with the development of myoglobinuria. With the manifestation of some symptoms of renal failure. There may be disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
- Anderson and Corey-Forbes syndrome over time leads to disruption of the liver and heart, as well as to the formation of contractures and the appearance of physical development defects in childhood, combined with moderate tissue damage.
- Maltase enzyme deficiency can manifest itself in the form of an infantile form of myopathy (the first symptoms appear from the first days of a child’s life) with symptoms of muscle hypotension. The disease gradually progresses and in most cases leads to the death of the child (often the patient does not live to see the age of two).
- The acquired form of the disease is manifested by impaired functioning of the lungs and weakness of the muscle tissue of the lower half of the body. The adult form of the disease is manifested by painful weakness of the muscles of the chest, back and shoulder girdle, as well as the muscle tissue of the lungs and lower extremities.
- Impaired absorption of lipids. Many neurological diseases are directly related to lipid deficiency. Manifestations of deficiency of some of them are limited only by deterioration of exercise tolerance.
- Insufficient production of the enzyme carnitine and CPT is the main manifestation of this disease. Carnitine deficiency syndrome manifests itself as muscle hypotonia, affecting mainly the muscles of the upper extremities, face and neck. The CPT enzyme deficiency syndrome, on the contrary, is manifested by muscle pain and cramps that appear during physical work. Typically, this type of myopathy occurs in men.
- Mitochondrial form of the disease. Affects the tissues of the upper extremities and the eyeball. The pathological process involves nervous tissue (cerebellar ataxia, epilepsy, dementia), heart muscle (cardiopathy), kidney cells (tubulopathy), liver and hearing organs. In most cases, this type of myopathy affects children and adolescents. However, this disease can manifest at any age.
Muscular hypotonia can be:
- general (affecting most muscle tissue and manifesting itself in the form of increased fatigue and poor tolerance to physical activity);
- local (has limited localization and manifests itself in the form of damage to the muscles of the limbs, face and eyes).
Mitochondrial myopathy is characterized by shortness of breath and headaches (often severe).
Selection of glasses and lenses
Incorrectly chosen glasses contribute to vision deterioration. The purpose of such correction is to normalize the focus of the image so that it falls on the retina. To correct myopia, glass that scatters light is used. When selecting glasses, the patient is seated at a certain distance from the Sivtsev table, and negative lenses are installed. If vision improvement is observed, the diagnosis is confirmed. Then the necessary lenses are selected.
A drug course of therapy is recommended for everyone who suffers from myopia, as this stops the process of its progression, and in some cases, surgical treatment of this problem is used. The following drugs are prescribed:
- ascorbic acid;
- calcium gluconate;
- medications that help normalize blood circulation in the visual structures: Picamilon, Galidor, Nihexin, Cavinton.
The article described the symptoms, degrees, causes and treatment of ocular myopathy.
Source: FB.ru
Treatment
When a diagnosis of “eye myopathy” is made at any degree, therapy is carried out using medications. They normalize metabolic processes in muscle tissue.
More often they resort to the use of vitamins E and C, the drugs Retabolil, Methylandrostenolone. In combination with them, medications are prescribed to normalize blood circulation in the tissues. For this, Trominal and Nikoverin are used.
To stabilize excitability and conductivity, a substance such as Mestinon or Galantamine is used. It is worth remembering that only a doctor who has received the full diagnostic result of this case can select a drug and determine the course of treatment. It also takes into account what concomitant pathologies there are and the characteristics of the body of a particular patient.
If myopathy is not treated, myopia will soon appear. And with her, the treatment will be different. It develops rapidly, and pathologies of the retina appear in the form of detachment, rupture, and dystrophy. There are eye hemorrhages and blindness.
In addition to the above-mentioned drugs, other methods are also used. They are prescribed to each patient individually: corrective glasses and lenses, pharmaceuticals, surgery, laser treatment and traditional methods.
Useful video
You can learn more about how to stop the disease by watching the video:
As you can see, eye myopathy can be stopped. To do this, it is enough to diagnose the pathology in time and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2029
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Myopia
Causes
1. Heredity. A scientific connection has been established between the myopia of parents and their children. If both parents have myopia, then the risk of developing this disease in their child under 18 years of age is more than 50%. When both parents have normal vision, the risk of their child developing myopia is 10%.
2. Intense visual loads to which the organs of vision are exposed. Myopia most often develops either during school or student years, precisely when the maximum load is placed on the eyes.
3. Incorrect vision correction. When selecting contact lenses or glasses for the first time, it is very important to follow all correction rules and also to exclude false myopia. To prevent the progression of myopia, you need to follow the recommendations and rules for wearing glasses and contacts, and do not forget to regularly check your vision.
It is worth noting that wearing contact lenses contributes to changes in the tissues of the ocular surface, which is often accompanied by discomfort and dry eye syndrome. A comprehensive solution will help ensure the healthy condition of the eye surface - the use of ophthalmic gel and eye drops. Eliminates the causes of discomfort with the Korneregel gel. It contains carbomer on a soft gel base, which maintains complete hydration, and dexpanthenol, which has a healing effect.
Those who experience discomfort and dryness 3 or more times a day should choose Artelak Balance drops, which combine a unique combination of hyaluronic acid and vitamin B12. Hyaluronic acid forms a film on the surface of the eye that provides long-lasting hydration. The action of hyaluronic acid prolongs the special protector. Vitamin B12 is the most powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage by free radicals.
For those who experience discomfort no more than 2-3 times a day, Artelak Splash drops are suitable, containing hyaluronic acid, which provides instant hydration.
Regardless of the symptoms, to prevent discomfort and dryness, it is good to use these eye drops in combination with a gel based on dexpanthenol.
4. Poor nutrition. Myopia can occur due to the lack of microelements and vitamins in the diet, which play a significant role in the synthesis of scleral tissue (the lining of the eye) and involved in light perception.
5. Vascular factors. If the blood supply to the eye is disrupted, then there is a high probability of developing myopia in the near future.
Symptoms
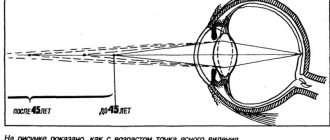
The main symptom of myopia is decreased distance vision, when all objects appear blurry and indistinct. A person, trying to improve the clarity of the picture, begins to squint. At the same time, a person with myopia sees objects located nearby clearly. In addition, symptoms of myopia include the following: headaches, visual fatigue.
Usually, the first signs of myopia appear at a fairly young age (7-12 years), after which the disease progresses in women up to 20 years, and in men up to 22 years. Then vision usually stabilizes, but may further deteriorate.
The development of myopia is not difficult to recognize. If you notice that your child often squints while looking at something, this is a good reason to seek advice from an ophthalmologist.
- Blurred vision
- Veil before my eyes
Devices
Degrees of myopia
There are three degrees of the disease:
1. Mild myopia (no more than three diopters).
2. Moderate myopia (3-6 diopters).
3. High myopia (more than six diopters).
According to the clinical course, myopia is divided into progressive and non-progressive:
Progressive myopia is a disease that requires an increase in lens power by more than 1 diopter per year. In this situation, serious complications may occur that require surgical intervention. Non-progressive myopia is a refractive error. Its clinical manifestation is decreased distance vision, which can be corrected and does not require any treatment.
Diagnosis of myopia
Only an ophthalmologist can diagnose myopia. For this purpose, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out, his visual acuity and a number of special studies are determined (ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy, fundus examination and others).
If you discover symptoms of myopia, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist, but not an optician, because it is not always possible to get advice from a specialist with a higher medical education (ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist). By going to an optician, where clients are advised by a regular optometrist (a person who has completed courses on the correct selection of glasses), you risk receiving incorrect information and harming your vision.
- Ophthalmoscopy
- Biomicroscopy
- Visometry
- Accommodation study
- Refractometry
- Skiascopy
- Tonometry
Complications of the disease
- retinal dystrophy;
- retinal detachment;
- retinal rupture;
- blindness.
Myopia treatment
Treatment of myopia is divided into several areas: correction, treatment and surgery.
1. Myopia is corrected using diverging lenses. When prescribing glasses or contact lenses, the doctor is based on the degree of myopia. If the degree is weak, glasses can not be worn all the time, but only when necessary.
2. Treatment of myopia. In childhood and adolescence, special exercises that train the ciliary muscle are recommended. In addition, special stimulating (hardware) therapy and restorative treatment are prescribed, including vitamins for vision with lutein (“Lutein Complex” for adults and “Lutein Complex for Children” for children).
Among the physiotherapeutic devices, one can highlight “Sidorenko Glasses” - a device that combines 4 methods of influence: infrasound, phonophoresis, pneumomassage and color pulse therapy. This complex effect improves blood supply to the tissues of the eye, trains the eye (ciliary) muscle, and enhances the effect of medications. The advantage of the device is that it can be used at home by patients of all age groups (both elderly people and children over 3 years old.)
3. Surgical intervention for myopia has become widespread:
To prevent the progression of myopia and the development of complications, scleroplasty is performed (strengthening the posterior wall of the eyeball).
To restore vision, laser correction (Lasik and PRK) is most often used. If it is impossible to use it, intraocular lenses are inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye.
Visual acuity in myopia can be improved by removing the lens and replacing it with an artificial one. This method is indicated for clouding of the lens (cataract) in people suffering from high myopia.
Prevention of myopia
Prevention of myopia requires an integrated approach. Ophthalmologists advise the following activities:
1. Correct vision correction.
2. Taking vitamins for vision containing lutein.
3. Compliance with the visual regime.
4. Doing exercises to train the eye muscles.
5. Physiotherapeutic and medicinal stimulation of blood circulation in the eye tissues.
Various types of myopia correction (spectacle, contact and laser), as well as laser coagulation of the retina and scleroplasty, can be performed in many eye clinics.
Comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of asthenopia can be performed in many metropolitan ophthalmological clinics. When choosing a medical institution, it is important to consider not only the cost of treatment, but also the level of specialists and the reputation of the clinic.
Lutein Complex Children's
dietary supplement
0 reviews 3
Lutein-Complex
dietary supplement
0 reviews 36
Operations
- Femto LASIK
- Epi-LASIK
- LASIK
- Super LASIK
- Scleroplasty
- Phakic IOL
Treatment of myopathies
Currently, there is no pathogenetic therapy for most myopathies, but methods of gene and cell therapy are being developed, and for myopathies associated with storage diseases, therapy is being developed to replace enzyme deficiency in the body. For some diseases, treatment is already available. These include Pompe disease.
In addition to pathogenetic treatment, symptomatic therapy is carried out. It includes various classes of drugs that enhance metabolic processes, increase muscle strength, and support the normal functioning of the nervous system, brain, heart, and digestive organs3.
Non-drug treatment includes a number of therapeutic techniques aimed at improving the quality of life and socialization. These include physical therapy, physiotherapy, psychological rehabilitation, massage, and others.
The prognosis of hereditary myopathies can be different. Timely diagnosis is extremely important.
References
- Antelava O.A., Nasonov E.L. Modern approaches to the classification criteria of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies // Scientific and practical rheumatology - 2007. - T. 45 - No. 5 - P. 41–46.
- Sparks SE, Escolar DM Congenital muscular dystrophies // Handb. Clin. Neurol. Elsevier. 2011; (101):47–79.
- Kurushina O.V., et al. Modern approach to the diagnosis and treatment of primary and secondary myopathies // Bulletin of the Volgograd State Medical University - 2021. - No. 1. -P. 16–22.
- MSD Manual Professional Version. Congenital Myopathies. 2021. URL: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/inherited-muscular-disorders/congenital-myopathies (accessed: 04/04/2019).
- Fedotov V.P., Ryzhkova O.P., et al. Miyoshi myopathy: diagnosis of a familial case of dysferlinopathy // Neuromuscular diseases - 2021. -T. 6 – No. 1.
- Zhdanova E.B., Kharlamov D.A., Belousova E.D. Somatic disorders in progressive Duchenne muscular dystrophy // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics – 2011. – T.56 – No. 5.
- ACMG Working Group on Management of Pompe Disease AWG on M. of P. et al. Pompe disease diagnosis and management guideline. // Genet. Med. Various. 2006;8(5):267–288.
- Skoromets A.A., Kazakov V.M., Rudenko D.I. Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and its connection with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. History, clinical picture, genetics and differential diagnosis. Litres. 2021.
GZEA.PD.18.09.0435b