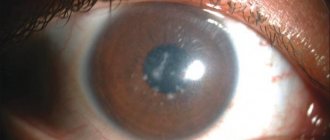
Thinning of the retina occurs as a result of trophic disorders associated with severe somatic diseases, injuries or hereditary predisposition. In this case, the patient complains of lacrimation, photophobia, distortion of the shape and color of objects, as well as the inability to distinguish small objects and read.
Visual impairment can be observed in the periphery or in the center of the visual field and is caused by areas with a thin retina and a lack of light-sensitive cells.
Risk group
The process that results in thinning of the mesh area is largely associated with age-related changes occurring in the human body. However, this does not mean that the disease is diagnosed only in elderly people. Very often, symptoms of the disease are observed in children. According to research data, women are more susceptible to the disease. A high degree of myopia, chronic types of diseases of the vascular system and diabetes mellitus are just a small list of diseases that result in the development of pathology.
Retinal thinning is an irreversible degenerative disease. The causes of thinning of the retina may be hereditary. The disease affects people who have a white skin tone and light-colored iris. Constant stress, visual strain, bad habits and an unbalanced diet increase the risk of developing the disease.
Prevention
Doctors dream that the time is not far off when parents will bring their very young children for preventive examinations and create a passport for each organ. And on the retina too. So that a person throughout his life documents the state of his body and clearly sees all the changes. We do not have such passports, but nothing prevents us from undergoing annual examinations now that we have learned about their necessity. And this will be the main step in preventing the disease.
Preventing a disease also includes eliminating those causes that contribute to its development. That is, you need to monitor your cholesterol levels, you need to quit smoking, not get carried away with alcohol, try to lead a healthy lifestyle so as not to accumulate in the body a large number of free radicals - destroyers of our cells, which also have a bad effect on the retinal epithelium. You need to eat more vegetables and fruits, take vitamins and not sit at the computer without interruption for 10 hours, that is, take care of your eyes.
Factors provoking the development of pathology
The main cause of retinal dystrophy is natural wear and tear of the organs of vision and age-related changes in the body. But this phenomenon is not at all necessary in old age; not all older people develop dystrophy of the visual organs. The risk group includes:
- those suffering from diabetes mellitus, kidney and adrenal dysfunction;
- hypertensive patients;
- patients diagnosed with high and moderate myopia - in this case, the retina overstretches, becomes thinner in certain areas and ultimately ruptures;
- people prone to vascular diseases;
- victims of severe intoxication.
It has already been proven that dystrophic changes in the retina are caused by genetic predisposition and can be inherited. For this reason, children of parents who have been diagnosed with such a pathology should especially carefully monitor the condition of their visual organs.
This is interesting: according to research, atrophic changes in the retina are more common in females with fair skin and blue irises. Moreover, the symptoms of dystrophy often begin to express themselves clearly during pregnancy in women.
Causes and risk factors
Thinning of the macula can be caused by the following diseases and pathological conditions affecting the human body:
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- renal failure;
- adrenal gland damage;
- intoxication;
- severe myopia;
- obesity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- atherosclerosis;
- frequent inflammatory lesions.
Most often, retinal dystrophy occurs in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and suffer from obesity.
Most often, the disease is found in people with fair skin and blue irises. Retinal dystrophy has a hereditary predisposition and most often occurs in patients prone to pathologies of the vascular system. People suffering from myopia or chronic inflammatory eye lesions are susceptible to damage to the macula. Pathology often occurs in women during pregnancy and childbirth, as well as in obese patients and those leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Causes
Experts divide the causes of retinal thinning into two categories: local and general. So, the following reasons fall into the general category:
- chronic hypertension;
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- eye infections;
- complications as a result of the flu;
- diseases of the renal system.
The local category includes mechanical damage to the visual organs, myopia and inflammatory diseases.
A very important nuance is that the disease is hereditary. If there is a person in the family with this diagnosis, then the rest of the family members are recommended to visit the ophthalmologist’s office as often as possible for timely diagnosis.
Subtypes of the disease
The disease is divided into two subtypes: acquired and hereditary. In the hereditary form of the disease, experts distinguish two main types:
- Pigmented - as a result of a malfunction of certain receptors, twilight vision is impaired.
- Dotted white – the disease manifests itself in childhood and has a slow development.
This disease is the most common cause of visual impairment in old age. The acquired type of disease is often associated with the aging of the body, since the development of the disease is observed only in people who have reached old age. In most cases, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of cataracts. The acquired type of disease is divided into:
- Peripheral thinning of the retina is a pathology that results in impaired quality of vision. In most cases, the occurrence of the disease is associated with trauma or inflammation of the organs of vision.
- Central retinal thinning is a process that results in the loss of central vision.
The central type of the disease has two pronounced forms:
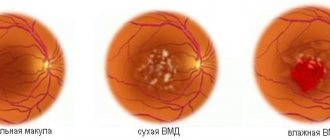
- Wet - with this form of pathology, the functioning of the vascular system of the eyeball is disrupted, as a result of which the fluid circulating in the vessels begins to accumulate under the retina.
- Dry - with this form of the disease, in the gap between the vascular system and the retina, there is an accumulation of products formed as a result of the breakdown of nutrients.
PRHD and PVHRD - what is the difference?
Dystrophies of the peripheral zones of the retina are conventionally divided into two groups:
PRHD and PVHRD.
In the first case, the pathology covers only the retina itself and the choroid. In PVCRD, trophic changes also affect the vitreous body.
The severity and prognostic risk of retinal dystrophy is also assessed by a number of other indicators. The following types of peripheral retinal dystrophy are distinguished:
Lattice dystrophy . This type of pathology is the most common. It has been noted that such retinal detachment has a high probability of inheritance. The disease is more often diagnosed in men than in women. As a rule, dystrophy affects both eyes. Localization of trophic disorders is most likely in the upper-outer quadrant of the fundus. The spatial location is equatorial or to the front of the equator of the eye. Examination of the fundus of the eye in this type of pathology gives the following picture: the degenerative areas are a series of narrow white stripes that look like fleecy lines, forming something like a lattice or rope ladder. The appearance of these stripes is due to obliterated vessels in the retinal tissue, between which reddish areas of tissue thinning are visible. It is in the areas between the stripes that there is a high probability of formation of ruptures and cysts. The overall picture may be complemented by areas with altered pigmentation (lighter or darker spots). The edges of the zones affected by dystrophic changes are connected to the vitreous body by “tractions”, which pull the retina and thereby increase the risk of ruptures.
Dystrophy of the “snail track” type . The picture visible when examining the fundus corresponds to the name of the type of pathology. Foci of retinal dystrophy are a wide strip formed by tiny points of thinning and perforation, streak-like notches and shiny inclusions. The localization of this type of dystrophy is characterized by the zone of the upper-outer quadrant. This thinning of the retina carries the risk of large, round breaks.
Frost-like dystrophy . This type of dystrophy most often occurs as a result of inheritance. Dystrophic changes in the peripheral zones are usually symmetrical in both eyes. Foci of thinning appear as large yellowish snowflakes or fragments of frost patterns protruding above the surface of the retina and localized near obliterated thickened vessels. The picture may also be complemented by areas of increased pigmentation. Frost-like dystrophy develops slowly and ends less often with ruptures and detachments than other types of pathologies.
Cobblestone pore degeneration typically affects the outermost peripheral areas of the retina. Examination of the fundus reveals free-standing rounded-elongated lesions located in the lower parts or (less often) along the entire perimeter. A large lesion may be surrounded by a scattering of small pigment spots.
Carpal (small cystic) dystrophy . Thinning areas appear as small, large and merging spots of bright red color. Their location is most often in the extreme peripheral zones. This type of dystrophy is dangerous because it leads to retinal tears from a fall, vibration, or as a result of blunt head trauma.
Retinoschisis . This type of pathology is a malformation of the retina and is usually inherited. However, cases of acquired retinoschisis are also known. Congenital diseases include retinal cysts and X-chromosomal juvenile retinoschisis. In the second case, thinning can affect not only the periphery, but also the central zones, which significantly affects visual acuity and quality of life in general. Acquired retinoschisis is typical for elderly and senile people, and can also be a consequence of high degrees of myopia.
With all types of peripheral dystrophy, pathology that extends beyond the retina and affects the vitreous body poses a particular risk. In this case, adhesions between the two structures cause tension in the already thinned retinal tissue and, under certain unfavorable conditions, lead to detachment and rupture.
Main symptoms
If a person has a thinned retina, then he experiences the following clinical signs:
Redness of the organs of vision and dryness of the mucous membrane may be symptoms of the development of pathology.
- presence of black spots before the eyes;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- headache;
- pressing sensations in the eye sockets;
- disturbance of general well-being;
- difficulty working with small objects and reading;
- inability to distinguish colors;
- sharp deterioration of vision in the dark;
- distortion of the shape of objects;
- redness and dryness of the eye mucosa.
Symptoms of retinal dystrophy
Different forms of dystrophy may exhibit different symptoms. Peripheral dystrophy can develop asymptomatically for a long time. Most often it is discovered by chance. The first symptoms of peripheral retinal dystrophy may appear when the retina is torn. These are floating “flies” in front of the eyes, flashes of light.
With chorio- and macular degeneration, patients may observe characteristic metamorphopsia (distortion of straight lines), central scotomas (loss of areas of the visual field).
Other typical symptoms include: decreased visual acuity, clouding and distortion of the visual field, changes in color vision, and impaired twilight vision.
Symptoms
Different types of the disease have their own distinct symptoms. Thus, with the peripheral form of retinal thinning, the initial stage of the disease occurs without certain pain or visual defects. The first symptoms may appear only at the stage of retina rupture. Very often, patients at this stage complain of bright flashes of light and the appearance of black spots in front of their eyes.
The wet form of the disease leads to visual distortion of the shapes of observed objects. The visual field can be significantly narrowed, which leads to the fact that some areas simply fall out of the visual field.
The risk group includes people suffering from myopia, as well as those who have vascular diseases, diabetes, hypertension
The following signs should be considered common symptoms of the disease:
- decreased visual acuity;
- difficulty navigating in a poorly lit room;
- impaired “twilight” vision;
- problems with color perception;
- the appearance of veil and cloudiness.
Thinning of the retina - what is it, how does it manifest itself?
Thinning of the retina is a complication of myopia. But this is not the only disease that ultimately provokes dystrophy. In the process of myopia, anatomical and physiological changes in the eye occur. At the same time, the eye increases in length and its membranes stretch and become thinner inside at the periphery.
Retinal thinning is not the most dangerous thing that can happen. Breaks in this area are truly an irreversible pathology that leads to the most severe ophthalmological disease - retinal detachment. Unfortunately, it is impossible to identify and cure this in the first stages. There are no symptoms in the initial period, and the patient feels well. Vision does not immediately deteriorate. When a detachment occurs, vision is lost suddenly and, often, irrevocably.
Retinal dystrophy is diagnosed not only in people suffering from myopia. There is a risk group of people who need to take care of the prevention of pathology.
What zones does the retina divide into?
The retina of the eye is divided into two main areas:
- The central zone (other names: macula, macula) is the main part of the retina, on which the quality of human vision depends by 90%. Its function is to provide subject and color perception of the surrounding world. A larger number of cones are concentrated here, which are responsible for the perception of color diversity. This is why any pathological changes cause major vision problems.
- Peripheral zone. Rods are located here - receptors that provide peripheral, spatial and twilight vision. If pathology occurs in this area, then the field of vision narrows significantly, and some areas disappear.
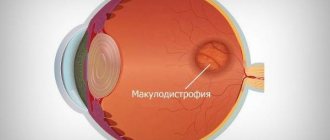
The problem of middle age
Doctors call it age-related macular degeneration. The macula is a small area of 50-100 microns in the center of the retina that provides us with central vision, allowing us to see both far and near. (In contrast to peripheral vision - the ability to see “out of the corner of the eye.”) And now one layer of the retina in this zone - the pigment layer - is damaged. The image reaches the pigment epithelium and impulses from it go to the brain, where the picture that we see is formed. If there are no intact and healthy epithelial cells, the impulse does not come from the retina, the brain does not see the picture of the outside world, and the person becomes blind.
Age-related retinal detachment is a common problem. According to WHO, it occurs in 15% of patients aged 65–74 years, in every fourth aged 75–84 years and in every third after 85 years. In Russia, 15% of the working population suffers from macular degeneration.
Treatment
The prescribed treatment is directly influenced by the degree of development of the pathology and its type. Unfortunately, in advanced cases of the disease, it is not possible to restore the original quality of vision. To treat the disease in its onset stages, medications with vasodilating properties are used. In addition, vitamin complexes and drugs that strengthen the body’s vascular system are prescribed. Very often, specialists allow the possibility of using physical treatment methods. Such techniques include:
- therapy using microwaves and ultrasound;
- laser therapy;
- influence using electrical impulses.
Today, laser therapy is one of the best measures for the prevention of diseases of the visual organs. This method is used when patients cannot undergo surgery.
The tendency to thin the retina is inherited
Endovitreal methods of treating retinal detachment
These techniques involve treating the eye from the inside. One commonly prescribed procedure of this type is a vitrectomy, which involves removing part or all of the vitreous humor. This gives the doctor access to the back wall of the eye. After this, he performs laser coagulation - soldering the detached mesh shell. The removed substance is replaced by a viscous transparent material - saline solution, gas, polymers. There are a number of contraindications to vitrectomy:
- optic nerve pathologies;
- corneal clouding;
- severe retinal diseases.
Vitrectomy is one of the most effective ways to treat detachment of the inner lining of the eye. However, even after such an operation there are complications:
- retinal hemorrhages;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- change in corneal curvature;
- repeated detachment;
- development of inflammatory processes;
- damage to the lens.
Video from our doctor on the topic
In conclusion, it is worth recalling that retinal restoration is possible and there are several medical methods for this. The prescription of a particular treatment method occurs for certain indications. These include: the degree of retinal destruction, its causes, and the patient’s physical characteristics. It is also necessary to remember that at the first signs of deterioration in visual functions, especially after an eye injury, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist as quickly as possible. Only in this case can we talk about timely treatment, which should bring good results.
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, each patient can be sure that some of the best Russian specialists will be responsible for the results of treatment. The high reputation of the clinic and thousands of grateful patients will certainly add to your confidence in the right choice. The most modern equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases and an individual approach to the problems of each patient are a guarantee of high treatment results at the Moscow Eye Clinic. We provide diagnostics and treatment for children over 4 years of age and adults.
{loadposition doc-vitamin}
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure or make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 (800) 777-38-81 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00, free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) or using the form online entries.
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna
A little history
For a long time, surgeons could not successfully invade the vitreal cavity, although the first surgical intervention on the vitreous body was performed back in 1863. In the seventies of the last century, Robert Machemer became the founder of vitreal surgery. And since then, the technique he developed has become widely used in the surgical treatment of vitreoretinal pathology.
At the Moscow MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" named after. S.N. Fedorov, V.D. Zakharov worked on the method of posterior vitrectomy. and Glinchuk Ya.I., who improved this technique and widely introduced it into clinical practice.
In 1995, Zuev A.V. proposed to perform phacoemulsification of cataract and prophylactic vitrectomy simultaneously in patients with cataracts and myopia. This combined surgery significantly reduces the risk of retinal detachment in the future.
However, it is worth mentioning that even with such intensive development of vitreoretinal surgery, it is not yet possible to completely solve the problem of treating patients with retinal detachment, since retinal reattachment can be achieved after surgical treatment only in 60-90% of cases, which is largely due to the stage of PVR. And repeated retinal detachments after posterior vitrectomy account for 14-77%.
Treatment of wet retinal thinning
In the treatment of this type of pathology, a large complex of medications is used. An ophthalmologist prescribes medications with antispasmodic effects, angioprotectors, antiplatelet agents and courses of vitamin therapy. This course of drugs is aimed at stopping the progression of the disease. Treatment of thinning of the retina with medications must be carried out at intervals of up to six months. The regularity of taking such courses directly determines whether it will be possible to stop the development of the disease. When the disease is severe or diagnosed at a late stage, specialists prescribe the following physiotherapy:
- exposure to areas of the retina using a magnet;
- stimulation of individual areas of the retina with electrical impulses;
- laser coagulation;
- photostimulation of the retina;
- irradiation of blood using a laser;
- surgical intervention.
These methods, as well as drug treatment, must be used at least twice a year. Only a competent specialist can determine the necessary treatment tactics, based on the collection of anamnesis data.
In the wet form of the disease, first of all it is necessary to carry out a laser therapy procedure to stop the formation of defective vessels. During such a micro-operation, a laser beam affects the affected areas and clogging of certain parts of the vascular system occurs. As a result of this effect, the liquid does not reach the affected areas of the vessels. This reduces the enormous risk of retinal detachment.
The laser coagulation procedure is a bloodless technique that does not cause pain. It can be carried out both in a hospital setting and on an outpatient basis. The duration of such an operation is about half an hour.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed a course of medications aimed at inhibiting the growth of the vascular system. This treatment is prescribed to stop pathological neoplasms that can cause the disease to develop in new areas.
Depending on the location of the lesion, dystrophy can be central or peripheral
Treatment of pathology
To eliminate the cause of the disease, medications are prescribed that help relieve inflammation and improve the condition of the retina.
Therapy for degenerative changes in the macula is aimed at eliminating the main cause that caused the development of the pathology. Features of pathogenetic therapy depend on the form of the disease. Drug treatment consists of prescribing angioprotectors, vasodilators, antioxidants and corticosteroids, which help reduce the severity of inflammation and improve the condition of the vascular wall of the macular arteries. For retinal edema, diuretics and biogenic stimulants are used. “Tauron” and “Emoxipin” will help strengthen trophic processes in the tissues of the eye.
Vitamin and mineral complexes with lutein and zeaxanthin will be useful. You can use photodynamic therapy and injections of substances that inhibit retinal dystrophy, which are made directly into the eyeball. If therapeutic methods are ineffective, surgical interventions with reconstruction of the vascular bed are used. If there is a threat of retinal detachment, laser coagulation of the choroid plexuses and adhesion of the macula to the underlying tissues must be done.
When the cause of dystrophy is hereditary, it is impossible to cure it.
Other symptoms of retinal detachment due to myopia
In this article
Myopia is not only changes in the fundus of the eye, it is also the thinning of the retinal pigment epithelium and the accompanying degenerative changes. Among the first changes are redistribution of pigment and blanching of the optic nerve head. Atrophy then occurs either around the disc or on one side of it.
Further changes appear on the temporal side of the disc in the shape of a crescent. The size of these changes corresponds to the area of thinning of the retina. Moreover, the progression of myopia is accompanied by further stretching of the fundus, a decrease in blood supply to the choroid and an increase in chorioretinal degeneration.
There are many types of diseases, as well as the causes of their occurrence. One of them is myopia.
Retinal detachment can occur in anyone, and patients with high myopia are at particular risk. With high myopia, a large eyeball provokes stretching of the retina and disruption of its nutrition. The latter causes a deterioration in metabolic processes in tissues and blood circulation, which causes hypoxia and retinal dystrophy.
There is peripheral and central chorioretinal dystrophy. In the most serious case, a “dry” or “wet” lesion of the macular region of the retina occurs. This significantly impairs vision and even leads to blindness. If the adverse changes in the retina are severe, the patient is diagnosed with myopic disease.
Myopic disease occurs quite rarely. As a rule, high myopia remains a harmless pathological change in refraction.
Timely preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of retinal detachment due to myopia or any other disease.
As mentioned above, the main preventive measure is laser coagulation. This is a fairly simple and not painful procedure, but if the eyes are very sensitive, pain may still occur. In this case, factors such as:
- volume of coagulation and zones of its implementation;
- model of laser equipment;
- features of the anatomy of the palpebral fissure;
- correct choice of contact lens;
- surgeon experience.
If the patient knows that the pain threshold is low or that he is uncomfortable during the procedure, it is better to warn the doctor about this in advance. The pain can be reduced with the help of special medications and then the procedure will take place without any difficulties.
Another symptom of retinal detachment is “morning improvement” - a sign in which a person, after a long period of inactivity, becomes able to see well: the veil fades or decreases. By lunchtime the patient's condition worsens, and by evening everything reaches its peak.
If the retinal tear is in the upper parts of the eye, then due to the descending fluid, retinal detachment occurs very quickly in myopia. If the gap is at the bottom, then the detachment slowly rises and occurs less rapidly, but the scars will be more pronounced, since there will be much more time for their occurrence.
To prevent retinal detachment due to myopia and other diseases of the visual organs, you need to regularly visit an ophthalmologist and carefully follow all his recommendations.
Symptoms and diagnosis
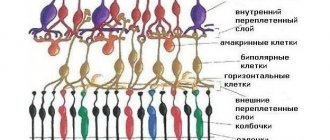
It is known that the retina covers most of the inner wall of the eye, consists of a number of zones with different functional purposes (for example, the foveal fovea in the macular “yellow spot”; the optic disc; the jagged edge devoid of photosensitive cells on the periphery) and has a multilayer structure. They include, in particular, the pigment epithelium, the ganglion layer, the outer and inner nuclear layers, etc. These layers and zones differ in the number and structure of photoreceptors, the concentration of light-sensitive pigments, and thickness - for example, the most sensitive to light and providing central vision, the foveal fossa is the thinnest zone and consists exclusively of cone cells.
It is obvious that with such a complex organization and narrow specialization of each structural element, full vision is possible only with complete coordination and normal functioning of all elements, and any disturbances in nutrition, oxygenation (oxygen supply) or, moreover, the integrity of the retina automatically become a serious ophthalmological problem that requires in immediate intensive treatment. Since the retina is the main and only receiver of the image focused by the eye optics (which must be transmitted to the optic nerve and then transmitted to the visual centers of the cerebral cortex), retinoschisis as a splitting of the receiving-transmitting tissue inevitably affects the quality of the final visual image built by the brain. Accordingly, the first and main complaint with retinoschisis is a significant deterioration in vision.
The localization of the dissection is of significant importance: dystrophic-degenerative retinoschisis, as indicated above, is more often manifested by disturbances or loss of peripheral visual fields (with probable subsequent spread to the central areas), while hereditary retinoschisis often affects the central visual field in the early stages.
With the increase in destructive changes, not only visual acuity often decreases, but also general light sensitivity: patients are increasingly less able to navigate in twilight or darkness. The progression of untreated retinoschisis leads to the most severe consequences for the eye, including retinal detachment and irreversible blindness - the risk of such an outcome accompanies almost any retinal pathology. A less common, but also quite likely complication of retinoschisis is hemophthalmos - extensive hemorrhage into the vitreous body.
To diagnose retinoschisis and differentiate it from other retinopathy, in addition to standard fundus ophthalmoscopy, visometry (precise measurement of visual acuity), perimetry (examination of visual fields), slit-lamp biomicroscopy, optical coherence tomography, electroretinography, etc. is used. A thorough study of anamnestic data is necessary. – in particular, the presence of background somatic or endocrine pathology (primarily diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis), unilateral or symmetrical nature of the lesion, age of manifestation of the disease, dynamics of progression, etc. are taken into account. If hereditary retinoschisis is suspected, a medical genetic consultation is required.
Our ophthalmology center has all the capabilities to provide high-quality and inexpensive care to patients diagnosed with retinoschisis. Retina specialists (laser and vitreoretinal surgeons) carry out diagnostics and effective treatment using modern equipment. We approach each patient individually, which allows us to achieve the best possible treatment results.
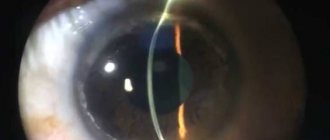
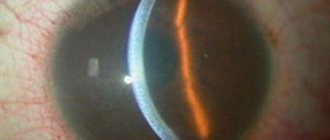
Laser coagulation
The laser treatment technique is used for almost all diseases associated with the visual organs. A huge amount of energy concentrated in a laser beam effectively affects areas affected by the disease. The concentration of laser beams in a specific area ensures that healthy areas of the retina are not affected during the operation. There are several specific laser treatment techniques and their use depends directly on the form of the disease.
One of these effects is laser stimulation of damaged areas. As a result of such intervention, in areas with thinning retina, abundant metabolic processes are activated. Exposure to laser beams has a beneficial effect and slows down the progression of the disease for many years to come.
Another example of laser surgery is the process of vascular coagulation. The essence of this effect lies in the need to separate vessels with a damaged structure from healthy ones. The laser beam affects the affected areas, where coagulants (adhesions) are formed as a result of protein breakdown. Such adhesions will protect pathological vessels from fluid penetration into them. As a result of the operation, an isolated network of the vascular system is created, through which nutrients do not circulate. This approach makes it possible to completely stop the progression of the disease, but this intervention does not protect against pathology occurring in other areas of the retina.
Laser vision correction: indications, pros and cons
Laser vision correction helps to achieve the required degree of refraction using the latest techniques.
To carry out the operation, special equipment is used, the basis of which is the action of a specialized beam on the cornea of the human eye.
Indications for use
Laser correction is performed if the following indications exist:
- farsightedness up to +6-9 D;
- myopia up to -15 D;
- astigmatism +/-6 D;
- combination of these diseases.
The question of whether the operation is advisable is decided with each patient individually during a diagnostic study. There are conditions (for example, congenital amblyopia) in which laser correction is pointless.
A dangerous symptom that requires immediate contact with a pediatrician is red circles under the eyes of a child.
A modern method of complete vision restoration
Find out what to do if a red spot appears under your eye here.
Contraindications
It is prohibited to perform laser vision correction on patients suffering from:
- tuberculosis;
- diabetes;
- tumor diseases of various origins;
- infectious conditions.
First, stabilization is carried out in a general medical institution, and then a decision is made about the possibility of surgery.
Contraindications also include:
- children's age (up to 18 years);
- old age (after 50 – 55 years);
- thinned cornea;
- wearing a pacemaker;
- serious refractive errors;
- some acute and chronic eye diseases (glaucoma, blepharitis, etc.);
- unstable visual conditions;
- high degrees of dry eye;
- disorders in the structure of the cornea and retina.
Not all contraindications are absolute. In some cases, surgery may be performed after treatment has been prescribed.
The article is for informational purposes only. To determine the need for laser vision correction and contraindications to it, you must consult a specialist.
When it is important to quickly start therapy - causes and treatment of retinal hemorrhage.
PRK
A proven antihistamine for topical use is Cromohexal allergy eye drops.
Laser vision correction methods
Depending on the degree of refractive changes and the individual characteristics of the patients, the appropriate method is selected.
Lasik is one of the most modern laser vision correction technologies.
Peculiarities:
- high security;
- no pain;
- used for patients with normal corneal thickness;
- more preferable for correcting myopia.
Super Lasik - the intervention is performed using the latest equipment, taking into account the peculiarities of the individual structure of the eye.
Modern operating unit
Femto Lasik - involves the use of a special femto beam.
Peculiarities:
- suitable for patients with thin corneas;
- used in cases of high myopia;
- allows you to calculate the individual size of the corneal flap;
- characterized by minimal risks (hemorrhage, infection, etc.).
FemtoSuper Lasik – combines the advantages of Femto Lasik and the use of individual eye parameters.
Presby Lasik – suitable for operations associated with age-related changes in visual function.
Epi-Lasik - used in rare cases of thinning of the corneal layer.
PRK is considered an outdated method of laser vision correction. It is used only if it is impossible to provide assistance to the patient using other means. It is characterized by increased pain and a long healing period.
Laser vision correction is only possible in a specialized clinic with multifunctional modern equipment. Visiting a medical institution that does not have a medical license to operate is fraught with serious health consequences.
In what cases is the use of Xalac eye drops indicated? Find out here.
Technologies differ in the degree of interference in the natural structure of the visual organ
An effective antiglaucoma drug is Xalatan eye drops.
Features of the operation
Each method of laser vision correction has its own distinctive features. There are also common features associated with the technological sequence of the process. Operations take place in several stages^
- Separation of the corneal flap (using a cutting instrument or beam).
- The flap is pulled back. The laser acts on the cornea until the necessary parameters are acquired.
- The flap is returned in place to heal.
The features of this type of operation are:
- bloodlessness;
- contactless;
- Vision correction occurs thanks to a laser beam through short flashes of light.
During the operation, local anesthesia is used, but unpleasant sensations may occur: burning or stinging in the eyes.
A neoplasm that is not life-threatening, but interferes with life, is xanthelasma of the eyelids.
The presence of a pacemaker is a direct contraindication
A disease that prevents vision at dusk and in low light is night blindness.
Advantages of the method
The undoubted advantages of laser vision correction include:
- safety of conduct (minimal risks);
- used for any visual impairment;
- large age interval;
- high speed of the process (10-15 minutes per eye);
- no need for inpatient monitoring;
- rapid restoration of visual function (the patient begins to see almost immediately after surgery);
- achieving stable results;
- fast rehabilitation.
The achieved visual acuity does not change. A decrease in the level of refraction at subsequent stages is associated only with the occurrence of age-related deviations.
LASIK technique (at the Fedorov clinic)
Complete control over increased intraocular pressure - L OPTIC eye drops.
Minuses
The disadvantages of the non-contact method of vision correction include:
- thinning of the corneal layer, which practically eliminates the possibility of repeating the operation;
- sometimes the eyes begin to adapt poorly to darkness and bright lighting;
- risk of pupil displacement;
- risk of subconjunctival hemorrhage;
- high price.
The price depends on:
- the clinic and the equipment used in it;
- method of performing the operation;
- degree of complexity of the intervention.
Usually the simplest operation costs around 20 – 25 thousand rubles. for 1 eye. The cost can reach 40 – 55 thousand rubles. for difficult cases. After the intervention, you will need to purchase sunglasses and medications for rehabilitation.
It is worth understanding that surgical intervention in the eye structure has a larger list of disadvantages. This is due to the establishment of contact between the patient and the medical instrument.
After surgery, you must strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. The examination is carried out on day 2 after the intervention. Next - in a month.
Surgery to reduce intraocular pressure - laser iridectomy.
The patient regains 100% vision the very next day after surgery
Restrictions
Restrictions apply to the postoperative period (2-3 weeks). At this time it is prohibited:
- engage in vigorous physical activity;
- visit the sauna and swimming pool;
- lose your eyes.
You should limit your time in front of the TV and computer. During the year, it is necessary to avoid eye trauma. There are no subsequent restrictions.
Good vision = high quality of life!
Pros and cons: patient reviews
Laser vision correction is the optimal method of intervention in the structure of the eye to correct refractive changes. It eliminates many risks and does not have the disadvantages of a surgical procedure.
There are some patients for whom this operation is contraindicated. There are few of them, but in some cases you have to refrain from laser correction.
Reviews from patients agree that the operation is painless and proceeds quite easily. Still, there are some cases in which the desired result is not achieved or is not achieved the first time:
- Georgy, 35 years old, Volgograd: “Last year I had Lasik done. A couple of hours after the operation, the eye began to see. A week later I discovered the smallest details in the world around me. I didn't have any problems after the intervention. The main thing is to follow all the recommendations - do gymnastics, use drops and sunglasses.”
- Svetlana, 40 years old, Tver: “Several years ago I had laser vision correction. According to the forecast, vision should have reached almost one, but this did not happen. I literally got a couple of diopters plus. A year later I had to make additional corrections. Now the numbers remain at the same level.”
Visimetry
Laser vision correction is a modern procedure for restoring refraction. As with any intervention, there are a number of contraindications and possible risks. At the moment, this method of intervention is the most effective and safe.
Surgical methods
Surgery may be required for severe retinal thinning. When the disease is in an advanced stage, treatment with medications and laser therapy does not bring a positive result. There are several types of surgical interventions, which can be divided into two conditional subgroups:
- Revascularization surgery is an intervention, as a result of which the surgeon removes abnormal neoplasms, and the vascular system, which has a normal structure, is opened;
- Vaso-reconstructive surgery - during such an operation, the surgeon installs special implants in order to normalize the microvascular bed of the eyeball.
Any surgical intervention should be carried out in a hospital, by specialists with extensive experience in such operations.
Typically, retinal thinning is caused by changes in the vascular system of the eyeball.
Technical progress in intravitreal surgery
Technical progress has become an integral part of modern vitreoretinal surgery. Today, tamponing materials such as silicone oil (SO), perfluoroorganic compounds (PFOS), and gases that remain in the vitreal cavity for a long time are widely used. Lighting systems (MIS and others) are used, with which the surgeon no longer needs to hold the light guide. Thus, it became possible to use bimanual manipulation techniques. Today, there are innovative vitreotomes with a high cutting frequency (up to 6000 per minute), which remove the vitreous body without tension on the retina. Technologies are used to reduce the size of sclerotomies, making it unnecessary to put sutures on them at the end of the operation. The diameter of the instruments has been significantly reduced, which reduces tissue trauma, removes the traction component and makes it possible to deal with thin structures adjacent to the retina.
Modern contrast techniques also provide invaluable assistance in removing the cortical layers of the CT. They greatly improve the visualization of transparent structures. For this purpose, it is customary to use a variety of dyes: membrane blue, trypan blue, fluorescein, Vitreocontrast, etc. Vitreocontrast particles, for example, have a high specific gravity, and its suspension does not shake when deposited on the posterior hyaloid CT, which distinguishes the drug from other solutions used for intravitreal manipulations.
Diagnostics
You can suspect that the retina is discharged and the number of light-sensitive cells on it has decreased if the patient has a clinical picture characteristic of this disease. To confirm the diagnosis, an ophthalmoscopic examination of the fundus is performed. To better identify structural abnormalities of the macula, the pupil can be pre-dilated. An ultrasound examination of the eyeball and its optical tomography are also performed. To identify abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels, angiography is performed, where an abnormal arrangement of blood vessels is detected, which means the wet form of macular degeneration. You can measure intraocular pressure and study the visual fields. It is also necessary to undergo a general and biochemical blood test.
A course of vitamins for thinning of the retina
When a patient is diagnosed with the initial stage of thinning of the retina, an ophthalmologist may prescribe a course of vitamins. Vitamins of groups “A”, “B” and “E” have the ability to normalize visual processes, improve blood circulation and nutrients in the body. This vitamin group improves the nutritional processes of eye tissues, and with a long course, stops the progression of the disease.
Vitamins from these groups should be taken in three specific forms:
- The first form is special vitamin complexes that come in tablet or injection form.
- The second form is vitamin supplements.
- The third form is food products containing the listed groups of vitamins.
These foods include leafy vegetables, cereals, fresh berries and fruits. These products are vital for people at risk to take. A properly balanced diet is the key to health and longevity of the whole body. Facebook
What is the retina
My example will probably be somewhat culinary, but I think this is a very suitable analogy. Let's say you decide to make jelly. To do this, you will need a deep round bowl - a mold, cling film, it is usually used to make it easier to remove the jelly from the mold and, accordingly, the jelly itself in a liquid state. This example is purely schematic, but the following can be understood from it. The eyeball resembles a cup in our example, that is, the inner part of the sclera, which figuratively “holds” our eye, the cling film is the same retina - just as thin, but very fragile, and the jelly is the vitreous body, which really resembles jelly or jelly and, in turn, makes our eye elastic.
So, if the film is slightly torn in some place, then the uncured jelly will begin to leak under the film. In cooking this is an aesthetic defect, but in ophthalmology it is catastrophic. Why? Gradually, through the existing gap, liquid will leak under the rest of the film, that is, the retina, peeling it off from the choroid ( retinal vessels ). Gradually this whole process leads to blindness.