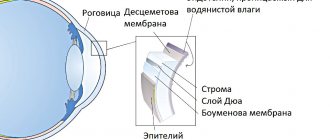
Marginal pellucid corneal dystrophy is a fairly rare degenerative disease that usually begins at a young age. It is characterized by bilateral eye damage and is accompanied by a characteristic thinning of the corneal tissue, with its protrusion and irregularity in the lower peripheral part.
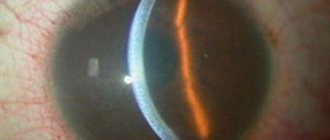
Appearance of pellucid dystrophy at the slit lamp
Signs of the disease
The incidence of marginal pellucid degeneration is sporadic (i.e., extremely rare). The dystrophy appears as a “ribbon” of thinned tissue approximately 1-2 mm wide, located along the lower edge of the cornea, which is separated from the limbus by a strip of normal corneal tissue.
Its symptoms include a gradual but steady decrease in vision that occurs at a young age. In subsequent stages, the disease manifests itself as acute loss of vision and may be accompanied by pain. The pain occurs due to the development of hydrops of the cornea. Patients have a high degree of irregular reverse astigmatism.
Corneal dystrophy. Treatment with conservative methods
Help at this stage is aimed at slowing down the development of pathology when it has not led to a decrease in vision and the appearance of clear other parameters. In general, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- drops with vitamins, ointments and keratoprotectors to protect the cornea (Taufon, Actovegin, Emoxipin);
- decongestants (glucose, glycerin);
- vitamins for the organs of vision (lutein, zeoxanthin).
If the swelling is already approaching the epithelium, additional antibacterial ointments and drops are prescribed. To reduce symptoms and additionally protect nerve endings and relieve pain, wearing therapeutic lenses may be prescribed. At the initial stage, good results are achieved by physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, laser stimulation), which in later stages provides only temporary relief.
Conservative treatment is prescribed in courses and is carried out continuously until the need for surgical intervention (before starting it, we recommend that you consult an ophthalmologist).
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, basic ophthalmological studies are prescribed, including biomicroscopy and computer topography of the cornea and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Narrow slit biomicroscopy reveals an area of 2 mm thinning of the corneal tissue of the inferior limbus. Above the “ribbon” of the greatest thinning of the corneal tissue characteristic of the disease is the zone of corneal protrusion. Fleischer's ring and Vogt's striae are absent. Acute hydrops of the cornea (hydrops) occurs extremely rarely.
In pellucid marginal degeneration, computer topography reveals significant irregular steepening of the cornea in the nasal and temporal region. In addition, the cornea has a characteristic protrusion zone that curves around its central part, and there is also a protrusion of the cornea in the limbus area.
Keratotopogram for various diseases of the cornea
Differential diagnosis of the disease is carried out with keratoconus, which is characterized by lower central thinning of the cornea. Moreover, the area of maximum thinning of the corneal tissue in keratoconus occurs in the area of greatest protrusion of the cornea. Depending on the stage of the disease, Fleischer's ring and Vogt's striae are detected.
Symptoms of Fuchs' dystrophy
Endothelial corneal dystrophy can clinically occur either latently or with severe symptoms. At the beginning of the development of the pathology, patients note deterioration, blurred vision, mild photophobia, especially after a night's sleep, halos around the light source, by the evening the condition of the eyes returns to normal. This is due to the fact that when the eyelids are closed, the evaporation of moisture from the surface of the outer shell of the visual organ does not occur and the liquid collects in an excessive volume in the cornea.
In the daytime, due to the evaporation of fluid, the swelling subsides and vision becomes better. With a long course of the disease, vision remains permanently reduced. There is also a feeling of sand in the eyes, and blindness when looking at the light. If the epithelium is involved in the process and bullae (bubbles) are formed, pain, a feeling of a foreign body, severe photophobia and increased sensitivity to glare occur.
Symptomatically, Fuchs' dystrophy manifests itself differently in everyone; only an experienced doctor can make an accurate diagnosis based on examination and the indications of the examination.
Treatment
For mild and moderate severity of pellucid marginal degeneration, its correction is prescribed by wearing hard contact lenses - primarily scleral ones, which can be selected in our contact correction department.
In our clinic, we also perform implantation of intrastromal corneal segments (IRS), which also provide high vision and are comfortable for the patient.
In advanced stages of the disease, a layer-by-layer or penetrating keratoplasty operation with a large diameter and downward displacement can be performed. Sometimes semilunar lamellar keratoplasty is performed.
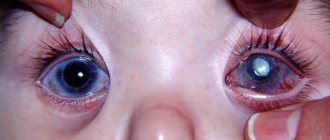
This is what the eye looks like after installation of intrastromal corneal segments (IRS)
ethnoscience
The use of folk remedies cannot act as an independent form of treatment, however, some tips are effective and can reduce the manifestation of symptoms. They can be used as additional therapy measures:
- The first is taking propolis, which must be consumed after every meal. The product can be found in pharmacies; it fights pain well;
- Second, you need to make an ointment from honey and royal jelly. To do this, you need to mix the listed components and dilute them with half a glass of warm water. The resulting gruel should be mixed well, allowed to brew, and then placed behind the eyelid.
Forecast
In the initial stages, in most patients, correction with hard contact lenses is considered as an option, because... it gives a good optical result.
In the advanced stage, it is quite difficult to achieve adequate lens fit, which is why the installation of intrastromal corneal segments (semi-rings) is becoming increasingly popular.
Good results are achieved by penetrating or layered keratoplasty, although due to the localization of pathology in the peripheral parts of the cornea, the success rate of the operation is somewhat lower than with keratoconus.
Contact our ophthalmology clinic, which specializes in the treatment of corneal diseases - preserve and improve your vision. We successfully help even in the most difficult cases!
Secondary eye dystrophies
Corneal dystrophies
Band-shaped corneal dystrophy
Initially, at the limbus at 3 and 9 o'clock, small-spotted superficial opacities of the cornea appear, limited in height by the open palpebral fissure. The pathology develops in eyes that are blind or visually impaired after severe illnesses, such as glaucoma, or injuries. It is also typical for children suffering from Still's disease for a long time (recurrent iridocyclitis, cataracts, polyarthritis).
As the dystrophic process increases, they become coarser and slowly but steadily move towards the center of the cornea. Eventually, when they close together, the opacities can form a continuous horizontal band. Calcareous salts are gradually deposited into its tissue, as a result of which it becomes dry and rough. If salt deposits begin to injure the mucous membrane of the eyelids, they must be removed. For indications, including cosmetic ones, altered areas of the cornea can be removed surgically. The resulting defect quickly epithelializes, because opacities are located no deeper than the level of Bowman's plate of the cornea.
Epithelial endothelial dystrophy of the cornea
In terms of clinical manifestations, this form of pathology is very similar to the primary genetically determined corneal dystrophy described above. However, in contrast, it is always a complication of either abdominal surgery on the eyeball (for example, cataract extraction with implantation of an anterior chamber or pupillary intraocular lens), or trauma of mechanical or burn origin. Initially, swelling occurs in a limited area - where a defect in the cells of the posterior corneal epithelium has occurred. Gradually, edematous fluid (aqueous humor) permeates all its layers in this zone, including the anterior epithelium. Bullous changes in the latter will lead to pain, photophobia with blepharospasm and lacrimation. If the healing process of the defect in the layer of the posterior epithelium of the cornea proceeds normally, then its swelling may disappear. Otherwise, it becomes more pronounced and spreads to neighboring areas.
Conservative therapy is the same as for primary edematous corneal dystrophy. In cases where swelling is induced by injury to the posterior surface of the cornea by the supporting element of the intraocular lens, surgical intervention is indicated to fix it to the iris or even remove the lens. In severe cases, with dense and widespread opacification of the cornea, subtotal penetrating keratoplasty is used.
Marginal corneal dystrophy
A rare form of pathology that slowly develops in both eyes at once. Due to thinning of the corneas, crescent-shaped defects are formed at the limbus. There are no signs of inflammation. Drug therapy is ineffective. In cases where tissue defects become deep, partial (marginal) lamellar keratoplasty is indicated.
Lens dystrophy
In this case we are talking about cataracts of post-traumatic origin - wound, contusion, burn and radiation. Each of them has its own characteristics. For example, wound cataract is always associated with macrodamage to at least the anterior, and in other cases, the posterior capsule of the lens. At the same time, its actively swelling substance can sometimes exit into the anterior chamber of the eye, causing an increase in intraocular pressure. It is also not uncommon for posterior synechiae to quickly form in the area of damage to the anterior capsule of the lens, which isolate its rupture, and therefore it becomes cloudy in such cases without signs of swelling.
Cataracts of burn origin (thermal or chemical) do not have any special clinical features. They develop with severe damage to the tissues of the eye. Usually, their removal is part of the combined intervention indicated for the victim.
Radiation cataracts are rare. Their full forms cannot be distinguished from cataracts of other origins. In other cases, i.e. with milder degrees of radiation damage, a cloudiness appears in the posterior cortex of the lens, which in transmitted light looks like a disk, less often - a ring or donut.
Retinal dystrophies
Secondary dystrophies include macular atrophy of the retina of traumatic origin, first described by Haab (Haab O., 1888). It is characterized by the appearance in the specified area of the fundus of small white atrophic foci and large lumps of pigment. It has been established that this pathology is a consequence of the unfavorable outcome of contusional retinal opacification.
Optic nerve dystrophy
The nosological structure of this form of pathology is represented by atrophies of the optic nerve head of post-neuritic, post-congestive and toxic origin.
Prices for treatment of pellucid corneal degeneration in Moscow
In our ophthalmology center we use various surgical techniques for diseases of the cornea (material for transplantation is included in the cost of operations) and correction with scleral lenses:
- Selection and production of scleral lenses (1 piece) - from RUB 30,000.
- Implantation of corneal segments (IRS) - 100,000 - 130,000 rubles.
- Anterior layered keratoplasty (DALK) - from RUB 300,000.
- Penetrating corneal keratoplasty (PKP) - from RUB 300,000.
The material was prepared by an ophthalmologist: Sagonenko Dmitry Alekseevich
You can ask clarifying questions and make an appointment at our clinic online or by phone in Moscow: Diagnosis and surgical treatment of keratoconus Selection of hard scleral contact lenses.
Classification of the disease
Based on the clinical manifestations of the defect and the affected layer of the cornea, dystrophy is usually classified. Band-shaped - affects the outer layer and the anterior membrane. This type of illness manifests itself after severe injuries or serious inflammatory processes. A predisposition to the development of a defect is low mobility of the eyeball, disruptions in microcirculation and nutrition of the organ, and oxygen deficiency.
A feature of the disease is its effect on the membrane of the cornea - it becomes somewhat rough. This occurs due to the deposition of salts on its surface. The consequence of this is drying of the epithelial layer and its detachment, which causes pain.
Stromal - the peripheral area of the cornea is affected, its significant thinning is observed. Grooves appear along the edges of the cornea. As a result, the cornea begins to lose its spherical shape, and its functions weaken. This type of dystrophy is more common among men.
“Kissing birds syndrome” is typical for young people, characterized by rapid deterioration of vision, which is accompanied by severe pain. Dropsy often forms on the cornea, leading to clouding and failure of function. Ophthalmologists believe that the defect develops against the background of autoimmune failures. The type of dystrophy is characterized by the formation of multiple erosions, which can go away on their own over time and then form again.