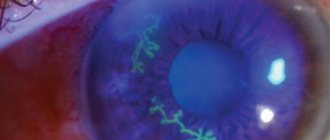
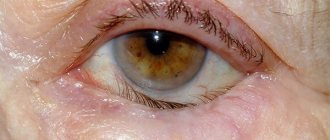
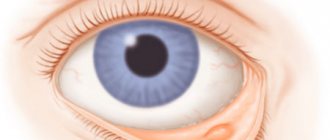
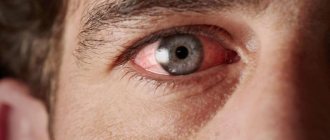
Temporal (giant cell) arteritis is a chronic inflammatory process that occurs as a result of a malfunction of one’s own immune system, affecting various arteries. Another name for this disease is Horton's disease. It received this name thanks to the doctor who described the pathology in detail.
The exact cause of temporal arteritis is currently unknown. But there is an opinion that its appearance is facilitated by the aging of the body. The fact is that with age, the walls of the temporal and ophthalmic arteries and veins become less elastic, which is why immune inflammation occurs. Since this disease affects the visual system, in rare cases, lack of treatment can cause complete blindness.
Also, according to some experts, Horton's disease has some genetic predisposition. Most often women are susceptible to it.
The disease has two forms - primary and secondary. In primary temporal arteritis, it occurs independently. This form develops due to age-related changes, usually in people over 50-60 years old. The secondary form indicates the occurrence of another disease, which is a catalyst for inflammation. Most often this concerns infectious diseases in a severe stage. The most dangerous among such infections are Staphylococcus aureus and the hepatitis virus.
Causes
Horton's syndrome is a rheumatic disease that has a very negative effect on the human immune system. Why this happens has not been studied. Most likely, the occurrence of the disease is associated with infectious processes in the body that were caused by viruses or bacteria, for example, rubella, chickenpox, pneumonia, hepatitis or influenza. In approximately 1/3 of those with this disease, a hepatitis marker and antibodies to it are detected in a blood test; in addition, this antigen is located precisely in the walls of the affected arteries. Also, another cause of temporal arteritis may be a genetic predisposition to this disease. People with HLA-DR4 proteins, which are localized in white blood cells, are most susceptible to this pathology.
Polymyalgia has been noted to be a comorbidity of temporal arteritis. It is also a pathology of a rheumatic nature.
Etiology of the disease
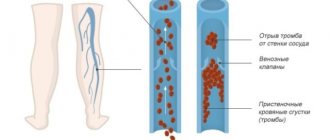
When Horton's syndrome occurs, the walls of blood vessels are damaged, inflammation and swelling appear, and their patency deteriorates. Blood, oxygen and essential nutrients begin to flow insufficiently. Late detection of the disease and lack of treatment threatens the formation of blood clots that can completely clog the vessel. A dangerous consequence is the development of an aneurysm - thickening of the vessel wall with subsequent possible rupture.
The exact causes of the malaise remain unknown. A common theory is the influence of the age of the patients. In old age, the walls of veins and arteries lose elasticity, which provokes inflammation. It has also been proven that representatives of the weaker sex are most often susceptible to the disease, especially if women have hormonal pathologies.
According to another version, inflammation has an infectious basis, in particular, it is influenced by the presence of hepatitis, influenza and herpes viruses in the blood of patients.
The opinion of some experts is inclined towards the genetic theory of the development of arteritis, according to which the disease depends on race. It has been proven that representatives of the white race are at risk.
Types of giant cell temporal arteritis:
- Based on the reasons of origin, primary and secondary forms of arteritis are distinguished. The primary form – vasculitis – develops as an independent disease in old age, the secondary – manifests itself against the background of the development of infections, among which the most dangerous are Staphylococcus aureus and the hepatitis virus.
- According to the nature of inflammation: specific, nonspecific.
- According to development - purulent, productive, necrotic.
- By location – local or widespread.
Symptoms
The symptoms of temporal arteritis depend on the stage of human vascular damage; they differ slightly from each other, but there are also those that are characteristic of all stages.
Often, a recent respiratory illness can be seen in the medical history. The symptoms are as follows:
- Headache. Its localization is mainly in the temporal region, but can also be felt in the parieto-occipital region. The pain is very similar to a migraine. Often, pain is present only on one side. Intensifies with pressure, chewing, turning the head or coughing.
- You feel tension and fatigue in your masticatory muscles. It may be that the patient cannot eat food during painful attacks.
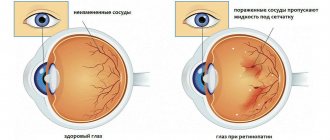
- If the optic nerve and ocular vessels are damaged, vision deterioration may occur. Characterized by sudden loss of vision in only one eye.
- Pain in the eyes when looking up, down, right or left.
- Increased fatigue.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile level.
- Loss of appetite and severe weight loss.
- Sudden jumps in blood pressure.
- The scalp in the hair area becomes thinner, which can cause pain when touched.
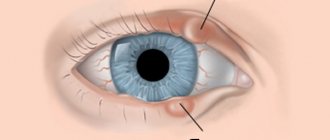
- Externally, you can notice a strong swelling of the temporal artery.
Diagnostics
If you suspect temporal arteritis, you should consult a rheumatologist or neurologist.
To diagnose and make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must:
- Palpation of the temporal region. A bulging and strongly pulsating artery is palpated, the patient feels pain, and nodules are palpated along the entire vessel.
- General and biochemical blood test. The blood will immediately show whether there is an inflammatory process. The main indicators are ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), CRP (C reactive protein).
- Biopsy of the temporal artery to identify changes in the walls.
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist, fundus examination.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of blood vessels, viewing the walls of the arteries and their changes that lead to a narrowing of the lumen.
Treatment
When temporal arteritis is confirmed, there are two treatment methods: surgery or drug treatment, which only helps to relieve the disease.
In drug treatment, drugs of the glucocorticosteroid group are prescribed. These are hormonal drugs, and the dosages are quite significant. The most common prescribed drug is Prednisolone, and there are many analogues. The dosage of Prednisolone must be prescribed by a doctor individually for each patient. The dosage depends on the picture of the disease, both normal and high are possible.
In the acute stage of the pathology, Prednisolone is often administered intramuscularly or intravenously. As soon as the acute attack is over, you can return to taking the medicine in tablet form.
The duration of drug therapy is also prescribed by the doctor, usually the treatment period is 14 days. When taking glucocorticosteroids, constant monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels is required.
If Prednisolone is prescribed for a very long period, then in parallel the doctor prescribes drugs that maintain the level of potassium in the patient’s blood.
A special diet must be prepared. This is done in order to prevent the occurrence of hypokalemia. Another mandatory drug, methandrostenolone, is introduced, its main goal is to avoid the occurrence of catabolism and osteoporosis. Contraindications for the use of Prednisolone are:
- Individual intolerance to the components;
- Frequent increases in blood pressure;
- Diabetes;
- Acute endocarditis;
- Nephritis;
- Stomach ulcer;
- Psychoses;
- Postoperative period;
- Active form of tuberculosis.
To prevent the formation of blood clots in the patient, heparin drugs are prescribed.
The dosage and method of administration are prescribed by the doctor individually for each patient. Anticoagulants are strictly prohibited if the patient has hemorrhagic diathesis and other diseases that initiate weak blood clotting. Contraindications for heparin:
- Increased vascular permeability;
- Severe disorders of the kidneys and liver;
- Anemia;
- Venous gangrene;
- Leukemia;
- Endocarditis;
- Bleeding;
- Aneurysm.
If the course of temporal arteritis is very severe, then the doctor may decide in favor of surgical intervention. This operation is called angioprosthetics. Represents the elimination of affected areas in the venous bed. The decision to perform surgery is made if there are complications of temporal arteritis.
The period of drug therapy with a confirmed diagnosis can be quite long. Usually it is from ten to twelve months, and sometimes much longer.
There are also traditional methods of treatment for temporal arteritis, but do not forget that this is a very serious disease.
Folk remedies are not ways to completely get rid of the disease, but will only help alleviate the condition. Herbal decoctions that help reduce headaches:
- Maryin root.
- Siberian elderberry flowers.
- St. John's wort.
- Peppermint.
- Coltsfoot.
- Common wormwood.
- Common oregano.
- Red clover.
- Valerian root.
- Dill seeds.
There are also various folk methods:
- Cut a small leaf of indoor aloe lengthwise to create two halves. Lie down in a dark room and apply the cut to the temporal area, remain in this position for about 30 minutes.
- Lubricate the temporal and frontal area with garlic juice.
- Add a few cloves of garlic to the milk and bring to a boil. Wait a little time to brew and cool until warm. Place 5-10 drops of the decoction into each ear canal, then tilt your head so that all the liquid drains out.
- Wrap slices of raw potatoes in gauze and apply to the temporal and frontal areas.
- Cool the boiled potatoes in their jackets a little and apply warm to the temporal and frontal areas.
- Relaxation, a state of complete peace and meditation.
- Raw potato juice should be drunk immediately after cooking.
- Eating potatoes throughout the day. It is necessary to boil one kilogram of potatoes, peeling them and without adding salt. Then, eat one potato at a time all day, dipping it in sugar.
- Lie down with your eyes closed or fall asleep.
You shouldn’t expect the impossible from folk methods. They will not be able to completely get rid of the disease, but will only relieve pain. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor so that he can prescribe the necessary treatment.
{banner_horizontalnyy3}
Temporal Arteritis
Temporal Arteritis or Horton's Syndrome (disease) refers to a rare group of diseases that occur as a result of a serious disruption of the arterial system. This disease most often occurs in old age.
Symptoms may indicate cerebral ischemia, but the main processes here are associated specifically with atherosclerosis. Conservative methods do not always help to cope with pathology. In this case, it is necessary to replace the affected vessels with prosthetics.
The photo is presented below.
Giant cell arteritis
Description
Temporal Arteritis causes damage to the arteries at the level of the aorta, and not in the temples, as the name of the disease might suggest. In this case, internal organs and arteries are affected; small vessels do not participate in the curling.
In 90% of cases, it is noted that the main reason why the disease manifests itself is inflammation. Foci of lesions may appear in the vessels due to the accumulation of plasma cells or lymphocytes in them. As a result, large cells appear there, consisting of many nuclei.
The walls of blood vessels and arteries become inflamed and swell, and swelling appears. This prevents blood and nutrients from reaching the brain fully. Since the blood velocity is also reduced with signs of giant cell temporal arteritis, fibrin and platelets are deposited in the vessels.
A blood clot may completely cut off the blood supply to the brain.
How the disease will develop in the future, and what symptoms of temporal arteritis will appear, depends on the speed with which blood clots form in the vessels, as well as the effectiveness of the method of eliminating them.
If the diagnosis is not made in time and the doctor does not prescribe the correct treatment, the following consequences may arise from giant cell arteritis with polymyalgia rheumatica:
An aneurysm will form, which will continue to develop as blood pressure rises, which can lead to a heart attack.
Causes
Until now, doctors are not clear on the exact reasons why giant cell arteritis can occur. But they argue that, undoubtedly, the root causes are changes in the human body, including blood vessels, that occur with age. This also includes hormonal changes. Currently, there are the following theories of the manifestation of the disease:
- Infectious . Acute and unpleasant symptoms occur after an infectious disease. A large number of antigens appear in the patient’s blood.
- Hereditary . When considering each case, doctors came to the conclusion that family ties also influence the appearance. This theory is supported by the fact that temporal arteritis often occurs in twins. This theory is also confirmed by statistics. There is some evidence that indicates that in some places around the world this disease is too common among the population.
- Autoimmune . This disease is related to collagenosis, as they have common symptoms and treatment methods.
Forms
Temporal arteritis or Horton's disease is divided into the following types:
In the first case, the manifestation of the disease is associated with the person’s age and it appears on its own. The second case is special in that the patient’s body has some other pathology, due to which arteritis develops. These are usually infectious diseases.
Symptoms
Symptoms are often determined by the narrowing of a certain part of the blood vessels. In this case, the patient feels pain in the muscles and joints. Such primary signs can take 3-4 weeks to make themselves felt. The patient will not be able to sleep and will feel unwell.
At the same time, this occurs:
- weakness;
- nausea;
- elevated temperature.
In some cases, these signs can appear quite acutely. As the disease progresses to the chronic stage, the patient sometimes experiences severe headaches and pain in the temples, neck, back of the head or shoulder. If you do not start treatment on time, then in half of the patients the pathology progresses sharply. After some time, additional ophthalmological symptoms appear:
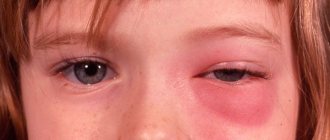
- pain in the eyes;
- loss of vision;
- double vision
This happens because the optic artery becomes inflamed and the retina and nerves are damaged. If left untreated, this can cause complete loss of vision.
Eye pain is a complication
The brain will also react. A person’s blood circulation will be impaired, and paralysis or paresis may occur. In some cases, encephalopathy or cephalgia develops.
Establishing diagnosis
A patient with certain symptoms may be prescribed various examinations, as well as a check with a rheumatologist. Blood tests will be required. This will help you understand why the inflammation occurred, as well as make a correct diagnosis. Also, as a result of a blood test, the doctor will detect anemia or increased blood clotting.
If the diagnosis confirms the presence of certain pathologies in the body, a cell biopsy is performed. This examination is done under local anesthesia. With such testing, the disease can be 100% confirmed. If the result is negative, then a diagnosis of arteritis cannot be made, since symptoms can also arise for other reasons, for example, due to changes in blood vessels.
Treatment
Temporal arteritis should only be treated by an experienced doctor. First, he conducts a complete examination of the patient. If not done early, it can complicate the diagnosis and affect the results. After this, the doctor prescribes a treatment method, which can be:
- Conservative . Here the patient is prescribed glucocorticoids. At the beginning, the doses are large. Then the dosage is gradually reduced. The course of such treatment usually lasts about two years. If complications appear in the eyes, special therapy is used, tablets are prescribed or injections are given. Also, during such treatment, it is imperative to take medications that will strengthen blood vessels and dilate arteries.
- Surgical . In this case, the surgeon inserts a shunt into the patient, through which blood bypasses the affected areas of the vessels. But such surgical intervention is not used so often. It is usually recommended for aneurysms, tumors and threats of rupture of blood vessels.
Traditional methods
From experience it is clear that it is impossible to get rid of Horton's syndrome using traditional methods. It is important to take medications without fail.
But at the same time, it is possible to further strengthen the immune system and support the body with folk remedies. This treatment can be carried out in combination.
But here you also need to remember that herbal decoctions and other folk methods should not negatively affect digestion or cause allergies. It is important!
For the elderly, during treatment with folk remedies and conventional therapy, you should avoid stress, hypothermia, and also take medications to dilate blood vessels. It is worth maintaining tone with healthy food and vitamins.
It is also important not to shy away from treatment when negative symptoms appear and not to endure pain, especially in old age. Symptoms can warn of illness.
Prevention
Since today the causes of this disease have not been fully studied by scientists, there is no accurate data on preventive measures. But since the disease occurs due to the development of viruses, you need to pay more attention to your immunity.
To do this you will need to follow these rules:
- eat properly and balanced;
- observe the regime;
- take vitamins and minerals in tablets.
When the first negative symptoms appear, contact your doctor immediately.
A balanced diet is important!
Complications and prognosis
The most serious consequences of the pathology are heart attack and blindness. Such conditions can manifest themselves when the disease is left untreated.
Doctors note that if a patient consults a doctor on time, he has a 90% chance of completely getting rid of this disease. On average, the course of treatment lasts 3 years.
Source: https://GlazExpert.ru/bolezni/drugie/visochniy-arteriit.html
Complications
If treatment of the disease is ignored, other arteries may be affected. Often, the kidneys are the first to suffer.
The most important complication of temporal arteritis is complete loss of vision or other problems in the field of ophthalmology. Complete blindness occurs due to the fact that there is a violation of blood flow through the inflamed arteries to the eyeball and optic nerve. As a result, the nervous tissue of the retina dies, and the patient may become completely blind. The consequences of the disease can be ischemic disorders leading to a stroke.
Also, as a complication of temporal arteritis, a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract is possible; against this background, other diseases may develop.
Prevention
Since today the causes of this disease have not been fully studied by scientists, there is no accurate data on preventive measures. But since the disease occurs due to the development of viruses, you need to pay more attention to your immunity.
To do this you will need to follow these rules:
- eat properly and balanced;
- observe the regime;
- take vitamins and minerals in tablets.
When the first negative symptoms appear, contact your doctor immediately.
A balanced diet is important!