Vision of children from birth to six years
In the period up to three months, the baby sees objects exclusively at a distance of 40 to 50 centimeters. Often parents think that his eyes are a little squinted. In fact, the child is undergoing final formation of the eyeball; his vision during this period is farsighted. Only at 6 months can a specialist diagnose a particular visual impairment, if any. After 3.5-4 months, the baby’s vision improves significantly, he can focus his gaze on a specific object and pick it up. You can develop your child’s vision from birth by following simple rules:
- Place the crib in a well-lit room with a combination of daylight and electric light, this will encourage active eye movement.
- Decorate the room in soft, soothing colors so as not to irritate your baby's eyes.
- The distance between toys and the bed should be at least 30 centimeters. Hang items of different colors and shapes.
- You should not accustom your child to watching moving pictures on a TV or tablet from infancy, as this increases the strain on his eyes.
From one to two years, the baby develops visual acuity, which is determined by the ability to see two points at once, located at some distance from each other. The norm for this indicator in an adult is one; in a child under two years old it varies from 0.3 to 0.5.
A child over 2 years old is already able to perceive the speech of adults and respond to their facial expressions and gestures. If the baby’s vision develops correctly, then his speech will improve. Otherwise, if the development of the visual organs is impaired, he will react poorly to the articulation of the parent’s speech, and therefore the child will have problems with speech reproduction skills. At three years old, it is necessary to have your child’s visual acuity checked by a specialist. As a rule, for this, doctors use Orlova’s table, consisting of ten rows of different images. This indicator is determined by the serial number of the row in the table. By the age of four, the norm for this parameter is 0.7-0.8. Often at this age, children begin to squint; this may be a sign of myopia (nearsightedness); in this case, the ophthalmologist may prescribe wearing glasses and eye exercises.
The vision of preschool children continues to develop, so it is important for the child’s parents to monitor its development and attend routine examinations. At the age of 5-6 years, children’s visual organs are subject to heavy load, as preschoolers begin to attend various clubs and sections. During this period, it is important to give the child’s eyes a rest: after a 30-minute lesson, it is necessary to take a break of at least 15 minutes. You should use a TV or computer no more than one and a half hours a day.
Visual analyzer. Functional meaning. Possible violations. Age characteristics
The meaning of the senses. Analyzer structure diagram. Main functional features, classification Read more: Hearing analyzer. Functional meaning. Age characteristics
24. Visual analyzer. Functional meaning. Possible violations. Age characteristics
During training, up to 90% of the load falls on the visual analyzer. The eye is the peripheral part of the visual analyzer. The optic nerve that exits the eye is the nerve fiber. The central section of the visual analyzer is located in the occipital cortex of each cerebral hemisphere.
The eye serves to perceive light stimuli and develops from the same cells as the brain. The increase in the mass of the eye and brain from birth to 20 years occurs in parallel.
The eye lies on a soft fatty lining in a special cavity - the orbit - and is almost completely protected by the bones of the skull. The eye consists of an eyeball and an auxiliary apparatus. The eyeball is spherical in shape, covered with three membranes and has a nucleus. The outer shell of the eye is fibrous, consists of two sections: the anterior one is the cornea, the posterior one is the sclera, or the tunica albuginea. The cornea is inserted into the anterior part of the sclera. It is transparent and convex like a watch glass. The cornea becomes visible when the eye is viewed in profile under transmitted light. Recent scientific research confirms the presence of sensitive nerve endings in the cornea. With injuries (mechanical, chemical, thermal), the cornea becomes cloudy and stops transmitting rays of sunlight. The tunica albuginea is dense, white, about 1 mm thick; it is called the white of the eye.
On the way to the cerebral cortex, light-sensitive cells are distributed unevenly: cones are located mainly in the central part of the retina, rods - in the periphery. The posterior part of the retina is called the fundus of the eyeball. A yellow spot can be seen in the fundus. This part of the retina contains the largest number of cones. The central fovea of the macula is the place of best vision; with its help, the eye is able to distinguish the smallest objects and read small print. Cones provide daytime vision and perceive color. Rods provide twilight vision; Thanks to them, we distinguish weak light and the outlines of objects. There are no light-sensitive cells at the exit site of the optic nerve (blind spot).
Increased intraocular pressure causes a serious disease - glaucoma.
The auxiliary organs of the eye are represented by the protective apparatus, lacrimal and motor. The protective apparatus includes eyebrows, eyelashes, eyelids. Eyebrows protect the eyes from dripping sweat, eyelashes trap dust particles, eyelids close the eyes. Tear fluid contains bactericidal substances; it moistens the cornea, protecting it from drying out, and then flows through the lacrimal ducts into the nasal cavity.
The motor system is represented by six muscles attached to the eyeball and providing combined eye movement, as well as the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid.
Age-related features of visual function.
With age, the lens loses its elasticity. The decrease in the volume of accommodation occurs gradually and for a long time has practically no effect on the quality of vision.
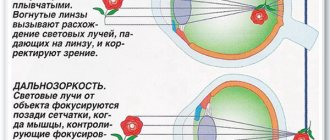
Myopia (myopia) occurs when the power of the refractive medium of the eye increases and its optical axis lengthens. In this case, the rays are focused not on the retina, but in front of it. Divergent rays hit the retina, as a result of which the image will be unclear and blurry. In order for the focus to fall on the retina, nearsighted people bring the object closer to their eyes or lean over it. Correction is achieved using glasses with concave lenses.
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is observed when the power of the refractive medium of the eye decreases and its longitudinal optical axis shortens. In this case, the light rays are focused behind the retina, and the image will also be blurry. In order for the image to become clear, it is necessary to increase the distance from the eyes to the object. Farsighted people examine the details of objects, read text at a distance of up to 50 cm. With farsightedness, a person cannot clearly see either close or far away objects without straining accommodation, however, looking at objects located at a distance causes much less stress. Vision correction is achieved using glasses with convex lenses.
Astigmatism is a refractive error associated with uneven curvature of the cornea in its individual meridians. As a result, light rays are not refracted equally, and a clear image is not obtained on the retina. Such an eye can simultaneously have both nearsighted and farsighted refractions. Vision correction is achieved using complex cylindrical glasses.
The main functions of the visual analyzer are light perception, acuity of central and peripheral vision, binocular and color vision. Light perception is the ability to perceive light and differentiate it by degree of brightness. This function of the visual analyzer manifests itself very early.
The human eye is capable of seeing in varying degrees of illumination. Adaptation to high levels of illumination (light) occurs within 1 minute; At the same time, the sensitivity of the eye decreases sharply. If light adaptation is impaired, a person's vision in the twilight is better than in the light. The eye's ability to see in low light is called tempo adaptation. It occurs gradually, the sensitivity of the eye increases maximally within 1 hour.
Light adaptation increases from 5 to 20 - 30 years, remaining maximum around 12 noon, minimum around 12 midnight. Photosensitivity is affected by the general condition of the body, poor nutrition, and fatigue.
Visual acuity is the ability of the eye to distinguish small details of objects under consideration. The smaller the distance between two distinguishable points, the greater the visual acuity. For good visual acuity, it is necessary that all parts of the visual analyzer function normally.
Various diseases of the visual organs in children can be divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory. It is necessary to remember the possibility of serious consequences of injury.
The most common inflammatory diseases in children's groups include conjunctivitis and diseases of the eyelids, including styes, caused by bacteria and viruses. The infection can be caused by dirty hands or personal hygiene items. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). It is characterized by burning and pain in the eyes (“sand in the eyes”), lacrimation, photophobia, and purulent discharge. Your temperature may rise. The child complains of a headache. Barley is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous or sweat glands. In this case, there is significant pain in the affected area, the eyelid swells sharply, and the child’s general condition worsens.
Of the non-inflammatory eye diseases, the most common visual impairment in children is myopia (myopia).
Myopia fell into the category of “school” diseases. It should be noted that among children entering 1st grade, 4% already have myopia.
In an effort to prevent the progression of myopia, we must not forget about the importance of the child’s health. It is necessary to strengthen the general condition of the body through hardening, rational, nutritious nutrition, appropriate physical education, and compliance with the work and rest regime.
To prevent myopia at school, it is necessary to adhere to an optimal regime of education, upbringing and rest. The correct selection of school furniture in accordance with the height of students and instilling the correct working posture are very important. Children with visual impairments should sit at the front tables in the first row away from the windows. It is recommended that students who were sitting in the third row from the windows be moved to the second or first row at least two or three times during the school year. The teacher must ensure that children who are prescribed glasses use them during lessons.
The meaning of the senses. Analyzer structure diagram. Main functional features, classification Read more: Hearing analyzer. Functional meaning. Age characteristics
Information about the work “Age-related physiology and school hygiene”
Section: Medicine, health Number of characters with spaces: 267972 Number of tables: 0 Number of images: 0
Similar works
Subject, tasks and methods of age physiology
179193
1
0
...increases. Educational influences aimed at improving internal inhibition play a significant role in this. Literature 1. Badalyan L.O. Neuropathology. – M.: Academy, 2000. – 384 p. 2. Belyaev N.G. Age physiology. – Stavropol: SSU, 1999. – 103 p. 3. Dubrovskaya N.V. Psychophysiology of the child. – M.: Vlados, 2000. – 200 p. 4. Obreimova N.I., Petrukhin A.S. ...
Age physiology
25766
0
0
...only in short-term memory. This shows that the development of mnemonic abilities is accompanied by an increase in the role of mental processing in memorization, i.e. operational and regulatory mechanisms. Age-related differences in mnemonic abilities manifest themselves both at the level of their natural component (functional mechanisms) and in the intravital operational and regulatory...
Physiology
69327
1
0
causes a change in the balance of cortical-subcortical interaction, resulting in an increase in generalized excitation and a weakening of internal inhibition. Compared to the previous age group, the formation of temporary connections becomes more difficult in adolescence. The rate of formation of conditioned reflexes to both primary and secondary signal stimuli decreases. ...
The influence of biorhythms on the physical performance of middle school children
63213
2
0
…: ð study the impact of biological rhythms on the physical performance of middle school students; ð consider the problems of disruption of biological rhythms; ð determine the influence of biorhythms on the level of physical performance during athletics in middle school children. 2.2. Research methods To organize a pedagogical experiment and ...
Vision in adolescence
The greatest strain on the eyes occurs during the period when a person reaches puberty. In addition to reading textbooks, watching TV and using a computer, vision is affected by hormonal changes in the body and its active growth. These factors often lead a teenager to such a visual deviation as myopia. During this period, it is important for parents to monitor changes in their child’s vision parameters by visiting the ophthalmologist’s office at least once every six months. At this age, doctors recommend using contact lenses. They will help not only correct vision, but also relieve the child of complexes. After all, unlike glasses, they are completely invisible to the eyes. Another advantage of eye lenses is the high image quality and improved vision more effectively than with glasses. However, before allowing your teenager to wear such optical products, familiarize him with the rules for their use, because lenses require careful care and compliance with hygiene standards.