The retina plays a critical role in the visual process, converting light rays into nerve impulses. Any pathology of the retina is fraught with serious consequences for visual function. Such disorders require an integrated approach to treatment, in which drops for the retina play a special role.
Pharmacological companies offer a whole line of ophthalmic drugs in the form of drops. Which of them have proven to be the best in terms of strengthening the retina? How to understand the assortment and understand that the drug is not suitable? Read on.
Causes of retinal detachment
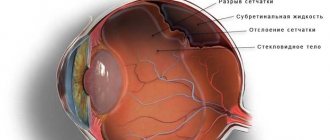
To understand what retinal detachment is, you need to have an understanding of the structure of the eye. The retina (retina) lines the inside of the eyeball. It is part of the brain. Perceiving an image, the retina converts information into impulses, sending it through the optic nerve to the brain.
The human eye has a rather complex structure
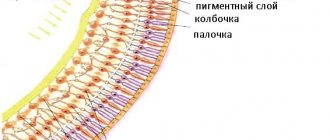
The retina consists of ten layers of cells and lies on the choroid (choroid), which is responsible for the supply of nutrients. The vitreous body (vitreum) occupies the cavity of the posterior part of the eyeball and consists of water, a small amount of protein and hyaluronic acid. Vitreum is responsible for maintaining the shape and tone of the eyeball and conducting light rays to the retina.
Important! The vitreous body does not have the ability to recover on its own if it is removed and lost.
The primary stage in the development of pathology is the destruction of the vitreous body, which is formed during its tension. The phenomenon leads to a rupture of the retina, which can cause its detachment from the choroid.
The most common cause of the problem is ophthalmological diseases:
- myopia;
- pseudophakia;
- aphakia.
In 40–50% of cases, these diseases lead to retinal detachment. The second, no less important reason is eye injuries. In almost 20% of cases, the disease develops after removal of the lens as a result of injuries.
The risk group includes people aged 40 to 70 years, patients with a history of eye injuries, as well as those who engage in sports such as boxing, ski jumping, and wrestling.
We recommend reading: The best vitamins for women over 40: reviews, names, which ones to choose
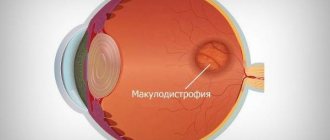
If the macula is damaged, macular degeneration occurs. Elderly people are most often affected by this group of changes. Vitamin complexes can help prevent these disorders.
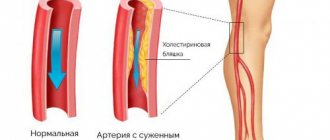
People with a history of vascular disease should pay special attention to eye health. It is vascular pathologies that can significantly reduce the quality of vision and provoke eye diseases.
Age-related decline in the quality of vision often occurs due to retinal dystrophy and problems with blood vessels (atherosclerotic changes). The price for staying at the computer for a long time is also deterioration of vision. Therefore, vitamin complexes will help ensure reliable protection of the visual apparatus.
Retinoprotectors in ophthalmology
Retinoprotectors (English retina - retina, protect - protect) is a generalized name for ophthalmic drugs, the main function of which is to protect the retina of the eye from external and internal aggressive factors (ultraviolet and other radiation, oxidation products, singlet oxygen, etc.).
Such drugs are safe, have high retinotropism (the ability to concentrate in the retina) and a powerful antioxidant effect (suppressing oxidative stress and neutralizing free radicals). The implementation of the latter effect occurs due to the presence of hydroxyl groups with conjugated double bonds.
The most famous natural retinoprotectors are:
- Lycopene is one of the most powerful antioxidants, synthesized only by plants, giving them their red color.
- Anthocyanins are compounds found in berries and fruits that are red and blue in color (very abundant in blueberries).
- Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin A, beta-carotene, found in foods of animal and plant origin.
- Lutein is a plant xanthophyll carotenide synthesized only by plants.
In ophthalmology, retinoprotectors are used in the form of eye drops, powders for injections, as well as oral medications (dietary supplements).
Direct-acting retinoprotective drugs – ophthalmoneuropeptides (peptide bioregulators, cytomedins) – are widely used in clinical practice today. They are able to induce differentiation processes of cells of tissue structures, increase cellular and humoral immunity, improve the state of homeostasis and other protective reactions.
The introduction of peptide drugs into the eye leads to the release of its own endogenous peptides (peptide cascade effect). The action of the peptide cascade is expressed in the activation and prolongation of its own synthesis of peptides, which continues after the decay of the inducer introduced from the outside.
Such drugs correct metabolic processes and prevent excitotoxicity and oxidative stress, and enhance the activity of Müller cells. They have a pronounced protective effect on the vascular endothelium, preventing apoptosis and reducing destructive changes in the retinal pigment epithelium in various forms of retinal degeneration, and have an immunomodulatory effect.
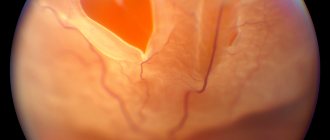
Symptoms of retinal detachment
The first signs of the disease appear in the form of photopsia - the appearance of lightning, flashes and sparks in the field of vision. Such manifestations are a consequence of irritation of the photosensitive cells of the eye.
The problem may be indicated by sudden formation of dark circles and cobwebs, which are considered signs of vitreous hemorrhage. A veil or curtain that appears before the eyes also indicates visual impairment due to detachment of the sensory layer of the retina.
Common symptoms of the disease include the following:
- decreased visual acuity;
- photopsia and the appearance of floating spots, flies, and veils before the eyes;
- deformation of the outlines of objects, nonspecific vibrations of objects;
- sudden loss of lateral vision;
- narrowing the field of view;
- increased stress when reading and working with office equipment.
Clinical picture
The main symptom of retinal dystrophy will be a decrease in visual acuity. Since this is what is typical for most eye pathologies, the correct diagnosis can only be made by an ophthalmologist after a special examination.
There are central and peripheral retinal dystrophy.
Central retinal dystrophy
otherwise called macular degeneration is damage to the cells of the macula (macula), the area of the retina responsible for central vision.
Predominant manifestations of macular degeneration:
- sensations of fog or veil before the eyes;
- visible curvature of straight lines;
- difficulty reading, recognizing people's faces, etc.
The disease may begin to develop first in one eye, but later the other always joins. In advanced cases, the patient loses the ability to distinguish between the time of day (day and night), and later complete blindness occurs.
Peripheral retinal dystrophy
often caused by or associated with other eye pathologies - long-term myopia or farsightedness. With this form, central vision does not suffer or suffers only slightly, but peripheral vision is narrowed.
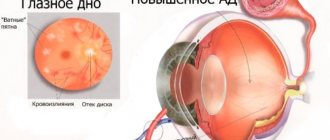
The initial stage is asymptomatic for a long time, but changes in the fundus are already present when the patient does not yet complain. When examining the fundus of the eye at the beginning of the disease, one can notice excessive growth of blood vessels in the retinal area and a number of other signs, and in the later period extensive hemorrhages in the retina, its ruptures and areas of detachment already appear.
What vitamins are needed to strengthen the retina of the eye?
The retina is sensitive to the effects of free radicals, so to strengthen it, you should include in your diet foods that include vitamins E and C, zentaxin, lutein, zinc, selenium and omega-3. Vitamins A and B are of no small importance. All of them are important for retinal detachment, as they have antioxidant properties.
Products useful for maintaining eye health
You can get these elements from the following products:
- cereals, bran, whole grain bread;
- dairy products;
- all seafood;
- vegetables, root vegetables, herbs, seasonings (ginger, cloves, hot pepper);
We recommend reading: Chili peppers: benefits and harms, properties, how to eat them
- fresh berries and fruits;
- porridges and pasta from dark varieties of wheat;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- vegetable oils.
We recommend reading: Benefits of bell pepper, properties
A balanced diet will help strengthen the retina, but pharmacy vitamin complexes produced in tablets, dragees, capsules and eye drops will help solve existing problems.
Important! Self-medication at the first signs of visual impairment is unacceptable! In some cases, retinal detachment may develop asymptomatically for a long time.
Even minor manifestations of decreased vision or strain require consultation with an ophthalmologist. Periodic examination is necessary for people at risk: people with bad habits, diabetes and hypertension.
Why does retinal dystrophy develop?
Retinal dystrophy is a severe pathology associated with the gradual death of photosensitive cells due to disruption of their nutrition. The nature of its occurrence has not been fully disclosed by scientists, but it is generally accepted that retinal dystrophy develops as a complication of other serious diseases:
- diabetes mellitus;
- poisoning of the body with metabolic products in diseases of the liver and kidneys;
- endocrine pathologies (hormone production disorders);
- autoimmune disorders (scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis);
- severe viral infections, including influenza or cytomegalovirus infection;
- diseases of blood vessels and internal structures of the eyeball;
- lack of food or impaired absorption of vitamins and minerals, mainly C, E, zinc and carotene derivatives;
- high blood pressure;
- bad habits, in particular smoking.
Early death of retinal cells can be a hereditary pathology, and in old age the development of dystrophy is considered as a natural sign of aging.
Find out what eye exercises for myopia are recommended by ophthalmologists.
You can read about how to restore vision using Dr. Bates’ method in this article.
The best vitamin complexes for the retina
To compensate for the lack of vitamins in the body, it is not enough to eat sources of nutrients. For example, to get the daily dose of vitamin A (carotene) from carrots, you will have to eat 2 kg of it.
Pharmaceutical preparations - biologically active additives and vitamin complexes that can strengthen the retina of the eye - will help solve the problem. Their intake helps improve trophism.
Ophthalmologists offer the following complexes and preparations:
- Will direct. Biologically active vitamin extract recommended for retinal dystrophy. The complex includes: vitamin A, C, P, group B, zinc, blueberry extract, eyebright, ginkgo biloba. The drug is prescribed in complex therapy to reduce the risk of destructive changes in the retina, lens and vitreous body. Available in tablets.
- Blueberry forte. Belongs to the class of dietary supplements. Used for prevention and eye diseases. The composition is similar to the drug Napravit. Available in tablets.
- Lutein complex. One of the most popular vitamins for strengthening the retina with lutein. The dietary supplement in tablet form contains: vitamins A, E, C, lutein, taurine, zinc, copper, selenium, blueberry extract. It is considered an effective means of preventing retinal detachment.
Lutein plays an important role in maintaining and restoring eye health - Vitrum Vision, in addition to a complex of useful substances similar to the previous drug, also contains zeaxanthin. The level of lutein in Vitrum Vision is higher in comparison with dietary supplements of this group. Taking the tablets is recommended for people experiencing increased visual stress.
Vitrum Vision provides the body with a daily dose of essential vitamins and microelements that strengthen the retina of the eye - Taufon is an eye drop that helps maintain eye health and visual acuity. Refers to vitamins prescribed for macular degeneration of the retina. In addition to the drug in drops, the manufacturer offers a vitamin complex in tablets - Taufon Tabs Lutein. Significantly reduces the load on the organ of vision during long-term work at the computer.
- Okuwait Lutein Forte is another effective complex of vitamins for strengthening the retina in tablets. Improves color perception, reduces stress, helps maintain visual acuity. Dietary supplements based on carotenoids (lutein, zeaxanthin), which act as a light filter.
Important! If the integrity of the retina is damaged, restoration of visual acuity during treatment with a conservative method is impossible. Therefore, it is important to take vitamin complexes for preventive purposes, having first received the doctor’s approval.
There are many medications to strengthen the retina. Only a doctor can decide which one is suitable in a particular case, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his state of health.
What to look for when choosing?
All drops for the retina can be divided into 2 groups:
- angioprotective – strengthen the walls of blood vessels, reduce their permeability, promote the resorption of blood clots and hemorrhages;
- antioxidant and metabolic – stimulate metabolic processes, fight dystrophies, and are used to improve blood circulation, respiration, nutrition and nerve conduction.
The remedy is selected based on the leading problem that was diagnosed during an ophthalmological examination. You cannot make a decision on purchasing this or that product on your own; you must obtain a doctor’s approval. When purchasing, you also need to pay attention to the expiration dates of the drug, contraindications and special instructions specified in the instructions.
REFERENCE! According to indications, the ophthalmologist can prescribe several types of drops at once for a complex effect on the retina.
Retina: anatomy and physiology
The retina is a neurovascular formation; it consists of photoreceptors, the axons of which form the optic nerve. Beneath the retina lies the choroid (choroid), separated from the nerve structures by a layer of pigment epithelium. In the center of the retina, closer to the nose, lies the optic disc, a part of the retina devoid of photoreceptors or the blind spot, through which the central retinal artery and vein also pass. Outside the blind spot is the macula or macula - the area of concentration of maximum vision and maximum density of photoreceptors.