It is known that among the most common diseases of the organ of vision, ophthalmologists around the world always mention cataracts - a condition of pathological clouding of the lens. A change in the transparency of the most important natural lens of the eye is associated with a violation of the properties of protein molecules at the cellular level, of which the lens is partially composed, and this process, in turn, can occur under the influence of various factors.
However, in addition to the primary form of pathology, which is most often diagnosed at an appointment with an ophthalmologist, according to the classification of diseases, there is also a secondary cataract
. This is a condition that occurs as a complication of surgery to correct initially identified disorders. Cataract surgery involves removing the lens and then replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). The artificial lens is selected individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s visual organ condition. In the future, repeated interventions are not required - the IOL fully performs all the functions of the optical element. However, any operation involves a risk of complications, despite the rapid development of microsurgical technologies. Therefore, in the case of lens extraction, no one can be protected from the formation of secondary changes in the form of repeated violation of transparency.
What is secondary cataract after surgery?
Cataract is a damage to the optical system of the eye when the lens becomes cloudy. During lens replacement, the posterior capsule is usually preserved, which serves as a support for the new intraocular artificial lens. It is subject to repeated clouding, wrinkling due to thinning of the walls, and pathological proliferation of epithelial tissue.
Secondary cataracts are divided into 3 forms:
- Fibrous cataract, when connective tissue elements grow.
- Proliferative cataract, when specific cells are identified, indicating a long-term course of the process.
- Thickening of the capsule, not accompanied by turbidity.
The first two forms of secondary cataract cause unpleasant symptoms.
Last news
Based on the results of a large-scale voting, our clinic was recognized as “Vision Restoration Center No. 1” in Belarus, and was also awarded the highest standard award - gold!
For the first time at the VOKA Eye Microsurgery Center, on March 20, 2021, personalized laser vision correction was performed using the 3D Custom Green method! Each eye is unique, and the surface of the cornea, the main lens of the optical system of the human eye, is like a fingerprint - unique.
The VOKA Eye Microsurgery Center presents a unique development from Alcon (USA), a recognized world leader in the ophthalmic equipment market - a high-precision excimer laser Wave Light EX 500 (Germany) with the latest software - GREEN SP 4 Update PERS 01.
Causes
The secondary form of the disease does not have a specific cause. There are predisposing factors:
- Leaving destroyed fragments due to the carelessness or inexperience of the surgeon.
- IOL materials. Acrylic lenses with a square edge are less likely than silicone lenses with a rounded edge to cause the development of secondary cataracts after surgery.
- Elderly age.
- Somatic diseases (autoimmune connective tissue diseases, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, thyroid dysfunction).
- Ophthalmological diseases (uveitis, high degree of myopia, glaucoma, retinal detachment, dystrophic changes in the organ of vision).
- Complications after phacoemulsification.
- Hypovitaminosis, vitamin deficiency.
- Factors that irritate the visual organ: frequent exposure to bright sun, welding, caustic fumes, smoke.
The development of secondary cataracts after lens replacement has no clear causes. No specialist can guarantee that you will not experience repeated changes in the lens during the recovery period or after a few years. Eliminating predisposing factors will only reduce the risk of occurrence.
Diagnostic examination
Before correction, the specialist conducts an extensive ophthalmological examination:
- visual acuity test;
- Using a slit lamp, a specialist determines the type of opacification and also excludes swelling and inflammation;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- examination of the fundus vessels and exclusion of retinal detachment;
- If necessary, angiography or tomography is performed.
Before treatment, a comprehensive examination of the visual organs is carried out, after which the doctor will tell you what to do next.
Symptoms
After eye surgery, a person may notice a progressive decrease in the quality of vision. This is how the first symptoms of secondary cataract begin after lens replacement. What other manifestations does the secondary form of the disease cause?
- Flashing flashes, sparks.
- The appearance of a veil, blurred vision.
- Double vision.
- Blurred vision.
- Impaired color perception.
- Fuzzy image, blurred contours.
- Focus problems.
- Decreased visual acuity. Spectacle correction is unsuccessful.
The clinical picture develops differently. For some, the secondary form appears sharply and suddenly, while for others it slowly progresses over years. Typically, the first symptoms appear no earlier than 3 months after phacoemulsification.
Video: Secondary cataract after lens replacement
Causes
Secondary cataracts are densification and opacities in the posterior capsule of the lens, which usually develop after surgical treatment of cataracts, and are characterized by deterioration of visual characteristics.
Many people have heard about the existence of such a disease as cataracts, but few know what it is. Eye cataracts are a disease common to most people whose age is or exceeds forty years (but can sometimes occur in children, especially if we are talking about a congenital disease).
This pathology is characterized by the fact that clouding of the transparent lens located inside the eyeball of the visual apparatus occurs.
The process of thickening and clouding of the lens capsule has long been noticed and studied by ophthalmologists. Several methods have been found to eliminate secondary cataracts; the most effective and humane of them are currently used.
Secondary cataract itself involves the process of clouding and thickening of the lens capsule. which leads to a significant deterioration in visual functions.
During surgery to remove a damaged lens, doctors preserve its capsule, where they implant an intraocular lens. The artificial lens is hidden in a thin elastic bag.
But epithelial cells can begin to grow around this capsule. Do not think that the reasons for this are the incompetence of surgeons.
Rather, they lie in the body's ability to perform certain cellular reactions.
- high rate of cell regeneration due to the patient’s young age;
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- the presence of additional ailments, for example, diabetes, thyroid pathologies, etc.
There is a high probability of this form of cataract occurring during the treatment of children. Only five to ten percent achieve an ideal result during the first operation. In adults, such cases occur much less frequently.
There is some connection with the lens installed by the surgeon. So, if the artificial lens is made of acrylic, the chance that the disease will not develop again is higher than with a silicone analogue. Whenever possible, ophthalmologists recommend using artificial lenses with square edges. They prevent the proliferation of epithelial cells.
Diagnostics
Repeated cataracts are treated by an ophthalmologist. First, a series of examinations is prescribed. The doctor measures IOP. Uses Sivtsev-Golovin tables to assess visual acuity (visometry). Performs perimetry: determines the boundaries and areas of loss of visual fields.
Examination using a slit lamp (biomicroscopy) evaluates the structures of the eye, allows you to see the localization of the pathological focus, its size, and characteristics. If macular edema is suspected, fluorescein angiography and OCT (optical coherence tomography) are performed.
If a person has diseases of internal organs, he is referred for examination to doctors of the appropriate profile. Treatment of the underlying pathology and normalization of laboratory parameters are required. Otherwise, repeated cataracts will recur after treatment.
Video: Secondary cataract after lens replacement and treatment
Diagnostic tests
It is difficult to identify secondary cataracts, so an expanded list of studies is used when making a diagnosis. Among them:
- Determination of visual acuity.
- Detection of opacities and dystrophies in the anterior chamber of the eye.
- Ultrasound of the visual organs.
- Determination of the condition of the posterior chamber of the eye using OCT.
- Blood analysis.
- Cytology analysis of film.
It is possible to detect pathology at the initial stage only through laboratory tests. Instrumental diagnostics help determine the presence of a disease only if deviations from the norm are visually manifested.
Treatment
Increasing visual impairment requires treatment of secondary cataracts. If left untreated, partial or complete blindness will develop over time. What removal methods are used to treat recurrent cataracts?
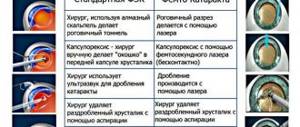
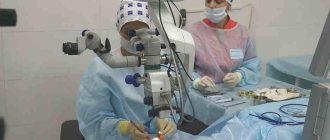
The best treatment for recurrent cataracts after lens replacement is laser dissection of the secondary cataract. Laser dissection is widely used and ophthalmic surgeons have extensive experience. Considered the gold standard of treatment, it is carried out quickly and does not require hospitalization.
Before the operation, mydriatics are instilled to dilate the pupil. A small hole is then created with a laser. Next, photodestruction of the altered tissue is carried out, i.e. dissection and destruction using a laser.
Treatment of secondary cataracts is a complex task. This is due to the frequent need for surgery and the impossibility of performing it due to concomitant diseases. In this case, conservative treatment methods help slow down the development of pathology and improve the quality of life. Patients are prescribed drops that have a positive effect on the condition of the lens, improve metabolic processes in it, and promote normal regeneration of damaged tissue. For example, a doctor may recommend Oftan Katahrom - Finnish eye drops with a proven clinical effect, which include the antioxidant cytochrome C, vitamin nicotinamide and the energy source adenosine.
Removal of secondary cataracts with a laser is low-traumatic; there is no need to insert surgical instruments into the eye cavity. 98% of people report significant improvement in vision. Contraindications to laser treatment of secondary cataracts: scars, opacities, swelling of the cornea, pathological changes in the fundus, inflammatory eye diseases.
The surgical method of removing secondary cataracts is outdated and rarely performed. It's called a capsulotomy. The essence of the method is to dissect the clouded lens capsule with surgical instruments. Surgical capsulotomy is dangerous due to the risk of traumatic damage to the structures of the visual organ. Has a long recovery period. Associated with an increased risk of infectious complications.
In the postoperative period, symptoms may be observed: redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation. This is the result of intervention on the visual organ. To improve a person’s condition, an ophthalmologist prescribes eye drops and ointments.
The goal is to prevent infectious complications, reduce inflammatory manifestations, and stabilize IOP. The course of local therapy is up to 1 week. During follow-up examinations after surgery, the doctor assesses the condition of the visual organ and decides whether to shorten or extend the course of therapy.
Who undergoes laser dissection of secondary cataracts?
Laser dissection of secondary cataracts is one of the types of surgical intervention in which the functioning of the visual apparatus is restored. After the procedure, the patient does not require long-term rehabilitation. Let's consider all the nuances of laser dissection.
What is secondary cataract?
Cataract is a disease characterized by clouding of the lens. This occurs as a result of insufficient nutrition. It loses its optical functions, as a result of which the patient loses vision. Treatment of primary cataracts involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an intraocular lens.
Secondary cataract is an opacification of the posterior wall of the capsule in which the intraocular lens was located. Over time, it becomes denser and stops transmitting light. In this condition, vision gradually deteriorates. Moreover, pathology does not always develop rapidly. As a result, secondary cataracts result in complete blindness and disability if timely treatment is not started.
Causes
Secondary cataracts may appear several months or years after surgery. The reasons for its occurrence are considered:
- Fibrosis of the posterior capsule. Usually occurs as a result of inflammatory processes in the surrounding tissue.
- Migration of hyperplastic epithelial cells. Appears due to excessive regeneration of epithelial tissues.
- Incorrect intraocular lens implantation. It is the result of fixation of the lens in the area of the ciliary sulcus.
Risks of manifestation
The risk group includes:
- Elderly people - about 60-70 years old. In the body of an elderly person, metabolic processes slow down and immunity weakens. The visual system receives less nutrients, tissues are restored more slowly.
- People with diabetes. Diabetics should be constantly monitored by an ophthalmologist, since with such a pathology the risk of developing eye diseases increases significantly. Secondary cataracts in this case often occur due to metabolic disorders.
- Inflammatory ophthalmological diseases, retinal detachment.
- Insufficient amount of vitamins in the body.
Signs
The first signs of secondary cataracts are observed some time after lens replacement surgery. A person's vision begins to gradually deteriorate, especially in the evening. After a person looks at a bright light, glare remains before the eyes. Then the following symptoms are added:
- black dots before the eyes, flashing sparks, flashes;
- blurred vision, increasing sensation of fog or smoke;
- incorrect perception of colors, shades;
- blurry outlines of objects;
- the patient cannot immediately focus his gaze.
Vision correcting medications no longer help.
Diagnostic algorithm
Before starting therapeutic actions, the ophthalmologist conducts a detailed study, which consists of carrying out the following activities:
- Assessment of visual acuity.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye using a slit lamp. The type of opacification of the posterior wall is determined. Also, such a diagnostic procedure allows us to exclude the absence of an inflammatory process in the front part of the eye.
- Measuring intraocular pressure.
- Fundus examination. It is necessary to check whether there is retinal detachment or pathology in the macular part.
Such diagnostic procedures help to fully assess the condition of the patient’s visual system and prescribe the necessary type of repeated surgical intervention.
Treatment
There are several types of treatment for secondary cataracts. Let's look at modern options.
Useful video
Treatment of secondary cataracts:
Surgical
Surgical treatment of secondary cataracts is performed under local anesthesia. The essence of the operation is to remove the clouded part of the lens capsule wall through a microincision. But this type of treatment is not carried out very often, since it shows less effectiveness, a greater number of side effects and contraindications.
Capsulotomy
Capsulotomy is an excision of the posterior capsule in which the lens is located, with the removal of overgrown epithelial tissue, which is what caused the clouding. Capsulotomy is performed mechanically - surgically. It is accompanied by eye injury, so long-term rehabilitation is required. Complications are also possible.
Laser dissection of secondary cataracts
The safest method of treating secondary cataracts of all those proposed. Its essence lies in the fact that the surgeon uses a laser to make a hole in the posterior wall of the capsule and eliminate overgrown epithelial cells. The entire procedure takes approximately 15-20 minutes. The advantage of laser discision is that this operation is non-contact, and therefore occurs with minimal injury to the eye.
Indications for surgery
Repeated surgery is prescribed in the following cases:
- significant decrease in vision in the postoperative period;
- repeated opacification of the capsule wall where the intraocular lens is located;
- rapid proliferation of epithelial cells in the operated part.
Contraindications
Note! Contraindications to laser discision for secondary cataracts are temporary. After eliminating the relevant problems, you can begin surgical intervention using a laser.
Laser dissection is not performed in the following cases:
- swelling of the macula of the retina;
- complete fit of the implanted intraocular lens to the capsule;
- swelling of the cornea, the appearance of fibrous cells in it;
- inflammatory processes in the iris;
- pathological proliferation of vascular tissues in the pupil membrane.
Laser dissection is possible only after 3 months after the initial operation to remove the lens without replacing it. Or 6 months after the introduction of the intraocular lens.
Preparation for the procedure
Laser dissection is carried out in specialized clinics and does not require special preparation. Before the procedure, the patient’s eyes are instilled with painkillers, as well as mediatric drops to dilate the pupils. If the patient has a tendency to increase intraocular pressure, he is given an injection of Iodipine.
Technique of the operation
Treatment of secondary cataracts using a laser does not require hospitalization. Surgical intervention is carried out as follows:
- local anesthesia is given;
- a laser beam makes special holes in the posterior capsule of the eye lens;
- Connective tissue is removed through the holes made.
The laser beam used in the process is absolutely safe for eye tissue. It focuses only on the selected part without damaging other areas. The laser does not have temperature reactions and coagulation properties. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid negative consequences.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient is placed in a room where he rests for 1 hour. On this day, in principle, it is strongly recommended to only rest. On the first day, the eyes are very sensitive to any irritants, so you should not scratch, rub, apply any ointments, or drink alcohol.
The day after laser discision it is already possible to:
- take a shower, but so that soap and water do not get into your eyes;
- write and read for a short time;
- work at a computer/laptop, watch TV, periodically dripping moisturizing drops into your eyes;
- apply makeup, but not on the eyes;
- lift weights no more than 3 kilograms.
On the third day after the operation, you can gradually engage in sports: running, training on an exercise bike. You should spend as much time as possible outdoors. But you must refrain from driving vehicles for 7 days.
In general, the entire rehabilitation period takes 1 month. It is after this period that a person can return to his usual way of life.
Possible complications
Despite the fact that laser discision is the safest method of treating secondary cataracts, no doctor can give a 100% guarantee of the absence of complications. Temporary complications after surgery include:
- the appearance of black spots in the eyes when trying to carefully examine a certain object;
- racemose swelling of the retina;
- getting an infection is a doctor’s mistake.
In rare cases, retinal detachment occurs. In such situations, an additional operation is performed to attach it. Other serious complications include intraocular hemorrhage and astigmatism.
Forecast
Properly performed laser dissection provides for the complete restoration of the functioning of the visual apparatus. In 98% of cases, vision in operated patients improves completely. They will feel this on the second day after the procedure. The likelihood of side effects and complications is extremely low.
Operation price
The cost of the procedure depends on the clinic where it is performed. As a result, prices may vary dramatically. On average, you will have to pay about 8,000-12,000 rubles for secondary restoration of the eye lens using a laser.
Patient reviews
Reviews from patients about laser discision in the treatment of secondary cataracts indicate that this is the most acceptable way to restore vision with this diagnosis. There are practically no complications observed, and the ability to see fully is observed in almost all those operated on.
Conclusion
Laser dissection is the best treatment for secondary cataracts. The procedure helps to completely restore visual acuity and has virtually no side effects or contraindications. And the rehabilitation period is reduced to a minimum. A person can soon return to their usual way of life.
RELATED ARTICLES: Sports after cataract surgery Cataract removal of complications after surgery Traditional treatment of cataracts with honey How to cure cataracts in the eye - without surgery Complications of overripe cataracts Initial senile cataracts of both eyes
Prognosis and prevention
Laser dissection proceeds, as a rule, without complications. Secondary cataracts require re-intervention in only 2% of people. Most often, IOP increases within 3 hours after surgery. To reduce blood pressure drops are prescribed. A follow-up examination is required the next day.
Anterior uveitis is the second most common complication after surgery. To prevent it, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory local agents are prescribed. It is extremely rare for the macula or iris to swell, the retina to detach, the IOL to be damaged, or hemorrhage to occur. The reasons lie in defects in the operation.
Almost all people with the secondary form have a favorable prognosis. At the beginning of the recovery period, the quality of visual functions returns. In the first month, people complain of floating dots and the appearance of flashes before their eyes. The complaints will go away when the organ of vision is completely restored. In general, a person begins to see clearly within the first days after laser treatment.
During the recovery period, follow the recommendations to maintain the positive effect of the operation:
- Wear sunglasses when going outside.
- Avoid eye makeup for 2-3 weeks.
- Instill the prescribed drops 3-4 times a day, duration is 1 week.
- Have a routine check-up the next day, a week and a month after surgery.
- At the first suspicious symptoms, immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Video: Do's and Don'ts for Cataracts
Follow all recommendations. Do not forgo topical medications during the recovery period. Protect your eyes from dust and foreign particles. Try to touch the visual organ as little as possible.
After the end of the recovery period, it is recommended to be observed by an ophthalmologist at least once a year. See your doctor even if you have no symptoms. Secondary cataracts can occur again. There is a risk, but it is minimal.
Share the article with your friends on social networks. Tell us about your experience in the comments. Take care of your eyesight. Be healthy.
Symptoms of the disease
At an early stage of the disease, vision may not be affected at all. The initial stage can last from 2 years to 10 years. Further, symptoms begin to appear, and object vision is lost.
Depending on which part of the lens the opacities form, the clinical picture may vary significantly. If a secondary cataract manifests itself on the periphery of the lens, then it may not affect the quality of vision. As a rule, it is discovered by chance during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
Approaching the center of the lens, the disease can already impair vision. Myopia may appear. deterioration in clarity of vision, doubling of objects. And the pupil itself will take on a gray or yellow tint. If any of the symptoms occur, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Depending on which part of the lens the opacities form, the clinical picture may vary significantly. If a secondary cataract manifests itself on the periphery of the lens, then it may not affect the quality of vision. As a rule, it is discovered by chance during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
Approaching the center of the lens, the disease can already impair vision. Myopia, blurred vision, and double objects may occur. And the pupil itself will take on a gray or yellow tint. If any of the symptoms occur, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Classification
Various signs are used to classify the disease:
| Signs | Form | Explanations |
| By time of appearance | congenital | limited in area, stationary in nature, non-progressive |
| acquired | there are progressive changes in the lens | |
| By etiology | senile | typical for older people |
| complicated | develop in eye diseases | |
| traumatic | as a result of eye injury | |
| radial | the result of damage to the lens by x-rays or other types of radiation | |
| chemical | after burns with alkalis, cataracts can develop late; when exposed to acids, they develop in the first hours, affecting the eyelids, conjunctiva, and corneas | |
| associated with common diseases | cataracts accompanying diabetes mellitus, tetany (convulsive attacks caused by impaired calcium metabolism in the body), severe general infectious diseases, large blood losses, prolonged fasting | |
| According to the location of the cloudiness in the lens | anterior polar | localized in the area of the anterior pole of the lens; the cloudiness forms as a round whitish or gray spot |
| posterior polar | located behind the lens; similar in color and shape to anterior polar cataract | |
| fusiform | located along the anteroposterior axis of the lens; shaped like a spindle, looks like a thin gray ribbon | |
| nuclear | located in the center of the lens | |
| layered (zonular) | localization: around the nucleus of the lens, there is an alternation of cloudy and transparent layers | |
| cortical (cortical) | occupies the outer edge of the lens shell; looks like whitish wedge-shaped inclusions | |
| posterior subcapsular | develops under the capsule behind the lens | |
| complete (total) | always bilateral, the entire substance and the lens capsule become cloudy | |
| By stages | initial | hydration of the lens is observed - accumulation of excess fluid in the cortical layer; opacities form outside the optical zone of the lens; this does not affect visual acuity |
| immature | opacities progress, localizing in the central optical zone of the lens; visual acuity decreases greatly | |
| mature | the lens thickens and becomes completely cloudy; the pupil becomes milky white or gray; visual acuity decreases | |
| overripe | a possible complication in the form of phacogenic glaucoma (macrophages and protein molecules clog the channels through which the intraocular fluid drains); in some cases, the lens capsule ruptures, which can lead to the development of phacolytic iridocyclitis (inflammation of the iris and part of the choroid) | |
| According to the speed of maturation | rapidly progressive | It may take 4-6 years from the onset of the disease to complete clouding of the lens |
| slowly progressive | cataracts mature in 10-15 years | |
| moderately progressive | lasts for 6-10 years |
Symptoms (signs)
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of cataract development. In the initial phase, there may be no noticeable deterioration in vision. Early signs include the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes, objects look “as if in a fog,” and may begin to double (diplopia) and acquire a yellowish tint. It causes difficulties in working with small details, writing and reading.
Clinical signs of the disease can be expressed:
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to light;
- blurred vision in the dark;
- decreased level of color perception;
- the need for bright lighting when reading;
- the appearance of a “halo” around any light sources.
Because cataracts change vision toward nearsightedness, people with severe farsightedness may notice as the disease progresses that they suddenly can see well without glasses.
The stages of immature and especially mature cataracts are characterized by a sharp decrease in visual acuity, sometimes only light perception is preserved. The pupil changes color, becoming milky white instead of black.