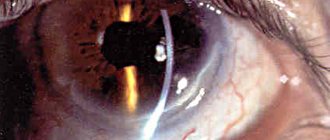
Various external influences can lead to retinal burns. In this case, a burn of retinal tissue differs from damage to other tissues. In particular, when various chemicals (household chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes, alkalis, medicinal solutions, alkalis) come into contact with the cornea, damage to this membrane of the eye occurs. The most severe burn damage occurs as a result of exposure of cells to caustic potassium, ammonia, slaked lime and ethyl alcohol. When the eye is burned, destructive processes occur that involve the membranes of the eyeball. Typically, eye burns occur at work, while in everyday life such injuries develop much less frequently.
The cause of a retinal burn is often bright light, laser radiation or the influence of welding. Ultraviolet (sun) burn of the retina is more common than others. Unlike a chemical burn, this type of burn is less traumatic, but also causes unpleasant consequences. First of all, in case of sun damage, the retina is destroyed. If you stay in the bright sun for a long time without protective glasses, you can get an ultraviolet burn. In addition, snow damage to the retina (snow blindness) is also known. In this case, it is not direct sunlight that hits the eyes, but the reflection reflected from the snow. Due to the fact that these rays are focused on the retina, they quickly lead to burns. For this reason, it is necessary to wear special safety glasses in the mountains, otherwise the risk of developing retinal damage increases.
The laser beam also has an adverse effect on the retina. This type of injury most often occurs in people who are in direct contact (for example, work) with laser radiation. Since the laser beam has enormous energy, retinal burns can be very serious. In production, an eye burn can be caused by accidental exposure to strong acids (sulfuric, acetic) and lime.
Causes
According to statistical data, the main cause of burns is unfavorable environmental factors. For everyday reasons, violations occur quite rarely; injury often occurs due to exposure to sunlight, laser radiation, and glare from welding. This happens when safety rules are neglected, which must be taken into account.
Ultraviolet radiation has an adverse effect on the retina, the trauma in this case is not so high, but negative consequences can also occur. The sun's rays pose a direct danger to the retina; burns occur as a result of prolonged exposure to the sun's rays without the use of protective equipment. The damage from such radiation also persists when light is reflected from snow and water, and in some cases snow blindness may develop. The disease occurs against the background of sunlight reflected from the snowy surface entering the eyes. Wearing sunglasses will help protect your eyes from harmful effects.
Laser radiation also poses a danger to the retina; prolonged exposure can lead to burns. The pathology is widespread among patients whose activities are directly related to laser technology. The laser is characterized by increased power; if the radiation hits the retina of the eye, it can lead to serious complications. Retinal burns can also occur due to contact of the mucous membranes with sulfuric acid, vinegar essence, and other chemicals.
Why does the condition occur?
There are 4 types of eye burns, the main causes of which are shown in the table:
| Type of damage | Cause |
| Chemical | Alkalis |
| Acids | |
| Perfumes | |
| Medicines | |
| Aerosols | |
| Vinegar essence | |
| Alcohol-containing substances | |
| Thermal | Hot air from fire |
| Steam | |
| Hot water or other liquids | |
| Ray | Ultra-violet rays |
| Infrared irradiation | |
| Radioactive radiation | |
| Combined | The cause is a combination of types of burns |
Symptoms
Signs of a thermal burn:
- Burning of the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Colored spots before the eyes;
- Increased humidity of the mucous membrane;
- Headaches of varying intensity;
- Redness of the white surface of the eyeball;
- Swelling of the eyelid, mucous membrane;
- Discomfortable sensations under light radiation;
- Feeling of a foreign object in the eye;
- Deterioration of visual function.
Why laser devices and pointers are dangerous for eyesight
Not all laser pointers are safe, so you should only use products that have received the appropriate certification. Unfortunately, not understanding the full danger of uncertified products, people continue to use them, forgetting to study the important characteristics. The powerful beams of a laser pointer, the effect of which can reach several kilometers, have damaging properties. This means that rays entering a person’s eyes, directly or already being reflected, can cause serious harm to eye health.
Why you shouldn’t shine a laser into your eyes:
- temporary loss of visual acuity is possible even with short-term exposure - bright light causes a sharp contraction of the pupils, which can cause unpleasant optical effects in the form of black dots to appear before the eyes, and vision becomes unclear and foggy;
- laser exposure causes increased lacrimation, headaches, burning and stinging in the eyes, redness of blood vessels;
- Prolonged exposure of the eyes to a powerful laser pointer can cause burns to the cornea and retina.
Black dots, “floaters” before the eyes, appear due to the fact that during a burn, individual segments of damaged tissue are separated from the retina and float in the vitreous body of the eye.
Deterioration of vision does not occur due to the burn itself, but due to the consequences of hemorrhage, therefore it is very important in the first hours after the injury to drain blood from the area exposed to thermal effects.
If you experience painful symptoms after your eyes have been exposed to a laser, consult a doctor immediately, as the consequences of the injury can lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to establish the cause of the lesion; diagnosis plays an important role. In some cases, consultation with a surgeon is required; in case of acute injury, first aid is provided immediately.
Diagnostic methods:
- Visual acuity testing;
- External examination using an eyelid lift device;
- Measuring intraocular pressure;
- Ophthalmoscopy;
- Carrying out biomicroscopy using dyes.
First aid
A burn is a serious injury to the eyeball, accompanied by acute pain.
Immediately after receiving it, the patient should be given first aid:
- Washing the eyes with low-concentrated solutions of boric and acetic acid is carried out provided that the burn occurred under the influence of alkali;
- Washing the eyes with a solution of ascorbic acid is indicated if aniline gets on the eyeball;
- Washing with water - used in other cases;
- Instillation of antibacterial drops;
- Applying tetracycline ointment - if the lesion spreads to the eyelid tissue, apply a cold compress.
To ensure patient comfort, it is recommended to close the curtains and turn off the lights. In the presence of pain, taking painkillers is indicated. If a burn occurs due to ultraviolet or laser radiation, eye rinsing is prohibited. You need to apply a special cooling compress to your eyelids and wait for the doctor.
Retinal burn: causes and treatment
Various external influences can lead to retinal burns. In this case, a burn of retinal tissue differs from damage to other tissues. In particular, when various chemicals (household chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes, alkalis, medicinal solutions, alkalis) come into contact with the cornea, damage to this membrane of the eye occurs.
The most severe burn damage occurs as a result of exposure of cells to caustic potassium, ammonia, slaked lime and ethyl alcohol. When the eye is burned, destructive processes occur that involve the membranes of the eyeball.
Typically, eye burns occur at work, while in everyday life such injuries develop much less frequently.
The cause of a retinal burn is often bright light, laser radiation or the influence of welding. Ultraviolet (sun) burn of the retina is more common than others. Unlike a chemical burn, this type of burn is less traumatic, but also causes unpleasant consequences.
First of all, in case of sun damage, the retina is destroyed. If you stay in the bright sun for a long time without protective glasses, you can get an ultraviolet burn. In addition, snow damage to the retina (snow blindness) is also known.
In this case, it is not direct sunlight that hits the eyes, but the reflection reflected from the snow. Due to the fact that these rays are focused on the retina, they quickly lead to burns.
For this reason, it is necessary to wear special safety glasses in the mountains, otherwise the risk of developing retinal damage increases.
The laser beam also has an adverse effect on the retina.
This type of injury most often occurs in people who are in direct contact (for example, work) with laser radiation.
Since the laser beam has enormous energy, retinal burns can be very serious. In production, an eye burn can be caused by accidental exposure to strong acids (sulfuric, acetic) and lime.
Treatment of retinal burns
When a foreign object enters the eye, a large number of different structures are usually affected. In this case, you need to rinse the eye with water or saline solution. To do this, use a large amount of liquid.
The procedure itself is carried out for 15-20 minutes, which allows you to remove most of the toxic substances from the surface of the eye. It is important not to waste precious time, but to rinse the eye immediately after the injury.
If this is not possible, then you should immediately seek medical help.
The exception is when alkali gets into the eye. In this case, it is strictly forbidden to wash your eyes with a rein, as this will intensify the symptoms of the burn. For these crevices, weak solutions of boric or acetic acids are used. Analine is often used in chemical production. In this case, a weak solution of ascorbic acid helps to cope with the burn.
If the patient has a thermal burn, it is advisable to apply an eye lotion with cold water or an antiseptic solution. After this, the damaged surface is treated with an antibacterial solution, and the patient is placed in a darkened room. Medical assistance should be provided as soon as possible.
In our ophthalmology center, all modern and effective methods of diagnosing and treating the retina are available: laser and surgical. By contacting our eye clinic, you can be sure of high treatment results and the professionalism of our specialists!
If the eyeball is damaged by a laser beam, ultraviolet light, or welding (mainly the retina is damaged), rinsing is not required. It is enough to apply a cooling compress, numb the pain in any available way and protect the eye from sunlight. After this, the victim should be taken to an ophthalmologist.
The doctor will examine the patient and give all the necessary recommendations, if followed, the burned retina and other eye tissues will be restored in the near future.
Source: https://ophthalmocenter.ru/setchatka-glaza/ozhog-setchatki-glaza.html
Treatment
In each case, the treatment uses medications whose action is aimed at restoring cells, as a result of which the patient’s condition improves. When treating a retinal burn, ophthalmological care is required, since the consequences can be very different.
Conservative therapy
Depending on the severity of the burn, therapy is prescribed; it can be carried out at home or in a hospital setting. One of the important elements of treatment are drops with scopolomine or atropine. Their use provides quick relief from pain and helps prevent complications. In rare cases, antibacterial agents are also prescribed.
For laser, thermal and chemical burns, the doctor prescribes tear fluid substitutes. Their action is aimed at moisturizing and restoring the mucous membranes; special gels (dexpanthenol, Actovegin) will help speed up the regeneration processes. The combination of drops and gels provides a longer healing effect; the mixture is not removed with tear fluid very quickly, which is appreciated by many ophthalmologists. When intraocular pressure increases, timolol is prescribed. Injections of glucocorticosteroids are prescribed for extensive damage to the visual system.
In addition to taking medications, regular eyelid massage and the use of physiotherapeutic methods are recommended.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in complex cases when other methods have shown complete ineffectiveness. During the operation, foreign objects are removed from the eye and corneal paracentesis is performed. If there is a risk of permanent loss of visual function, emergency surgery is indicated.
Folk recipes
The use of folk recipes will help speed up the recovery process; most often they are prescribed for thermal and chemical burns. Before using traditional methods, you should consult an ophthalmologist. Doctors recommend including fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, grated carrots mixed with sour cream in your diet.
Honey will help get rid of swelling and prevent complications; it is used in the form of compresses that are applied to the eyelids after the general inflammation has been relieved. Aloe leaves, which contain a large number of useful substances, also show high efficiency. The plant is used as a lotion, which is recommended to be applied to the eyelids several times a day.
When rinsing, instead of ordinary water, it is recommended to use a decoction of calendula, which is brewed like regular tea; it should be used after infusing for several hours. It is recommended to use the decoction several times a day.
Retinal burn: causes, first aid, symptoms, treatment
A retinal burn is a severe damage to the visual system that can cause vision loss. This type of damage is associated with exposure to external factors. When the retina is burned, vision deteriorates significantly, so if characteristic symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Retinal damage occurs due to:
- ultraviolet rays. The lesion does not cause loss of vision, but has a negative effect on the condition of the retina. More severe consequences occur when exposed to sunlight reflected on a layer of snow. In this case, the rays sharply enter the retinal area and can cause visual impairment. Damage also occurs if you do not protect your eyes during a solar eclipse;
- laser Laser burns can occur during laser coagulation and other procedures performed using laser devices. Damage occurs if the laser radiation is strictly directed. As a result, hemorrhage occurs, and if left untreated, visual function is partially or completely lost;
- chemical substances. The retina is affected when acids, alkalis, aerosols, paints, perfumes, medications, and alcohol-containing substances come into contact with the eyes;
- high temperatures. A retinal burn occurs due to hot liquid (water, oil) or steam getting into the eyes. Damage is also associated with exposure to molten metals and flames on the eyes;
- quartz lamp. Damage to the structures of the organs of vision can occur in a hospital or residential premises when quartzing is carried out with a special lamp.
There is also a combined burn, in which several factors act on the retina of the organ of vision. A classic example is a welding burn. In this case, the eye is exposed simultaneously to sparks and ultraviolet radiation generated during the operation of welding equipment.
An eye burn can be caused by instilling solutions into the eyes that are not intended for this purpose (drops for the ears or nose, alcohol tinctures). Damage can also occur during the process of eyelash extensions, due to poor-quality glue or incorrect procedure, or dyeing eyelashes with paint.
The risk of damage to the retina increases if a person, when in contact with harmful substances or devices that produce radiation, does not use personal protective equipment.
First aid
If you receive a retinal burn, you must call an ambulance. Before the arrival of doctors, you can perform first aid measures. They are to:
- Stop eye contact with ultraviolet rays and other light sources. To do this, you need to close the curtains tightly, turn off the bright lamps;
- Wear sunglasses to give the affected eye rest;
- apply a cold compress to the damaged eye for sunburn;
- rinse the eye with a weak solution of citric or acetic acid (a few drops per 500 ml of water). This should be done if the retina has been damaged by alkali;
- treat the affected organ of vision with a weak soda solution. This method is suitable if acid gets into the eye.
If the lesion is accompanied by severe pain in the eyes, then you can drip a solution of Novocaine or Lidocaine (2%).
To prevent the possibility of tissue infection, instill an antibacterial agent (Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin).
An eye with a burned retina should not be rubbed with your hands. It is also prohibited:
- wipe your eyes with dry wipes, a towel or clothing;
- apply a hot compress to the affected area;
- Continue contact with the source of the burn.
Until paramedics arrive, the victim must be in a horizontal position.
Degree of damage
Depending on the severity of the burn, the following degrees of retinal damage are distinguished:
- first. Features: redness of the skin around the eyelids, swelling of the cornea, burning sensation in the eye. At this stage, only the superficial part of the organ of vision is damaged;
- second. The cornea becomes cloudy, and white areas—dead cells—form on the surface of the mucous membrane. Colored spots flash in front of the affected organs of vision. This degree is characterized by damage to the deep tissues of the eye;
- third. A dense gray-white film forms on the surface of the burned eye. The victim feels severe pain. The conjunctiva becomes dirty yellow, the cornea loses its transparency;
- the fourth, the most difficult. Necrosis of all tissues occurs, the cornea is damaged or completely destroyed. Vision deteriorates significantly. Injury to the vitreous body and lens occurs.
First degree injuries can be treated safely. More severe injuries entail consequences that affect the victim’s ability to fully see.
Symptoms of a retinal burn
When the retina of the eye is burned, cells of the damaged tissues die, the blood circulation process is disrupted, and intoxication develops as a result of tissue breakdown.
As a result of eye damage from rays, chemicals or high temperatures, the following symptoms occur:
- redness of the eyeball;
- headache;
- inflammation of the choroid;
- burning, cutting pain in the organs of vision;
- intolerance to bright light;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- decreased visual acuity;
- profuse lacrimation;
- change in field of view;
- red-green spots before the eyes;
- redness or swelling of the skin of the eyelids;
- the appearance of yellow and white spots on the cornea.
The danger of an eye injury such as a burn is that its symptoms may not appear immediately. Sometimes this occurs only 8-10 hours after the lesion.
Diagnostics
To confirm the fact of a burn and establish the degree of its complexity, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- visual inspection;
- perimetry to determine the boundaries of vision;
- assessment of visual acuity using ophthalmological tables;
- assessment of intraocular pressure level;
- biomicroscopy to assess the extent of the lesion;
- fundus examination.
After obtaining a complete picture of the eye condition, the specialist will prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.
Burn treatment
Patients with damaged retina are prescribed the following groups of medications:
| Group and purpose | Names |
| Mydriatics (dilators for dilating the pupil, used for inflammatory processes, treatment of injuries and blockage of blood vessels in the eye) |
|
| Antioxidant drops (preparations for restoring visual function, improving the functions of the lacrimal gland and protecting the visual organs from adverse external factors) | |
| Local antibiotics (to combat the infectious-inflammatory process and prevent the addition of a bacterial infection) |
|
| Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal and steroidal (relieve the inflammatory process of non-infectious nature) |
|
| Metabolic (improves metabolic processes in the affected tissues of the eye and accelerates the process of their recovery). Such drugs are produced in the form of eye gel and drops. |
|
| Preventing dry mucous membranes |
|
At home, for first-degree burns and only with the permission of a doctor, you can use the following treatment methods:
- compress of grated raw potatoes. You need to apply the mass to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes;
- decoctions of chamomile or calendula. To prepare, pour a teaspoon of dry raw material into a glass of boiling water and let it brew. Use for rinsing affected organs of vision only when cooled down;
- lotions with aloe juice. Squeeze out the juice from large aloe leaves. Dilute a teaspoon of juice in a tablespoon of water. Soak a cotton pad in the resulting mixture and apply to the affected area for 10-15 minutes.
Surgical intervention for burn lesions of the retina is required in especially severe cases. Thus, a fourth-degree chemical burn requires removal of areas of necrosis.
Patients, depending on the degree of tissue damage to the organ of vision, are indicated for keratotomy (incisions on the cornea to restore visual function) or penetrating keratoplasty (transplantation of a healthy donor cornea in place of the damaged cornea).
Possible consequences
Chemical, radiation, thermal damage to the retina can cause:
- irreversible loss of visual function;
- cataract;
- secondary glaucoma;
- death of the eyeball;
- cicatricial changes in the eyelids;
- corneal clouding;
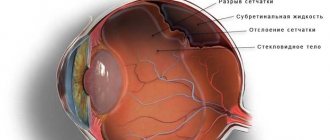
- retinal detachment;
- dry eye syndrome;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- fusion of the mucous membrane of the eye with the eyelids;
- obstruction of the lacrimal ducts.
Some complications can be corrected surgically, but treatment can begin no earlier than a year after receiving the burn.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of burn injury to the retina, you need to:
- strictly follow safety rules when working with chemicals, fire, and devices that are sources of harmful radiation;
- protect your eyes from the sun with glasses with high-quality lenses;
- Apply hairspray or perfume at a distance of at least 30 cm from the face.
At the first symptoms of thermal, radiation or chemical damage to the retina, you should consult a doctor. The sooner treatment measures are started, the greater the chance of maintaining visual function.
Source: https://oculistic.ru/bolezni/ozhog-glaz/prichiny-ozhoga-setchatki-glaza-simptomy-vozmozhnye-oslozhneniya
Consequences
The most severe consequence of a retinal burn is complete blindness; it can be temporary or permanent. Adequate treatment will help restore visual function; in severe cases, the cells are not restored.
Other consequences:
- Glaucoma - accompanied by atrophy of the nervous tissues of the visual organs, the phenomenon is observed against the background of increased eye pressure, which leads to blindness, the development of the pathology can only be slowed down, the disease cannot be stopped;
- Cataract is a film that forms on the surface of the eyeball, as a result of which visual function deteriorates; surgery is considered the only cure;
- Retinal detachment - occurs due to disruption of circulatory processes;
- Clouding of the cornea is often visually noticeable; medications are used in treatment;
- Scarring of the retina threatens degenerative tissue changes, the pathology develops slowly.
With burns of 2-4 degrees, the likelihood of burns increases significantly. A timely visit to an ophthalmologist allows you to avoid negative consequences. The doctor will help you get rid of the damage and prescribe therapy, which is carried out in a hospital setting.
Prevention
In practice, it is almost impossible to protect the retina from burns. Such injuries are most often associated with professional activities, so it is recommended to comply with all safety standards and rules in the workplace. When working with chemicals, it is recommended to wear safety glasses or a mask. To carry out welding work, you must wear a special mask. Special dark glasses will help protect your eyesight from sun and water glare.
An excellent preventive measure is visiting an ophthalmologist, performing special exercises, and taking multivitamin complexes. These actions will not protect against retinal burns, but will help strengthen and maintain visual function at the proper level.
What are the dangers of laser?
Technological innovations are always received with delight by consumers; they often rush to use devices whose effects are unclear and have not yet been studied. Laser devices and pointers are really convenient for work and study. In addition, such pointers are readily used by tourists on hikes as a signaling device or for setting firewood on fire, etc., but even low-power laser radiation can harm the eyes with prolonged exposure.
Those who use it should always remember the dangers of a laser: under no circumstances should its beams be directed into the eyes.
Laser contact with the eyes can cause painful, blinding injuries. The rays can cause burns to the eyes and cornea, and such thermal damage can lead to vitreous hemorrhages due to damage to blood vessels. The painful state of laser damage lasts several days; a person experiences unpleasant reactions to light, pain, and dry eyes.