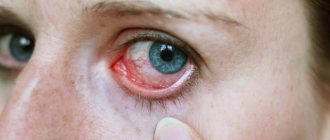
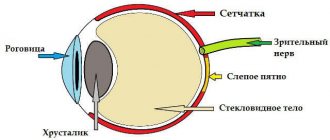
Retinal detachment is a serious eye disease that, without surgical treatment, most often leads to complete loss of vision. The human eye can be simply compared to the structure of a camera, the lens of which is the cornea with a lens, and the photographic film is the retina, an extremely complex multilayer structure, which is connected to the visual parts of the brain with the help of nerve fibers. Therefore, we can consider that the retina is part of the brain.
Retinal detachment most often takes the patient by surprise - before it appears, a person may have excellent vision and may not have any complaints. The rate of spread of the process is quite rapid, treatment in the vast majority of cases is surgical.
The timeliness of the operation gives a chance to preserve vision; in Germany, according to the standard, the operation must be performed within 24 hours after diagnosis. There are no such standards in Russia. But I tell every patient that retinal detachment is “like freshly frozen fish” - after a couple of days it is no longer “the first freshness”. There are many methods for treating retinal detachment, they differ in their mechanism of action, can be combined with each other, there are no better or worse among them - everything is very individual.
Prevention (but not immunity) for retinal detachment exists - this is laser photocoagulation of areas on the retina that can cause it. These are certain types of dystrophies, tractions, ruptures - but, unfortunately, not every patient believes in the need for these procedures, especially if nothing bothers them.
Early symptoms
The main symptomatic manifestations of the onset of the process of rhegmatogenous detachment are:
- Formation of floaters before the eyes. Such symptoms do not always signal retinal problems. If the symptom does not go away within a few hours, it is recommended to visit an ophthalmologist to prevent the development of the disease in the early stages.
- Flashes appear before the eyes. They develop as a result of disturbances in the perception of rays emanating from objects.
- Cloudy or blurry picture. With pathology, a veil appears before the eyes that cannot be eliminated on your own. Traditional methods are also powerless in the presence of fogging. For a quick diagnosis, the doctor needs to determine the period of onset and development of the disease. In the initial stages of the disease, clouding of the picture is observed after a night's sleep, which is due to the horizontal position of the body. When rising after waking up, there is a lag in the area of the organ of vision from the eyeball.
- Shadow in the central zone of vision. In this pathological condition, a ring is formed in the center of the gaze, which is called a Weiss ring.
- Complete loss of vision in one eye. Occurs due to disturbances in the metabolism of the organs of visual perception.
- Rapid loss of lateral vision. Due to the detachment of a section of the retina from the eyeball, the death of cones and nerve fibers is observed, which cannot be completely restored. Reduction or loss of lateral vision is also possible after the appearance of hemorrhages in the vitreous body.
- Deformation of objects. When the central zone of the eye surface is detached, visible objects may be distorted. There is also a change in letters when reading or the loss of several fields from the visible zone.
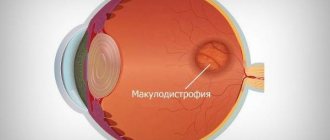
Complete detachment very rarely occurs rapidly. The manifestations of pathology can only be eliminated by surgical intervention, which must be carried out in a timely manner. In the initial stages of exudative detachment, an increase in visual defects is observed. When the macula is involved in the process, there is a noticeable decrease in the quality of the perceived image.
SYMPTOMS OF RETINA DETACHMENT
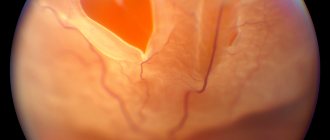
Comparing the eye with a camera containing film, we can say that somewhere on the edge of the frame a scratch has appeared on the emulsion layer. So what of this, you say, because almost the entire frame and most importantly - the center of the “composition” - are still clearly visible. It turns out that this is not entirely true. Fluid begins to penetrate through the gap, flowing under the retina and thereby peeling it off from the underlying choroid. On photographic film, it looks as if the emulsion layer around the scratch begins to swell with bubbles and peel off from the substrate. At this moment, a person sees a rather characteristic picture of a “gray curtain” at the edge of his field of vision. Depending on the location of the gap, the “curtain” can either quickly (over several tens of hours) spread, covering the entire field of view, or creep more gradually (over weeks, and in some cases months) to the central part of the field of view.
Vision during the development of retinal detachment
Quite characteristic of fresh retinal detachment is the symptom of “morning improvement”, when a person in the morning (after a long sedentary lying position) discovers a significant improvement (reduction of the curtain, its paleness and the ability to see through it). By lunchtime it gets worse again, and in the evening it gets even worse.
It is clear that if the rupture is located in the upper parts of the eye, then the liquid quickly falls down and peeling occurs rapidly. If the gap is located below, then the detachment slowly “creeps” upward, and progression will be slower. However, in this case, adhesions between the retinal zones and scars will be more pronounced - there will be more time for their formation.
Diagnostics
Timely detection of the pathological process makes it possible to prevent complications that develop as a result of detachment. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- vision level analysis;
- peripheral vision test;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- electrophysiological examination;
- study of the fundus;
- Ultrasound of the eyeball;
- slit lamp examination;
- biomicroscopy.
Having studied the anamnesis and the data obtained as a result of the diagnosis, the doctor makes a presumptive diagnosis and prescribes the necessary therapy.
DIAGNOSIS OF RETINAL DETACHMENT
The process of optical coherence tomography of the retina (OCT) in our clinic
Diagnosis of retinal detachment includes, first of all, a complete ophthalmological examination with testing of vision, intraocular pressure, examination of the fundus in various ways - contact and non-contact. Inspection in both vertical and horizontal positions may also be necessary.
Special additional diagnostic methods are:
1. Perimetry. A common symptom of detachment is a “veil” or “curtain” in front of the eye, it looks like this:
2. Ultrasound scanning in 2- or 3-dimensional mode. Allows you to determine the detachment through the opaque optical media of the eye or areas inaccessible to inspection... You can determine its height, the contents under it, the relief, the thickness of the membranes - this is important.
3. Electrophysiology - like an eye cardiogram - records electrical potentials from the functioning areas of the retina, indicating the degree of its damage.
4. Optical coherence tomography – we obtain linear sections of the retina to determine the anatomical parameters of the smallest sections in the central and areas close to it. The result can be a two- or three-dimensional image.
5. X-ray CT scan of the retina - provides visualization of the structures of the eye, down to the smallest details.
6. MRI - shows the degree of impairment and makes it possible to create a three-dimensional image of the eye.
Preparing for surgery
Emergency surgery is performed only in the presence of injuries to the apple of the eye and retinal detachment. Preparation for surgery consists of the following stages:
- 7 days before the procedure, complete abstinence from anticoagulants is necessary;
- before the intervention, it is forbidden to eat for 6 hours;
- It is not recommended to drink alcohol and smoke tobacco;
- If there are prescriptions for the constant use of medications, you must notify the treating ophthalmologist about this.
Classification of pathology
Clinical classification T.A. Bagdasarova, distinguishes three stages of retinoschisis:
- First. The retinal split is limited to a separate area, there is no vascular elevation, and there is no intraretinal fluid.
- Second. Retinal splitting progresses without a definite boundary between the affected area and the healthy retina. The formation of microcysts is detected in its layers.
- Third. The lesion with extensive cysts is localized in several quadrants of the retina. Their cavities rupture under the retina. There is a risk of transition of the pathological process to a limited detachment.
Surgical intervention
Retinal detachment can only be eliminated through surgery. When detachment of the epithelium with nerve fibers requires the following manipulations:
- Pneumoretinopexy. Air is used to eliminate the detachment. Using pressure, complete contact of the retina with the eyeball is created. Air bubbles resolve on their own within a month.
- Laser coagulation. The peeled tissue is sealed using a laser.
- Scleroplasty. The ophthalmologist glues the detached areas with a silicone strip and presses them down. The procedure allows you to return the retina to its place.
- Vitrectomy. During the surgical procedure, the vitreous body is removed and the space is filled with gas or a special silicone substance. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia, which is especially important in complicated forms of detachment of part of the visual organ. A small amount of silicone substance is introduced into the vitreous cavity. The duration of the procedure is from 2 to 4 hours.
Causes of retinal detachment
To understand the reasons, let's consider the mechanism of the disease. The development of the disease can be provoked by physical overstrain, sudden pressure on the surface of the retina, resulting in the appearance of small defects, with the appearance of which fluid from the vitreous body moves into the space under the retina. The resulting fluid begins to separate the retina. The more fluid leaks out, the larger the detachment area will be.
Basically, this disease is observed only in one of the eyes, but at the same time, it negatively affects the other eye. Therefore, both eyes are examined with equal care.
- The disease can occur through eye injury (penetrating injury). In addition to the retina, other membranes of the eye can be injured.
- Another reason for the appearance of the disease is diseases of the visual organs (uveitis, tumors of the vascular membranes, retinitis, age-related macular degradation, diabetic retinoptia and other diseases).
- The occurrence of peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophies, which cause visual impairment and can occur even in healthy people. In such cases, the disease can be detected using a three-mirror Goldmann lens.
Risk factors that provoke the disease:
- eye injury;
- retinal detachment in the fellow eye;
- the presence of this disease in close relatives;
- peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy of the retina;
- activities associated with constant physical stress and heavy lifting;
- the presence of various retinal pathologies.
Who is at risk?
- people diagnosed with diabetes mellitus;
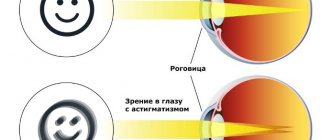
- people suffering from high myopia, astigmatism (as these conditions provoke thinning of the retina);
- athletes involved in hazardous sports (weightlifting, boxing, wrestling).
Rehabilitation and recovery
As a result of the intervention, the patient remains under medical supervision for several hours. Patients are prohibited from leaving the hospital on the day of the procedure. After surgery, side symptoms may appear:
- attacks of nausea;
- blurring of the picture;
- pain syndrome.
After the manipulation, a sterile bandage is applied to the organ of vision, which is necessary to prevent injury and reduce the load on the visual apparatus. Only a doctor can remove the bandage for examination or when indicated. It is not recommended to visit a sauna, steam bath or other thermal procedures during the rehabilitation period. The recovery period due to the manipulation ranges from 1 to 2 weeks.
Treatment
Treatment of rhegmatogenous and traction retinal detachment is only surgical. If local retinal detachment is detected, the first step is to attempt laser treatment on an outpatient basis. For widespread retinal detachments, it is recommended to be hospitalized in a specialized ophthalmological hospital as soon as possible after diagnosis to perform surgery under general anesthesia. Surgical treatment methods are extrascleral, intravitreal and combined. The choice of treatment method is determined by the vitreoretinal surgeon in each case individually and depends on the nature of the detachment, the duration of the process, the area of the lesion and the presence of concomitant intraocular and general somatic pathology. In the postoperative period, general and local anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is carried out. The rehabilitation period is long and can take up to 2 months from the date of surgery. In addition, in the postoperative period there is a strict ban on physical activity and thermal procedures.
The fundamental prognosis factor for the outcome of treatment and restoration of visual functions is the fact that the detachment has spread or not spread to the macular area.
If the detachment does not involve the macula, then the prognosis for visual acuity is favorable, but if the detachment extends to the central parts of the fundus and exists for more than 2 weeks, the final result will be questionable. However, surgery should be performed in almost all cases of rhegmatogenous or traction retinal detachment, since if normal anatomical interactions of the eye structures are not restored, complications may develop in the future (secondary glaucoma, subatrophy of the eyeball), which will pose a danger to the preservation of the eye as an anatomical organ. Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna
Prevention
There are no specific methods for preventing retinal detachment. However, by adhering to certain rules, you can diagnose the pathological process in time:
- if the first symptomatic manifestations occur, seek medical help;
- in case of injuries to the visual apparatus, visit an ophthalmologist;
- in the presence of any infectious processes in the area of the visual organs, carry out timely treatment;
- if you are nearsighted or farsighted, you must visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year;
- avoid sudden lifting of heavy objects;
- beware of blows to the head;
- It is not recommended to overstrain the visual apparatus;
- control physical activity.
It is impossible to completely prevent detachment using prophylaxis, but it will be possible to notice the pathological process in time.
Symptoms
Patients complain about:
- General decrease in vision.
- Distortion of visible objects.
- Partial loss of objects from the field of view.
- Poor peripheral vision.
- The appearance of a veil before the eyes.
The photo shows an example of how the field of vision narrows in a person with retinal detachment in an advanced stage.
The appearance of the provided signs subsequently of a fall, bruises, physical activity is direct evidence of retinal detachment in the patient. One of the most important signs is a narrowing of the field of vision.
Useful video
The symptoms of retinal detachment are not always pronounced, especially in the early stages. In the case of a pathological process, it is important to diagnose fiber detachment in time and prescribe therapy. Drug treatment does not give the desired result. Therefore, detachment at any stage of progression requires surgical intervention.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2029
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 3 ratings, average: 3.67 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Causes
The causes of retinal detachment, as mentioned above, may be the following factors:
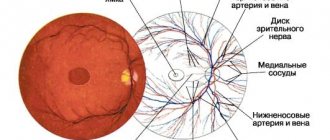
The photo shows a schematic representation of the process of retinal detachment
- Head injury.
- Eye injury.
- Myopia.
- Strong physical activity.
- Changes in the choroid.
- Modifications in the vitreous body.
- Untreated inflammatory processes of the eye;
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for the development of acquired retinoschisis is generally favorable. During treatment, it is possible to avoid the development of complications and preserve vision. To prevent the development of a pathological process, it is recommended to limit eye strain, get enough sleep, avoid fatty fried foods, and take enough fruits rich in vitamins.
With congenital retinoschisis, obtaining a favorable prognosis, in which there are completely no symptoms of pathology, is impossible without surgical intervention. Prevention of genetic changes responsible for the development of retinal separation is difficult.
Author of the article: Igor Mikhailovich Krivoguz, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.