The brain's ability to form new neural connections is important in the recovery of certain types of traumatic brain injuries. But today this process is difficult to study, and many questions remain. The results of a new study show that neurons can make new connections with the right types of photoreceptors to restore selective communication after injury.
Photo: Getty Images
Is it possible to restore vision?
Detachments vary in type and location. Doctors say that the most favorable prognosis for vision preservation can be given with peripheral detachment. If the pathology has affected the central part of the retina, the chances are less, but they still exist.
The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the higher the chance of saving his vision. But in any case, surgery will be required. Today this is the only way to stop the detachment and prevent blindness.
If a person has been diagnosed with retinal detachment, the ophthalmologist will offer one of the treatment options - ballooning, extrascleral filling, vitrectomy or laser coagulation. The choice of technique depends on a number of factors—the area of the detachment, the rate of progression of the pathology, concomitant diseases, and the patient’s medical history.
Filling and ballooning involve the installation of a balloon or fillings inside the eye, which press on the eyeball, ensuring a tight fit of the retina to the choroid in areas of detachment. Vitrectomy is a surgical operation in which the vitreous body is removed, and the vacant space is filled with a special fixing compound that does not allow the retina to move.
In the early stages of detachment, as well as when it threatens, laser coagulation is effective. This method is considered minimally invasive; patients easily tolerate this treatment. In the process of laser coagulation, the doctor uses a laser to “solder” the retina to the choroid, strengthening it in places of thinning and tears.
Early diagnosis of retinal detachment greatly increases the chances of preserving vision and allows for more gentle treatment methods. Therefore, at the first signs of pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Relevance of the problem
“We're not getting new neurons into the central nervous system, and even if we learn how to introduce new neurons, we still need them to integrate properly,” said Alexander Sher, study author at the University of California, Santa Cruz. (UC Santa Cruz).
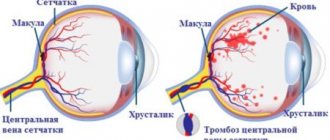
Vision loss from diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa results from degeneration of the light-sensitive photoreceptors in the retina. Medical researchers have begun to explore potential therapeutic methods to replace lost photoreceptors. However, this approach can only work if the new photoreceptors can be properly connected to the neural circuitry of the retina.
"Our results provide some hope that if new photoreceptors can be introduced and take root, the correct connections can be restored," said Alexander Sher.
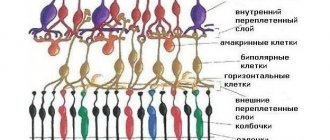
Like most mammals, ground squirrels have two types of photoreceptors for color vision: S-cone photoreceptors, sensitive to short-wavelength light, and M-cone, sensitive to medium-wavelength light. Neurons that connect to and transmit signals from photoreceptors are called bipolar cells. In dry proteins, each S-cone bipolar cell connects to only one S-cone photoreceptor and vice versa, resulting in a one-to-one connection between S-cones and S-cone bipolar cells.
How to understand that detachment has begun?
The following symptoms may indicate retinal detachment:
- Dark areas, cobwebs. Their location in front of the eyes is a projection of the detachment zones.
- Flickering, lightning before the eyes.
- Ring-shaped opacities.
- Distorted perception of the shape and size of visible objects.
- Deterioration of visual acuity.
- Fog or white veil before the eyes.
- Sudden loss or deterioration of lateral visibility.
Detachment is an insidious pathology because it is painless. Because of this, patients often consult a doctor at a late stage, when it is much more difficult to save their vision. Therefore, it is very important to be attentive to any ophthalmic symptoms. And if you notice at least one of the above, be sure to consult a doctor. Remember that the likelihood of avoiding blindness is much higher for those who start treatment on time.
Results of scientific work
“Scientists have developed antibodies that we can use to label both the S-cone photoreceptors and the S-cone bipolar cells in the retina and see what happens,” Sher said.
Researchers have discovered that bipolar cells left without a photoreceptor connection begin to grow new branches called dendrites.
. Because new S-cone bipolar cell dendrites randomly explore the layer of the retina where there are synapses, they bypass any M-cones they encounter and form only new synapses with S-cones.
"This tells us that selective connectivity can be restored in an adult mammal," Sher said. “How this might work in other parts of the brain, we don’t yet know. But for the retina, we will be able to create connections after the photoreceptors are lost.”
The authors of another study claim that an artificial retina will help restore vision.
Diagnostics
You can suspect that the retina is discharged and the number of light-sensitive cells on it has decreased if the patient has a clinical picture characteristic of this disease. To confirm the diagnosis, an ophthalmoscopic examination of the fundus is performed. To better identify structural abnormalities of the macula, the pupil can be pre-dilated. An ultrasound examination of the eyeball and its optical tomography are also performed. To identify abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels, angiography is performed, where an abnormal arrangement of blood vessels is detected, which means the wet form of macular degeneration. You can measure intraocular pressure and study the visual fields. It is also necessary to undergo a general and biochemical blood test.
Methods for restoring the retina
The choice of method for restoring the retinal membrane is influenced by the indications, the complexity of the damage, and the individual characteristics of the victim. There are three methods - peptide, laser, using stem cells. Each has its own contraindications and rehabilitation period.
Peptide
This method of recovery involves treatment without surgery. Peptides are used for therapy. These are short fragments of proteins of natural or artificial origin, consisting of 2-3 amino acid residues.
The effect is carried out at the cellular level, which as a result leads the tissue to a young age. The peptide method slows down the processes of photoaging and tissue wear.
The peptide technique restores metabolism and protein synthesis. The retina is strengthened. Treatment is prescribed by specialists, since it is necessary to take into account the degree of destruction of the retina.
Non-surgical eye treatment in 1 month.
Laser treatment
Laser treatment is carried out for serious violations of tissue integrity. This method of therapy strengthens the retinal tissue and prevents the development of detachment.
There are two types of laser treatment - slit lamp and Navilas®. Both methods of therapy differ in the method of application, that is, how precisely the laser is positioned on the retina.
Advantages of the innovative Navilas® technique:
- excellent accuracy and safety;
- convenient and comfortable;
- relapse is minimized.
Laser coagulation is an excellent prevention of degenerative processes of the retina, leading to a significant decrease in visual acuity.
After the procedure, vision becomes slightly blurry.
After a few hours, visual perception begins to recover, sometimes taking several days. After laser coagulation there will be a slight feeling of discomfort and headache. After retinal restoration, you cannot drive a car and you must undergo a rehabilitation course. For some time, the patient will need help from an outsider in performing simple household chores.
Stem cells
For the first time, stem cells were used to restore visual perception in 2021. Pigment epithelium was transplanted into a woman with macular degeneration. He has been living for more than 2 years and doctors have not found any signs of rejection or its further growth in other areas of the eye.
Stem cells are obtained from human umbilical cord blood, grown and regenerated a variety of organs and tissues. Therefore, parents hand them over after the birth of their child. Stem cells can be stored for up to 15 years and help in the treatment of not only eye diseases.
A new form of retina treatment will be available to everyone in the near future, a group of scientists claim. At the moment, an innovative method of retinal restoration is being tested; vision was restored to two elderly patients in March 2018.
The manipulation lasts 45 minutes under local anesthesia. From one embryonic cell, doctors obtained a 6-mm section with 10,000 pigment cells. Subsequently, patients require 12 months of clinical follow-up.
In Britain, after stem cell transplantation, scientists noticed significant improvements in vision. However, careful examination has shown that they are not an ideal replacement. Doctors found slight signs of rejection, but both patients saw well and remained relatively healthy.
Stem cells not only help regenerate the retina, they take part in the growth of new healthy tissues that fully function.
After receiving a positive result, the new form of retinal restoration was allowed to be tested on another 8 patients. If the technique proves effective, the result will be better than the previous one, but this technique will be introduced into clinical practice around the world.
This method of treatment can be used both for serious injuries to the visual analyzer and for preventing degenerative processes that arise due to age-related changes.
Retinal restoration occurs quickly, rehabilitation does not take much time.
Causes
Experts divide the causes of retinal thinning into two categories: local and general. So, the following reasons fall into the general category:
- chronic hypertension;
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- eye infections;
- complications as a result of the flu;
- diseases of the renal system.
The local category includes mechanical damage to the visual organs, myopia and inflammatory diseases.
A very important nuance is that the disease is hereditary. If there is a person in the family with this diagnosis, then the rest of the family members are recommended to visit the ophthalmologist’s office as often as possible for timely diagnosis.
Subtypes of the disease
The disease is divided into two subtypes: acquired and hereditary. In the hereditary form of the disease, experts distinguish two main types:
- Pigmented - as a result of a malfunction of certain receptors, twilight vision is impaired.
- Dotted white – the disease manifests itself in childhood and has a slow development.
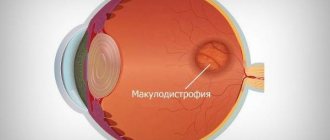
This disease is the most common cause of visual impairment in old age. The acquired type of disease is often associated with the aging of the body, since the development of the disease is observed only in people who have reached old age. In most cases, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of cataracts. The acquired type of disease is divided into:
- Peripheral thinning of the retina is a pathology that results in impaired quality of vision. In most cases, the occurrence of the disease is associated with trauma or inflammation of the organs of vision.
- Central retinal thinning is a process that results in the loss of central vision.
The central type of the disease has two pronounced forms:
- Wet - with this form of pathology, the functioning of the vascular system of the eyeball is disrupted, as a result of which the fluid circulating in the vessels begins to accumulate under the retina.
- Dry - with this form of the disease, in the gap between the vascular system and the retina, there is an accumulation of products formed as a result of the breakdown of nutrients.
Treatment
The prescribed treatment is directly influenced by the degree of development of the pathology and its type. Unfortunately, in advanced cases of the disease, it is not possible to restore the original quality of vision. To treat the disease in its onset stages, medications with vasodilating properties are used. In addition, vitamin complexes and drugs that strengthen the body’s vascular system are prescribed. Very often, specialists allow the possibility of using physical treatment methods. Such techniques include:
- therapy using microwaves and ultrasound;
- laser therapy;
- influence using electrical impulses.
Today, laser therapy is one of the best measures for the prevention of diseases of the visual organs. This method is used when patients cannot undergo surgery.
The tendency to thin the retina is inherited
Causes
The causes of retinal detachment depend on its type.
Rematogenous
So rhegmatogenous retinal detachment occurs for reasons such as:
- Peripheral retinal dystrophy with the presence of thinned areas.
- High and moderate myopia.
- Complications after cataract removal.
- Liquefaction of the vitreous body, detachment of its membrane.
- Genetic diseases (Stickler syndrome, homocystinuria, etc.).
- Inflammation and infection of the posterior segment of the eye.
Traction
Traction detachment occurs due to the appearance of dense adhesions. Their appearance is provoked by such serious diseases and injuries as:
- Diabetes.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Eye injuries and contusions.
Exudative
Causes of exudative retinal detachment:
- Congenital anomalies (coloboma of the choroid and optic nerve, vitreoretinopathy, etc.).
- Inflammation (ulcerative colitis, sarcoidosis, scleritis, etc.).
- Infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.).
- Kidney problems.
- Oncological diseases.
- Complications after eye surgery.
- Systemic diseases.
Are common
Common causes of retinal detachment:
- Problems with poor circulation;
- Viral infections;
- Stress;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Eye injuries.
Symptoms
The symptoms of retinal detachment are very characteristic, so it is difficult to confuse it with other diseases.
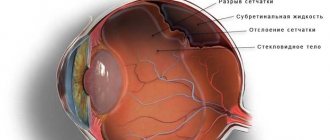
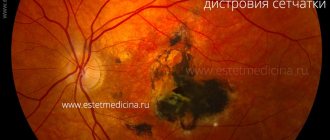
A person who has had a detached retina complains of a “curtain” appearing before his eyes, and it does not go away if he rubs his eyes or drops drops into them. Another characteristic symptom is flashes, floaters and lightning. If the detachment occurs in the central area, vision deteriorates and objects in front of the eyes are distorted. Fields of vision may become narrower.
This is what a person sees when the retina is detached
During detachment, a person does not feel any pain.
If the detachment occurs in peripheral areas, then visual acuity may not change, but if it is total, then this causes a significant deterioration in the quality of vision.