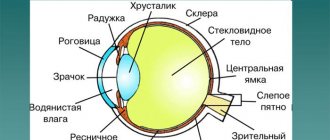
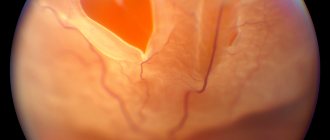
Angiography is one of the imaging methods that is used for a detailed study of the structural features and functioning of various parts of the vascular system. Retinal angiography allows you to obtain detailed information about the structure of the vascular wall, the state of the lumen and the functioning of the blood vessels of the fundus, in particular the retina and choroid, as well as the optic nerve.
Retinal angiography is used to detect changes in the vascular wall in certain pathologies (aneurysms and microaneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, vasculitis, hemangiomas, neovascularization), to identify benign and malignant neoplasms of the eye, occlusion of retinal arteries or veins, etc.
Principle of optical coherence tomography method
The principle of the method is close to that of ultrasound diagnostics, when tissue is examined using a reflected sound signal. OCT is based on the properties of tissues of different density to reflect differently the light signal directed at them.
OCT uses infrared radiation with a wavelength of 820 nm for scanning. A coherent infrared light beam is focused on the target tissue, partially scattered and partially reflected from internal microstructures. The reflected signal reaches the receiving device, undergoes computer processing and the result is displayed on the computer screen in the form of a color image. All information obtained during the study is stored in the form of graphic files - images in the database.
To improve perception, the tissue density on the tomogram is transformed into a color image with different shades that reflect the properties of the tissues. For this purpose, a special color scale has been adopted, where media that are transparent to a light beam are designated black, while denser structures are designated red and white.
The picture obtained during the study is very clear; the method greatly expands the diagnostic capabilities of the ophthalmologist.
Advantages of the OCT method
- The main advantage of OCT is the ability to study the finest structures of the organ of vision at the micron level, which ensures highly accurate results;
- OCT allows not only to identify, but also to quantify and record the condition of the retina, optic nerve, measure the thickness and determine the transparency of the cornea, and examine the condition of the iris;
- Objectively assess the degree of pathological changes in tissues;
- Accurately establish the localization of pathological foci, their number, size and other characteristics;
- Light scanning is performed in different directions, which makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the elements under study and record them in a series of images.
- The method is non-invasive, which means non-contact, does not require preparation, and has no age restrictions;
- There are no restrictions on the number of examinations, the possibility of multiple repetitions and saving the results in a computer database allows you to track the dynamics of the disease and monitor the results of treatment.
Information content of the method
As already mentioned, the method of light scanning of the eye, due to the accuracy of its results, opens up wide opportunities in the diagnosis of ophthalmological diseases. In terms of information content, optical coherence tomography can be compared with histological examination, only in the case of OCT a biopsy is not required.
OCT is most informative when examining the following eye structures:
- Front and rear cameras;
- Retina;
- Corneas;
- Optic nerve.
Types of angiography
Traditional angiography involves filling the vascular bed with a contrast agent. Thus, for retinal angiography, the fluorescein angiography (FA) method is used, in which the substance fluorescein is injected intravenously into the patient. As it is distributed throughout the vascular system, the contrast agent fills the vessels of the eye, which allows the doctor to assess the condition and functional capacity of the vessels of the head. Due to the need to administer a contrast agent, the method has a number of contraindications. For example, this study is contraindicated in case of allergy to contrast agents, severe renal failure, severe heart disease, multiple myeloma, severe diabetes mellitus, and dehydration.
Currently, methods that are safer for the patient are increasingly being used to visualize the vessels of the eye. One of these methods is optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the retina in angiography mode. The method allows the ophthalmologist to obtain an image of the vessels of the fundus of the eye without introducing contrast agents. The OCT angiography method is successfully used in leading ophthalmology clinics in Europe and America. We are pleased to announce that in our clinic you can also take advantage of the unique opportunity to perform OCT angiography of the retina.
Indications for optical coherence tomography
Due to the high sensitivity and accuracy of the method, the indication for its use can be almost any disease or damage to the organs of vision. Most often, OCT is prescribed for the diagnosis of the following pathological processes:
- Macular edema, macular holes and pre-breaks, degenerative changes in the macula
- Traction vitreomacular syndrome
- Various types of retinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa;
- Various corneal opacities, including after laser vision correction operations;
- Iridociliary dystrophies;
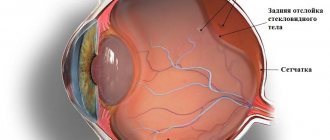
- Diseases and damage to the retina: degenerative processes, detachment, ruptures
- Myopia
- Neoplasms
- Acute conditions of retinal vessels: thrombosis, aneurysms, ruptures
- Glaucoma: in glaucoma, OCT allows assessing the functioning of the drainage system of the anterior chamber of the eye
- Atrophy and other diseases of the optic nerve head
- Diseases of the cornea: keratitis of various etiologies; damage;
- Structural anomalies
Optical coherence tomography is included in the complex of examinations in preparation for operations:
- Laser vision correction (LASIK, SuperLASIK, FEMTOLASIK and others)
- Keratoplasty
- Lens replacement operations.
The essence of optical coherence tomography
The essence of optical coherence tomography as a diagnostic method in ophthalmology is the ability to display the biological structure of eye tissue in microscopic detail.
This OCT study of the eye uses a low-power infrared emitter, which eliminates side effects.
In addition to known eye diseases, this diagnostic method makes it possible to identify rare, complex diseases of the visual organs and monitor the process of ophthalmological treatment.
Optical coherence tomography is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing vision.
What does OCT provide - optical coherence tomography?
Thanks to the detailed mapping of the structure of the eye, research using optical coherence tomography makes it possible to identify early abnormalities in the tissues of the eye, especially the anterior and posterior parts of the eyeball, optic nerve, retina, fundus, corneal transparency, macular holes, edema, dystrophies.
OCT results provide an opportunity not only to diagnose the early stages of abnormalities, but also to monitor the dynamics of the treatment prescribed by the ophthalmologist and its effectiveness.
How is optical coherence tomography (OCT or OCT) done?
No special preparation is required to perform OCT (OST). Optical coherence tomography of the retina and fundus is done without contact.
The optical coherence tomography procedure of the eye is done very quickly. For an OCT (OCT) examination, it is enough to fix your gaze on a special mark with your eye. Eye scans are completely painless.
OCT indications (OST)
Optical coherence tomography of the retina and fundus is indicated and prescribed in preparation for laser vision correction, keratoplasty, retinal detachment, macular edema and ruptures, thrombosis, diabetic retinopathy, edema, optic nerve atrophy, changes in the retina, glaucoma, keratitis, patients with intraocular lenses and in cases where accurate eye diagnostics is necessary.
Contraindications for optical coherence tomography (OCT, OCT)
OCT has virtually no contraindications and can be performed at any age, even for children over 7-8 years old. Optical coherence tomography is not prescribed for advanced cataracts, diseases of the vitreous causing its cloudiness, or the inability to fix the gaze within a few seconds of scanning.
This limitation is not due to contraindications, but to the impossibility, in these cases, of obtaining an accurate study result due to the lack of transparency of the eye being examined.
How does the procedure work?
Optical coherence tomography is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Patient registration, including last name, first name, age, study number.
- The patient is positioned in front of the fundus camera lens and is asked to fix his gaze on the mark. If the patient is visually impaired, he is asked to simply look straight ahead.
- The camera of the device is brought closer to the eye under the control of the retinal image on the monitor. As soon as the image appears, the camera is stopped.
- The camera is fixed at the found distance and the clarity of the image on the monitor is adjusted.
- Scanning in progress.
- Computer processing, alignment and removal of interference from the received data is carried out.
- Measurement of the objects under study, their optical density is analyzed.
- The results are saved in the computer's memory.
How is the OCT procedure performed?
To conduct an OCT examination, the patient does not require any prior special preparation. While sitting in front of a special installation, he needs to fix the gaze of the examined eye on a special mark. The operator performs several scans, and then the best quality and most informative image is selected from the resulting images.
The examination results are displayed in the form of various maps, tables and protocols, which enable the doctor to visually determine changes in the structures under study. For comparison, the OCT device is pre-installed with a normative database, which is inserted into the memory of the on-board computer by the tomograph manufacturers. The database also indicates the percentage of the number of healthy people with similar parameters of the examined tissues. Thus, the less often such indicators are detected in the population, the higher the likelihood that changes in the results obtained are a sign of pathology.
Decoding the results
When deciphering the obtained data, an analysis of the qualitative and quantitative indicators of the objects under study is carried out.
Qualitative (morphological) criteria:
- Changing the external contour of structural elements and layers of tissue;
- Changing their relative position;
- Relationships between the areas under study and neighboring tissues;
- Increase or decrease transparency;
- Are there pathological inclusions?
Quantitative indicators (measurements):
- Thinning or thickening of the studied structures and layers;
- Determination of volume
- Drawing up a map of the surface being studied.
Accounting for the results of optical tomography of the cornea
Structural pathological changes in the cornea and their localization are identified. The parameters of the found deviations are measured. The thickness of the cornea is calculated. Depending on the results obtained, methods are selected, treatment tactics are determined, and dynamics are monitored. In some situations, OCT is the only opportunity to carry out the entire diagnostic complex, since the method is non-contact.
Optical tomography of the iris
With OCT, the irises are studied:
- Anterior boundary layer;
- Stroma;
- Pigment epithelium.
Optical tomography of the iris allows you to identify diseases at the earliest stages, called preclinical - when there are no obvious clinical symptoms yet. It is possible to diagnose the following abnormalities and diseases of the iris:
- Frank-Kamenetsky syndrome;
- Pseudoexfoliation syndrome;
- Pigment dispersion syndrome;
- Essential mesodermal dystrophy.
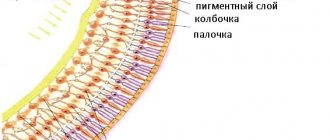
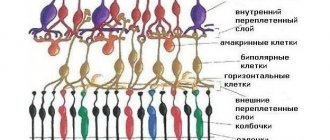
Optical computed tomography of the retina
Normal: the macula has a regular profile, the retinal layers are of uniform thickness, without focal changes. The thickness of the layers is measured; in the area of the fovea, the normal thickness of the retina is about 161-163 microns, at the edge - 234-236 microns.
Optic nerve OCT
The thickness of the nerve fiber layer is measured, which directly correlates with deviations in functional indicators, especially changes in visual fields. Optical scanning of the optic nerve head can be carried out in the annular and radial direction, which makes it possible to study its structure on a cross section and, after computer processing, obtain both averaged indicators and data for specific segments (on the clock dial) or quadrants (upper, lower, temporal, nasal). The obtained data are compared with the standards of normal indicators.
Such depth and accuracy of localization of foci makes it possible to identify both diffuse changes, for example, diffuse atrophy, and local defects of the optic nerve head in neurodegenerative diseases of the retina.
Fill out an application on the website, we will contact you as soon as possible and answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
What diseases can be detected using retinal OCT?
Optical coherence tomography is one of the most important studies in patients with pathologies of the optic nerve and retina. The method is indispensable for eye pathologies affecting the macular area. OCT is used in patients with:
- Glaucoma
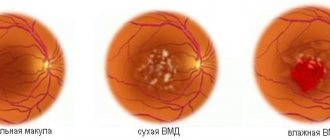
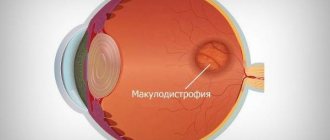
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Dystrophies of the retina (central and peripheral) and choroid
- Edema and macular hole
- Thrombosis of the central retinal vein
- Inflammatory diseases of the retina and choroid
- Neoplasms of the retina and choroid
You can undergo optical coherence tomography in our clinic quickly and without queues. Timely and high-quality diagnostics guarantee an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment that will preserve your vision!
To perform OCT, specialists at the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of the Retina use a new generation optical spectral coherence tomograph RTVue-100 (Optovue, USA) and the only Topcon DRI OCT Triton tomograph in Russia with an angiography function (OCTA). Thanks to the excellent detail of the resulting image, the devices make it possible to identify eye pathologies that cannot be detected using other methods. Among the features of tomographs, it should be noted the possibility of conducting a wider range of studies, the speed of the device, which reduces the time of eye examination, as well as the ability to obtain a two- or three-dimensional reconstruction of the area under study, and the possibility of performing retinal angiography without the use of a contrast agent.
Fig. 2 - Retinal angiography (OCTA) using the Topcon DRI OCT Triton device