A modern method of ophthalmological diagnosis, which is based on the injection of a contrast agent (for example, fluorescein sodium salt) into the patient’s vein and high-frequency photography of the fundus vessels, is called retinal fluorescein angiography , abbreviated FA.
The method allows you to record the passage of a contrast agent through the blood vessels of the retina and identify various vascular, inflammatory and degenerative changes in the fundus.
The essence of the diagnostic method
Fluorescein angiography (FA) is considered an informative ophthalmic diagnostic method, which is used to assess the condition of the retina and choroid of the eye. Briefly, the essence of the study is to contrast the vessels with a special dye, which can glow under the influence of light of a certain wavelength.
Fluorescein (a dye) is injected into a patient's vein, and then the ophthalmologist uses instruments to evaluate how the dye moves through the vessels of the eyes, and based on the observation results, draws conclusions about the condition of the retina or choroid.
Eye diseases
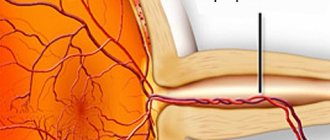
Angiogram of the Eye
An angiogram of the eye uses yellow (fluorescent) contrast and a special camera to take pictures, which then assess blood flow through the vessels in the back wall of the eye (retina).
During an angiogram, a contrast agent is injected into a vein in the arm. After administration, the contrast takes 10 to 15 seconds to distribute into the bloodstream throughout the body. When the contrast reaches the vessels of the eye, a series of images are taken to determine the patency of the vessels and the speed of blood flow in them. Several more photographs are taken after the contrast has passed through all the vessels of the eye to determine where the contrast is leaking from the vessels. If the contrast agent leaks from the vessels, it stains the tissues and fluids of the eye. Special filters on the camera allow you to see areas in the images that are stained with contrast. Fluorescein can be replaced with a contrast agent called indocyanine green. This allows specialists to see whether the vessels under the retina are damaged or leaking.
Unlike other angiograms, an ocular angiogram is not an x-ray procedure, so no radiation exposure is involved.
Why is this procedure needed?
An angiogram of the eye is performed in order to:
- Confirm the presence of abnormal blood vessels in or under the retina.
- Check for and locate bleeding vessels in the retina, especially if you have symptoms that indicate retinal damage or swelling, such as blurry or distorted images. The cause is often diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration.
- Helps detect inflammation or tumors in the eye.
- Accurately localize the area on the retina for subsequent laser surgery.
- Helps detect a blockage in the blood vessel that supplies or drains blood from the retina (retinal arteries and veins).
How to prepare
If you wear contact lenses, they should be removed before this procedure. After the procedure, do not put soft contact lenses back in your eyes for at least 4 hours, as they may be stained by the contrast agent used for the angiogram.
Before the procedure, be sure to tell your doctor if you have:
- In the past, there have been allergic reactions to X-ray contrast agents, iodine (which is part of the indocyanine green contrast agent), fluorescein, or drops to dilate the pupil.
- She had glaucoma, including closed-angle glaucoma. Some eye drops may be discontinued for you during the procedure. Before the test, the doctor may not use drops to dilate the pupils or replace them with others.
- You are taking any prescription or prescription drugs.
- You are pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Most doctors do not use this test during pregnancy, especially in the first 3 months of pregnancy and during breastfeeding.
Talk to your doctor about your concerns about having this test, the risks, how it will be done, and what results it might help you get.
After the study:
- Your vision may be blurry for up to 12 hours.
- You should not drive until the effect of the pupil dilating drops wears off. It is better to have someone take the doctor home.
- Until your pupil size returns to normal, you should wear sunglasses. Bright and sunlight can damage your eyes.
results
An ocular angiogram uses yellow contrast (fluorescein) and a special camera to take pictures and assess the state of blood flow through the vessels of the back wall of the eye (retina).
The study takes about 30 minutes. The results of the study are available immediately after the end of the procedure.
| Ocular angiogram | ||
| Norm: |
| |
| Pathology: | ||
| ||
Angiogram results are affected by many different diseases. Your doctor will discuss any abnormal angiogram results with you, taking into account your symptoms and medical history.
What might affect the study?
Factors that must be considered when interpreting results and affecting their accuracy include:
- Cataract.
- Insufficient pupil dilation.
- Inability to keep eyes wide open during examination.
note
- Most doctors do not recommend this test during pregnancy, especially in the first 3 months.
- Because contrast dye may pass into breast milk, you should not breastfeed your baby for 24 to 48 hours after the end of the test. During this period, it is better to pump out the milk with a special pump and pour it out until the milk becomes safe for the baby again. During this time, you can collect some milk in advance or prepare an artificial formula.
- The contrast agent is filtered through the kidney filter and excreted in the urine within 48 hours. Your urine may be light yellow or orange.
- Fluorescein is also used during applantation tonometry, a test that measures intraocular pressure. For more information, see the medical research section Tonometry.
- To diagnose eye diseases, it is better to use a contrast called indocyanine green, which can also be used instead of fluorescein. This allows doctors to determine the presence of bleeding abnormal blood vessels under the retina.
For what ophthalmic pathologies can a doctor prescribe FA?
Indications for performing FA may include various pathologies of the retina, capillary system, and choroid.
- Dystrophic changes in the retina, which were provoked by impaired blood flow and are accompanied by significant damage in the macular area (age-related macular degeneration, central serous retinopathy).
- Retinopathy developed against the background of diabetes mellitus.
- Acute conditions in which sudden blockage of blood vessels occurs and blood circulation in the retina is disrupted (thrombosis, occlusion of veins and arteries).
- A tumor or inflammatory process in the choroid.
- Optic nerve disc damage.
The method is used to confirm or clarify the diagnosis, in order to detect the localization of pathologies, the area of distribution, track the course of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen therapy. FA also allows you to determine whether there are indications for laser coagulation of the retina.
Fluorescein angiography of the retina in Moscow
To conduct angiographic examination of the retina, high-tech diagnostic equipment is used - a retinal camera. Using photo-video recorders equipped with the retinal camera, a contrast image of the fundus vessels is displayed on the monitor in front of the ophthalmologist.
In the Moscow clinic "OkoMed", when conducting FA, a modern retinal camera TRC 50EX (Japan) is used, which allows the study to be carried out quickly and with maximum effect.
For more information about undergoing fluorescein angiography of the retina in Moscow, please contact the consultants of the OkoMed clinic.
How is a diagnostic test performed?
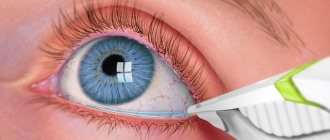
The patient sits in front of a machine called a fundus camera. The doctor instills a mydriatic drug into his eyes to dilate the pupil. At this stage, the first photograph of the fundus is taken, which will serve as a control. After this, an intravenous infusion of a fluorescent dye solution is given and the fundus of the eye is photographed every second for half a minute. After 20 minutes, if necessary, the retina is photographed again.
The main advantage of this diagnostic method is its high sensitivity, thanks to which the ophthalmologist can obtain information about even the smallest capillaries of the eye. To date, no other method provides such accurate information about the condition of the ocular vessels.
FA procedure
At the first stage of the procedure, the patient is instilled with drops that have a mydriatic effect. To ensure that the pupil dilates sufficiently, perform 2 instillations over 15-40 minutes.
After the pupil has dilated, the patient is seated in a chair facing the retinal chamber. The person being examined should wear comfortable clothing that does not put pressure on the neck and does not interfere with being in a sitting position. The patient's chin is placed on the stand, the forehead should rest against the bar.
Fluorescein injected into the patient's cubital vein quickly spreads throughout the body; the contrast reaches the retina in approximately 15 seconds. After this, a beam of light with a certain wavelength is directed into the eye that needs to be examined, and the contrast begins to glow. 25-30 images of the fundus are taken at a frequency of 1 image per second. If necessary, the patient is allowed to rest for 20 minutes, after which another 5-10 images are taken.
It should be emphasized that retinal fluorescein angiography findings should be interpreted by a trained and experienced ophthalmologist. By means of FA, the following are detected:
- neovascularization (excessive formation of new blood vessels);
- microaneurysms;
- porosity of the vascular wall, retinal edema;
- arteriovenous shunts;
- arterial occlusion;
- venous stenosis;
- recanalization of vessels during occlusion that has existed for a long time;
- leakage of dye into the disc area when the optic disc is congested;
- inflammatory and dystrophic processes.
During the FA study, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fever and other signs of dye intolerance, so the patient is under continuous medical supervision. If necessary, the patient is provided with immediate assistance.
Possible consequences of diagnosis
Immediately before the procedure, the doctor must warn the patient that FA in some cases can cause complications and unpleasant consequences.
- After FA for a couple of days, urine and skin may have an uncharacteristic color, which is due to the retention of fluorescein in the blood. To speed up the process of its elimination, it is recommended to drink more water and other liquids.
- Also, in the first days after diagnosis, the patient may have difficulty seeing close up, complain of pain in the eyes, or see objects in a red tint. Usually such symptoms go away quite quickly.
- Sometimes vomiting or nausea may occur.
- In rare cases, fainting, allergic reactions, and cardiac arrest are possible. Doctors in such situations always have the means to provide emergency assistance.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Preparation for retinal angiography
The examination is preceded by certain preparation of the patient:
- they explain to him what the essence of the research is;
- the patient gives consent to the study in writing;
- the doctor finds out whether the patient suffers from glaucoma, as well as an allergy to drops to dilate the pupil and contrast agents (a patient with glaucoma will have to refrain from instilling miotic drugs on the day of the procedure);
- the doctor informs the patient about the temporary side effects of contrast administration (changes in skin tone and urine color), short-term nausea, dizziness.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The main advantage of the FA method is its high sensitivity, which makes it possible to analyze the state of the vascular network, including capillary branches, the state of the optic nerve head and pigment epithelium, as well as choroidal vascularization.
The information obtained during the procedure makes it possible to recognize inflammatory and degenerative processes localized in different ocular structures and to judge the possible causes of lesions.
However, in the process of its implementation, serious complications cannot be excluded. These include allergic reactions that are dangerous to the patient’s health (bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, anaphylactic shock, respiratory arrest), in addition, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are possible. To minimize the risk of their occurrence, the procedure should be carried out in a room equipped for resuscitation measures. In particular, in case of anaphylactic shock, to help the patient, the doctor will need to administer adrenaline, antihistamines, and glucocorticoids. In this regard, performing FA requires medical personnel to have special training or carry out the procedure under the supervision of a resuscitator.
There are descriptions of fatal FA cases in the scientific literature, but their likelihood in practice is negligible. That is why fluorescein angiography is considered a completely safe research method, and most patients tolerate it without any discomfort. Moreover, before it is carried out, an intradermal test is done (according to the principle of the Mantoux reaction) in order to avoid potential complications of fluoroscein intolerance.
There is no alternative procedure that can provide equivalent information for the diagnostician, i.e. This procedure is unique in its own way.
In terms of implementation, FA is not the most complex research method, but high-quality interpretation of the resulting images requires the highest qualifications from a specialist. Today, this study is carried out in many ophthalmological clinics and centers, but when choosing a medical institution to perform it, you need to make sure that there is an experienced, qualified diagnostician.