Ultrasound of the eyeball (ophthalmoechography) is a modern diagnostic technique that allows you to assess the condition of the retina, lens, optic nerve, muscles and other structures. With the help of ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can obtain the most detailed information about the structure and functioning of the patient’s visual organs. If necessary, the procedure can be performed in conjunction with Doppler ultrasound, which shows the speed and volume of blood flow, as well as the patency of the blood vessels supplying the eye.
Indications for ultrasound of the eye and orbit
The ultrasound research method is prescribed for the purpose of:
- assessment of the bony receptacle of the eye (orbit);
- measurements of parameters of optical media;
- diagnostics and monitoring of treatment;
- detecting opacities in optical media;
- eye injury inspections;
- searching for a foreign body inside the eye: its location, position relative to the ocular structures, mobility, ability to be magnetized.
- examination for myopia and farsightedness, lens luxation, glaucoma, cataracts;
- inspection of the situation with retinal detachment: determining the type of detachment and stage of the disease, even in turbid environments;
- detection of optic nerve disease;
- determination of destruction of the vitreous body: ultrasound allows one to distinguish effusion from hemorrhages in the vitreous body, opacities from adhesions;
- measuring the thickness of fatty tissue localized behind the eyeball to differentiate different forms of exophthalmos - “bulging eyes”;
- determination of pathologies of the extraocular muscles;
- diagnostics and monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment of vascular diseases;
- identifying congenital abnormalities of the structure, as well as the blood supply to the eye.
- inspection of the condition after surgical interventions: assessment of the position of the implanted IOL, its dislocation and the possibility of fusion with adjacent structures;
- assessing the situation for the occurrence of complications in diabetes mellitus, hypertension, kidney disease, and increased blood pressure.
- Doppler examination of the fundus makes it possible to identify and conduct dynamic monitoring during:
- spasm or obstruction (blockade) of the central retinal artery;
- anterior ischemic neuroopticopathy;
- narrowing of the carotid artery (internal), which can affect the speed and direction of blood flow in the arteries supplying the eye;
- thrombosis of the vessels of the eyeball: central retinal vein, superior ophthalmic vein, cavernous sinus.
Ultrasound of the eyeball at the Miracle Doctor clinic in Moscow
- Fast Diagnostics takes about 20–30 minutes, a description of the results is prepared immediately.
- Painless ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure during which the patient does not experience discomfort.
- Informative For some eye diseases, ultrasound is the only approved diagnostic technique.
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
- suspicion of foreign body penetration;
- intraocular inflammatory processes;
- retinal detachment;
- tumor processes of any nature;
- identifying the causes of clouding of the optical media of the eye;
- pathologies of the extraocular muscles and vitreous body;
- before surgery to clarify the location and extent of eye damage;
- checking the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
As a rule, a study is prescribed if the initial examination by a doctor does not allow making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment.
Contraindications for ultrasound of the eyes
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most gentle and comfortable methods, so it has practically no restrictions. The examination is not scheduled or postponed in the following cases:
- the patient is in serious condition;
- there are open injuries (wounds, burns) on the eyelids;
- acute inflammatory process on the cornea of the eye.
In all other cases, diagnosis is carried out. Pregnant women and children can also be tested.
Study conditions
Ultrasound of the eye does not require special preparation or changes in your usual lifestyle. The only peculiarity can be considered a ban on applying makeup to the eyelids and eyelashes due to the use of a gel-like substance during the study, however, this restriction applies only to ladies.
It was clinically revealed that there are no contraindications to the study. Ultrasound examination of the eye is allowed for pregnant and lactating women, as well as for oncological and hematological diseases.
What does an eye ultrasound show?
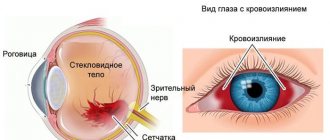
This study determines the size of the eye sockets, the composition of fatty tissue, its thickness, composition, the state of the optical media, muscles, the width of the optic nerve, and the length of the axis of the visual apparatus. Thanks to ultrasound, lens opacities, conglomerates with increased echogenicity, and hemorrhages are detected. To summarize, the diagnosis detects congenital and acquired pathologies, inflammatory processes, degenerative conditions and malignant neoplasms - things that threaten visual function and can lead to blindness.
Types of ultrasound of the eye (orbit)
Mode A (one-dimensional)
With it, the specialist sees a graph where the horizontal axis is the distance to the structure under study, traversed by ultrasound per unit time, and the vertical axis is the amplitude and strength of the echo signal.
This method is indispensable in determining the characteristics of eye tissue; it can be used to make various measurements, which is especially important before operations, however, the method is rarely used as an independent study.
Mode B
Shows a two-dimensional picture of the eye, where the amplitude of the echo signal is represented by dots of different brightness. This scan is necessary to reveal an accurate picture of the internal structure of the eye.
A+B-mode combined
Combines all the strengths of one- and two-dimensional research.
Three-dimensional echoophthalmography
Using computer programs, a three-dimensional three-dimensional image of the ocular media and vascular system is obtained; the program is capable of analyzing static dimensions and changes in curvature when the research plane moves.
Color duplex scanning
Analysis of a two-dimensional image of the eye in parallel with measuring velocity, as well as identifying the nature of blood flow in nearby vessels of any size.
Ultrasound of the eye at ON CLINIC
At the Ophthalmology Center ON CLINIC, ophthalmoechography is performed using expert-class equipment. Ultrasound of the eye is performed by experienced ophthalmologists who are certified to conduct ultrasound diagnostics of the visual organs. The excellent equipment of the Center allows for a comprehensive examination of the ocular apparatus in the shortest possible time at an affordable cost. Diagnostics are carried out by appointment and with a reserve of time, which allows the doctor to devote the time necessary to assess visual function. The conclusion is given to the patient immediately after ophthalmoechography.
Trust your vision to professionals - contact ON CLINIC!
Ultrasound examination procedure
An A-mode ultrasound examination involves the patient sitting to the left of the doctor and introducing an anesthetic into the eye being examined to numb the eye and ensure its immobility. Then, a sterile probe is used to conduct a study on the eye that is not covered by the eyelid.
B-scanning and any variants of Doppler ultrasound are carried out with a special sensor through a closed eyelid; the use of anesthetics is not required. A special gel is applied to the eyelid, which can be easily removed with a napkin after manipulation. The procedure is carried out within 15 minutes.
How is an ultrasound of the eyeball performed?
The Miracle Doctor clinic has high-quality specialized equipment for conducting various methods of scanning the visual organs. We can undergo a comprehensive examination for the most accurate diagnosis of eye diseases.
The ultrasound scanning procedure depends on the type of examination:
- To perform a B-mode scan, three-dimensional echography or CD, the patient enters the office, lies down on the couch and closes his eyes. A special gel is applied to the skin of the closed eyelids, after which the doctor begins to move the ultrasound device over them. The specialist may ask the patient to freeze or, conversely, move his eyes in a chaotic manner.
- A-mode scanning and ultrasound biomicroscopy are performed differently. The patient enters the office and sits in a chair. After this, the doctor instills anesthetic drops into the eye being examined. This is necessary in order to ensure the immobility of the eyeball, as well as to eliminate discomfort during the procedure. After this, a sterile device is applied to the surface of the eye and a scan is performed.
Prices for ultrasound of the eyeball are affordable for most patients, so postponing the examination if indicated is not recommended.
What will the examination show?
The interpretation of ultrasound data should be carried out by the attending physician. In order to determine treatment tactics, the specialist compares the results obtained with average parameters, which are considered to be the norm. Thus, a healthy lens and vitreous body are not visualized during the examination, since they do not reflect ultrasound waves. Interpretation of diagnostic results is the area of competence of the attending ophthalmologist. Based on the data obtained, the specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Ultrasound results
The interpretation of the results of the ultrasound examination is carried out by the attending physician on the basis of the obtained measurement data and the conclusion of the sonologist (ultrasound diagnostic specialist). So, normally:
- the lens is not visible (it is transparent), but its posterior capsule is visualized;
- the vitreous body is also transparent;
- the length of the eye axis is 22.4-27.3 mm;
- the refractive power of the eye is 52.6-64.21D;
- the optic nerve is presented as a hypoechoic structure 2-2.5 mm wide;
- the thickness of the internal shells is within 0.7-1 mm;
- the anteroposterior axis of the vitreous body has a length of 16.5 mm, its volume is about 4 ml.
Recording of ultrasound results
20/02/21
There are no unambiguous, strictly regulating documents on this issue, and different specialists record the results of their research almost arbitrarily. But there are still general principles for recording ultrasound results that should be followed in practical work: any ultrasound must be recorded. Conducting an inspection without issuing a written protocol is unacceptable.
— three options for drawing up an ultrasound protocol are possible: recording by hand in the outpatient card (doctors very often write illegibly), recording on a special form (template) (part of the protocol is again written by hand - illegible) and drawing up an electronic protocol on a computer in a special program with archiving the electronic version and printing a paper copy for the outpatient card (one copy is given to the patient). It is the latter option that is used by our clinic. The electronic version is preferable, since all information is archived at the same time and there is an opportunity at any time to familiarize yourself with the results of the studies performed, as well as print a copy of the protocol, which is especially important if the patient suddenly lost it.
— any protocol in our clinic consists of two parts: The first of them is descriptive. This is a large part of the text in which the doctor records the echographic picture, lists the examined organs and gives their echographic characteristics, indicating the sizes of the organs. This part of the protocol is mostly needed for the doctor himself and his fellow specialists. The second part of the protocol is the conclusion. This is a short summary of what the identified structural changes mean.
— it is necessary to separately note the eligibility and need to accompany the ultrasound protocol with the issuance of echograms (photos). You should know that an echogram is not a medical document, since there is no strictly standardized layout in which this echogram was obtained, and it is impossible to clearly indicate the patient’s position on a specific echogram. Accordingly, “foreign” echograms are not subject to consultation, but rather are needed as evidence of the actual existence of some pathological focus. A doctor who has received an image recorded on an echogram can always navigate it better than his colleague who has not seen the patient (with the exception of only a few studies). In our clinic, echograms are recorded in the protocol, but only if there is a need for this (this issue is resolved by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist in each specific situation and mainly only in the case of a pathological process). In the absence of any echographic changes in the organs, echograms are not printed in the protocols.
— in addition to the components of the ultrasound protocol listed above, some protocols can be supplemented with additional parameters (adequacy of patient preparation, recommendations if there is a need for another research method, etc.).
In our clinic, ultrasound doctors in their protocols indicate as much as possible (complete) all the necessary information for your treating doctor.