Oculist or ophthalmologist – which doctor should I make an appointment with?
There is a common misconception that an ophthalmologist is a doctor who sees patients in a clinic and is more involved in diagnosing health problems, and also recommends preventive measures to maintain visual acuity. These same people are sure that an ophthalmologist is a different doctor who sees in a hospital, performs complex manipulations, performs operations, and prescribes serious treatment. This opinion is wrong.
The doctor who tests your vision is both an optometrist and an ophthalmologist. Even in translation, both words will be translated only as “eye”. Only “oculus” is a Latin word, and “ophthalmos” is Greek. Both names give names to professions, but such doctors do one thing - eliminate eye diseases.
Just a couple of decades ago, Soviet clinics consisted mostly of oculists. But many years ago this should have been abolished, and all specialists were transferred to a new one - ophthalmologist. Oculist is more of a popular name, which is pronounced by many in the old fashioned way.
Jaundice of newborns
A couple of days after birth, the baby’s skin and the whites of the eyes take on a yellowish tone. This condition is caused by the oversaturation of the fetal blood with a huge number of red blood cells during intrauterine formation. After birth, the body no longer needs so many red blood cells, for this reason some of them begin to break down.
Jaundice in newborns is the result of accumulation of red blood cell destruction products. After 7 or 10 days, the yellowness of the skin and eye whites decreases. If this does not happen, there is reason to assume the development of pathology in the newborn.
When should you make an appointment with an ophthalmologist?
This is a vision doctor who sees both in clinics assigned to certain areas and in hospitals - in hospitals. Specialists help people diagnose the problem and find a way to get rid of the disease. Once you find out which doctor checks your vision, you can safely make an appointment with someone who:
- Wears glasses or uses lenses to correct vision. Periodic examinations, like other doctors, are recommended on a regular basis.
- Can't see well or feels like he's losing his sight. Often prescribed glasses or suggested lenses do not solve the problem of visual acuity, which can sharply or gradually decrease.
- Suffered eye injuries, which require immediate examination by a doctor.
- Due to the nature of his service, studies, and scientific activities, he spends a long time behind a computer screen.
- Has a genetic predisposition to developing certain eye diseases.
- More hypertension or has problems with blood vessels, hormonal levels, diabetes, etc.
- Reached the age of 45 years.
- He previously underwent eye surgery, and therefore any condition requires monitoring by a doctor.
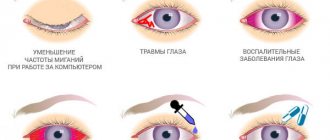
- Has inflammatory processes in the organ of vision - they are indicated by itching, burning, pain, pain, redness, purulent discharge, etc.
- Complains of poor vision - this could be a different disease. Among the most common are myopia (nearsightedness), farsightedness, astigmatism, glaucoma, cataracts, strabismus, etc.
Both children and adults should visit a doctor. The former are at risk of losing visual acuity due to the fact that they spend a lot of time reading books, studying, and playing with gadgets. The frequency of examination is determined by the doctor, but as a preventative measure it is recommended to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
What is post-Covid syndrome?
The National Institute for Care Excellence (NICE) in the UK has developed recommendations that if signs and symptoms of the disease persist for 4 to 12 weeks, it is ongoing symptomatic COVID-19; If symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks and are not explained by an alternative diagnosis, then it is most likely post-Covid syndrome.
So, recovery time is different for everyone: for many, symptoms last less than 12 weeks after an infection, for others it lasts longer. If symptoms do not disappear or new ones appear within 4 to 12 weeks, it is recommended to consult a doctor and get tested.
I would like to especially note: there is no need to engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. Only a doctor can interpret research results and prescribe therapy if parameters deviate from the norm, as well as monitor test results over time.
What diagnostic tests does a doctor perform when checking your vision?
In the office of an ophthalmologist (old - ophthalmologist), the doctor conducts a visual examination of the patient, studies the medical history, if any, and also asks questions to the patient. Only after this can equipment and various techniques be used to test visual acuity. Among the methods used by an ophthalmologist to diagnose his patient:
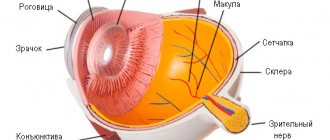
Ophthalmoscopy - the doctor will use special instruments to examine the fundus of the eye. This method allows you to assess the condition of the vascular network, optic nerve and retina.
This method is good for diagnosing the cause of vision impairment. An experienced vision examiner will be able to make an accurate diagnosis, which may be hypertension or diabetes.
- Tonometry. A special instrument is used to check eye pressure.
- Skiascopy. This is a process that in practice can be called “shadow testing”. It involves studying the characteristics of light refraction in the eye in a dark place.
- Biomicroscopy. This technique is often used by ophthalmologists in their practice. It does not cause any inconvenience to the patient, but involves examining the anterior segment of the eye under a microscope - a special magnifying glass and a slit lamp.
- Visometry is a procedure that absolutely all patients who see an ophthalmologist undergo. The technique involves testing visual acuity.
- Iridology. This is a fairly rare technique, but it is also sometimes used by ophthalmologists. They check for pathological changes in the iris of the eye.
To check visual acuity, a tabular section is used, which has 12 lines. The first ten should ideally be considered by people with 100% vision. The bottom two can be seen by people with farsightedness or acute vision. Depending on which row in the table is visible to a person, the disease or its absence will be determined. It may also be that the eyes see differently, and therefore each one will be checked separately.
Liver problems
The yellow color of the whites of the eye in certain cases can be explained by an increase in bilirubin levels. Bilirubin is a kind of enzyme that contains red blood cells. Its breakdown leads to the appearance of yellowish spots. This enzyme is formed by the liver, for this reason the presence of yellowness in the whites of the eyes can be explained by liver disease. In this case, a visit to the doctor is necessary, since malfunctions in the functioning of this organ negatively affect the state of health as a whole. After all, the liver is the main filter of the body, and its damage leads to general intoxication.
Preventive actions
It is also important to pay increased attention to tips for preventing yellowing of the sclera of the eyes in people of different ages:
- You should adhere to a diet that excludes alcohol, smoking, pickling, fried foods, and flour.
- Balance sleep, rest and activity (sleep at least 8 hours).
- Set intervals when working on a PC and do eye exercises.
- Taking multivitamin complexes and specialized eye vitamins will help avoid many problems.
The main preventive measure to avoid various diseases is considered to be taking care of the immune system, which consists of leading a healthy lifestyle.
Factors and causes of the disease
Under what circumstances does stye appear? One and often the only causative agent of this pathology is Staphylococcus aureus. This microorganism lives everywhere, on the skin, on the hair. Very rarely, streptococci cause this disease. There are a number of factors that cause microorganisms to penetrate and multiply:
- staying in the cold for a long time;
- stressful conditions;
- hard physical labor;
- excess load, both physical and mental;
- violation of eating habits;
- malnutrition;
- diets for weight loss;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of various parts of the digestive system (absorption of essential vitamins and minerals is impaired);
- carriers of Staphylococcus aureus;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- the presence of worms in the human body;
- heredity to the development of barley;
- gross violations of personal hygiene rules;
- use of lenses;
- weakening of the immune system.
Symptoms of styes on the visual organ
In order to correctly diagnose this pathology, you need to know a number of symptoms. It is very easy to diagnose if it is an external stye. A visual examination of the patient is sufficient. When externally there are the following symptoms:
- swelling of the eye;
- burning;
- hyperemia;
- excessive production of tears;
- the patient's complaint about a foreign body in the eye;
- yellowish bubble;
- unpleasant sensation and discomfort when blinking;
- palpation of the eye causes moderate pain;
- local temperature increase.
The above symptoms begin to appear sequentially.
With internal barley, damage occurs inside the organs of vision, along the inner surface of the eye, where there is a mucous membrane. In 80% of cases, internal stye is complicated by chronicity of the process and chalazion. A yellowish-gray bubble at the site of inflammation occurs with both external and internal barley. This bubble appears on the 5th day from the moment of illness. The bubble itself begins to open on the 4th day from the moment it appears. The autopsy is characterized by copious discharge of pus and mucus.
In patients who have bilateral stye, some other symptoms also appear:
- regional enlargement of lymph nodes:
- general malaise;
- weakness, apathy;
- febrile body temperature;
- sleep and appetite disturbances.
Rules for caring for eyelids with blepharitis
Patients who have been diagnosed with blepharitis are advised to start their day with eyelid hygiene. You cannot use cold water to carry out water procedures for blepharitis: if you are used to taking a contrast shower, you can do this, the main thing is that this water does not get on the affected eyelids. Cold water can cause venous congestion and aggravate blepharitis, making treatment more difficult. Therefore, it is worth rinsing the eyelids with warm water, which causes arterial hyperemia, which brings you several steps closer to recovery.
After washing, you need to drip your eyes with a solution of “Novocaine” or “Dicaine” - this will help eliminate discomfort and prepare the eyes for the massage that needs to be carried out at the next stage. To make the task easier, you can purchase a special glass rod with a ball (used for applying ointments) and a spatula (indispensable for massage) at the pharmacy.
During the massage, you need to make small pressures, moving from the middle to the edges of the eyelids. During the procedure, bubbles or clots of secreted secretion will appear on the edge of the eyelids. It is necessary to massage both the upper and lower eyelids.
When the massage procedure is completed, the eyelids should be wiped with an ether-alcohol mixture, which the attending physician will help you choose. A cotton swab needs to be moistened in the solution, squeeze out excess liquid (it should not get into the eyes) and begin removing the secretion, moving from the inner corner of the eye. The same composition can eliminate scales and crusts.
At the last stage of the daily multi-step care regimen, it is necessary to apply drops to the eyes or apply an ointment prescribed by the attending physician. You should not take the initiative and select medications yourself, especially antibiotics. Incorrectly selected products can worsen the course of the disease, causing irritation or allergic reactions.
Classification of blepharitis
Let's figure out how blepharitis develops and how this disease is classified.
Anterior blepharitis occurs after a staphylococcal or seborrheic infection, as well as tick infection. Usually in these cases the edge of the eyelid is affected, near the eyelashes. A characteristic feature of this type of blepharitis is a change in the structure of the eyelashes and the sebaceous glands located in close proximity to them.
If blepharitis occurs as a consequence of a staphylococcal infection, then at the base of the eyelashes there is an elevation of the upper layer of the epidermis. If a “sleeve” forms at the base of the eyelashes, then blepharitis was caused by a mite.
With a seborrheic infection, the sebaceous glands become more active, resulting in eczema and ulcers. This feature entails serious complications, for example, deformation of the ciliary row, entropion of the eyelids and profuse lacrimation.
Posterior blepharitis is characterized by the appearance of papillomas, the cause of which lies in proliferative inflammation. Meibomitis occurs due to blockage of the excretory ducts and problems with the outflow of secretions from the sebaceous glands. The secretion is good food for bacteria that penetrate the tissue layer and provoke the development of the inflammatory process. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea, causing the appearance of keratitis, dry eye syndrome and a number of other diseases.
How to get rid of blepharitis?
Scientists have made significant progress in developing ways to get rid of such a complex disease as blepharitis. Medicines were created and effective physiotherapeutic techniques were developed. However, it is still impossible to get rid of blepharitis quickly and without the help of a specialist. The treatment will be complex and quite long, it requires persistence and thorough implementation of all instructions. The most important stage is identifying and eliminating the cause of the disease. Otherwise, it will continue to progress and recur.
General rules for the treatment and prevention of blepharitis
To prevent the progression of the disease, you should not try to cure yourself and use traditional medicine without consulting a specialist. Often, in an attempt to relieve themselves of unpleasant symptoms, some people purchase over-the-counter drugs and begin treatment that turns out to be ineffective. As a result, blepharitis not only cannot be cured, but it develops even more.
To detect vision problems in a timely manner, you need to regularly have your vision tested in the ophthalmologist's office. This is especially necessary for those whose age exceeds 40 years, because during this period the refractive power of the lens decreases, and therefore the eyes begin to quickly get tired and problems arise when working with objects at close range. All this can cause blepharitis.
If blepharitis develops as one of the symptoms of diabetes or diseases of the digestive system, then special attention should be paid to treating the root cause and strictly follow the diet prescribed by the doctor.
If blepharitis occurs as an independent disease, you do not need to follow a diet. There is only one rule in this case: the diet should be full of foods rich in vitamins and microelements. The ideal option is a dairy-vegetable diet, without fast food, fried foods and other harmful foods. In this way, you can increase the secretion of gastric juice and improve the condition of the eyelids with blepharitis.
It is also necessary to pay special attention to the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, try to avoid colds - all this contributes to the exacerbation of blepharitis.