With age, the human body undergoes profound changes, leading to tissue wear and a slowdown in metabolic processes.
If a person has bad habits and leads a sedentary lifestyle, this aggravates his condition. Against the background of rapid fatigue and general fatigue, various “sores” begin to appear in the body. This list includes retinal atrophy .
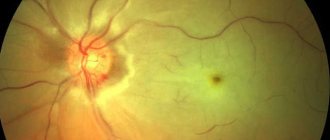
Retinal atrophy as a consequence of dystrophy
Retinal atrophy as a consequence of dystrophy Source: tvoiglazki.ru Retinal atrophy is a consequence of the lack of treatment for dystrophy - a dangerous disease that affects the retina of the eyes.
It is very important to recognize the disease in time and eliminate it, since tissue atrophy can be an irreversible process leading to their subsequent death. Retinal atrophy is one of the most common causes of vision loss in older people. In medicine, atrophy is understood as a decrease in size of an organ with loss of its function, caused by a significant decrease or cessation of nutrition.
The word “atrophia” is literally translated from Greek as lack of food, starvation. Due to the fact that the cells do not receive the necessary nutrition, serious visual impairment occurs, which can lead to blindness.
Atrophy is a process of reducing the size and volume of tissues and organs, which has a pronounced change in cell structure. An atrophied retina can completely deprive a person of vision.
It all starts with a slight deterioration of the image and leads to its disappearance. The presented process is the next stage after dystrophy.
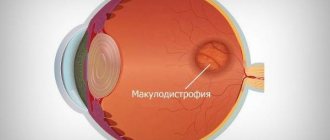
Accordingly, atrophic changes in the retinal area lead to degeneration of its tissues, especially the central region, called the macula or macula. Dystrophic changes in this area lead to a person’s loss of central vision. Otherwise, this pathological process is called age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Macular degeneration refers to a whole group of pathological changes that lead to the same result, the development of blindness in older people (55 years and older).
The pathological process is based on the phenomena of ischemia, that is, a violation of the nutrition of the retinal tissue. They lead to hypotrophy and then degeneration of tissues on which a person’s central vision depends.
With atrophy begins its thinning and loss of vitality. First of all, the macular area of the retina, which is responsible for the clarity and sharpness of the image, is affected. Therefore, one of the very first symptoms is a blurry picture before the eyes, which is not associated with the presence of objects near or far.
Over time, the disease progresses, and it becomes increasingly difficult for a person to carry out even ordinary household chores, not to mention some more serious work.
Of course, wearing glasses and other things will not help in this situation. Without knowing what exactly is happening to the eyes, a person loses time and the chance to stop the progression at least where it is at the moment.
Given the lack of wide-spectrum symptoms, it is simply impossible to independently figure out what is happening to the eyes. An in-person appointment with an ophthalmologist is required to examine the fundus and make a diagnosis. There can be no independent treatment in this case.
However, a significant difference is the fact that the disease does not go away on its own or from the influence of external factors, no improvements occur, on the contrary, the clarity of the image becomes worse and worse. The sooner a person worries and applies, the better the outcome awaits him as a result of treatment.
Of course, most of the changes are irreversible, but in the initial stages of the disease it is still possible to preserve vision at least at some level, and in some cases it is possible to help with the help of modern treatment methods.
The mechanism of its development
Retinal atrophy is also called the process of age-related macular degeneration. The only symptom of the disease is decreased visual acuity. Atrophy is the next stage after dystrophy. It can be mild or severe. The main symptom of the disease is progressive loss of vision.
The causes of the disease may be the following factors:
- Blood diseases. The presence of problems with the circulatory system impairs the nutrition of the retina. In the absence of the necessary substances and elements, it ceases to function normally.
- Heredity. If there are people in the family with such a diagnosis, it is most likely that it will manifest itself in one of the family members. As a rule, it is diagnosed at an early age.
- Hormonal disbalance. The process can be activated due to imbalance of hormones, infectious diseases and problems with the endocrine system.
- Violation of material metabolism. A lack of nutrients in tissues can lead to their atrophy. Atrophy can also be caused by various eye injuries, chronic diseases of the organs of vision, heart problems, myopia and others. Bad habits also have a negative effect on the retina: smoking and drinking alcohol.
Types of atrophy and how it manifests itself
Source: o-glazah.ru Retinal dystrophy leads to vision impairment.
It is a process of degeneration that is irreversible. There are the following types of dystrophy:
- Central. It manifests itself as a decrease in central vision, while peripheral vision remains normal. A person with this form of the disease is unable to fully drive, write or read.
- Peripheral. Provides peripheral vision damage. It may not be diagnosed for a long time, as it does not have pronounced symptoms.
- Chronic. Caused by the aging process. Sometimes it can appear together with cataracts.
- Hereditary. There are two types: pigmented - causing damage to twilight vision receptors, dotted white - diagnosed at an early age.
Types of disease
The retina is an important part of the human peripheral analyzer that perceives visual information. The area that has the maximum number of receptive elements (cones and rods) is called the macula (macula).
It is in this part of the retina that the image is focused and is responsible for clarity of vision. It is the macula that is directly responsible for a person’s ability to see images in color.
With age, processes of tissue death begin in the tissues of the macula. This applies to both the pigment area and the vascular network that feeds the macula. The onset of changes does not always occur in old age.
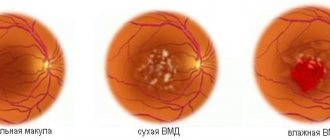
A person can notice the first signs of pathology even before the age of 55. By old age, the process develops so much that complete loss of vision is possible. The disease occurs in 2 forms - dry and wet:
The dry form is more common; it develops due to decreased nutrition of the macular area and its thinning or due to pigment deposition. Sometimes both changes appear one after the other. The diagnosis of dry AMD is made when tissue breakdown products are deposited around the macula.
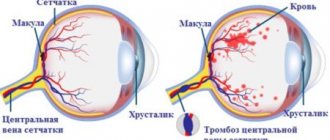
The wet form is more severe, progresses faster, and occurs against the background of dry atrophy. It is characterized by the germination of blood vessels in the retinal area where they should not be. In its extreme stage, the pathological process can take on a scar form, leading to complete loss of vision.
This happens if the pathological process develops against the background of metabolic or vascular disorders (diabetes, obesity). In severe cases of the disease, the retinal tissue peels off and is replaced by connective tissue. A scar forms.
Classification
Depending on the characteristics of the pathological process, there are 2 forms of retinal atrophy:
- Dry. Occurs in 90% of cases, occurs against the background of deteriorating nutrition of the macular zone and deposition of pigments, causing its thinning. The progression of the pathological process occurs gradually over a long period of time. In most cases, one eye is affected first and then the other.
- Wet. It occurs against the background of advanced dry atrophy of the retina and is characterized by pathological growth of blood vessels into the retina area. This form is characterized by a more severe and rapid course. If left untreated, scarring begins, causing complete loss of vision. Scars are usually formed as a result of metabolic disorders or vascular pathologies. Wet atrophy predominantly occurs in people suffering from obesity and diabetes.
Taking into account the mechanism of development, the pathological process is of the following types:
- Non-exudative atrophy. It occurs most often, occurring against the background of age-related changes in the structure of the retina and metabolism. A drusen forms under the macula, which causes areas of atrophy. Progressive atrophy leads to gradual loss of vision.
- Neovascular. New vessels begin to appear in the structure of the retina, which provoke fluid accumulation. This leads to swelling of the macula and subsequent degeneration. It can be classic, hidden and mixed.
- Scarring macular degeneration. Pathological changes lead to retinal detachment, as a result of which scars form and the person becomes irreversibly blind.
Retinal atrophy can be central or peripheral. In the first case, there is a decrease in central vision, and in the second - peripheral vision. Central degeneration occurs severely, accompanied by difficulties in performing normal activities.
Separately, there is geographic atrophy of the retina, in which, as a result of dystrophic changes, the fundus of the eye takes on the appearance of a geographical map, and unusual spotty pigmentation is observed.
Factors contributing to the development of pathology
Source: bolezniglaz.ru Doctors don’t know for sure what kind of disease this is.
His clinic is described clearly and in detail, but the reasons cannot be clearly determined. Various hypotheses are put forward and disputed, studies are conducted that confirm a statically reliable connection of this pathology with some negative factors, for example, smoking. Age-related changes in the human body themselves are a significant factor that triggers the mechanisms of atrophic vision loss. Today, the leading factors influencing the development of the pathological process are:
- genetic predisposition;
- gene mutations;
- deficiency of nutrients and monounsaturated fats;
- smoking;
- infections.
People whose relatives suffer from atrophic changes in the retina have a higher risk of developing AMD than those people whose relatives are free from this disease. Moreover, Europeans have a higher risk of losing central vision than Africans.
Scientists have discovered genes that can cause hereditary retinal angioedema.
- with a deficiency of zinc, ascorbic acid and vitamin E, the risk of macular atrophy increases several times;
- with a deficiency of antioxidant substances and macular pigments (for example, lutein), the likelihood of developing the disease increases;
- long-term smoking increases the risk of atrophy in the macula by 2-3 times;
- the role of cytomegalovirus in the development of macular degeneration was revealed;
- some role is given to vascular pathologies, as a result of which the trophism of retinal tissue deteriorates;
- metabolic disorders make the macula more prone to dystrophy;
- disturbances in the flow of lymph impair the nutrition of the eye and contribute to the onset of dystrophic changes.
Factors that provoke this disorder may be chronic diseases of the organ of vision, intoxication and poisoning, and traumatic eye damage.
Poisoning includes alcohol intoxication, overdose of vascular drugs, barbiturates and other medications that can affect vascular tone and worsen the nutrition of the macula.
People with light-colored irises are at risk for developing this disease. People whose eyes are exposed to direct sunlight for a long time are more likely to suffer from macular degeneration.
Reasons for development
The main cause of the disease is the age of the patient, as discussed above. In addition, there are a number of cases where retinal atrophy is a concomitant disease.
Among them:
- Diseases associated with the circulatory system. In this case, the blood ceases to perform its main function of transporting vital substances. So, as a result of impaired metabolism in the retina (lack of important elements), atrophy begins;
- Hereditary factor. Moreover, as a rule, the disease manifests itself already during school years;
- Disturbances in the lymphatic system;
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Infectious diseases;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Myopia;
- Hypermetropia;
- Eye injury;
- Chronic diseases of the eyes, heart, etc.;
- Alcohol and smoking abuse.
Symptoms of retinal atrophy
Source: medbooking.com In the dry form of atrophic changes, the clinical picture develops slowly, and at the initial stage of the disease, a person simply does not focus on changes in the brightness of image perception and deterioration in clarity.
If he notices these changes, he usually attributes them to age-related myopia or farsightedness. Typical signs of macular degeneration are:
- distortion of straight lines;
- hazy central image;
- difficulty recognizing faces.
With the development of dystrophy, the pictures received by the brain become more faded, and the central part of the image is completely replaced by a blurry spot. At the same time, lateral vision is preserved. The patient cannot read, watch TV shows, etc.
With the wet (exudative) form of the disease and the formation of scars, deterioration occurs quickly. If left untreated, complete blindness develops. With timely treatment, the process can be slowed down, but modern medicine is not yet able to completely stop atrophy or restore vision.
As a rule, symptoms manifest themselves in the form of the following deviations:
- the appearance of flashes and white spots in the eyes;
- image distortion;
- the loss of some elements from the overall picture;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- blurred visual field;
- changes in color perception;
- decreased twilight vision.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Source: Likar.info Diagnosing dystrophy and atrophy has the same principles.
The research package includes:
- determination of vision quality;
- assessment of visual fields;;
- fundus examination;
- identifying the quality of color perception;
In order to examine the fundus of the eye, special drugs are used that dilate the pupil. To obtain the most accurate data about the state of the eye structure and its functioning, the following methods are used:
- double-mirror Goldmann lens – allows you to view the fundus of the eye;
- optical coherence tomography – makes it possible to examine the retina of the eye using a three-dimensional image;
- electrophysiological methods - allow you to study the functioning of nerve endings and retinal cells;
- Ultrasound – used in some cases.
Diagnosis of pathology comes down to examination by an ophthalmologist and checking the patient’s fundus. At the same time, modern hardware allows doctors to take an image of the fundus and clearly see the disorder. You may need to administer a contrast agent.
When diagnosing the dry form of the disease, the doctor notes the insufficiency of the retinal pigment layer and whitish foci of atrophic changes. In case of wet AMD, the doctor notes foci of neovascularization (sprouting of new vessels). The liquid part of the blood penetrates into the tissues outside the vascular bed, swelling develops, possibly the formation of hematomas.
Additional Methods
Additional examination methods include visual acuity testing, stereoscopic biomicroscopy, and visual field testing (perimetry).
This disease rarely causes complete loss of vision, but it significantly reduces a person’s quality of life, limits the ability of the brain to receive visual information, making it difficult to carry out normal everyday operations.
Diagnostics
Based on the data obtained from the patient’s words, the doctor builds an approximate picture of the disease . If signs of retinal atrophy are detected, the ophthalmologist prescribes the following studies :
- blood tests (general, RW, sugar) and urine tests;
- ophthalmoscopy is the most significant method;
- visometry (determining distance visual acuity);
- biomicroscopy (examination of the ocular segment using a slit lamp);
- Ultrasound of the eyeball;
- radiography;
- CT orbits;
- MRI of the eye.
Traditional treatment for retinal atrophy
To a greater extent, the goal of treatment is to inhibit the development of the disease and possible vision correction using modern methods. Treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
There are 3 methods:
- Mild form (“dry”);
- Severe form (“wet”);
- Circular shape (macular atrophy).
When treating a mild form, you can get off with just vitamin complexes, which will normalize metabolic processes in the retinal tissue. They will slow down the development of the disease and help prevent progression to a severe form and loss of vision.
In drug therapy, an integrated approach is also used, prescribing drugs from the following list:
- Medicines that can prevent the proliferation of blood vessels (Lucentis).
- Antiplatelet agents. Required to eliminate the possibility of blood clots appearing in blood vessels. Usually Aspirin, Ticlodipine, Clopidogrel are selected.
- Polypeptides. These medications are made exclusively from biological materials (Retinolamine).
- Products that improve microcirculation.
- Medicines that prevent high cholesterol.
- Vitamin complexes containing most of vitamin B.
- Vasodilators and angioprotectors. Medicines in this category are designed to strengthen the bloodstream and expand it.
- Eye drops are also prescribed to improve metabolic processes and regulate regenerative processes in the eye. Taufon, Emoxipin, Oftan-Katakhrom, Taurine, etc. are usually prescribed.
The selection of drugs and the development of a dosage regimen are carried out by the doctor only individually for each patient. As a rule, it is necessary to repeat treatment several times a year to prevent the disease from developing.
Much better results of conservative therapy are achieved through physiotherapeutic techniques. For eye atrophy, the following types of procedures are selected:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrical stimulation of the retina;
- low-energy laser radiation;
- laser irradiation of blood;
- electrophoresis;
- photostimulation.
Treatment of a complex form requires direct surgical intervention and the introduction of medications into the eye, the most common of which are Avastin and Lucentis. These substances reduce tissue swelling, which prevents further progression of the disease.
One of the most modern treatment methods is laser coagulation. By means of high temperature, the retina and choroid of the eye are fused, resulting in an improvement in metabolic processes in the retina. The capabilities of the laser make it possible to perform surgery without affecting healthy tissue.
This “miraculous creation” will not restore a person’s vision, but it will allow the process to be frozen at the stage at which surgery is performed. That is why the sooner a person seeks help, the better, the greater the likelihood of maintaining good vision as far as possible.
In some cases, vitrectomy is indicated. In this case, the vitreous body is completely removed, replacing it with saline solution or artificial polymers. Surgical intervention is used to improve tissue metabolism and prevent fluid accumulation in the retina.
Effective treatments
In order to prevent retinal atrophy from progressing, treatment must be as effective as possible. Now there are several methods that can slow down the progression of the disease and even improve vision.
When a mild form of the disease is present, special vitamins can be used to reduce the risk of it becoming severe.
Treatment of atrophy must be comprehensive, since it can be caused by various reasons. In this case, both the underlying disease that caused the atrophy process and the visual impairment itself are eliminated. In primary forms, the main emphasis is on improving cellular metabolism.
As for the severe form of the disease, use the following methods:
- The use of special drugs that are administered retrobulbarly. The substances included in the composition reduce the stimulation of angiogenesis, reduce tissue swelling and prevent the subsequent development of the disease. The most popular drugs are Lucentis and Avastin.
- The use of laser coagulation, based on the action of high temperatures, ensuring tissue coagulation. Laser correction is considered the safest and most effective. The laser has the ability to fuse the retina and choroids of the eyes.
For the dry form of macular degeneration, complex treatment is prescribed, the basis of which is vitamin preparations. Drugs containing lutein, drugs that improve blood microcirculation in the vessels of the retina (Preductal), and venotonics (drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels) may be prescribed.
This therapy is considered to be of questionable effectiveness. Some experts claim that by using these remedies, you can significantly slow down the process of vision loss, while others believe that the dry form of AMD does not require treatment.
It proceeds slowly, and the methods available in the arsenal of modern medicine cannot have any significant effect on degenerative processes. Some results are observed while taking the medication, but after stopping treatment the processes occur again at the same speed.
Diet therapy
It is believed that diet therapy shows good results. Diet cannot completely stop degenerative changes, but with proper nutrition, you can slow down the process and maintain the ability to see for the rest of your life.
The menu of an elderly person should contain a minimum of animal fats, preference should be given to plant foods. You need to eat regularly and in small portions. It is advisable to avoid frying and prepare dishes using gentle methods (boiling and baking).
Treatment of the rapidly developing wet form involves specific drug therapy. A special drug called Ranibizumab, better known as Lucentis, is injected into the eye tissue. It suppresses the growth of new blood vessels and helps maintain and improve vision. The course of treatment requires about 2 years.
There are precedents for the use of the highly toxic anti-cancer drug Bevacizumab, better known as Avegra or Avestin. It is not patented as an ophthalmic drug. When used to treat eye pathologies, it had many side effects, but it can be used if necessary.
Surgical methods include laser correction, coagulation of new vessels, or photodynamic treatment of AMD using the drug Visudin. The effect of using this method lasts about one and a half years.
At the present stage, preference is given to laser correction. This technique, applied in a timely manner, allows you to restore vision. But re-development of atrophic changes in the future is not excluded.
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent atrophic changes in the retina. The basis for the prevention of this pathology is considered to be a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet and avoidance of direct sunlight on the retina.
As additional measures, timely treatment of vascular and metabolic pathologies, taking vitamin complexes and minerals in the form of medications and dietary supplements are recommended.
Treatment methods
To get relief as quickly as possible, treatment of retinal atrophy must be comprehensive. To do this, you need to visit a qualified doctor who will select the necessary list of medications for you.
Keep in mind that the sooner you start treatment, the higher the likelihood of obtaining a positive result. At the same time, you need to know that even the correct approach to the treatment of retinal atrophy does not always allow you to return 100% of vision.
It is necessary to begin treatment of retinal atrophy with measures that allow you to stop the effects of harmful factors on the eye. You must take medications that relieve diseases that affect the condition of the retina.
After such therapy is started, the specialist will select drugs directly for the treatment of atrophy. Patients are usually prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs that restore blood circulation.
Argon laser is an effective method for treating retinal atrophy. This procedure allows you to significantly strengthen the retina, which protects against pathological processes in the future.
Such therapy is prescribed exclusively in advanced stages, when medications are not able to bring any relief.
Argon laser therapy minimizes the likelihood of future retinal detachment. Its essence lies in the thermal effect, due to which the tissues begin to curl.
Surgery for retinal atrophy is painless and bloodless. An argon laser is a high-precision device that allows targeted action on individual areas. With this procedure, you will be able to heal dissected vascular lines.
The duration of such an operation is less than an hour. During this period, the specialist does all the necessary manipulations. The very next day a person can return to a full-fledged lifestyle - he will not experience any painful sensations.
Surgery
Source: kremlin-vision.ru Surgical intervention is chosen for severe stages of atrophy, as well as in cases where it progresses rapidly. There are 3 main types of operations:
- Vitrectomy. In this case, the vitreous body must be completely removed. During the intervention, it will be replaced either with a special polymer or with a saline solution. This will stop the accumulation of fluid in the retina, and metabolism in the surrounding tissues will improve.
- Vasoreconstructive and revascularization operations
- Laser coagulation is the most preferred intervention option because it is easier to tolerate, quickly produces results, has fewer contraindications and is completely bloodless. At the time of the operation, a laser beam fuses the choroid with the retina using high temperature.
After laser intervention, you will need to take several types of medications. This category should also include drugs that are part of the group of angiogenesis inhibitors.
This will prevent the growth of pathological vessels. Often other types of surgery are required to restore vision, but the above techniques can stop the progress of the detachment and prevent its complete loss.
Content
- 1 Types of PRA 1.1 Generalized PRA
- 1.2 Rod-cone dysplasia 1.2.1 Rod-cone dysplasia type 1
- 1.2.2 Rod cone dysplasia type 2
- 1.2.3 Rod cone dysplasia type 3
- 1.12.1 Commonly affected breeds
General recommendations
Regardless of which treatment course is chosen, patients with retinal atrophy should regularly visit a doctor for a preventive examination.
Throughout the entire period of treatment and after recovery, you will need to follow the following recommendations:
- Regular courses of vitamins will ensure a constant supply of useful substances to the eyeball.
- You should avoid eye strain and arrange rest periods during prolonged eye strain.
- Regardless of whether your stay on the street is short or long, you must wear glasses to protect yourself from ultraviolet radiation.
- Diet correction. A new diet should be built on basic principles so that the body regularly receives useful substances and is not overloaded with useless calories.
- Quitting alcohol and cigarettes will have a beneficial effect not only on the visual vessels, but also on the body as a whole.
- Don't overload yourself and lift weights. You will also have to give up hot showers and baths.
Folk recipes
With this disease, traditional methods are used exclusively as a supplement to the main treatment. In no case should you exclude medications, since not a single herbal component is capable of providing the therapeutic effect that the medicine provides!
If your doctor allows it, you can prepare any of the decoctions that can have a beneficial effect on the eyes:
- Method 1
Grind and dry the celandine, and as soon as the raw material is ready, take 1 spoon of it and brew it in boiling water. In the same container, the mixture should be put on fire and boiled well for several minutes. Immediately it is filtered, and after cooling, it is dripped into the eyes with a sterile pipette.
The course is carried out for a month, and the procedure is repeated 3 times a day.
Collect the green parts of birch, mustard, lingonberry and horsetail, take each ingredient in equal parts and brew in a glass. After insisting, take orally. This tea is prepared 3-4 times a day.
- Method 2
Take the freshest goat milk and mix it with water (boiled!) in a 1:1 ratio. Boil the mixture, cool and apply drop by drop into the eye affected by atrophy. After this, immediately cover it with a dark cloth. Treatment continues for a week.
- Method 3
Pour a glass of water into a container and add 1 tbsp. l. caraway seeds, boil for 5 minutes. Add the collected cornflower petals in the same proportion to the broth and let it cool. Once it has cooled and been strained, it is used as drops twice a day.
- Method 4
Take the following ingredients: onion peel (2 spoons), rosehip berries (2 spoons), pine needles (5 spoons). Pour the collected mixture 2 tbsp. water and boil for 10 minutes. You need to drink the strained drink at least half a liter per day, dividing this amount into equal parts.
Remember that the lack of proper treatment will lead to you simply losing your vision. It will no longer be possible to reverse this situation even with surgery, so you need to regularly monitor your eye health and follow treatment recommendations.
There are methods for treating retinal atrophy in traditional medicine. However, you should not self-medicate without obtaining qualified medical advice. Since traditional medicine has no justification as such and does not provide any guarantees.
However, with a mild form, it is quite possible to replace vitamin complexes with various herbs. Moreover, if you consider that most of them contain not only vitamins, but also other beneficial substances, such as anthocyanins (blueberries) and flavonoids, which have a beneficial effect on the eyes.
The former strengthen the vascular network, improving the quality of vision in the dark, and the latter are involved in metabolism. Ripe, ripe berries, colored red, blue and purple, are rich in flavonoids.