The second pair of cranial nerves is the most important element of the visual system, because through it the connection between the retina and the brain occurs. Although other structures continue to function correctly, any deformation of the nervous tissue affects the properties of vision. Optic nerve atrophy cannot be cured without leaving a trace; nerve fibers cannot be restored to their original state, so it is better to carry out prevention in a timely manner.
Basic information on the disease
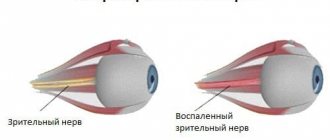
Optic nerve atrophy or optic neuropathy is a severe process of destruction of axons (nerve tissue fibers). Extensive atrophy thins the nerve column, healthy tissue is replaced by glial tissue, and small vessels (capillaries) are blocked. Each of the processes causes certain symptoms: visual acuity decreases, various defects appear in the visual field, and the shade of the optic nerve head (OND) changes. All pathologies of the optic nerves account for 2% of the statistics of eye diseases. The main danger of optical neuropathy is absolute blindness, which occurs in 20-25% of people with this diagnosis.
Optic neuropathy does not develop on its own; it is always a consequence of other diseases, so a person with atrophy is examined by different specialists. Typically, optic nerve atrophy is a complication of a missed ophthalmological disease (inflammation in the structures of the eyeball, swelling, compression, damage to the vascular or nervous network).
Diagnostics
First of all, the field of view is checked for white and colored objects. Then X-ray, electrophysiological and fluorescein angiographic studies are carried out. The type of damage to the optic nerve and the nature of the disease that accompanies it are established. Blurred boundaries indicate that the pathology has developed as a result of edema or an inflammatory process in the disc. When assessing the degree of disc pallor and loss of color, the general background of the fundus is taken into account.
Causes of Optic Neuropathy
Despite the many causes of optic nerve atrophy known to medicine, in 20% of cases they remain unclear. Usually these are ophthalmological pathologies, central nervous system diseases, autoimmune disorders, infections, injuries, intoxications. Congenital forms of ADN are often diagnosed together with cranial defects (acrocephaly, microcephaly, macrocephaly) and hereditary syndromes.
Causes of optic nerve atrophy from the visual system:
- neuritis;
- arterial obstruction;
- myopia;
- retinal dystrophy;
- uveitis;
- retinitis;
- oncological lesion of the orbit;
- unstable eye pressure;
- local vasculitis.
Injury to nerve fibers can occur during a traumatic brain injury or even the mildest injury to the facial skeleton. Sometimes optic neuropathy is associated with the growth of meningioma, glioma, neuroma, neurofibroma and similar formations in the thickness of the brain. Optical disturbances are possible with osteosarcoma and sarcoidosis.
Causes from the central nervous system:
- neoplasms in the pituitary gland or cranial fossa;
- compression of chiasmata;
- multiple sclerosis.
Atrophic processes in the second pair of cranial nerves often develop as a result of purulent-inflammatory conditions. The main danger is brain abscesses, inflammation of its membranes.
Systemic risk factors
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- anemia;
- avitaminosis;
- hypertension;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Wegener's granulomatosis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- giant cell arteritis;
- multisystem vasculitis (Behcet's disease);
- nonspecific aortoarteritis (Takayasu disease).
Syphilis, tuberculosis and similar severe infections often lead to the death of optic nerve axons. Less commonly, atrophy is detected after influenza, ARVI, measles, rubella and similar viral diseases. The influence of some parasites (toxoplasmosis, toxocariasis) cannot be ruled out.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment for the disease is aimed at stopping the progression of vision loss. In a small number of cases (with secondary damage, for example, multiple sclerosis, brain tumors, etc.), lost vision can be partially or completely restored. That is why the greatest importance in the secondary mechanism of development is given to the treatment of the underlying disease.
For treatment, medications, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises for the eyes are used. Among the medications used for treatment, angioprotectors, repair stimulants, metabolic and neuroprotective agents are used, and local agents are also used (for example, emoxypine drops). Therapeutic exercises are an auxiliary method, but in some cases they can lead to good results. In some cases, various laser surgery techniques are indicated.
Classification of optical neuropathy
All forms of optic nerve atrophy are hereditary (congenital) and acquired. Congenital diseases are divided according to the type of inheritance; they often indicate the presence of genetic abnormalities and hereditary syndromes that require in-depth diagnosis.
Hereditary forms of ADS
- Autosomal dominant (juvenile). Predisposition to nerve destruction is transmitted in a heterogeneous manner. The disease is usually detected in children under 15 years of age; it is recognized as the most common, but weakest form of atrophy. It is always bilateral, although sometimes the symptoms appear asymmetrically. Early signs are detected by 2-3 years, and functional disorders only at 6-20 years. Possible combination with deafness, myopathy, ophthalmoplegia and distance.
- Autosomal recessive (infantile). This type of ADN is diagnosed less frequently, but much earlier: immediately after birth or during the first three years of life. The infantile form is bilateral in nature and is often detected in Kenny-Coffey syndrome, Rosenberg-Chattorian, Jensen or Wolfram disease.
- Mitochondrial (Leber's atrophy). Mitochondrial optic atrophy is the result of a mutation in mitochondrial DNA. This form is considered a symptom of Leber's disease; it occurs suddenly and resembles external neuritis in the acute phase. Most patients are men 13-28 years old.
Forms of acquired atrophy
- primary (squeezing of neurons in the peripheral layers, the optic disc does not change, the boundaries have a clear appearance);
- secondary (swelling and enlargement of the optic disc, unclear boundaries, replacement of axons by neuroglia is quite pronounced);
- glaucomatous (destruction of the cribriform plate of the sclera due to surges in local pressure).
Destruction can be ascending, when the axons of the cranial nerves are affected, and descending, involving the nerve tissue of the retina. According to symptoms, they distinguish between unilateral and bilateral ADN, according to the degree of progression - stationary (temporarily stable) and in constant development.
Types of atrophy according to the color of the optic disc:
- initial (slight blanching);
- incomplete (noticeable blanching of one segment of the optic disc);
- complete (change in shade over the entire area of the optic disc, severe thinning of the nerve pillar, narrowing of the capillaries).
Live broadcast with pediatric ophthalmologist Natella Sukhanova
Natella Sukhanova is a doctor at the National Medical Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, a member of the Association of Children's Ophthalmologists of Russia, a member of the Scientific Committee of the ICPBA "Rainbow", a specialist in rare eye diseases.
Answers on questions:
Hello! Is there a clinic in Moscow that performs operations to correct strabismus by injection into the eye? After a month, supposedly the muscles begin to work correctly and everything gets better. This is true? Please express your opinion on this topic, what are the pros and cons, how long will the effect last?
- Yes, there are such operations, it’s true. A drug based on botulinum toxin is injected into the muscle. Sometimes the operation is carried out in several stages, it depends on the type of strabismus. What are the advantages: a cosmetic defect is corrected. The validity period varies, depending on the angle of strabismus - from 3 months to several years. The operation may have to be repeated.
If this surgical procedure is recommended to you, do not refuse this method, because... it gives very good results, and there are practically no complications. What can happen: the squint may not be corrected, but this is the maximum.
Our daughter is 3.5 months old, congenital coloboma of the retina of the optic nerve, her left eye is healthy. I would like to understand what is in our power, what can be done at an early age?
— This pathology can only be supported symptomatically so that it does not lead to further complications. Unfortunately, there is nothing more that can be done. And to figure out what kind of coloboma this is, first of all you need to contact a geneticist.
Please tell us in detail about partial atrophy of the optic nerves.
— Partial atrophy of the optic nerves can imply many different pathologies of the optic nerve, so it is necessary to work with each child individually and understand it.
How often should premature babies be seen by an ophthalmologist if the risk of retinopathy has been eliminated?
— If the risk of retinopathy is removed, a child born before the 26th week is observed for up to a year, 1 time every 3 months; born before 31 weeks - once a month until 6 months of passport age, then once every 3 months; born at 32 or more weeks - observation every six months. Preventive examinations are carried out during the child’s year of life. If no pathologies are identified further - at 3 years, 5 years and 7 years before school.
A 1 year old child (10 months corrected age) has pupils of different sizes. How can this be treated if the situation does not correct itself?
— You need to see an ophthalmologist to measure your refraction. Perhaps the child has congenital myopia.
Is it possible to correct vision without surgery?
- Depending on the diagnosis. If this is a spasm of accommodation, it is corrected with the help of gymnastics - daily, long-term.
A set of exercises can be easily found on the Internet today. The most popular: near-distance exercises: we train the lens, pointing it either at a close distance or at a far distance. For example, the well-known exercise “Mark on glass”. You draw a black dot with a diameter of 4-5 mm on the glass, sit in front of the window at a distance of 30 cm and look at this dot. Then look away to the farthest object you see in the window. Do 1 time a day for 15-20 repetitions.
My premature twins have grade 3 retinal detachment. They said we had to go to St. Petersburg for surgery. I can't get through to the hospital. I do not know what to do.
- I recommend not delaying this. It's difficult to get through to there. If there is a recommendation, you need to go urgently, since retinal detachment can lead to complete loss of vision. The hospital website shows how to get to them.
What is the treatment for partial optic atrophy? Do you need "Retinolamine "? How often?
— Partial optic nerve atrophy cannot be treated. " Retinolamine " depending on examination data.
Prematurity 4 months, angiopathy. Recommendations?
- According to the doctor's recommendations.
How often does a child after three years need to be seen by an ophthalmologist? 28 weeks, there was optic nerve atrophy, aggressive posterior retinopathy.
— Once every 6 months to control refraction, check the fundus and perform additional examinations so that the child can adapt to school.
Is there a treatment protocol for dacryocystitis for up to a year? My daughter’s eye was seriously festering; ophthalmologists (there were 3 of them) prescribed everything except Vitabact . "Tobrex ", "Signitsef " and "Okomistin ". As a result, the child’s eyes became covered with sores. After such experiments, I would like to understand: why do doctors not prescribe Vitabact ? It was he who helped the older children.
" Vitabact " is prescribed to children from birth. In this case, there may have been a secondary infection, so Vitabakt would not have been able to cope. More serious medications were prescribed.
Peripheral choreodystrophy - what is it?
— Peripheral choreodystrophy is dystrophy of the retina, which occurs secondary, for example, after high myopia, surgical laser interventions.
After an illness, a child develops a chalazion. What to do? 1.9 years.
— Chalazion requires local treatment: anti-inflammatory, antibacterial. And if it does not resolve - surgical. The appearance of chalazions is caused by a decrease in immunity; you need to consult a pediatrician to check your immune status.
Our son was born at 29 weeks, we are almost a year old. Stage 1 retinopathy, regression, we are under observation. I noticed that I rarely squint my eyes. I'm worried, we made an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
— Yes, you definitely need to see an ophthalmologist, because... Most likely, the child has developed a refractive error, which must be treated by wearing glasses.
Our baby's pupils are different sizes, they are the same outside during the day, but different in room lighting. What could it be? The child is 3 months old. The ophthalmologist at the children's clinic did not attach any importance to this - she said that she would outgrow it.
— Most likely, the child is predisposed to myopia, so refraction needs to be checked for a wide pupil; perhaps this is the beginning of myopia.
I had stage 2 retinopathy and went into regression. Recently I noticed my child’s pupils were different sizes. Where to run, what to do?
- You need to urgently contact an ophthalmologist.
Is the diagnosis of PANN (partial optic nerve atrophy) made during a routine examination or using special equipment?
— It is first detected during examination of the fundus, then visually evoked potentials are prescribed, and then, if necessary, an MRI of the brain.
Twins were born at 35-36 weeks. The girl has +5 vision, the child is 5 months old. Now they diagnose hypermetropia of the 3rd degree, they said there is a tendency to strabismus. Wait until a year? Can it be avoided? Are there treatment methods?
- No, it is necessary to prescribe glasses now. Maybe it will show up, maybe not. If there is farsightedness and prematurity, you need to contact an ophthalmologist again. To begin with, spectacle correction is prescribed, then occlusion and after 4 years - treatment with a synoptophore.
Peripheral retinal dystrophy in premature infants occurs under what conditions?
— Dystrophy cannot just arise. These are traces of laser coagulation, or congenital genetic dystrophy.
We did laser coagulation, now 8 months. The disc is pale and cannot be treated with anything. What to drip to avoid CHAZN?
— The pallor of the disc indicates that the child was born prematurely, you just need to wait out this moment, drops, unfortunately, do not help, and there are no drops to prevent CHAZN. You need to do visually evoked potentials and if everything is normal, you should not worry.
The diagnosis of CHAZN has not been confirmed. You say there is no treatment. Is confirmation of the diagnosis then necessary?
- Yes, definitely. Do visually evoked potentials - this is a very accessible method that helps the doctor determine whether the optic nerve is altered or not.
The child is 9 months old, vision +3 - is this normal for his age?
- Yes, good.
The child was born at 26 weeks, the doctor set 0 tbsp. retinopathy. But the pupils either increase or decrease. Is this normal?
- This is a normal pupillary reaction to light.
“Dexamethasone ” and “Emoxipin drops ?
— Dexamethasone is a hormonal steroid drug. "Emoxipin" improves blood circulation and nourishes the vascular wall. They are used for retinopathy if there is a risk group and in the active phase.
I have five children under my care, two of them have astigmatism. As the blood parents assure, this is an acquired strabismus. Can a diagnosis based on nervousness arise based on the removal of children from the family?
— No, there are two types of astigmatism: either congenital or acquired. Congenital usually occurs in young children, acquired - after injury or eye surgery.
During the examination, they said that CHAZN is in question, and they recommended a drug to improve blood circulation. What to do in such a situation?
— If only a neurologist prescribed a nootropic drug, then take it, an ophthalmologist does not treat such diagnoses.
The baby was born at 25 weeks, now 1.9. The diagnosis was grade 1 hypermetropia in both eyes with reverse complex astigmatism. Please tell me what does this mean?
“This means that the child has an abnormal structure of the cornea. Consequently, the child sees the image poorly, in a more distorted form, and here, of course, spectacle correction is necessary.
Is it necessary to wear glasses if you have astigmatism?
- Necessarily. Because with astigmatism, a person sees a distorted image both near and far. Glasses correct the image. Children especially need to wear it, because... The central zone of the retina develops, which is responsible for a clear image. If a child with astigmatism does not wear glasses, then by the age of 6, when the retina finishes its development, amblyopia may begin - this is a “lazy eye”, which, unfortunately, cannot be corrected after 6 years.
Born at 29 weeks, now 5 months. The ophthalmologist diagnoses retinopathy. He said it would be checked in 6 months. If there is no deterioration, the diagnosis will be removed. How often will my eyes need to be checked if the diagnosis is removed?
— Your eyes will need to be checked once every 6 months.
There are a lot of questions about retinopathy, so I’ll tell you more. Retinopathy is one of the main causes of blindness, low vision and visual impairment in young children in all developed countries, including Russia. The earlier a child is born, the higher the risk of retinopathy. The incidence of retinopathy in children with birth weight less than 1000 grams reaches 90%. Premature babies require mandatory examination by an ophthalmologist.
All premature babies normally have signs of fundus immaturity and the process of retinal formation is not complete. From birth, retinal development can occur in two ways: normal growth, when retinopathy does not occur. And pathological - in which retinopathy develops.
An ophthalmologist, using modern ophthalmological equipment, identifies all changes in the maturing retina in premature infants. The first examination by an ophthalmologist (he must have a certificate in retinopathy) is carried out at 4-6 weeks of the child’s life.
At stages 1-2, retinopathy can stop on its own and do not require any treatment - just observation.
But if retinopathy progresses to stage 3, it will not stop on its own - it is necessary to take measures, such as laser coagulation of the retina - the timing is determined by the ophthalmologist.
If treatment is not carried out, or even after treatment, retinopathy continues to progress to stages 4 and 5, in which retinal detachment develops, this naturally leads to decreased vision, which is then not restored. In these cases, surgical treatment is performed to remove the scars that form after retinal detachment.
How long after laser coagulation of the retina can a child be placed on his stomach?
- Depending on the picture in the fundus. If there are no signs of inflammation and the retina is calm, it will be possible to post it. You need to ask the doctor who examined and operated.
Can a baby watch TV at 8 months? Born at 27 weeks, retinopathy grade 1-2, regression.
- Of course you can (laughs - note: “The right to a miracle”).
Operated congenital stabilized glaucoma of both eyes, PAI of both eyes. Complex hypertrophic astigmatism in both eyes. The ophthalmologist prescribed Taufon and treatment from a neurologist. Do you need to wear glasses?
— If there is astigmatism or refractive error, of course it is necessary to wear glasses so that the child does not lose residual vision functions.
During the examination, they said that the nerve in one eye was pale and sent me to a neurologist. Is this treatable?
“Perhaps these are signs of anemia.” Yes. This child should be jointly managed by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist, and neurology should be excluded.
Retinopathy 1st degree. At 5 months they diagnosed hypermetropic astigmatism and told me to watch it for now. Is there a chance that it will go away?
— There is a chance up to 3 years. Depending on the type of astigmatism and how many diopters, it may decrease up to 3 years. Observation required. Naturally, no one will pick up the glasses now.
The ophthalmologist’s examination report indicated “vessels of zone 1. ” A week later - “vessels of zones 1-2 ”.
“This means that the active phase is underway, the vessels are sprouting, very careful observation by an ophthalmologist is necessary so that this does not lead to retinal detachment in the future.
Born 1100 grams at 26 weeks. I was diagnosed with grade 1 retinopathy. A week later they left it at the same grade 1. What are the forecasts?
— With proper supervision by an ophthalmologist and pediatrician, the most favorable conditions. Most often this is what happens.
— If confirmation of the diagnosis of CHAZN does not imply further treatment, why confirm it?
— Most likely, there are pathologies in the brain; you need to at least understand at what level the problem is occurring in order to support the child’s vision. It is only necessary to confirm or exclude CHAZN.
If a blood vessel bursts in your eye, is it necessary to go to the doctor? History of grade 1 retinopathy.
- Yes, definitely see an ophthalmologist, because... We don't know what caused the hemorrhage.
Is it possible to do massage and exercise therapy after discharge? Born at 24 weeks, now 32, stage 2 retinopathy, they said they would monitor me.
— Massage should absolutely not be done, as this can provoke further growth and activity of blood vessels and more serious complications. When a massage is performed, the vessels become active, including in the eyes - swelling may appear, and we fight it. As soon as the ophthalmologist gives permission, you can have a massage.
How do you feel about measuring intraocular pressure with an eye icare tonometer?
— I treat it very well, depending on the thickness of the cornea and the pathology of the child.
How can I get an appointment with you?
— At the National Medical Research Center for Children's Health, we receive both premature babies and children with various pathologies, such as refractive error, myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism, rare eye diseases of children, congenital pathology, retinopathy of prematurity. All information on how to get to us is on our website https://nczd.ru/. There is no long queue for compulsory medical insurance, maximum 1 week. A paid visit to an ophthalmologist costs 2,600 rubles if the patient is a citizen of the Russian Federation.
17.06.2019
Symptoms of optic atrophy
The degree and nature of optical disturbances directly depends on which nerve segment is affected. Visual acuity can decrease critically very quickly. Complete destruction ends in absolute blindness, blanching of the optic disc with white or gray spots, and narrowing of the capillaries in the fundus. With incomplete ONH, vision stabilizes at a certain time and no longer deteriorates, and the pallor of the ONH is not so pronounced.
If the fibers of the papillomacular bundle are affected, the deterioration in vision will be significant, and the examination will show a pale temporal zone of the optic disc. In this case, optical disorders cannot be corrected with glasses or even contact lenses. Damage to the lateral zones of the nerve does not always affect vision, which complicates diagnosis and worsens the prognosis.
ADN is characterized by various visual field defects. The following symptoms allow one to suspect optic neuropathy: scotomas, concentric narrowing, tunnel vision effect, weak pupil reaction. In many patients, the perception of colors is distorted, although more often this symptom develops when axons die after neuritis. Often changes affect the green-red part of the spectrum, but its blue-yellow components can also be distorted.
Read also
Myopia
Vision plays a huge role for a person.
Through the eye we experience the entire amazing and diverse world. A person receives 80-90% of information from the surrounding world through vision. Therefore, it is a huge tragedy... Read more
Red eye
*Red eye syndrome* is a group of diseases that are accompanied by redness or hyperemia of the eye. Redness of the eyes (hyperemia) occurs due to dilation of the vessels of the conjunctiva of the sclera and can...
More details
Contact lenses/contact correction
Vision is one of the senses through which we learn about the world around us. Good vision is essential for a high quality of life. The most important characteristic in diagnosis is the acuity...
More details
Blindness
Vision is a unique gift that nature has given us. We can truly appreciate it only when we lose. With a number of diseases, vision loss may decrease, sometimes almost to the point of complete blindness. Often…
More details
Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm is a chronic disease characterized by involuntary squinting of the eyelids due to increased tone of the orbicularis oculi muscles. Most often, the causes of blepharospasm are extremely difficult to establish or...
More details
Diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy
The expressive clinical picture, physiological changes and functional disorders greatly simplify the diagnosis of ADN. Difficulties may arise when actual vision does not match the degree of destruction. To make an accurate diagnosis, the ophthalmologist must study the patient’s medical history, establish or deny the fact of taking certain medications, contact with chemical compounds, injuries, and bad habits. Differential diagnosis is carried out for peripheral lens opacification and amblyopia.
Ophthalmoscopy
Standard ophthalmoscopy allows one to establish the presence of ADN and accurately determine the extent of its spread. This procedure is available in many regular clinics and does not cost much. The results of the study may vary, but some signs are detected in any form of neuropathy: changes in the shade and contour of the optic disc, a decrease in the number of vessels, narrowing of the arteries, and various venous defects.
Ophthalmoscopic picture of optical neuropathy:
- Primary: clear disc boundaries, optic disc sizes are normal or reduced, saucer-shaped excavation is present.
- Secondary: grayish tint, blurred disc borders, enlarged optic disc, no physiological excavation, peripapillary reflex to light sources.
Coherence tomography
Optical coherence or laser scanning tomography allows us to study the nerve disc in more detail. Additionally, the degree of mobility of the eyeballs is assessed, the reaction of the pupils and the corneal reflex are checked, visometry is performed with tables, visual field defects are examined, color vision is checked, and eye pressure is measured. Visually, the ophthalmologist determines the presence of exophthalmos.
Plain radiography of the orbit allows you to identify pathologies of the orbit. Fluorescein angiography shows dysfunction of the vasculature. To study local blood circulation, Doppler ultrasound is used. If atrophy is due to infection, laboratory tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are performed.
Electrophysiological tests play a key role in confirming the diagnosis. Optic nerve atrophy changes the threshold sensitivity and lability of the nervous tissue. The rapid progression of the disease increases the retino-cortical and cortical time indicators.
The level of reduction depends on the location of the neuropathy:
- when the papillomacular bundle is destroyed, sensitivity remains at a normal level;
- damage to the periphery causes a sharp increase in sensitivity;
- atrophy of the axial fascicle does not change sensitivity, but sharply reduces lability.
If necessary, check the neurological status (x-ray of the skull, CT or MRI of the brain). When a patient is diagnosed with a brain tumor or unstable intracranial pressure, a consultation with an experienced neurosurgeon is prescribed. In case of orbital tumors, it is necessary to include an ophthalmic oncologist in the course. If destruction is associated with systemic vasculitis, you need to contact a rheumatologist. Pathologies of the arteries are dealt with by an ophthalmologist or vascular surgeon.
How is optic atrophy treated?
The treatment regimen for each patient with optic neuropathy is always individual. The doctor needs to get all the information about the disease in order to create an effective plan. People with atrophy require immediate hospitalization, while others are able to maintain outpatient treatment. The need for surgery depends on the causes of ASD and symptoms. Any therapy will be ineffective if vision weakens to 0.01 units or below.
It is necessary to begin treatment of optic nerve atrophy by identifying and eliminating (or stopping) the root cause. If cranial nerve damage is caused by intracranial tumor growth, an aneurysm, or unstable cranial pressure, neurosurgery must be performed. Endocrine factors influence hormonal levels. Post-traumatic compression is corrected surgically by removing foreign bodies, removing chemicals, or limiting hematomas.
Conservative therapy for optic neuropathy is primarily aimed at inhibiting atrophic changes, as well as preserving and restoring vision. Drugs are indicated to expand the vasculature and small vessels, reducing capillary spasm and accelerating blood flow through the arteries. This allows all layers of the optic nerve to be supplied with sufficient nutrients and oxygen.
Vascular therapy for ADN
- intravenously 1 ml of nicotinic acid 1%, glucose for 10-15 days (or orally 0.05 g three times a day after meals);
- Nikoshpan tablet three times a day;
- intramuscularly 1-2 ml No-shpa 2% (or 0.04 g orally);
- intramuscularly 1-2 ml of Dibazol 0.5-1% daily (or orally 0.02 g);
- 0.25 g of Nihexin three times a day;
- subcutaneously 0.2-0.5-1 ml of sodium nitrate of increasing concentration 2-10% in a course of 30 injections (increase every three injections).
Decongestants are needed to reduce swelling, which helps reduce compression of the nerve and blood vessels. Anticoagulants are used to prevent thrombosis; the vasodilator and anti-inflammatory Heparin is recognized as the best. It is also possible to prescribe antiplatelet agents (prevention of thrombosis), neuroprotectors (protection of nerve cells), glucocorticosteroids (combat inflammatory processes).
Conservative treatment of ADN
- To reduce inflammation in the nervous tissue and relieve swelling, dexamethasone solution is prescribed in the eye, intravenous glucose and calcium chloride, and intramuscular diuretics (Furosemide).
- Strychnine nitrate solution 0.1% in a course of 20-25 subcutaneous injections.
- Parabulbar or retrobulbar injections of Pentoxifylline, Atropine, xanthinol nicotinate. These drugs help speed up blood flow and improve trophism of nervous tissue.
- Biogenic stimulants (FIBS, aloe preparations) in a course of 30 injections.
- Nicotinic acid, sodium iodide 10% or Eufillin intravenously.
- Vitamins orally or intramuscularly (B1, B2, B6, B12).
- Antioxidants (glutamic acid).
- Orally Cinnarizine, Riboxin, Piracetam, ATP.
- Instillation of Pilocarpine to reduce eye pressure.
- Nootropic drugs (Lipocerebrin).
- Drugs with antikinin effect (Prodectin, Parmidin) for symptoms of atherosclerosis.
In addition to medications, physical therapy is prescribed. Oxygen therapy (use of oxygen) and blood transfusion (urgent blood transfusion) are effective for ADN. During the recovery process, laser and magnetic procedures are prescribed; electrical stimulation and electrophoresis (administration of drugs using electric current) are effective. If there are no contraindications, acupuncture (use of needles on active points of the body) is possible.
Surgical treatment of optic neuropathy
One of the methods of surgical treatment of the optic nerves is hemodynamic correction. The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia: a collagen sponge is placed in the sub-Tenon's space, which stimulates aseptic inflammation and dilates blood vessels. In this way, it is possible to provoke the growth of connective tissue and new vascular network. The sponge dissolves on its own after two months, but the effect lasts for a long time. The operation can be performed repeatedly, but at intervals of several months.
New branches in the vascular network help improve blood supply to nerve tissue, which stops atrophic changes. Correction of blood flow allows you to restore vision by 60% and eliminate up to 75% of visual field defects if you go to the clinic in a timely manner. If the patient has severe concomitant disorders or atrophy has developed to a late stage, even hemodynamic correction will be ineffective.
For partial atrophy of the optic nerve, the use of a collagen implant is practiced. It is impregnated with antioxidants or drugs to dilate capillaries, and then injected into the eyeball without stitches. This method is effective only when eye pressure is stable. The operation is contraindicated in patients over 75 years of age, with diabetes mellitus, severe somatic disorders and inflammation, and vision less than 0.02 diopters.
Prognosis for optic atrophy
To prevent AD, it is necessary to regularly check the condition of those organs that regulate the functioning of the visual system (central nervous system, endocrine glands, joints, connective tissue). In severe cases of infection or intoxication, as well as severe bleeding, urgent symptomatic treatment must be carried out.
It is impossible to completely restore your vision after neuropathy even in the best clinic. A case is considered successful when the patient’s condition has stabilized, ASD does not progress for a long time, and vision has been partially restored. Many people have permanently reduced visual acuity and also have defects in lateral vision.
Some forms of atrophy continually progress even with adequate treatment. The ophthalmologist’s task is to slow down atrophic and other negative processes. Having stabilized the symptoms, it is necessary to constantly prevent ischemia and neurodegeneration. To do this, long-term maintenance therapy is prescribed, which helps improve the blood lipid profile and prevent the formation of blood clots.
The course of treatment for optic nerve atrophy must be repeated regularly. It is very important to eliminate all factors that can affect the optic nerve axons. A patient with optic neuropathy should regularly visit specialists as indicated. It is necessary to constantly prevent complications and improve lifestyle. Refusal of therapy for optical neuropathy inevitably leads to disability due to total death of nerves and irreversible blindness.
Any changes in the layers of the optic nerve negatively affect a person's ability to see. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo timely examinations for people with a predisposition and treat all diseases that contribute to optic nerve atrophy. Therapy will not help restore vision to 100% when optic neuropathy has already developed enough.
Sources used:
- Ultrasound diagnostics in ophthalmology / Sing Arun D. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2015.
- Ophthalmology / Wilhelm Happe. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2005.
- New standards for inpatient ophthalmological care. Textbook / A.N. Amirov, R.N. Tokinova, E.I. Mingazova. - Moscow: IL, 2015.
- Volgograd State Medical University