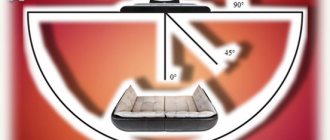
More and more often, our clients are asking for CCTV cameras with a viewing angle of 120 degrees or more. Most people ignorant of this topic are sure that this is a typical value for standard video cameras. Let’s be honest, many of the sellers also claim that cameras with a 2.8 mm lens have a horizontal viewing angle of 120°. Let's look at the real values. We have already measured the real angles of car DVRs, and have debunked the myth that most of them have a viewing angle of 120 degrees or more.
When selecting equipment for a security surveillance system, it is of course important to take into account the viewing angle of CCTV cameras, which determines the size of the monitored area. Its value is influenced by 2 parameters - the focal length of the lens and the diagonal of the matrix, with an increase in which the viewing angle will expand. But as the field of view angle increases, the image detail decreases. To increase detail, you need higher resolution or a camera with a narrower viewing angle.
To visually compare field of view angles on cameras with different lenses, an experiment was conducted, which is described later in the article.
We used 4 IP cameras with different lenses:
- 3.6mm - PN-IP2-B3.6 v.2.6.3
- 2.8mm – ST-181 IP HOME
- 1.9mm - PNL-IP2-B1.9MPA v.5.5.2
- 1.4mm - PDL-IP2-B1.4MPA v.5.8.9
The tested video cameras differ in the focal length of the lens. Cameras with 3.6 and 1.9mm lenses have the same matrix size of 1/2.9 inches, while a camera with a 2.8 lens has a slightly larger matrix - 1/2.7". And the resolution of all cameras is 2 megapixels.
All video cameras were placed at a height of about 2 meters opposite the “test” wall in our office. The camera view was aligned to the center to better assess the difference in the width of the field of view. One photo was taken for each of the following three cameras:
Lateral or peripheral vision
Asymmetrical perception of the environment primarily determines the size and shape of the optical activity of the retina. As paradoxical as it may sound, the field of vision of each eye is elongated in relation to the outer corner.
| Photoreceptors (rods and cones) are responsible for a person’s ability to see and distinguish shades. They are distributed unevenly over the surface of the retina. If the rods are located in almost every area, then the cones are located only in the center. |
For this reason, peripheral vision is weaker, since the rods do not provide the necessary detail in the image. For some individuals, the perception of optical information is more developed due to a specific activity or hobby (driving a car, team games, etc.).
There are a number of exercises aimed at expanding the visual field and increasing eye sharpness. However, the eye is not perfect and sometimes “blind spots” appear on it. As a result, a person does not even see what is at arm's length.
This can be represented more clearly this way:
Video cameras with a small field of view have a higher pixel density, which means better image detail. For many, this viewing width will be sufficient, which is why such cameras remain popular in video surveillance. If you need to capture a larger area for surveillance, you will need a camera with a wider viewing angle.
Calculation of viewing angles of CCTV cameras for all 3 cases
The viewing angle of a video camera can be calculated using the formula:
a = 2arctg (d/2f),
Where:
a – viewing angle of the video camera, in metric degrees; arctg — trigonometric function (arctangent); d – matrix width in millimeters; f – effective focal length of the lens in millimeters;
For 3.6mm, PN-IP2-B3.6 v. 2.6.3
a1=2*arctg(5.376mm/2*3.6) = 73 degrees
For 2.8mm, ST-181 HOME 2.8
a2=2*arctg(5.47mm/2*2.8) = 89 degrees
For 1.9mm, PNL-IP2-B1.9MPA v.5.5.2
a3=2*arctg(5.376mm/2*1.9) = 109 degrees
Loss of visual fields in humans
In the absence of disturbances in the functioning of the eyes, we can examine the fingers moved to the side at least eighty-five degrees. If the angle is smaller, then a narrowing of the visual field is observed. Surgeries aimed at restoring the functionality of the eyes are becoming increasingly popular.
And if with each eye a person sees only part of the space placed in an imaginary corner, this indicates a loss of optical fields. This is a dangerous symptom that signals the development of pathologies of the brain or nervous system.
Local loss of ½ or ¼ of the field is called hemianopia. The anomaly is most often bilateral, i.e. it affects both eyes at the same time. There is also concentric loss, when a person’s gaze is fixed at almost one point. A similar manifestation is characteristic of optic nerve atrophy and the last stage of glaucoma. However, the phenomenon can also be temporary, caused by a psychosomatic condition.
Physicians call focal loss of visual fields scotomas. The pathology is characterized by the formation of islands, which a person perceives as shadows or spots. Sometimes the patient does not even realize that he has developed an anomaly. It is detected only during a medical examination. Loss of the area in the center signals the development of macular degeneration (age-related damage to the macula).
Reasons for violations
The nature of the loss of optical fields directly depends on the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. Most often these are anomalies affecting the light-receiving apparatus of the organ of vision.
If the loss of the field is accompanied by the formation of a curtain on one side, the reason lies in the detachment of the retina or the development of pathology of the conductive paths of the optical system. Also, with such a defect, the size of the drop-down fields changes depending on the time of day.
| In some cases, patients say that they look as if through a wall of water, the picture seems to “float”. Retinal detachment can be caused by trauma or a high degree of myopia. If the outer halves of the field (from the temple) fall out in both eyes, then the pituitary gland can be suspected. |
If the pathology is accompanied by the formation of a dense curtain on the side of the nose, there is a high risk of developing glaucoma. At the same time, patients complain of blurred vision, the appearance of rainbow circles when looking at a luminous object.
Loss of optical fields in the form of a translucent curtain on either side can provoke pterygium, cataracts, and vitreous opacification. If “blind spots” occur in the center, the cause should be sought in macular degeneration or partial atrophy of the optic nerve.
What does loss of visual fields mean?
If a person has disturbances in the range of vision, then this is a symptom of serious problems at different levels. For the eyes, such damage to the receptors is nothing more than blindness in a certain area. It is provoked by glaucoma, neuritis and some other diseases of the visual system. Blindness in some area is caused by retinal detachment, hemorrhages and the formation of tumors on the retina.
For signal pathways, this is a sign that indicates damage to neural axons. At the brain level, damage occurs to the areas responsible for vision in the occipital region. Most often this is caused by traumatic brain injuries, tumors, and stroke.
Diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, multiple sclerosis and even hyperthyroidism negatively affect the field of vision. Eye injuries and burns can lead to tragic consequences. The visual field can be affected by vegetative-vascular pathologies, pituitary adenoma, and vitreous opacities.
All these disorders provoke such serious problems as:
- Scotoma. This is the so-called blind spot or lack of perception in a certain area, it can be of different sizes. Most often the spot is in the middle of the field of view.
- Hemianopsia. This is essentially blindness in half of the entire visual field.
- Narrowing of the viewing angle. It is concentric when the angle narrows along the entire radius of the visual field. As well as local narrowing, when the angle decreases only in a separate section of the radius.
After conducting the research, all data obtained must be deciphered by a specialist. Any loss indicates pathology.
If scotomas were found in special conditions, then this is a sign of glaucoma. If there is a narrowing of vision of a centric, bilateral or spectral nature, the patient has serious problems with visual function.
Therefore, to complete the picture of disorders, it is important to examine not only a person’s visual field, but also his ability to navigate in space.
Diagnostic methods
A variety of procedures are used to make a diagnosis. In this case, the condition of each eye is analyzed separately. The doctor asks the patient to look at one point, noting the appearance of an object in different areas. The eyes that are not being checked are covered with a special shield or palm.
Main diagnostic methods:
- Test. It makes it possible to evaluate optical fields, takes a minimum of time and does not require specialized equipment. The main condition is that the doctor has no deviations in the visual field. During the examination, the patient notes where fingers or other objects appear.
- Kinetic. It is carried out using a manual perimeter. The patient's chin is fixed on a stand. As soon as you see a glowing object on the screen in your peripheral vision, tell your doctor about it.
- Static. Conducted using automatic perimeter. The computer shows the illuminated object in different areas, increasing its brightness until the patient notices it and presses a button.
- With double frequency. When diagnosing, a person examines vertical stripes of white and black. They flicker at different frequencies, which creates a visual doubling effect. If the patient does not see them at a certain frequency, this indicates a pathology of the optic nerve or retina.
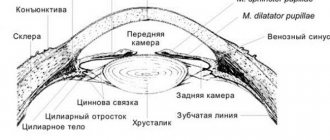
Size of human field of vision
Good vision is the ability to focus your gaze and distinguish objects. The field of view is usually called the angular area visible to the eye. In this case, the head should not move, and the gaze should linger on any object and not move. This is the totality of everything that a person sees when concentrating on only one point. For example, if you look at someone standing on the street, you can still see the street itself and other people.
The size of the visual field is of great importance in everyday life:
- The driver can simultaneously observe what is happening on the road ahead, to the side and in the rearview mirror, only thanks to the wide field of view. It is thanks to him that he assesses the situation on the road as a whole, all the dangers, and can make maneuvers.
- During the lesson, students see the entire board, as well as the entire sheet of a notebook or textbook. This helps them take all the details into account. Otherwise, academic performance decreases. This broad overview is important for developing speed reading skills.
- Mom can simultaneously do household chores (ironing, cooking) and keep an eye on the baby. Due to the large viewing angle, you can do several things at the same time.
- For many types of work, observation is a direct responsibility. The security guard and machine operator must keep track of everything at once.
Human vision is divided into central and peripheral. The first is usually equated to sharpness; it is measured by the familiar SB table. Peripheral is everything that a person sees when he fixes his gaze. This is the field of view.
The ability to see and recognize surrounding objects is provided by peripheral vision. Its quality is determined by the number of points recorded by the eye. During the examination, each eye is checked separately, measurements are taken in the horizontal and vertical plane.
Changes in field of view
Despite the diversity of this defect, it can be conditionally classified into two types:
- Focal (scotomas).
- Narrowing of visual field.
Correction of optical fields for various anomalies of the nervous system is a common occurrence. This symptom is considered one of the most important in diagnostics.
The absence of optical vision in a certain area, the contours of which do not coincide with the lateral edges of the visual field, is called scotomas. In most cases, patients do not even notice such a deviation. It is detected during special diagnostics. These are the so-called negative scotomas.
Sometimes patients note the appearance of spots or shadows in their field of vision before their eyes. A positive scotoma interferes with normal vision and causes discomfort. Pathology can have different shapes and be located in any area.
If the optical function is completely absent in the area of the scotoma, it is called absolute. In case of focal lesions, relative scotoma is diagnosed.
In addition to pathological deviations, there are physiological ones. An example of such a phenomenon is the “blind spot”. Absolute scotoma, oval in shape. Usually located in the temporal viewing area. It is a projection of an optical disk that does not have photosensitive elements.
| Physiological scotomas have clear sizes and locations. If their volume increases, this indicates the development of pathology. |
The narrowing of the optical view is global or local. In the first case, the pathology leads to tubal vision, in the second the defect affects a specific area.
The anomaly may be minor or pronounced. Diseases of the nervous system (hysteria, neurasthenia) most often lead to the development of the defect. In this case, the pathology of the optical fields will be functional.
However, most often the cause of concentric narrowing of vision is hidden in damage to the organ of vision. To identify the type of disorder in a patient, diagnostics are carried out using objects that differ in size. They are located at different distances.
In case of a functional deviation, the dimensions of the object and the degree of remoteness have practically no effect on the results of the examination.
Hemianopsia
Bilateral absence of ½ of the visual field indicates damage to the optical path in the chiasm area. Patients often discover pathology on their own. Hemianopsia can be homonymous when there is a loss of the temporal visual field on one side and a loss of the nasal field on the other. A heteronymous defect is also identified. Symmetrical loss of nasal or parietal areas on both sides is diagnosed.
Hemianopsia is further divided into bitemporal and binasal. In the first case, the outer half of the visual field falls out. An anomaly indicates damage to the optical path in the intersection area. Often develops in the pituitary glands.
A binasal defect is accompanied by loss of internal areas of the visual field. The disease damages uncrossed fibers of the optical path.
In tabular form it will look like this:
Lens
| Corner | Camera | |
| 1.9 mm | 109° | PNL-IP2-B1.9MPA v.5.5.2 |
| 2.8 mm | 89° | ST-181 IP HOME |
| 3.6 mm | 73° | PN-IP2-B3.6 v.2.6.3 |
And again we get the value of 120 degrees, which is less familiar to everyone. To get a horizontal viewing angle of 120°, the lens of a 2 megapixel camera must have a focal length of no more than 1.57mm . And this is provided that the matrix size of a camera with an aspect ratio of 16:9 is at least 1/2.7 inches.
If you really need a camera with a viewing angle of 120° or more, pay attention to the inexpensive panoramic IP cameras FE-ITR2000, D2-SUP-fisheye-01, or AHD cameras GF-VIR4306AHDFY180.
You can view viewing angles of cameras with different lenses and matrices here
| Previous article: Why do hackers need to hack IP cameras? | Next article: Outdoor 4G camera with cloud recording |
Latest articles in the section:
- Face recognition. Comparison of multiple devices
- Video surveillance in the elevator
- IP camera + Youtube - broadcast video to your website
- F22, SC2235 and IMX291. Testing 3 IP cameras on different matrices
- CCA - what is it and what is it eaten with?
Popular articles in the section:
- How to find out the IP camera address
- Russian solutions for cloud video surveillance
- Live cameras in Samara
- Signal transmission from IP cameras over a distance of more than 100 m
Diseases
Deviation in the fields of peripheral vision signals the development of a number of anomalies:
- Ophthalmological diseases (glaucoma, cataracts, peripheral retinal dystrophy).
- Failure in the functioning of the optic nerve (atrophy, neuritis).
- Pathologies affecting the brain (neoplasms, congenital diseases of the vascular system).
| After analyzing the size and shape of visual defects, the doctor identifies where exactly the destructive process is concentrated. |
Methods of treatment and recovery
The course of therapy depends on the cause that provoked the loss of optical fields.
- When diagnosing glaucoma, doctors monitor the dynamics of the development of the disease or prescribe medications and procedures.
- In case of macular degeneration, it is first of all important to identify the nature of its damage to the retina. If possible, treat the underlying cause first (for example, medication or physical therapy).
- Surgical intervention is prescribed for retinal detachment.
If the optic nerve is damaged, there is a significant disruption in the nutrition of brain cells, after a stroke and ischemia, a course of restorative treatment is prescribed.