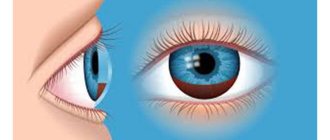
The structure of chamber formations
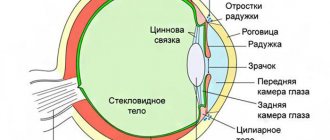
The anterior chamber of the eye is located directly behind the cornea. The peculiarity of the “element” is that it has different depths along its entire length. The greatest depth is in the area of the pupil, the indicator reaches three and a half millimeters, it decreases towards the periphery. Aberration in camera parameters can become a symptom of an eye disease. For example, the depth increases after removal of the lens or decreases when the mucous membrane is detached.
The posterior chamber of the eye is located directly behind the anterior chamber and contains many tiny zonules of Zinn, which act as a “connecting” element between the lens and the ciliary body. They are also responsible for the contraction of the ciliary muscles, whose task is to transform the shape of the lens. Thanks to this, a person sees well at any distance.
Both chambers are filled with a liquid identical in composition to blood plasma. Moisture contains a large amount of useful substances that are transferred to the organ of vision and ensure its smooth operation. The liquid also accepts metabolic products from the eye, after which it “redirects” them to the circulatory system. Moisture is produced through the ciliary processes of the ciliary body, and outflow occurs through the drainage system.
| The volume of the posterior and anterior chambers holds from 1.23 to 1.32 cubic centimeters of intraocular fluid. It is important to maintain a balance between the decrease and increase of moisture inside the eye. When the indicator shifts, the smooth operation of the visual apparatus is disrupted. |
If more fluid is produced than comes out, glaucoma develops. In the opposite situation, there is a high risk of eye subatrophy. Any slight imbalance has a negative impact on the functioning of the eyes and can even lead to blindness.
The volume of chamber formations in the visual apparatus must be stable; this is the only way to ensure uninterrupted production of intraocular moisture and its outflow.
The structure of the eye chambers and their functions
The anterior chamber of the eye is located just behind the cornea. Therefore, on the outside it is limited by the endothelium of the cornea, consisting of a single layer of flat cells.
On the lateral sides, the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye is limited. And the reverse surface of the cavity represents the anterior surface of the iris and the body of the lens.
The depth of the anterior chamber is variable. It has its maximum value near the pupil and is 3.5 mm. With distance from the center of the pupil to the periphery (lateral surface) of the cavity, the depth uniformly decreases. But when the crystal capsule is removed or the retina is detached, the depth can change significantly: in the first case it will increase, in the second it will decrease.
Below the anterior chamber is the posterior chamber of the eye. It is shaped like a ring, since the central part of the cavity is occupied by the lens. Therefore, on the inside of the ring, the chamber cavity is limited by its equator. The outer part borders on the inner surface of the ciliary body. In front is the posterior layer of the iris, and behind the chamber cavity is the outer part of the vitreous body - a gel-like liquid whose optical properties resemble glass.
Inside the posterior chamber of the eye there are many very thin threads called zonules of cinnamon. They are necessary to control the lens capsule and ciliary body. It is thanks to them that contraction of the ciliary muscle is possible, as well as ligaments, with the help of which the shape of the lens changes. This structural feature of the visual organ gives a person the opportunity to see equally well both at short and long distances.
Both chambers of the eye are filled with intraocular fluid. Its composition resembles blood plasma. The liquid contains nutrients and transfers them to the eye tissues from the inside, ensuring the functioning of the visual organ. Additionally, it receives metabolic products from them, which are subsequently redirected into the general bloodstream. The volume of the chamber cavities of the eye is in the range of 1.23-1.32 ml. And it is all filled with this liquid.
It is important that a strict balance is maintained between the production (formation) of new and the outflow of spent intraocular moisture. If it shifts to one side or another, visual functions are disrupted. If the volume of fluid produced exceeds the volume of moisture that has left the cavity, then intraocular pressure develops, which leads to the development of glaucoma. If more fluid goes into the outflow than it is produced, the pressure inside the chamber cavities drops, which threatens subatrophy of the visual organ. Any imbalance is dangerous for vision and leads, if not to loss of the visual organ and blindness, then at least to deterioration of vision.
The production of fluid to fill the eye chambers is carried out in the ciliary processes by filtering the blood flow from the capillaries - the smallest vessels. It is secreted in the posterior chamber space, then enters the anterior chamber. Subsequently flows through the surface of the anterior chamber angle. This is facilitated by the pressure difference in the veins, which seem to absorb waste fluid.
Physiological role of eye cameras
Their main purpose is to “monitor” the circulation of intraocular fluid. The production of moisture occurs in the ciliary processes by filtering the capillary blood flow. First it appears in the posterior chamber (secreting), then moves to the anterior one. Afterwards, due to low blood pressure, moisture leaves through the UPC, which is responsible for the outflow of fluid.
Also, chamber formations have a number of additional functions:
- Responsible for the conduction of light rays,
- Form “good relationships” between all structures of the eye and intraocular tissues,
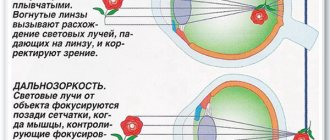
- On “their shoulders” lies light refraction. Thanks to this, the rays are focused on the retina, i.e. cameras act as conductors of sorts.
Organ functions
The main task of the cameras is to regulate the relationships between the tissues of the eyeball. Thanks to them, light rays enter the retina of the eye. Together with the cornea, the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye provide refraction of rays: the optical properties of the cornea and intraocular fluid allow the visual apparatus to capture and form images. In addition, in the second part, with the help of ciliary processes on the celiac body, intraocular aqueous fluid is produced. It then travels through the drainage systems to other parts of the eyeball. The front part is responsible for the outflow of moisture from the organ.
Angle of the anterior chamber - general structure
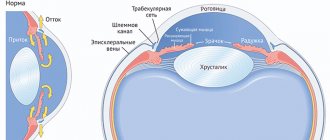
The UPC is a peripheral plane where the cornea smoothly flows into the sclera, and the iris into the ciliary body. The main value of the anterior chamber angle is the drainage system, which is responsible for the outflow of intraocular moisture into the circulatory structure.
It includes:
- Venous sinus, located in the white membrane of the eye,
- Trabecular diaphragm, which is a network with a porous-layered structure. It decreases in size closer to the outside, this has a positive effect on the outflow of intraocular fluid,
- Collecting tubules.
First, the moisture released in the eyes enters the trabecular diaphragm, then it is “directed” into the lumen of Schlemm’s canal (located near the limbus in the sclera of the eyeball).
In some cases, the outflow of intraocular fluid occurs in a different way, through the uveoscleral pathway. Thus, approximately fifteen percent of the total volume of moisture penetrates into the bloodstream. In this case, it first enters the ciliary body, then moves in the direction of the muscle fibers and penetrates the suprachoroidal space. From here, the fluid passes through the veins into Schlemm's canal or the white membrane of the eye.
Collecting tubules in the sclera remove moisture in three directions:
- In the episcleral veins,
- In the vessels of the ciliary body,
- In the venous plexus located on the surface of the white membrane of the eyes.
You will learn more about the structure of the anterior chamber and its functions from the video
Return to contents
Eyeball.
The human eyeball consists of a nucleus and three membranes: outer, middle and inner.
The outer layer of the eyeball is divided into the sclera and the cornea.
- Sclera. It's opaque. The white of the eye is the sclera, white in adults and often bluish in newborns. Its main function in the structure of the eye is to maintain the shape of the eyeball and its nucleus inside. It is to the sclera that the eye muscles are attached, which control the direction of gaze and synchronous eye movement. The sclera also performs a protective function; it protects the eye both from mechanical influences and from excess light entering the retina. Another function of the sclera is stabilization. It is involved in maintaining normal intraocular pressure.
- Cornea. Transparent and light-transmitting shell, thickness from 500 to 650 microns. The cornea has a multilayer structure, which allows it, while transmitting light rays, to also perform focusing and protective functions.
- The tunica media is the choroid of the eye. It contains the vascular part itself (responsible for nutrition and metabolic processes), the ciliary body (the lens is supported on it, it is also responsible for its accommodation and, in addition, is involved in the production of moisture) and the iris (retaining light, working on the principle of a diaphragm, pigmented part of the shell). The pupil is an opening in the iris; the dilation or contraction of the pupil occurs due to the muscles of the iris.
- The inner layer of the eye is the retina. It is she who is responsible for the perception and transformation of electromagnetic radiation into nerve impulses and its further transmission to the central nervous system. Inside the retina is the macula macula, the place of best vision, and the blind spot, where the optic nerve exits.
Posterior chamber of the eye
It is protected in front by the iris and on the back by the vitreous body. On the outside it has a boundary, the role of which is played by the ciliary body; on the inside, a part of the lens acts as a limiter. The entire space of the chamber is filled with connecting threads, which are responsible for the weakening and tension of the ciliary muscles.
Thanks to this function, a person can equally well distinguish between objects located at close and far distances.
You will learn a lot of interesting things about the structure of the rear camera and its functions by watching the video
Should a car enthusiast choose a Parktronic system or a DVR with a mirror?
Useful tips for car enthusiastsAdjusting rear view mirrors
Along with video recorders equipped with rear cameras, the Parktronic parking alarm system and mirrors with a built-in video recording element have become quite widespread. The advantages of using the Parktronic complex are:
- Transmitting information to the driver about events occurring at a certain distance along the entire length of the bumper;
- Lack of sensitivity to changes in weather conditions and temperature;
- Ability to work in the absence of lighting (in complete darkness).
It is recommended to install video recording elements with rear cameras, since they have spatial sensors, and under normal weather conditions they have greater functionality than the Parktronic line. The combination of a DVR with mirrors provides the opportunity to get a good overview. The driver will see the events taking place in several planes: in the mirrors and on the recorder monitor. The rear camera is an addition to the standard mirrors. Currently, car enthusiasts prefer DVRs that have a built-in navigator.
The video shows an overview of the multifunctional video recorder:
Using an integrated video recorder with navigator function
The navigator built into the video recording device is a successful technical solution and allows you to perform several functions simultaneously. Using the navigator, you can determine the desired trajectory of movement by initially setting the necessary parameters (for example, street name and house number).
The integrated recorder kit includes:
- DVR;
- Charger;
- GPS navigator;
- Fastening element;
- Instructions for setup and operation.
In general, the navigator has the following parameters:
- Availability of built-in memory and removable storage;
- Recording events during navigation;
- The navigator supports the cyclic recording function;
- Recording audio information;
- Watching video on GPS;
- Reproducing information on the screen;
- Availability of a set of network cards (as a rule, the navigator uses Google maps);
- The navigator has high resolution;
- A specific navigation program.
A navigator with a DVR is an expensive device, but you can choose models at a fairly reasonable price. The presence of a navigator allows you to receive and display the following parameters:
- Route;
- Time;
- Speed;
- Coordinates (a navigator with a GPS module displays coordinates relative to the generally accepted world system using a satellite).
The navigator can not only indicate the road, but also display all road signs and traffic algorithms in unfamiliar areas. Some models have a prohibition function. The driver can program sections of roads on which he does not want to travel. In this case, the route on a different road will be displayed.
The navigator turns on automatically after starting the engine and turns off when there is no ignition. Using such an integrated complex, you can receive information about what is happening in the parking lot.
Diseases affecting chamber formations
Ailments that affect the back or front of the eye are classified into congenital and acquired. The first category includes:
- Lack of angle in the “facade” chamber,
- Abnormal attachment to the iris from the anterior edge,
- Blocking of the UPC by rudiments of embryonic matter.
The group of acquired pathologies includes:
- Failure in the outflow of intraocular fluid due to blocking of the anterior angle by a pigment spot or enlarged iris,
- Accumulation of purulent discharge,
- Uneven change in the depth of the “facade” chamber. The cause of the deviation may be previous damage to the visual apparatus, displacement of the lens or asthenopia of the zonules,
- Blood condensation (hyphema),
- Formation of connecting cords,
- Cracking of the UPC,
- A hard deposit forms on the endothelial layer of the cornea,
- Glaucoma occurs due to a disruption in the circulation of moisture produced by the eyes,
- Rupture of the anterior part of the ciliary body,
- Injury to the lens or damping of the ligaments responsible for its support, as a result, the depth of the anterior chamber changes,
- Reduction in the size of the anterior chamber, the cause of the pathology most often becomes a closed pupil.
To maintain visual acuity, do not ignore visits to the ophthalmologist. Only a professional doctor, with the help of special tests and examinations, will be able to identify the pathology and select the optimal therapy to prevent its progression. As a preventative measure to prevent eye diseases, visit an ophthalmologist once every twelve months.
| If eye problems begin suddenly, pain appears, or you notice the appearance of blood clots on the whites, visit the doctor unscheduled. |
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the pathological condition depends on the degree of development. The disease has 4 stages.
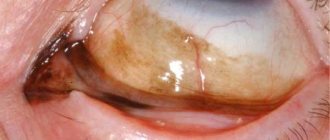
At stage 1 of the pathology, blood fills the anterior chamber by ⅓. At stage 2 of development, hemorrhage occupies 40-50%, at stage 3 - over 50%, at stage 4 - the space between the iris and cornea is completely filled.
The development of hyphema is indicated by a decrease in the acuity of visual perception, the appearance of a veil before the eyes, pain, and photosensitivity.
As the pathological condition progresses, the iris fills with blood; this is clearly visible even without examining the eye with special instruments; it becomes dark red. At the 4th stage of development, it is almost black in color.
Even after drug therapy, the color of the iris may remain red. This is due to trace amounts of enzyme elements and also negatively affects visual functions.
Hemorrhage increases IOP, and neurological signs may appear, such as:
- cephalgia;
- loss of orientation in space;
- flies.
The last stage is characterized by a complete loss of visual perception. Some patients retain only light perception.
Photo
Symptoms of damage to the chambers of the eye
If there are deviations in the functioning of the “elements” of the organ of vision, the following signs are observed:
- Cloudiness of the cornea,
- Painful sensations
- The appearance of new growths or spots on the eyes,
- Fear of bright light
- The resulting image is unclear, has blurry contours,
- Problems with visual acuity,
- With hemorrhage in the anterior chamber, a change in the color of the iris is observed.
If dangerous symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately to identify the disease at an early stage. Return to contents
WHERE CAN YOU BUY A GOOD REVERSE VIEW CAMERA FOR A CAR CHEAP?
Rear view camera for BYNCG car on a rotating bracket
Communities Car cosmetics detailing, tests, tips Blog Glue for gluing the rear view mirror to the windshield.
Customer reviews:
Review No. 1: The goods were delivered to the department within a month, but our post office extended the delivery over two months. Well done seller! I added a free license plate frame to the camera. The camera has dynamic markings, works adequately, and the picture quality is normal. Connecting cables included in complete set. Easy to install.
Review #2: Very fast delivery. 7 days from China to the Post Office in Moscow. Everything works on the table. I bought some dredge for advice. He's been plowing for a year now. The picture is clear. Thank you.
Review #3: The camera is good. The viewing angle is easy to understand. The case is waterproof. The pictures show the couple. I recommend to everyone.
Car frame with rear view camera OTERLEEK
Customer reviews:
Review No. 1: Ordered on 5.02, received 11.02 by courier at home, the packaging is excellent, everything works when connected, the image is good, I installed it on the Hyundai Jazz. Everything is shown clearly. secludes himself with his iPhone via Wi-Fi.
Review #2: Very fast delivery! The camera is in a neat cardboard package, an annotation in English is included. Everything arrived safe and sound. Just great at work! I recommend.
Review #3: Very fast delivery by SDEK. The camera was tested on the stand. Works great. Parking lines appear when you cut the desired wire. I recommend the product and the seller. The seller is recommended to include a monitor in the set.
Parking monitor with rear view camera for Podofo car
Customer reviews:
Review #1: The camera shows, the LEDs are shining. Medium quality. The number fits without trimming
Please note that the camera is quite large; for example, it interferes with opening the trunk. But I didn’t grow up
Overall, great stuff!
Review #2: Everything is intact. Thanks to the seller for the fast shipping. Delivery is also fast. I recommend. Everything works great, video works great both day and night. The only thing that is inconvenient is that the camera is fixed and there is no possibility of adjusting the height. Otherwise everything works well. I recommend.
Review #3: Great camera! Good packaging, mega fast delivery. The number frame is of good quality. If you are thinking about installing a parking camera, then don’t even think about it, get it here. The price is more than reasonable, delivery is instant by courier to your home.
Reversing camera for Aupart cars
Customer reviews:
Review #1: The seller sent it the next day after ordering, it arrived in 5 days, I expected it later. Everything is working. The quality is good, suitable for parking, and the price is reasonable. And the quality of the product itself is good, nothing sticks out, the body is smooth. Not LEDs, but spotlights. I did not communicate with the seller, there was no need. Happy as an elephant after a bath. I recommend.
Review #2: The camera arrived very quickly. I haven't installed it yet. I installed it, everything works, the angle is not great, but quite good, I recommend it.
Review #3: Delivery is fast. The picture is color, does not flicker, there are colored distance marks. I connected it to the TV for testing. Quite normal. We'll go and test it.
Diagnosis of eye chamber pathologies
If the development of a particular disease is suspected, the ophthalmologist sends the patient for several examinations:
- Biomicroscopy. It is carried out using a slit lamp,
- Microscopy of the anterior chamber. Helps detect glaucoma
- Analysis of intraocular moisture, study of its circulation process,
- Coherent optical tomography,
- Ultrasonography,
- Pachymetry. Used to measure the depth of the anterior chamber,
- Automated tonometry. It is used to determine the level of pressure exerted by intraocular moisture.
| Modern equipment and innovative technologies will help detect any abnormality at an early stage, and the doctor will be able to select treatment to block its progression. |
Treatment
Treatment begins after identifying any eye hazards or other life-threatening conditions. Because anterior ocular hemorrhage often results from trauma, patients require endotracheal intubation for other injuries. Succinylcholine is used, it is a depolarizing muscle relaxant.
Ketamine is also used for open bruises or increased intraocular pressure.
Any patient with orbital compression syndrome requires immediate consultation with an ophthalmologist and a canthotomy with cantholysis of the lateral angular ligament. This is required to reduce IOP, increase visual acuity and restore the afferent pupillary defect.
Intraocular pressure is measured before and after the procedure. Determination can be difficult as hyphema can cause increased IOP, relative afferent pupillary defect, and decreased visual acuity.
Treatment aimed at hyphema begins with raising the head on the bed to 30 degrees. An eye shield is installed and worn until the disease is completely eliminated.
To alleviate the condition, topical analgesics are prescribed. Intravenous medications will be needed if oral medications do not help.
If nausea occurs, intravenous administration of Ondansetron up to 12 mg is indicated. Vomiting will cause an increase in intraocular pressure and may cause rebleeding, as well as worsening intraocular hypertension.
Once acute glaucoma has been ruled out, medications are prescribed to eliminate traces of hemorrhage. These are hemostatic and vascular-strengthening medications that resolve and normalize IOP/BP.
Some ophthalmologists recommend steroid therapy. They reduce the risk of rebleeding.
Surgery is a last resort. This is a radical method, indicated for the formation of clots, staining of the cornea with blood, no improvement within 10 days and persistently elevated IOP.
At stages 3 and 4 of the pathological process, surgical intervention cannot be postponed.