Pupil dilator muscle
Muscle tissue is located in the iris, in the area of pigmentation. They function via the sympathetic nervous system. Some categories of people can control pupil dilation.
The muscle tissue that dilates the pupil is called a dilator. It contains spindle-shaped epithelial cells.
Pupil dilation is necessary to improve the quality of vision at dusk and in darkness. At this time, bright sunlight does not pass into a person’s eyes, so dilation of the pupil will not damage the internal structures of the eyes.
Constantly dilated pupils, even in bright sunlight, can occur in people who use opioid drugs. The use of these substances leads to depression of the central nervous system, so the muscle tissue of the pupil ceases to function for the duration of the drug.
Diagnostic methods for pupil damage
If pupillary pathology is suspected, the patient is examined:
- Inspection and determination of pupil symmetry;
- Studying the reaction to a light source;
- Pupillometry, which is performed in cases of severe pathology;
- Study of the reaction of the pupils with the participation of other muscles of the organ of vision.
It should be noted once again that the pupillary opening plays an important role in the formation of a clear visual image by regulating the number of light rays hitting the photoreceptors. With pathology of the pupillary opening, visual function suffers. There is also a change in the pupil in various systemic pathologies of the body. To detect the disease on time, you should not neglect routine eye examinations.
Muscle that constricts the pupil
The muscle tissue that dilates the pupil is located in the iris, where pigmentation spreads. The muscle approaches the opening of the pupil. It is well innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
When a person is indoors in daylight or artificial light, a signal from the eyes enters the central nervous system, from where an impulse is sent to constrict the pupil. This condition is called miosis. It is necessary to protect the internal structures of the eyes from excessively bright light. A person does not need to dilate the pupil, since in daylight all objects are clearly visible.
The muscle with which the pupil contracts is called sphincter. Methods for testing central nervous system reflexes are based on pupil constriction. They are not subject to independent human control. Therefore, when a bright light is directed at the eyes, the pupil should narrow to a point. If such a function is absent, this means that the central nervous system has ceased to function.
Pupil function
There is a popular phraseology among the people: “to take care of it like the apple of your eye,” but few people these days know that in the old days it was the pupil that was called the apple. This expression has been used for a long time and perfectly shows how we should treat our eyes - as the most valuable and expensive.
The human pupil is regulated by two muscles: the sphincter and the dilator. They are controlled by different groups of nerves belonging to the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
The pupil is essentially the hole through which light enters the retina of the eye. It acts as a regulator, narrowing in bright light and expanding in low light. Thus, the pupil of the eye protects the retina from burns and increases visual acuity.
Causes of constricted pupils, how to constrict pupils
The first reaction that the gaze of a person whose pupils are narrow reflexively evokes is doubts about his adequacy: it immediately seems that he has taken some kind of psychotropic drug. What if we are talking about a close relative or yourself? Then the constricted pupils of the eyes can even cause panic or anxiety disorder.
Our article is designed to take your anxiety into a direction that is less destructive to your psyche. So, by comparing all the existing symptoms with those described below, you can assume a certain diagnosis and go straight to the right specialist, without wasting time on a lengthy diagnosis. We will also talk about which drops constrict the pupils.
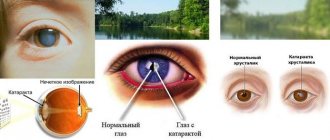
Normal pupils and who provides it
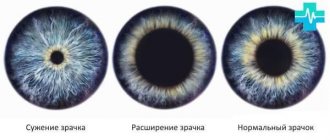
The pupil (pupilla) is a circle of black (red for albinos) in the center of the iris. It should be round, and in normal room lighting, if a person is not looking at the light, be 2-6 mm in diameter. In the dark, the pupils have a larger diameter: 4-8 mm.
The pupils of both eyes should be the same, but a difference of 0.4-1 mm is allowed. Wherein:
- both of them react to light by uniformly contracting;
- in the light the interpupillary difference is less noticeable than in the dark;
- the person himself does not feel that his pupilla have a different diameter: he is not bothered by double vision, photophobia, or a feeling of “stiffness” of the eyes;
- instillation of mydriatic drops (dilating the pupilla) eliminates the difference between them.
The pupil is the hole between the edges of the iris. Its task is to protect the retina from bright light, so in such conditions it narrows, allowing fewer rays to reach the retina. It will also narrow when viewing objects located close to the eye.
The narrowing of the pupilla is called miosis, and the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (the one that controls the internal organs without conscious participation) is responsible for it. It is she who gives commands to the muscle that constricts the pupil (its medical name is sphincter pupillae).
The sphincter pupillae is located at the very edge of the iris. It is localized along the perimeter of the pupillary opening and has a thickness of about 0.1 mm and a width of 0.6 to 1.2 mm (this is about 1/10 of the iris).
The muscle fibers of the pupillary sphincter, slightly further from the edge of the pupilla, are located in three planes. Along the perimeter of the pupillary opening, the muscles have a circular orientation. Between the individual bundles of muscle fibers lie thin sections of connective tissue in which the vessels are “wrapped.” The muscle constrictor pupilla is divided into 70-80 segments (a different number for each person) with the help of small nerve branches: one nerve fiber of small diameter approaches one segment. These fibers originate from the parasympathetic part of the oculomotor nerve, which does not immediately branch into 70-80 parts, but reaches the ciliary ganglion (a kind of “switch” in the fatty tissue of the orbit, which consists of approximately 2.5 thousand neuron bodies). And from this node small segmental branches emerge, which penetrate the white membrane of the eye and approach the iris and pupillary sphincter.
On the subject: How to eliminate thigh muscle spasms
Whether the pupils are dilated or constricted depends on the joint work of the sphincter of the pupil and the muscle that dilates it. They are controlled by the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems, respectively, so if their work is disrupted, there will also be one of the states: either greatly dilated or constricted pupils. A change in the diameter of the hole in the iris will also occur in diseases of the central nervous system, in which the centers that control the autonomic nervous system are located.
What function does the pupil perform?
The pupil performs several important functions:
- By changing its diameter, it regulates the amount of light falling on the retina, resulting in full focusing of the image.
- Screens out light flows penetrating to the periphery of the lens, helps eliminate the halo effect (glow) around objects.
- In the presence of too bright light, it minimizes its entry into the retina area, protects the retina, and prevents burns.
At dusk, the pupil becomes larger in size. At the same time, color perception deteriorates and visual acuity decreases. At the same time, the retina’s ability to perceive low-intensity light increases, and a person retains the ability to spatial orientation and visualize objects located nearby.
Main types of pupil constriction
The condition when the pupils are constricted (miosis), depending on the reasons, happens:
- functional (physiological), when the pupils react to natural causes. This is a variant of the norm;
- drug-induced, occurring in response to drugs that either stimulate the pupillary sphincter or paralyze the muscle that dilates it. Drug-related includes not only miosis that occurs during the treatment of an eye or other disease, but also that which occurs during poisoning with dyes, organophosphorus and other compounds, during poisoning with ethyl alcohol, nicotine and certain types of narcotic drugs;
- syphilitic, which occurs when the causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum, enters the brain or the membranes surrounding it. Narrowing of the pupilla in both eyes, observed with diagnoses of encephalitis, meningitis and even stroke, indicates the need for examination for syphilis;
- paralytic, resulting from paralysis of the dilator pupilla muscle. This is possible with the development of pathological processes in the area of either the carotid plexus or the center (ciliospinal) where the sympathetic cervical nerve originates. Miosis may also indicate damage to the cervical center of the sympathetic nervous system - the sympathetic trunk. Such a lesion usually causes constriction of one pupil;
- spastic. It occurs as a result of spasm of the pupillary sphincter, which is caused by stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system. This is caused by tumors in the brain, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, and renal failure at the last stage - uremia. Miosis is observed during an attack of epilepsy, when the body and limbs do not twitch, but stretch.
Let's look at the causes of constricted pupils in more detail.
Physiological role of the pupil
The main role of the pupillary opening is to regulate the number of light rays that pass through the pupil and vitreous body and enter the retina. In order for the image to be clear, a certain amount of light is needed to illuminate the objects. Due to the reflection of light rays, the eyes, and then the human brain, receive information about the object. Due to the fact that the pupil is able to change its size, the eye can perceive images in different lighting conditions.
The principle of operation of the pupil hole is similar to the operation of the diaphragm in a camera. If there is an increased level of illumination, the aperture decreases, which reduces the intensity of irradiation of the film or matrix. The result is a clear image. If there is insufficient illumination, the diaphragm expands, resulting in an increase in the number of penetrating light rays. This also helps ensure clear images. Likewise, the pupil increases or decreases depending on the level of illumination. The pupillary reflex is responsible for this action.
When the pupils are constricted in both eyes
Constricted pupils can be a sign of many conditions, both pathological and normal.
Fine
Miosis (but not pinpoint pupils, but with a diameter of 2-3 mm), if this symptom is not accompanied by blurred vision, headache, nausea, and there is a pupilla reaction to light, can be considered normal in such cases:
- if this is a child under one year old (the muscles that provide accommodation are still poorly developed);
- if this is a person over 70 years old (the muscles of the pupil are developed, but already weakened);
- in a person with large degrees of farsightedness;
- if there was significant fatigue - physical or mental, which led to temporary fatigue of the pupillary muscles;
- in bright light;
- if a person sleeps with his eyes half-closed, then it is clear that his pupil is narrow.
As a result of taking medications
The answer to the question of why the pupils are constricted may be hidden in the drugs used for treatment:
- hypertension, angina pectoris, ischemic heart disease or arrhythmia. These are beta blocker drugs. These are “Atenolol”, “Anaprilin”, “Metoprolol”, “Corvitol” and many others;
- glaucoma, temporary increase in intraocular pressure, retinal vein or artery thrombosis, optic nerve atrophy or vitreous hemorrhage. These are eye drops “Pilocarpine” (they are also produced under the commercial names “Pilogel”, “Salagen”, “Humacarpine”);
- myasthenia gravis, neuritis, botulism, atony of the intestines, stomach or bladder. These are anticholinesterase drugs: “Proserin”, “Neuromidin”, “Axamon”, “Amiridin”;
- severe pain (for example, during oncological processes): Tramadol, Morphine and analogues.
In case of poisoning and drug use
If constricted pupils are found in a person who works with substances such as:
- aniline dyes;
- poison for insects - organophosphorus compounds;
- nerve agents,
You need to urgently sound the alarm and not wait for other symptoms to appear, but hospitalize the victim in the toxicology department.
If a loved one has severely constricted pupils and behavior that is unusual for him, but he does not work with any of the above substances, he may be taking narcotic drugs. So, miosis can be caused by:
- chloral hydrate (hypnotics and anticonvulsants);
- clonidine (a blood pressure lowering agent that also has a pronounced hypnotic effect)
- alcohol;
- nicotine (when a large number of cigarettes have been smoked);
- opiate (morphine-like) drugs: heroin and its cheaper analogues. In this case, the pupils turn into “dots” that do not react to light. The eyes become half-closed, drowsiness appears, and appetite disappears. The lips of a person addicted to opiates are red and swollen; he scratches constantly: he touches his nose and face more, but notices itching in other parts of the body.
Constricted pupils can also be a symptom of mushroom poisoning (especially fly agarics) or drinking too much coffee. The victim himself can help distinguish such food poisoning from taking narcotic substances: he will say that he drank coffee or ate mushrooms that he collected himself (a drug addict, except for those with great “experience”, does not admit to using opiates). In both of these cases, medical care must be urgently provided in a hospital setting.
For illnesses
Now let's talk about what constricted pupils mean if a person does not suffer from farsightedness and it is possible that he has been poisoned or is taking any addictive substances. Such a symptom can develop in many diseases, but in this case it is necessarily accompanied by accompanying symptoms.
On the subject: How Arnold pumped up his muscles
Liver failure
In this case, constricted pupils are the “lesser evil” against the background of the observed symptoms:
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- unpleasant sweetish (similar to the smell of boiled liver) odor from the mouth and skin;
- increased bleeding: gums bleed if a person brushes his teeth, heavy periods are observed in women, blood can also be in vomit and feces;
- nausea, vomiting;
- inappropriate behavior;
- daytime drowsiness and nighttime insomnia, which develop into constant drowsiness as the disease progresses.
Kidney failure
Constriction of the pupil is observed at the final stage of the disease - uremia. Miosis in this case is the most “insignificant” symptom against the background of other signs:
- decreased amount of urine;
- smell of ammonia (like ammonia) from the mouth;
- headache at normal and even low (up to 35°C) body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- stomach ache;
- the skin becomes thin, dry, covered with “powder”;
- drowsiness;
- tendency to bleed.
Constriction of the pupils as a sign of cerebral edema
A large number of diseases can lead to cerebral edema, one of the signs of which is depression of consciousness up to coma:
- diabetes mellitus, when blood glucose becomes either very high, or, conversely, decreases below 3 mmol/l (the latter condition is usually caused by taking insulin or glucose-lowering tablets, after which a person forgot to eat, or when he took them against the background of an infectious disease that has developed) ;
- uremia;
- liver failure;
- Brain tumors: mainly those localized in the cerebellum, pons or midbrain. In this case, the pupils are “pinpoint” and do not react to light;
- inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or its membranes (meningitis);
- stroke, often hemorrhagic, which is a hemorrhage into the cranial cavity or into the brain itself;
- if the coma has developed as a result of taking drugs.
The main symptom in this case is extreme drowsiness, when at first it is possible to wake a person, but not for long, then he wakes up, but cannot answer a simple question even in monosyllables (“yes” or “no”). When a coma develops, it is impossible to achieve a response, even if you strongly “stimulate” the person. Intracranial pressure increases, which causes constricted pupils.
Of all the described cases, coma can develop quickly, in a matter of hours (less often - minutes), only with an overdose of opiates, hemorrhagic stroke and a decrease in sugar levels. With other diseases, their gradual development is observed, accompanied by various complaints. For example, thirst and frequent urination will be observed with diabetes, and headache, drowsiness, fever and nausea will be observed with meningitis and encephalitis.
The speed of development of the disease from the first symptoms to coma varies: with a brain tumor or diabetes mellitus it can take years; Kidney and liver failure and inflammation of the brain lead to such depression of consciousness within a few days without treatment.
When a coma develops, uniformly constricted pupils are not the worst sign. It is much worse if the coma develops against the background of a condition when one pupil is dilated and the other is narrowed. This most likely indicates that, against the background of cerebral edema, there is a displacement of its temporal lobe into the opening of the dura mater, which in this area has formed a structure called the tentorium of the cerebellum. This condition is called brain dislocation syndrome.
If in this case urgent measures are not taken in the conditions of the neurosurgical department, the death of a person will occur. Transportation if this disease is suspected is only possible with extreme care, lying down, accompanied by medical personnel. You can’t go down the stairs or ride in a car while sitting – it’s dangerous.
Unilateral pupil dilation
If only one pupil of the eye is constricted, this is a less dangerous condition (except for brain dislocation syndrome) compared to bilateral miosis.
They can be caused by various reasons:
Constriction of one pupil is normal
In 20% of the population, a condition may occur when one pupil is 0.4-1 mm narrower than the other. They say that this is the norm:
- normal reaction to light;
- if you dilate your pupils with the help of drops, they will become identical;
- in the dark the difference between the diameters of the pupils is more visible;
- vision is not impaired: there is no double vision, no blurred vision, no fog before the eyes.
Such normal constriction of the pupil can be congenital, or it can develop in people who use monocles in their work (jewelers, watchmakers).
Medical dilation of one pupil
If you drop drops that constrict the pupils (we'll talk about them below) into only one eye, then only one pupilla will be constricted.
Horner's syndrome
This is the name for the manifestation of unilateral damage to sympathetic nerve fibers, the causes of which can be:
- cluster headache;
- injury on one side of the neck;
- cutting of sympathetic endings in the neck during surgery on its organs;
- otitis media from the constriction of the pupil;
- tumor of the apex of the lung on the side of the pupillary constriction;
- aortic aneurysm and its dissection;
- multiple sclerosis;
- enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter);
- Klumpke-Dejerine palsy;
- thrombus in the cavernous sinus of the brain;
- thyroid cancer;
- syringomyelia and some others.
The disease manifests itself as drooping of one eyelid, in the same eye the pupil is narrowed, does not react to light, the eyeball “sinks” into the orbit. On the same side there is a deterioration in sweating, resulting in dry skin.
Paralysis or paresis of the oculomotor nerve
This condition is most often caused by a tumor or inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) in the area where the oculomotor nerve originates. Sometimes this structure is affected due to deterioration of blood supply due to diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis of the vessels supplying the nerve.
On topic: Right calf muscle goes numb
The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- turning the eye with the dilated pupil down and out;
- on the same eye the eyelid droops;
- the dilated pupil does not react to light, but it can narrow (and you could see it at that very moment) when an object approaches and during certain eye movements, the pace of which is set by the healthy eye;
- double vision is noted.
Foreign body or corneal ulcer
The symptoms of these two pathologies are identical. Only with a foreign body does a person know that there has been an eye injury (metal shavings, wooden splinters, and so on). An ulcer develops as a result of infection of this membrane of the eye after touching the eyes with dirty hands, chemical trauma to the eyes, the use of uncleaned contact lenses, and also as a complication of corneal dystrophy or keratoconjunctivitis.
Both conditions appear:
- severe pain in the eye;
- redness of the eye;
- lacrimation;
- miosis on the affected eye;
- There may be strabismus and loss of vision in the injured eye.
Only an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) can make a diagnosis after examination.
Uveitis
This name has inflammation of the choroid of the eye. Sometimes ophthalmologists clarify this diagnosis and say:
- iridocyclitis – if the iris and ciliary body are inflamed;
- peripheral uveitis - when inflammation affects the vitreous body, the choroid (choroid) and the retina;
- choroiditis: the retina, choroid, optic nerve are inflamed;
- panuveitis, when all of the listed structures are inflamed, that is, the entire choroid of the eye.
The diagnosis must be clarified by an ophthalmologist during examination; the symptoms of inflammation of one or more structures of the choroid will be the same. This:
- deterioration of vision up to its complete loss;
- “fog” before the eyes;
- redness of the eye;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia.
In every fourth person, the disease leads to either severe loss of vision or even blindness, so you need to see an ophthalmologist urgently.
This is an inflammation of the iris of the eye. It is a special case of uveitis and manifests itself with the same symptoms as uveitis.
Traumatic hyphema
This is the name for hemorrhage in the anterior chamber, the cause of which was an eye injury. Symptoms of the condition include eye pain, photophobia, constriction of the pupil and decreased vision. If blood has filled more than a third of the anterior chamber, then it becomes visible to the naked eye: it accumulates in front of the iris and pupil and looks like blackening of the iris. If blood fills the entire anterior chamber, the eye appears black.
Structure of the eye
The human organ of vision is a complex optical system. Its main purpose is to transmit images through the optic nerve to the brain.
The eyeball, which has the shape of a sphere, is located in the orbit and has three membranes: fibrous, vascular and retinal. Inside it are aqueous humor, the lens and the vitreous body.
The white segment of the eyeball is covered with mucous membrane (sclera). The front transparent part, called the cornea, is an optical lens with high refractive power. Below it is the iris, which acts as a diaphragm.
The stream of light reflected from the surfaces of objects first hits the cornea and, having been refracted, enters through the pupil onto the lens, which is also a biconvex lens and enters the optical system of the eye.
The next point on the path of the image visible to humans is the retina. It is a shell of light-sensitive cells: cones and rods. The retina covers the inner surface of the eye and transmits information to the brain through nerve fibers through the optic nerve. It is in it that the final perception and awareness of what is seen occurs.
Pupil constriction and pressure
Miosis is a sign of:
- increased intracranial pressure (including temporary, resulting from poisoning);
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure, the causes of which are loss of fluid (vomiting, diarrhea), blood loss, all types of shock (traumatic, septic, hemorrhagic), taking drugs that lower blood pressure;
- persistently elevated intraocular pressure in glaucoma. In an acute attack of glaucoma, on the contrary, there is a dilation of the pupil and its lack of reaction to light.
Midriaz
With mydriasis, the pupils are always dilated, which can be a consequence of various situations:
- paralysis of the eye muscles;
- taking certain medications (estrogens, antidepressants, anesthetics);
- general poisoning of the body;
- mechanical damage to the iris;
- neurological disorders, unsuccessful surgery.
Treatment of mydriasis consists of eliminating the main cause that caused the dilation of the pupils. During therapy, it is recommended to wear sunglasses outdoors and indoors to avoid eye irritation when light enters the pupil.
How to shrink dilated pupils
Taking into account all the diseases discussed above, as well as the connection between pupil diameter and various types of pressure (intraocular, intracranial, arterial), you can understand how to narrow the pupils:
- or reduce intraocular pressure;
- or increase the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- or lower blood pressure;
- or cause injury to the eye;
- or increase intracranial pressure.
Each of these principles allows you to narrow the pupil of the eye, but is dangerous to health, especially the one that suggests increasing intracranial pressure. The safest of all is the use of drugs that will lower intraocular pressure and cause a spasm of accommodation. These are eye drops or ointments:
- “Pilocarpine hydrochloride” and analogs with the same name with the addition ) “Isopto-carpine”, “Humacarpine”, “Salajen”;
- "Carbachol" 0.5% (analogs: "Isopto-carbachol", "Carbacholin", "Oftan Carbachol");
as well as drugs for systemic use:
- "Aceclidine" 2% for subcutaneous injection;
- “Prozerin” for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration and its analogues “Physiostigmine”, “Neuromidin”;
- "Guanethidine" ("Octadine") - tablets and their analogues "Isobarin", "Sanotensin", "Ismelin".
All these drugs should be prescribed by a doctor, since it is not enough just to narrow the dilated pupil; it is also necessary that with such a decrease in intraocular pressure, the structures of the eye can receive the necessary nutrition and oxygen supply. The use of miotics (drops that narrow the pupilla) without prescription can lead to side effects such as:
- decreased vision, especially at night;
- headache in the area around the eyes and temples;
- cataract;
- myopia;
- lacrimation and discharge of a large amount of discharge from the nose;
- inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva;
- dermatitis of the eyelids (redness, swelling and soreness).
People who take drugs use another method to constrict their pupils after taking drugs. They affect the parasympathetic nervous system. One of them - "Becarbon" - is taken to treat gastritis with high acidity and intestinal spasms. Its side effects are dry mouth, drowsiness, dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and impaired accommodation. It is “Becarbon” and drops that reduce intraocular pressure that are used by drug addicts who are looking for a way to narrow their pupils after a hair dryer (amphetamine).
What to do if your pupils are constricted
What should a person do when this symptom appears? - Just see a doctor. How to choose it?
- If miosis is accompanied by confusion, headaches, difficulty swallowing, breathing, facial asymmetry or fever, you should call an ambulance.
- If miosis appears after working with pesticides or dyes, emergency assistance is also needed.
- Miosis after eye injury requires consultation with an ophthalmologist. In the evening, eye trauma departments in multidisciplinary hospitals in large cities operate for this purpose.
- If constriction of the pupil is accompanied by redness of the eyes, lacrimation, blurred vision, it is best to start the examination with an ophthalmologist.
- In all other unclear cases, but provided that there are no symptoms from points 1 and 2, contact your doctor.
Source