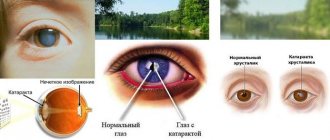
Different pupils (or anisocoria) are a common ophthalmological abnormality. In adults, differences in pupil size occur in 20 people out of 100 and are considered a physiological norm. At the same time, anisocoria is a symptom of serious neurological diseases (cerebral hemorrhage, oculomotor nerve palsy, and others). In patients of this profile, this sign is detected in 50% of cases. Elimination of anisocoria is carried out by treating the underlying disease.
Why do adults have different pupil diameters?
Anikozoria can be of three types:
- physiological;
- congenital;
- acquired
Read more about each type below.
Physiological
human eye structure diagram
This is a harmless type of pathology. With the physiological nature of anicozoria, the difference between the diameter of the pupils is from half to one millimeter. What is chorioretinitis can be found here.
Statistics from medical specialists indicate that physiological anicozoria occurs in approximately one fifth of the world's population.
Congenital
This type of pathology is more dangerous than the first. Eyes with different pupils due to the congenital nature of the disease may also have different levels of vision. As a rule, the reason here is a genetic predisposition or a special structure, damage to the nervous system of the visual organs.
You can read about the causes of convergent strabismus here.
Acquired
pupil structure
All other types of anicorrhysia that appear in a person during his life as a result of injuries, diseases, and other reasons are classified as acquired.
When to visit a doctor
If, in addition to unequal pupil diameters, the patient has other symptoms, it becomes mandatory to contact a specialist. It is necessary to visit a doctor in cases where anisocoria is accompanied by:
- unbearable headaches;
- frequent dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- discharge of pus from the eyes;
- nausea, vomiting that does not cause relief;
- double image;
- weakening of visual acuity;
- disorientation.
In some cases, a patient with anisocoria may suddenly lose consciousness. Such a situation requires an urgent call to the Ambulance and emergency medical intervention.
Reasons and what determines the size of a person’s pupils
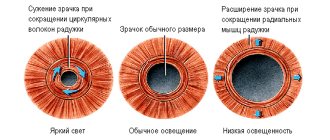
The pupil in the human eye is responsible for regulating the light rays that constantly hit the retina when the eyes are open. It is the quantity and quality of light falling on the pupil that leads to a decrease or increase in its diameter. So, in dim lighting the pupil narrows, and in bright light it expands.
How to treat a chalazion on the upper eyelid can be found on our website.
Ideally, both pupils should be the same size - and this is what they are for most people. However, if there is a slight “skew” in the diameter of one of the pupils, and it is slightly larger in size than the second, doctors advise not to sound the alarm. If the deviation is insignificant and the level of vision does not drop, this fact is considered normal and acceptable. However, if the size of the pupils differ greatly and noticeably, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist.
Important: it is considered acceptable to exceed the diameter of one pupil by one millimeter, no more.
The causes of pathology can be various factors; below we will consider the most common of them.
Genetics
pupil reaction to light
One of the main factors determining the appearance of anicozoria in humans. In this case, the problem will manifest itself from an early age. Note that hereditary anicozoria does not cause any harm to health, and a drop in the level of vision does not occur in this case.
Medicines
The use of certain medications may cause temporary dilation of the pupils. Such medications are usually mydriatic drops, as well as drugs for the treatment of asthma in the form of inhalers.
Muscle work
If the eye muscles malfunction, the size of the pupil may be distorted when light rays enter the eyes.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome
With this disease, the pupil dilates in a person in adulthood, and, having dilated, it stops responding to light stimuli. The syndrome appears as an individual sensitivity of the body to pilocarpine. This expansion is detected randomly, since it does not cause any negative aspects in a person.
In addition, the causes of this pathology can also be:
- damage to the optic nerve;
- neurological pathologies;
- atrophy and aneurysm of the visual organs;
- taking drugs (opium, cocaine, etc.)
constriction and dilation of the pupil depending on external factors
Often the cause of this phenomenon is developed myopia - in this case, the pupil will be dilated in the eye that sees worse.
Pathological, dangerous causes of anicozoria are also possible, among them the following are especially likely:
- bleeding as a result of injuries, bruises of the head;
- tumor-like formations in the brain;
- infection of the lining of the brain, manifested as meningitis or encephalitis;
- pathological damage to the oculomotor nerve;
- glaucoma and migraine;
- cancer of the lung (upper part);
- lymph node cancer;
In addition, if there are pupils of different sizes with different colors of the iris or slightly drooping eyelids, we can talk about Horner's syndrome. This is a congenital pathology, but manifests itself only in adulthood. The “trigger” that triggers Horner’s syndrome is spinal injuries, osteochondrosis of the cervical area, injuries to the spinal and cervical muscles.
It is possible to accurately establish the cause of anicozoria only with a professional ophthalmological examination.
Causes
Physiological anisocoria is usually caused by genetic characteristics. The congenital pathological form of the deviation occurs against the background of underdevelopment of the visual organs and is accompanied by the progression of strabismus (observed from birth).
Other causes of the disease can be divided into types of anisocoria. So, among the ophthalmological prerequisites:
- Injuries and mechanical damage to the eyeball, supporting muscles and iris of one of the two eyes;
- Iridocyclitis (inflammatory processes on the ciliary body and iris);
- Infections (eg herpes);
- Glaucoma (accompanied by a systematic increase in fluid pressure inside the eye).
Serous iridocyclitis as a cause of anisocoria
Neurological causes:
- Hemorrhage and stroke;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms (including in the brain);
- Aneurysm;
- Head injuries.
With these pathologies, there is a disruption of the optic nerve as a result of compression.
Syndromes and diseases:
- Horner's syndrome. Accompanied by drooping eyelids and, in some cases, a change in the color of the iris.
- Agail-Robertson. It is a sign of the development of syphilis, characterized by immobility and changes in the shape of the pupils.
- Paralysis of the oculomotor system;
- Eydie. It occurs due to infection and paralyzes the supporting muscles.
Paralysis of the oculomotor system as a cause of anisocoria
Other factors of occurrence:
- Taking strong medications and drugs and substances prohibited for sale and use;
- Neurosyphilis;
- Meningitis;
- Encephalitis;
- Consequences of the development of tuberculosis;
- Injuries and lesions of the neck and spine, brachial plexus.
Symptoms
a normal pupil contracts in daylight and dilates in poor light
As a rule, this pathology is detected at an early age, and signs of anicozoria are usually visible to the naked eye.
If the excess pupil diameter in one eye is significantly pronounced, then this fact can be noticed immediately. Often with this pathology, nausea and vomiting occur.
Sometimes distortions of objects, things that a person is looking at are possible. The contours of objects may blur and take on distorted, irregular shapes. In addition, the phenomenon of bifurcation of objects often appears.
The eyes begin to react too intensely to light, especially sudden and bright ones.
Phenomena of a febrile nature, chills and temperature can also accompany anicozoria.
Headache, eye pain, and vomiting are possible. In children with this disease, torticollis is often observed.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following symptoms are added to the existing discrepancy in pupil size:
- fever;
- photophobia;
- headache;
- nausea;
- swelling and drooping of the eyelid (upper);
- rapid decline in vision.
What provokes it?
Normally, the pupils dilate and constrict at the same time, even if the light beam is directed at one eye. Physiological anisocoria is a congenital feature. The condition is observed in 20% of adults and children. In this case, one pupil is less than 1 mm larger than the other.
Let's consider the causes of anisocoria in children. There is no need to worry if someone in your family has had the same symptom. In other cases, the cause of a congenital anomaly may be various pathologies:
- Diseases of the eye structure.
- Deviation from the norm in the development of the optic nerve, often accompanied by strabismus.
- Congenital Horner's syndrome. With this disease, anisocoria is observed along with drooping of the eyelid on the problematic side. In this case, the eyes may be different colors.
It is important to know in which diseases the condition can suddenly manifest:
- Due to encephalitis.
- Due to tumors inside the brain.
- The phenomenon may indicate an aneurysm of the vessels of the cranial cavity.
- Develops after a severe head injury.
- For meningitis complicated by cerebral edema.
- In case of poisoning.
- As a result of inflammatory processes in the iris.
- After an overdose of certain medications.
- Eydie syndrome is characterized by dilation of the pupil in one eye and lack of constriction in bright light.
The causes of the condition when one pupil is larger than the other in adults may be the same as in childhood. There is also a percentage of physiological phenomenon here. Let’s add to the list of pathologies that appear more often in adults:
- As a result of Robertson's syndrome (manifests at the initial stage of development of syphilis).
- At the time of stroke and during the rehabilitation period.
- After taking drugs.
- For diseases of the musculoskeletal system, namely the upper part.
Children
disturbance of pupillary reactions
This pathology is more typical of children, since it is most often recorded in infancy or preschool age. The causes of childhood pathology are similar to adults, these are:
- genetic factor considered safe;
- the use of medications that dilate the pupils;
- deformation of the optic nerve;
- injuries.
You can read about the effectiveness of treating dry eye syndrome in our article.
If we are talking about a baby, then in this case the most common cause is heredity, which is not dangerous, or disruption of the child’s nervous system, which already requires treatment. If anicozoria appeared suddenly in a baby, and he was born with normal pupils, then in this case the causes of the problem may be:
- brain tumors;
- bruise of brain tissue;
- aneurysm;
- encephalitis.
As you can see, the reasons are too serious to turn a blind eye to this problem.
Read what rheumatic uevitis is here.
Note that anicozoria that appears as a result of hereditary factors is not treated, since it does not have a negative effect on the level of vision. If the pathology does not cause visual impairment in the child, does not lead to distortion of objects, blurriness, or other negative consequences, there is no reason to worry.
If your child complains of poor vision or unclear vision of the world around him, it is imperative to visit an ophthalmologist.
Information: as a rule, pathological anicorrizia in children is also aggravated by strabismus.
Toddlers and anisocoria
The causes of anisocoria in newborns are the same as in preschool children, adolescents or.
With a congenital anomaly of a pathological nature, the infant may have abnormalities in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system or pathology in the development of the iris. A newborn is immediately born with such a pathology. It does not cause additional symptoms that affect the child's behavior. In addition to such a symptom as one pupil larger than the other, the baby may experience drooping eyelids or strabismus.
If all probable causes of the pathological nature of anisocoria in an infant have been excluded, but a discrepancy in the size of the pupil diameter is present, it is generally accepted that the pathology is congenital. According to statistics, the size of the diameter of the pupils of the right and left eyes with a congenital anomaly disappears by 5 years of age. It is possible that this feature will not go away, but will remain for life.
With congenital anisocoria, which does not have a pathological cause for its origin in children, in addition to the fact that one pupil differs in size from the other, different eye colors may be observed.
If parents notice that the baby's pupil is larger than the other, it should be shown to a doctor.
Pathology can arise as a result of the following circumstances:
- After falling and hitting your head on a hard object. In infants, the skull bones are not yet strong enough. The percentage of injuries with aggravating consequences at such a young age is quite high.
- Brain tumor (malignant, benign). The causes of tumors in the brain can also be triggered by a fall, even from a small height. It is not always possible to find out the reason why a tumor has formed.
- Meningitis and encephalitis tick bite. Symptoms do not appear immediately after the bite, but after a few days. In addition to anisocoria, the patient feels sluggish and lethargic.
- A bulge in the wall of a blood vessel is an aneurysm. In addition to anisocoria, this pathology can lead to hemorrhage in the brain.
- Andy syndrome. The reasons for its occurrence have not yet been fully studied. In addition to the different sizes of pupil diameters, their deformation is observed. After exposure of the affected eye to a light beam, the reaction may be completely absent or a slow process of convergence may be observed.
Diagnostics
If this problem occurs, you need to visit an ophthalmologist for examination and diagnosis. The doctor must study the patient’s medical record and establish a connection between anicozoria and the diseases and injuries that the person had or has. What episcleritis is can be read in our article.
The diagnosis itself takes place in several stages and involves the following types of examinations:
- biochemical blood test;
- spinal puncture;
- head examination on a computer;
- MRI;
If glaucoma is suspected, tonometry is prescribed.
Horner's syndrome or simple anisocoria
A very rare disease, the basis of which may be compression of the sympathetic nerve in the chest or neck, paralysis of the eye muscles. Anisocoria in Horner's syndrome is a delay in the dilation of one pupil.
If you shine a flashlight on your face and then turn off the light, you can watch this happen. At first, the pupils will be distinctly different from each other; in the dark this will be clearly visible for only 5 seconds, after which the difference will decrease, since the pupil will still dilate.
In addition to anisocoria, the following may be present:
- ptosis – drooping of the upper eyelid;
- miosis – constriction of the pupil (most often noticeable in the dark);
- pseudo enophthalmos - apparent retraction of the eyeball;
- anhidrosis – lack of sweat on the face.
The reasons for the development of Horner's syndrome are not known for certain; practice shows that these are mainly disruptions in the activity of the nervous system. As well as osteochondrosis, damage to the ternary nerve, spinal injuries, malignant tumors, strokes and migraine attacks. True, this is more often observed in adults.
In young children, Horner's syndrome is mainly a congenital pathology. It can also be caused by birth trauma. In such cases, the iris on the affected side is always lighter. Even if there was no birth trauma, a thorough examination (CT and MRI) may be necessary to determine the causes.
With the development of heterochromia (different iris colors), a chest x-ray, a tomogram of the head and neck, and a daily catecholamine test for neuroblastoma, a malignant tumor of the sympathetic nervous system, are prescribed.
Treatment
If a connection between an increase in pupil size and heredity is identified, the pathology cannot be treated. In all other cases, therapeutic measures are prescribed, and sometimes urgent surgical care is required. If blood vessels burst in the eyes, the reason may be poor sleep and fatigue.
This pathology is especially dangerous if it arose as a result of an eye or head injury suffered by a person. In this case, it is necessary to undergo examination and begin treatment as early as possible.
Various means are used to eliminate anicozoria, including:
- drugs to combat migraine;
- means to reduce swelling of brain tissue;
- corticosteroids;
- anticonvulsants;
In case of meningitis and other infectious diseases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If the cause of the problem is tumor formations, the latter are eliminated with the help of appropriate surgical intervention.
Absolute scotoma requires immediate treatment.
In addition to the above, during the treatment process, if necessary, analgesics, antitumor drugs and others are used as prescribed by the doctor.
When using medications with the effect of dilating the pupil, the problem appears only for a certain time, and goes away on its own as soon as the medication is finished. However, in any case, it is necessary to inform the attending physician about the effect of this medicine: perhaps the doctor will consider that it is better to replace the drug.
A complication of viral conjunctivitis can be blurred vision.
Self-medication for anicozoria is strictly prohibited, since the causes of the disease can be pathologies that cannot be identified by any self-diagnosis methods.
How to treat anisocoria
Depending on which factor provoked the development of this deviation, the course of treatment may vary. Let us consider in more detail the principle of treatment of anisocoria in accordance with the causative factor.
Table. Features of the treatment of anisocoria in adults.
| Cause of pathology | Features of treatment |
| Multiple sclerosis | A serious autoimmune disease that is accompanied by damage to the nerve fibers of the patient’s spinal cord and brain. To treat the pathology, doctors can prescribe glucocorticoids, donor immunoglobulins, and immunosuppressants. The duration of the therapeutic course and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician. |
| CNS damage | First of all, during treatment, the doctor performs surgical removal of the hematoma, which caused the displacement of the stem section. During the surgical procedure, the patient undergoes craniotomy. After this, restorative agents are prescribed that accelerate regeneration and metabolic processes in the body. |
| Herpetic infection | A recurrent infection of a chronic nature, for the treatment of which doctors usually prescribe interferons. The most effective of them is Acyclovir. |
| Food intoxication | A common pathological condition that every person has had to deal with. If the body is poisoned, it is necessary to lavage the stomach to eliminate toxic substances from it. Also, in case of intoxication, enterosorbent drugs are prescribed, for example, Smecta, Sorbex, Polysorb, etc. |
| Migraine | Migraine occurs, as a rule, when blood circulation in the brain, or more precisely, in one of its hemispheres, is impaired. In parallel with the dilation of blood vessels, the patient's intracranial pressure increases. Medications such as Naproxen, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol and Aspirin are used in treatment. |
The course of treatment depends on the cause
In almost all cases, different pupil sizes indicate a serious illness that requires immediate treatment. Therefore, you cannot ignore the symptom, because this is fraught with serious consequences.
Physiological anisocoria does not affect vision or eye health. Therefore, it does not require treatment.
With pathological anisocoria, the cause of the appearance of different pupils is first identified. Then they carry out treatment.
For example, for a brain infection, treatment is carried out in a specialized hospital. A course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs is prescribed.
Head tumors and aneurysms of the head vessels require surgical treatment.
For glaucoma, treatment is aimed at normalizing eye pressure and preventing the development of glaucoma attacks.
In case of inflammatory eye diseases, a course of treatment with antibiotics is carried out.
For eye tumors, surgical treatment is indicated.
In the case of physiological anisocoria, treatment of the symptom is not required.
The presence of pathological anisocoria indicates serious diseases of the eyes or head. Therefore, if the cause is not identified and treatment is started on time, serious complications may arise and life-threatening conditions may develop for the patient.
Prevention
The main thing for successful treatment of this pathology is to pay attention to the problem in time and consult a doctor. In this case, in the absence of a threat to vision and health in general, it will be possible to limit oneself only to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and observing general preventive measures. If the pathology is dangerous, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment that will avoid the dangerous consequences of anicozoria.
The key to successful treatment of eye cancer is timely diagnosis.
There are no specific preventive measures for this disease. We can only advise compliance with general health recommendations: maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eliminating bad habits, caution when engaging in traumatic sports, work, taking additional vitamin complexes.
We learned what eye pathology called anicozoria is. As you can see, pupils of different sizes can be a purely external feature of a person that does not pose a threat to his health, but they can also mean a dangerous pathology. To accurately find out this fact, you need to contact an ophthalmologist for examination. With timely treatment of anicozoria, the prognosis in most cases is favorable, including in pediatrics.
Causes
It is worth paying attention to relatives, since if there is a similar feature in family genetics, then there is a chance that this phenomenon may repeat in one of the newborns. In this case, there should not be much concern, since this is just a hereditary transmission of the genetic code
It usually appears shortly after birth and does not cause any emotional or mental delay in development. Very often this phenomenon disappears by the age of 5-6 years, sometimes it remains for life.
The effect of different pupils can occur due to frequent and long-term use of eye drops. Some drugs can cause changes in the eyes, in particular, dilate the pupils. The characteristics of the drugs have different effects.
A child may have pupils of unequal size if the muscles responsible for their dilation do not function correctly. This usually happens when the light changes and their darkness enters the illuminated room.
With inflammatory processes in the membrane of the eye, there may also be a problem with access to information inside the eye about the brightness and intensity of the light flux. And this causes different reactions of the pupils and therefore one of them may slow down and not dilate in time.
With injuries and tumor lesions of areas of the brain, deviations may be observed. In cases of aneurysm of the cerebral vascular system. For encephalitis.