The pupil is an important part of the eye. It reacts to light, medications and other stimuli. The normal pupil diameter under daylight conditions is 2–6 mm.
Any deviation from it indicates dangerous processes in the body. In many cases, narrowing or, conversely, widening of the pupil becomes an indicator of poisoning, the development of glaucoma and other diseases, sometimes this occurs for natural reasons in conditions of bright directional light.
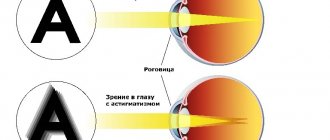
Constricted pupils in humans
When the pupils are narrowed, this indicates certain processes in the body:
- The natural reason is bright light, because of this the size of the pupil changes and it narrows. This occurs in blinding sun or directional light.
When the irritant is removed, the apple of the eye will expand again and return to its normal state. This is a reaction that occurs in all healthy people.
- This effect may be associated with taking medications or other medications. They sometimes cause temporary narrowing of this organ of the eye.
A constricted pupil is often examined during ophthalmic procedures.
- In case of injury, the effect of expansion of the pupil occurs. But there are cases when the opposite process occurs.
If the organ is narrowed and does not return to normal for a long time, this indicates a strong decrease in intracranial pressure. And this condition is expressed in the narrowing of the organ in question,
- When a small dot remains instead of a pupil, this indicates the possible use of psychotropic drugs, anesthetics, alcohol or narcotic drugs. For example, opium, marijuana.
| There is also a medical term for severe constriction of the pupil. This is called miosis. It is characteristic of both eyes, but can also occur in one of them. |
Moreover, the difference is so pronounced that even the interlocutor will notice it. Thus, the effect of miosis is determined by a variety of reasons. Return to contents
How pupils work
It is a key component of the eye, located in the center of the iris. The main task of the pupils is to collect light rays, which are then perceived by the retina of the eye.
There are muscles around the pupils that, by contracting, regulate the illumination of the retina.
For example, when a person enters a dark room, his pupils dilate to catch light, and in a brighter room, his pupils constrict accordingly.
How does the pupil react to light?
This is an important system that allows you to obtain the maximum amount of information from the environment under different lighting conditions. But if pupil function is impaired, serious problems can arise. The degree of illumination in the room is not the only reason for changes in pupil size.
On a note! A similar phenomenon can also be observed under the influence of uniform lighting, so a small difference (no more than 1 mm) may occur between the diameters of the pupils. This indicator is the norm, and if the difference is exceeded, the help of a specialist is necessary.
Natural causes of pupil dilation
Causes of the pathological condition
As noted earlier, anisocoria can develop in people regardless of their age or gender. But there are many factors that can cause this disorder, and all of them may differ depending on whether the patient is a child or an adult.
If in newborns the disease can be triggered by a developmental disorder or genetic predisposition, then in infants anisocoria develops against the background of food poisoning, encephalitis, brain injury, cancer or aneurysm.
Anisocoria
Now let's look at the main causes of anisocoria in adults:
- severe migraine;
- inflammatory eye diseases (iridocyclitis, keratitis and others);
- consequences of using certain medications, for example, Atropine;
- infectious diseases (encephalitis, meningitis, etc.);
- mechanical damage to the organs of vision resulting from injury;
- glaucoma;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- Horner's syndrome;
- development of benign or malignant formations.
Pupils of comatose patients
A factor such as genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out, because anisocoria is one of those diseases that can be inherited . Therefore, if one of your parents or loved ones has previously encountered this disease, then there is a chance that after some time you will be diagnosed with it too.
Additional symptoms
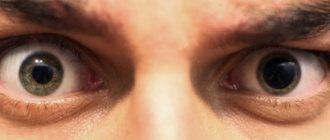
Different pupil sizes
Along with changes in pupil size, the patient may experience other symptoms, including:
- decreased performance;
- blurred vision;
- development of torticollis (pathology accompanied by changes in the nerves, skeleton and soft tissues of the neck);
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the eye area;
- feverish condition;
- Strong headache;
- begins to see double;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- blurred vision.
Strong headache
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Only timely contact with a specialist will allow you to eliminate the problem at an early stage of development, which will eliminate the likelihood of serious complications.
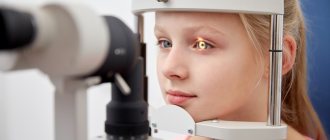
Diagnostic features
You need to contact an ophthalmologist who will conduct a neurological and physical examination of the patient. As a rule, when diagnosing anisocoria, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- checking the reaction of the pupils in a light and dark room;
- X-ray examination of the cervical spine or skull;
- if the development of glaucoma is suspected, the patient undergoes tonometry;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- laboratory analysis of cerebrospinal fluid;
- urine and blood analysis.
Examination by an ophthalmologist
On a note! Based on the test results, the doctor can make a diagnosis. Only after the exact cause of the pathological condition has been established, the patient is prescribed a course of appropriate therapy.
How to treat
Depending on which factor provoked the development of this deviation, the course of treatment may vary. Let us consider in more detail the principle of treatment of anisocoria in accordance with the causative factor.
Table. Features of the treatment of anisocoria in adults.
Cause of pathologyFeatures of treatment
| Multiple sclerosis | A serious autoimmune disease that is accompanied by damage to the nerve fibers of the patient’s spinal cord and brain. To treat the pathology, doctors can prescribe glucocorticoids, donor immunoglobulins, and immunosuppressants. The duration of the therapeutic course and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician. |
| CNS damage | First of all, during treatment, the doctor performs surgical removal of the hematoma, which caused the displacement of the stem section. During the surgical procedure, the patient undergoes craniotomy. After this, restorative agents are prescribed that accelerate regeneration and metabolic processes in the body. |
| Herpetic infection | A recurrent infection of a chronic nature, for the treatment of which doctors usually prescribe interferons. The most effective of them is Acyclovir. |
| Food intoxication | A common pathological condition that every person has had to deal with. If the body is poisoned, it is necessary to lavage the stomach to eliminate toxic substances from it. Also, in case of intoxication, enterosorbent drugs are prescribed, for example, Smecta, Sorbex, Polysorb, etc. |
| Migraine | Migraine occurs, as a rule, when blood circulation in the brain, or more precisely, in one of its hemispheres, is impaired. In parallel with the dilation of blood vessels, the patient's intracranial pressure increases. Medications such as Naproxen, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol and Aspirin are used in treatment. |
The course of treatment depends on the cause
In almost all cases, different pupil sizes indicate a serious illness that requires immediate treatment. Therefore, you cannot ignore the symptom, because this is fraught with serious consequences.
Is it possible to change the size of the pupils?
Many people wonder whether it is possible to influence the size of their pupils on command. For example, you need to narrow or dilate your pupils during a photo shoot. In fact, there is nothing complicated about it. Below are step-by-step instructions, following which will lead you to the desired result.
Step 1. Go into a dark room. As noted earlier, in a dark room the pupils dilate as they try to “catch” more light. If it is not possible to completely turn off the light in the room, then simply turn away from the windows, thereby protecting yourself from light sources.
Go into a dark room
Step 2. To constrict your pupils, turn towards a light source in your home and remain in this position for a few seconds. If you are on the street, then all you need to do is look up. Of course, looking at the sun is bad for your eyes, so it's best to focus your gaze on something else.
Turn towards the light source
Step 3: Another easy way to constrict your pupils. Just look at the object that is located next to you. When focusing the gaze, the pupils constrict. Alternatively, you can place your finger in front of your eye and focus your attention on it.
What should be the normal pupil size?
The zenica is a full-fledged eye organ. Therefore, for her there is no concept of norm. The eye pupil develops differently in each person. Accordingly, its size cannot be the same for everyone.
Another factor is the conditions under which the pupil is measured. This organ is very sensitive to light. Therefore, under different lighting conditions, the norm will be expressed by different indicators.
However, you can take natural light as the norm. It is typical for a sunny day, but without blinding rays directed into the eye. In this state, the diameter will be no more than 6 mm.
But it’s difficult to talk about the minimum. The minimum normal limit is considered to be 2 mm. But the reasons listed above can cause a narrowing of the pupil and its diameter will be the same 2 mm only in a normal state in such a person the pupil size is 5 or 6 mm.
Therefore, the concept of miosis is difficult to generalize and make recommendations for everyone. Everyone can measure the approximate diameter of their pupil in normal lighting and accept this as the norm. Accordingly, a long-term decrease in the organ will indicate its narrowing.
Pupil diameter
The main task of the pupil is to regulate the amount of light entering through it into the vitreous body and retina.
It is a hole in the iris that has no color.
To regulate the flow of light into the retina, the sphincter and dilator are activated. By changing the diameter, a person is able to perceive light and see at different degrees of illumination.
Normal pupil diameter values
The size of the apple of the eye depends on the brightness of the lighting in the room. Normally, its diameter is 2–8 mm. Maximum visual acuity occurs at a diameter of 3–4 mm.
Its size depends on the state of the light-refracting structures of the eye. That is, a person with absolutely healthy visual organs and a farsighted person have a different norm.
Table. Diameter depending on age and pathology (values are indicated in mm)
Age Myopia People with 100% vision Hyperopia
| up to 12 months | 2,0 | ||
| 20–30 | 3,55 | 3,25 | 3,25 |
| 30–40 | 3,6 | 3,45 | 3,3 |
| 40–50 | 3,6 | 3,2 | 3,1 |
Reasons for expansion
Normally, the pupils dilate in the dark. The process is asymmetrical, the reaction occurs in both eyes. If an increase in diameter occurs during the daytime or only on one organ of vision, then this is a pathology.
Causes of mydriasis:
- Emotional and mental experiences. This is considered a physiological norm. The increase in the diameter of the pupils occurs due to the high activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Glaucoma. When intraocular pressure increases, mydriasis appears on the affected side. The dilation of the pupil itself does not affect the patient’s well-being. Glaucoma is manifested by deterioration of visual perception, pain, eye pain and cephalgia.
- Holmes-Ady syndrome. The pathology is characterized by paralysis of the eye muscles. On the affected side, the eye is not sensitive to light, so the pupil stops changing in size.
- Drugs. Only a few drugs can lead to mydriasis. These are antihistamines, Botox, muscle relaxers and medications that are used to treat Parkinson's disease. There are drugs that are specifically used to expand the pupil. They are used for detailed study of the fundus.
- Neuropathy of the 3rd cranial nerve. It causes paralysis, which interferes with the body's ability to control the eye muscles.
- Infectious diseases. Mydriasis develops due to the death of nerve fibers. The disease can also develop after surgery for infection.
- Diabetes mellitus and botulism. Pathological data are considered indirect. They disrupt the functioning of the visual analyzer and its structures.
- Aneurysm. The disease affects the posterior communicating artery, which is located next to the nerve responsible for the movements of the eyeballs and the sphincter. If the nerve is damaged, the functioning of the optical system is disrupted. An aneurysm leads to mydriasis or miosis.
The cause of pupil dilation may be increased dilator tone, accommodation spasm and paralysis of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It also appears as a response to intoxication of the body and due to neurological disorders.
Reasons for narrowing
Normally, constriction of the pupils occurs in bright light when a person goes outside. In this way, the eyes protect themselves from harmful ultraviolet radiation. If the apple of the eye is narrowed in the dark or twilight, or is one-sided, this is a malfunction in the functioning of the optical system.
In medicine, pathological constriction of the pupil is called miosis. The main reasons for bilateral reduction:
- advanced age and hypermetropia;
- dream;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- coma;
- chemical poisoning;
- the effect of certain medicinal agents;
- some sexually transmitted pathologies and somatic diseases.
Unilateral miosis develops for other reasons. More often these are diseases of the optical system.
Causes of unilateral constriction of the pupil:
- Horner's syndrome. The disease is associated with damage to the sympathetic nervous system. It leads to disruption of the visual apparatus and vascular system. There are congenital and acquired Horner's syndrome.
- Local eye damage. If a foreign body enters the eye, miosis may occur. It occurs as a defensive reaction to a foreign object on the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Pupillary dilator paralysis. The dilator is a sphincter antagonist muscle that is responsible for dilatation. If it is damaged, atrophied or paralyzed, the pupil does not dilate and remains narrowed constantly.
- Neurosyphilis. This pathology refers to syphilitic damage to the brain or spinal cord. The clinical manifestations of late neurosyphilis appear at the 7th–8th year of infection. Leads to miosis and anisocoria.
- Spasm of the sphincter of the pupil. The sphincter is responsible for reducing the size of the pupil. During spasm it decreases even more.
Miosis can also be caused by irritation of the third pair of cranial nerves. When irritated, neuralgia occurs, manifested by paroxysmal pain.
If the pupils are asymmetrical
For different pupil diameters, consultation with an experienced specialist is required. The ophthalmologist will determine which pupil has been affected pathologically. This condition is called anisocoria.
Diameter regulation occurs asynchronously, that is, one pupil remains motionless, and the diameter of the second changes depending on the brightness of the lighting. The disease can be hereditary or acquired.
The cause of the development of anisocoria is damage to the parasympathetic innervation system, traumatic brain injury or brain tumors pressing on the optic tract or nerve.
If the pupils are asymmetrical, an ophthalmological examination is performed using light. Rays of light are directed into the eyes. If the smaller diameter pupil does not expand, it is this eye that is affected.
To determine the cause, a series of tests and ophthalmological tests are performed. In some cases, an MRI or CT scan is required.
If the doctor suspects vascular abnormalities, contrast angiography or Doppler ultrasound is performed.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 1.00
Source: https://proglazki.ru/stroenie-glaza/diametr-zrachka/
Causes of constricted pupils in healthy eyes
If the eye disease is not diagnosed, then the number of causes is significantly reduced. For example, pregnancy and the physiological processes associated with gestation are quite capable of leading to miosis.
The entry of the active substance into the body also causes this reaction. This is not about illness. This may be a reaction of a healthy eye to the components of a particular medication.
Miosis can often be observed in infants. But this is a normal condition of the pupils of a newborn. After all, he is just learning to use his eyes, his visual function is developing and his eyes are adapting to new conditions. There's nothing wrong with that either.
Another cause of miosis is strong emotions. Any stimulus matters. For example, anger, rage, anger lead to temporary miosis. This is especially pronounced if a person tries to hide his feelings. But this is not a disease and this condition does not require treatment. The miosis will pass along with the emotional intensity and the pupil will become normal.
Return to contents
Pupils of different sizes in an adult: reasons why diameter and size
Among the variety of ophthalmological pathologies, so-called anisocoria is often encountered - the pupils of the eyes are different in size. The defect is possible in both adults and children.
To find out the reasons why this pathology appears, what causes different sized pupils in humans, how to treat it, and what preventive measures to take, we will consider all these issues in detail in the article.
Why do adults have different pupil diameters?
Anikozoria can be of three types:
- physiological;
- congenital;
- acquired
Read more about each type below.
Physiological
human eye structure diagram
This is a harmless type of pathology. With the physiological nature of anicozoria, the difference between the diameter of the pupils is from half to one millimeter. What is chorioretinitis can be found here.
Statistics from medical specialists indicate that physiological anicozoria occurs in approximately one fifth of the world's population.
Congenital
This type of pathology is more dangerous than the first. Eyes with different pupils due to the congenital nature of the disease may also have different levels of vision. As a rule, the reason here is a genetic predisposition or a special structure, damage to the nervous system of the visual organs.
You can read about the causes of convergent strabismus here.
Acquired
All other types of anicorrhysia that appear in a person during his life as a result of injuries, diseases, and other reasons are classified as acquired.
Reasons and what determines the size of a person’s pupils
The pupil in the human eye is responsible for regulating the light rays that constantly hit the retina when the eyes are open. It is the quantity and quality of light falling on the pupil that leads to a decrease or increase in its diameter. So, in dim lighting the pupil narrows, and in bright light it expands.
How to treat a chalazion on the upper eyelid can be found on our website.
Ideally, both pupils should be the same size - and this is what they are for most people.
However, if there is a slight “skew” in the diameter of one of the pupils, and it is slightly larger in size than the second, doctors advise not to sound the alarm.
If the deviation is insignificant and the level of vision does not drop, this fact is considered normal and acceptable. However, if the size of the pupils differ greatly and noticeably, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist.
Important: it is considered acceptable to exceed the diameter of one pupil by one millimeter, no more.
The causes of pathology can be various factors; below we will consider the most common of them.
Genetics
One of the main factors determining the appearance of anicozoria in humans. In this case, the problem will manifest itself from an early age. Note that hereditary anicozoria does not cause any harm to health, and a drop in the level of vision does not occur in this case.
Medicines
The use of certain medications may cause temporary dilation of the pupils. Such medications are usually mydriatic drops, as well as drugs for the treatment of asthma in the form of inhalers.
Muscle work
If the eye muscles malfunction, the size of the pupil may be distorted when light rays enter the eyes.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome
With this disease, the pupil dilates in a person in adulthood, and, having dilated, it stops responding to light stimuli. The syndrome appears as an individual sensitivity of the body to pilocarpine. This expansion is detected randomly, since it does not cause any negative aspects in a person.
In addition, the causes of this pathology can also be:
- damage to the optic nerve;
- neurological pathologies;
- atrophy and aneurysm of the visual organs;
- taking drugs (opium, cocaine, etc.)
constriction and dilation of the pupil depending on external factors
Often the cause of this phenomenon is developed myopia - in this case, the pupil will be dilated in the eye that sees worse.
Pathological, dangerous causes of anicozoria are also possible, among them the following are especially likely:
- bleeding as a result of injuries, bruises of the head;
- tumor-like formations in the brain;
- infection of the lining of the brain, manifested as meningitis or encephalitis;
- pathological damage to the oculomotor nerve;
- glaucoma and migraine;
- cancer of the lung (upper part);
- lymph node cancer;
In addition, if there are pupils of different sizes with different colors of the iris or slightly drooping eyelids, we can talk about Horner's syndrome. This is a congenital pathology, but manifests itself only in adulthood. The “trigger” that triggers Horner’s syndrome is spinal injuries, osteochondrosis of the cervical area, injuries to the spinal and cervical muscles.
It is possible to accurately establish the cause of anicozoria only with a professional ophthalmological examination.
Symptoms
a normal pupil contracts in daylight and dilates in poor light
As a rule, this pathology is detected at an early age, and signs of anicozoria are usually visible to the naked eye.
If the excess pupil diameter in one eye is significantly pronounced, then this fact can be noticed immediately. Often with this pathology, nausea and vomiting occur.
Sometimes distortions of objects, things that a person is looking at are possible. The contours of objects may blur and take on distorted, irregular shapes. In addition, the phenomenon of bifurcation of objects often appears.
The eyes begin to react too intensely to light, especially sudden and bright ones.
Phenomena of a febrile nature, chills and temperature can also accompany anicozoria.
Headache, eye pain, and vomiting are possible. In children with this disease, torticollis is often observed.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following symptoms are added to the existing discrepancy in pupil size:
- fever;
- photophobia;
- headache;
- nausea;
- swelling and drooping of the eyelid (upper);
- rapid decline in vision.
Children
disturbance of pupillary reactions
This pathology is more typical of children, since it is most often recorded in infancy or preschool age. The causes of childhood pathology are similar to adults, these are:
- genetic factor considered safe;
- the use of medications that dilate the pupils;
- deformation of the optic nerve;
- injuries.
You can read about the effectiveness of treating dry eye syndrome in our article.
If we are talking about a baby, then in this case the most common cause is heredity, which is not dangerous, or disruption of the child’s nervous system, which already requires treatment. If anicozoria appeared suddenly in a baby, and he was born with normal pupils, then in this case the causes of the problem may be:
- brain tumors;
- bruise of brain tissue;
- aneurysm;
- encephalitis.
As you can see, the reasons are too serious to turn a blind eye to this problem.
Read what rheumatic uevitis is here.
Note that anicozoria that appears as a result of hereditary factors is not treated, since it does not have a negative effect on the level of vision. If the pathology does not cause visual impairment in the child, does not lead to distortion of objects, blurriness, or other negative consequences, there is no reason to worry.
If your child complains of poor vision or unclear vision of the world around him, it is imperative to visit an ophthalmologist.
Information: as a rule, pathological anicorrizia in children is also aggravated by strabismus.
Diagnostics
If this problem occurs, you need to visit an ophthalmologist for examination and diagnosis. The doctor must study the patient’s medical record and establish a connection between anicozoria and the diseases and injuries that the person had or has. What episcleritis is can be read in our article.
The diagnosis itself takes place in several stages and involves the following types of examinations:
- biochemical blood test;
- spinal puncture;
- head examination on a computer;
- MRI;
If glaucoma is suspected, tonometry is prescribed.
Treatment
If a connection between an increase in pupil size and heredity is identified, the pathology cannot be treated. In all other cases, therapeutic measures are prescribed, and sometimes urgent surgical care is required. If blood vessels burst in the eyes, the reason may be poor sleep and fatigue.
This pathology is especially dangerous if it arose as a result of an eye or head injury suffered by a person. In this case, it is necessary to undergo examination and begin treatment as early as possible.
Various means are used to eliminate anicozoria, including:
- drugs to combat migraine;
- means to reduce swelling of brain tissue;
- corticosteroids;
- anticonvulsants;
In case of meningitis and other infectious diseases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If the cause of the problem is tumor formations, the latter are eliminated with the help of appropriate surgical intervention.
Absolute scotoma requires immediate treatment.
In addition to the above, during the treatment process, if necessary, analgesics, antitumor drugs and others are used as prescribed by the doctor.
When using medications with the effect of dilating the pupil, the problem appears only for a certain time, and goes away on its own as soon as the medication is finished. However, in any case, it is necessary to inform the attending physician about the effect of this medicine: perhaps the doctor will consider that it is better to replace the drug.
A complication of viral conjunctivitis can be blurred vision.
Self-medication for anicozoria is strictly prohibited, since the causes of the disease can be pathologies that cannot be identified by any self-diagnosis methods.
: we make a diagnosis based on the condition of the pupil
Sometimes the condition of the pupils may indicate a particular disease. You can find out more in our video.
Prevention
The main thing for successful treatment of this pathology is to pay attention to the problem in time and consult a doctor.
In this case, in the absence of a threat to vision and health in general, it will be possible to limit oneself only to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and observing general preventive measures.
If the pathology is dangerous, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment that will avoid the dangerous consequences of anicozoria.
The key to successful treatment of eye cancer is timely diagnosis.
There are no specific preventive measures for this disease. We can only advise compliance with general health recommendations: maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eliminating bad habits, caution when engaging in traumatic sports, work, taking additional vitamin complexes.
We learned what eye pathology called anicozoria is.
As you can see, pupils of different sizes can be a purely external feature of a person that does not pose a threat to his health, but they can also mean a dangerous pathology.
To accurately find out this fact, you need to contact an ophthalmologist for examination. With timely treatment of anicozoria, the prognosis in most cases is favorable, including in pediatrics.
Source: https://ProOko.online/zabolevaniya/glaza/raznaya-velichina-zrachkov-prichiny-i-lechenie.html
Causes of constriction of the pupils as a disease
The most common cause is low blood pressure. The eye is full of blood vessels called capillaries. Their narrowing and partial blockage leads to minor hemorrhages. This condition can cause miosis. But in itself it is not a disease, but only a manifestation of another disease.
In addition, in medicine there is the concept of pathological miosis. This means that a person has had this effect for many years. However, it is not associated with injuries, poisoning or other listed reasons. This is a physiological condition that is normal for such a person and will not lead to problems with visual function.
However, it is necessary to list the diseases that are expressed in constriction of the pupils:
- Meningitis,
- Hypothyroidism. This is a dysfunction of the thyroid gland,
- Iridocyclitis, that is, the process of inflammation of the iris.
Pupil diameter
The human eye detects light thanks to a hole in the iris. The pupil diameter in healthy men and women ranges from 2 to 6 mm.
It can vary depending on the lighting, psycho-emotional and physical state of a person. But with some pathological processes in the body, the pupil size increases.
In this case, asymmetry is observed - uneven diameter in the right and left eyes. This symptom is alarming and requires a comprehensive examination.
Normal pupil sizes in people of different ages
In the medical encyclopedia, the symptom of excessive dilation of the pupils is called mydriasis, and constriction is called miosis. The difference between the diameters of the pupillary openings in the right and left eyes is called anisocoria.
The size of the pupils depends on the state of the light-refracting structures of the eye. These include the cornea, anterior chamber and vitreous body.
In patients suffering from myopia (myopia), the pupil diameter is larger.
This is explained by the fact that the visual organ of these patients needs more light so that the optical zones of the occipital part of the cerebral cortex can identify the picture.
In people with farsightedness (hyperopia), the opposite situation is observed, when the pupil becomes narrower with age. So the visual organ seems to protect the retina from excessive light rays hitting it.
The latter are picked up by rods and cones and travel along the optic nerve directly to the brain. The table below shows the diameters of the orbits depending on age and the pathology present.
| Age, years | Patients with myopia, mm | People with normal vision, mm | Patients with farsightedness, mm |
| Children under one year old | 2,0 | ||
| 20—30 | 3,55 | 3,25 | 3,25 |
| 30—40 | 3,6 | 3,45 | 3,3 |
| 40—50 | 3,6 | 3,2 | 3,1 |
Reasons for the increase
An increase occurs with such pathologies of the organs of vision as increased intraocular pressure.
Mydriasis is a clinical symptom for the following dysfunctions:
- Volumetric processes in the frontal, parietal or temporal regions of the brain.
- Poisoning with drugs such as antihistamines, antidepressants and estrogen hormones.
- Instillation of atropine into the eye. A large pupil width in this case is evidence of the normal state of the main reflex.
- Surgery, traumatic effects or age-related degradation that involve the ciliary muscle in the process. This applies to an older organism.
- Traumatic brain injury with hemorrhage under the meninges.
- Glaucoma. This medical term refers to a persistent increase in intraocular pressure.
- Syringomyelia is a chronic lesion of the spinal structures, which is characterized by the formation of cysts and constant progression.
- Poliomyelitis is an infectious disease in which the white matter of the brain and spinal cord is involved in the pathological process.
- Meningitis and meningoencephalitis. They are also infectious in nature and can be of viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic etiology.
Prerequisites for asymmetry
It is inappropriate to judge how much the pupil weighs, since it is just a hole in the iris, although it looks like a dark structure located in the center of the eyeball.
Pupillary asymmetry occurs mainly when a person sees worse in the right or left eye. But a sharp difference between the diameters of the pupils can also appear in many severe brain lesions.
These include traumatic brain injury, hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke, transient vascular attacks and malignant neoplasms. All of these ailments affect the eyeballs, as intracranial pressure increases.
For example, when a large tumor grows or a hemorrhage occurs in the right hemisphere, the eye on the corresponding side suffers.
Source: https://EtoGlaza.ru/anatomia/vazhno/diametr-zrachka.html
Bad habits and addiction as a cause of constricted pupils
Miosis is often caused by drug use. As a rule, this is marijuana or opium and their derivatives. The use of such substances leads to temporary miosis.
Therefore, this effect can be regarded as a manifestation of drug use. But such an assessment must have other confirmations. For example, inappropriate behavior of a person that does not correspond to the situation around him. In addition, there are cases where drinking alcohol in large quantities led to constriction of the pupils.
But a state of severe intoxication is characterized by dilation of the pupils, not their narrowing. However, the body can react to poisoning from alcohol-containing products precisely with the effect of miosis.
Return to contents
Symptoms
Pupils of different sizes are most noticeable in low light conditions. Under such conditions, one of the pupils dilates, trying to let in the maximum amount of light, while the other, on the contrary, narrows.
With good lighting, the differences between structural elements can be minimal and remain unnoticeable. This is caused by Horner's syndrome, provoked by a malfunction in the sympathetic nervous system and occurring against the background of impaired sweating.
The reaction of the affected pupil to the stimulus is slow. In addition, if mechanical damage occurs, the anatomical structure will not respond not only to light, but also to medications that help dilate the pupil.
In the case of physiological anisocoria, treatment of the symptom is not required.
The presence of pathological anisocoria indicates serious diseases of the eyes or head. Therefore, if the cause is not identified and treatment is started on time, serious complications may arise and life-threatening conditions may develop for the patient.
a normal pupil contracts in daylight and dilates in poor light
As a rule, this pathology is detected at an early age, and signs of anicozoria are usually visible to the naked eye.
If the excess pupil diameter in one eye is significantly pronounced, then this fact can be noticed immediately. Often with this pathology, nausea and vomiting occur.
Sometimes distortions of objects, things that a person is looking at are possible. The contours of objects may blur and take on distorted, irregular shapes. In addition, the phenomenon of bifurcation of objects often appears.
The eyes begin to react too intensely to light, especially sudden and bright ones.
Phenomena of a febrile nature, chills and temperature can also accompany anicozoria.
Headache, eye pain, and vomiting are possible. In children with this disease, torticollis is often observed.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following symptoms are added to the existing discrepancy in pupil size:
- fever;
- photophobia;
- headache;
- nausea;
- swelling and drooping of the eyelid (upper);
- rapid decline in vision.
Why can only one pupil be constricted?
First of all, general influences should be excluded. For example, a psychological state, alcohol or drug use has an impact on the entire body as a whole. Accordingly, miosis will be synchronous and appear in both eyes.
If it is present on only one of them, then we are talking about local processes. These may be the consequences of injuries or individual physiological characteristics:
- Head injury
- Past infectious diseases
- Injury to the organs of vision
- Development of myopia
Causes of dilated pupils
The physiological norm for pupil diameter is 3–5 mm. The size changes depending on the level of illumination in the room and the mood of the person. The pupils dilate or contract for various physiological reasons. That is, this condition is considered normal.
During the day, the pupil constantly changes in diameter depending on the following natural factors:
- Emotions. When a person is in a state of panic, stress, fear and on the verge of a nervous breakdown, there is a reaction in the iris muscles; under the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system, a reflex increase in diameter occurs.
- Reaction to light. This is an important reflex mechanism that occurs when regulating the amount of light. When the light is too bright, narrowing occurs to prevent damage to the visual analyzer by UV radiation. In poor lighting, the pupil dilates, it tries to let in enough light so that a person can navigate in the dark. The diameter changes mechanically. In the dark they expand to 3.8 mm. After 5 seconds in a dark room up to 5.8 mm. This happens all the time.
- Feelings. A person cannot control the contraction and dilation of the pupil. These actions happen automatically. This is a more persistent channel, in which an instant reflex occurs, but the more persistent is the humoral one. For example, an increase in adrenaline (a component of the hormonal “love cocktail”) tends to expand them. Scientists have found that this reaction occurs when a man looks at a naked woman or his child. That is, hormones of happiness are released, a person experiences love and attraction.
- Drugs. To diagnose certain diseases, ophthalmologists use special drops. They are called mydriatics. Medicines dilate the pupil. Thanks to them, the ophthalmologist can examine the fundus of the eye. The effect after using eye drops lasts up to three days.
Diagnostic methods
Anyone can be diagnosed with miosis. To do this, just look in the mirror and pay attention to the state of your pupils. If it does not go away for a long time, you need to undergo a full examination. Obviously, it is necessary to exclude alcohol and drugs.
If such facts occur, then it is better to wait until the effect of the substances wears off and not take them anymore. If this is not the case, then serious research will be required. It is necessary to measure intraocular pressure, check the blood and the condition of blood vessels. In addition, do an MRI, which will assess intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics
For diagnostic methods for identifying anisocoria, the doctor first of all determines which eye does not respond to differences in lighting conditions, because we can talk about both the inability to narrow and the inability to expand. The doctor prepares information regarding accompanying problems associated with vision: he clarifies whether there is double vision, whether there is pain in the eyes. Then a number of mandatory procedures follow:
- Taking a blood test.
- Tomography of the skull.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasonography.
- Angiography.
- Monitoring blood pressure indicators.
- X-ray examination of the cervical spine and skull.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Read what an iris colomb is here.
If this problem occurs, you need to visit an ophthalmologist for examination and diagnosis. The doctor must study the patient’s medical record and establish a connection between anicozoria and the diseases and injuries that the person had or has. What episcleritis is can be read in our article.
The diagnosis itself takes place in several stages and involves the following types of examinations:
- biochemical blood test;
- spinal puncture;
- head examination on a computer;
- MRI;
If glaucoma is suspected, tonometry is prescribed.
Anisocoria is detected when visiting an ophthalmologist. The specialist resorts to the following diagnostic measures:
- Taking an anamnesis - the doctor asks the patient about the duration of the disease and the characteristics of the observed symptoms.
- Identification of the affected pupil. The doctor monitors the reaction of the structural unit to changes in lighting conditions.
- Examination of the organs of vision for lesions and inflammatory processes.
- Pharmacological tests. A specialist puts special agents into the eyes that help identify Horner's syndrome.
If the doctor suspects that the disease is caused by diseases of the central nervous system or vascular pathologies, he refers the patient to a neurologist. In such circumstances, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- MRI or computed tomography;
- radiography of the head and neck;
- tonometry;
- blood tests, etc.
Treatment Options
Everything will depend on the cause of the miosis. After all, it is not a disease in itself. No local effect will have the desired result. After all, internal pathology will still lead to narrowing of the pupils.
Therefore, it is necessary to follow the doctor's instructions. For example, in case of injury and changes in intracranial or intraocular pressure, vascular medications should be taken. They should normalize the pressure. The “system”, taking vitamins and other procedures have a good effect.
What absolutely should not be done with anisocoria
You should immediately consult a doctor if anisocoria is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- blurred vision, fog before the eyes;
- double vision;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- eye pain;
- temperature increase;
- loss of vision;
- photophobia.
Anisocoria can be a sign of very serious illnesses that require emergency medical attention.
Therefore, consult a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- temperature increase
- Strong headache
- nausea and dizziness
- double vision
- drooping and swelling of the upper eyelid
If you have suffered a head injury and the pupils of your eyes have become different sizes, be sure to consult a doctor.
If a symptom of different pupils appears, you should not:
- independently instill drops that can affect the size of the pupils
Prevention of the syndrome
It is necessary to exclude dangerous conditions that can be caused by exposure to toxins or alcohol. It is necessary to stop taking drugs and undergo addiction treatment. Taking vitamins is recommended as a preventative measure. There are a lot of them sold in pharmacies. Such courses should be taken once every six months. In addition, you need to avoid eye strain.
For example, when working on a computer for a long time, you should take breaks of 10–15 minutes every hour. It is important to take vascular medications, including eye drops. For example, taufon normalizes the functioning of capillaries, perfectly reduces tension and restores muscle tone.
Return to contents
Treatment of anisocoria
If a congenital pathology is detected, a specific therapeutic course is not required. In other cases, treatment measures are aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease.
Drug therapy is carried out by taking the following drugs:
- anticholinergic drugs;
- antimicrobials;
- antibacterial agents;
- multivitamin complexes;
- drugs to improve vision.
In some cases, detoxification therapy and procedures aimed at restoring water-salt balance are required. For mechanical damage to the eye, surgical intervention is indicated. The type of surgery depends on the type of injury.
Very rarely, medications and surgery do not bring the expected results. In such cases, they resort to the appointment of special lenses to increase visual acuity and mask the cosmetic defect.
The prognosis of the treatment depends on the form and severity of the disease. In most cases it is favorable.
Consequently, pupils of different sizes can act as both a pathological and physiological phenomenon. In the first case, we are talking about a condition that accompanies the course of the underlying disease. The diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist; in some cases, the specialist requires the help of a neurologist.
Treatment of this disease depends entirely on the identified cause of the pathology. If this is a hereditary or physiological condition, then there is no need for treatment. If the cause is infectious or inflammatory processes, then treatment may be prescribed for a suitable nosology. Local or systemic antibiotics are used.
And also about visual scotoma here.
Therapy depends on the cause of the symptom:
- No treatment is required for congenital or physiological anisocoria.
- For inflammatory eye pathologies, treatment includes local and systemic antibacterial drugs.
- For tumor formations, surgical treatment is indicated.
- For meningitis and encephalitis, treatment is complex.
Thus, anisocoria can occur either with disturbances in the structure of the iris, or with inflammation of the structures of the eyeball (including the pupillary sphincter or dilator), or be associated with diseases of the nervous system: its autonomic part, peripheral nerve fibers, central nervous system or iris receptors.
In any case, anisocoria is always a reason for medical consultation, and its treatment depends on the identified cause of the pathology.
If a connection between an increase in pupil size and heredity is identified, the pathology cannot be treated. In all other cases, therapeutic measures are prescribed, and sometimes urgent surgical care is required. If blood vessels burst in the eyes, the reason may be poor sleep and fatigue.
Various means are used to eliminate anicozoria, including:
- drugs to combat migraine;
- means to reduce swelling of brain tissue;
- corticosteroids;
- anticonvulsants;
In case of meningitis and other infectious diseases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If the cause of the problem is tumor formations, the latter are eliminated with the help of appropriate surgical intervention.
Absolute scotoma requires immediate treatment.
In addition to the above, during the treatment process, if necessary, analgesics, antitumor drugs and others are used as prescribed by the doctor.
When using medications with the effect of dilating the pupil, the problem appears only for a certain time, and goes away on its own as soon as the medication is finished. However, in any case, it is necessary to inform the attending physician about the effect of this medicine: perhaps the doctor will consider that it is better to replace the drug.
A complication of viral conjunctivitis can be blurred vision.
Anisocoria in infants
Most often, the cause of different pupil diameters is congenital pathology of the iris or underdevelopment of the autonomic nervous system. Such anisocoria is present from birth and is not accompanied by drowsiness or, conversely, hyperexcitability of the child. May be accompanied by squinting or drooping eyelids.
Anisocoria, which suddenly developed in an infant, may be a sign of:
- brain contusion;
- brain tumors;
- encephalitis;
- aneurysms of the vessels of the cranial cavity.
Anisocoria in older children
The cause of this symptom may be the following pathologies:
- Trauma to one part of the brain.
- Meningitis or encephalitis, accompanied by cerebral edema (in this case, other symptoms are also observed).
- Eye trauma, operations on the internal structures of the eye, during which the iris or its sphincter were damaged.
- Inflammation of the iris.
- Poisoning with certain poisons.
- Overdose of drugs.
- Aneurysm of cerebral vessels.
- Brain tumor.
- Eydie syndrome, the cause of which is unknown; It manifests itself as unilateral dilation of the pupil with a change in its shape, lack of reaction to light and a slow reaction to convergence.
Anisocoria in adults
The causes of this condition in adults are varied.
- “Ophthalmological” causes develop due to:
- uveitis;
- iritis and iridocyclitis;
- previous eye surgeries or injuries;
- a lens implanted into the eye cavity.
- "Neurological" reasons:
A. With pronounced anisocoria in the dark. In this case, the smaller pupil is considered “pathological”:
- Horner's syndrome: slight constriction of the pupil with a delay in its expansion when moving into a dark room, drooping of the upper eyelid in the same eye (may be accompanied by raising of the lower eyelid), decreased production of tear fluid in this eye, decreased sweating on this side of the face. The syndrome develops in a huge number of diseases of the head, neck and even in cancer of the apex of the lung;
- Eydie syndrome is a disease of unknown cause;
- non-ischemic damage to the fibers of the oculomotor nerve.
B. Anisocoria is more pronounced in bright light (in this case, the “pathological” pupil is the one that is wider):
- oculomotor nerve palsy due to aneurysm, stroke, tumor or inflammation of the brain;
- herpes zoster in the ciliary ganglion;
- use of sympathomimetic or anticholinergic drugs (Atropine, Scopolamine, amphetamine, cocaine).