Anonymously
Around the clock
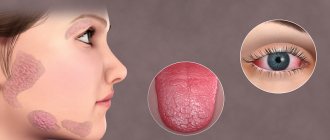
Recognizing a person who uses drugs is not that difficult. Drug addiction rapidly destroys the human body, which leads to serious changes in its appearance.
- What drug addicts look like
- Drug addict face
- Acne in drug addicts
- Ulcers
- The eyes of a drug addict
- Why do drug addicts have red eyes?
- Dilated pupils
- No reaction to light
- Bruises under the eyes
- Drug addict look
- Heroin eyes
- Hashish eyes
- Eyes under pills
- Hands of a drug addict
- Brushes
- Swollen
- Vienna
- Injection marks
- Addict's legs
- Addict's nails
- Drug addict's teeth
- Addict's body
- Addict's groin
- Addict skin
- The body of a drug addict
- What do drug addicts turn into?
- Character of a drug addict
- Appearance of a drug addict
- Drug addict behavior
- Drug addict sniffles
- Constantly smiling
- The gait of a drug addict
- Why do drug addicts itch?
- How does a drug addict talk?
- Signs of a typical drug addict
- Behavior of a former drug addict
- Social portrait
- Psychology of a drug addict
- People who are drug addicts: what they look like (photo)
We will select an individual treatment plan
Free consultation 8-800-200-27-23
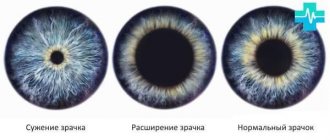
Types of anisocoria
Sometimes a person may have one pupil smaller in size compared to the other.
Experts distinguish physiological and congenital anisocoria. In the first case, the difference in pupil size is no more than one millimeter, and during the examination the doctor does not detect any ophthalmological disorders. This feature can occur in absolutely healthy people. The congenital form is formed due to defects of the visual apparatus. Moreover, visual acuity is different in each eye. Congenital pathology can also be a consequence of damage to the nervous system of the eyes. This type of anisocoria appears from birth. At the same time, the child does not have a lag in physical and mental development. In some cases, this feature can go away on its own by the age of five, while in others it remains for life.
Acquired anisocoria in adults can be a consequence of injury or ophthalmological diseases. In some cases, this condition may be caused by exposure to inorganic substances, such as belladonna or atropine.
Depending on the degree of damage, the pathology can be unilateral or bilateral. Affecting both eyes is quite rare.
If one pupil is larger than the other, you should consult an ophthalmologist
Additional symptoms
Different pupil sizes
Along with changes in pupil size, the patient may experience other symptoms, including:
- decreased performance;
- blurred vision;
- development of torticollis (pathology accompanied by changes in the nerves, skeleton and soft tissues of the neck);
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the eye area;
- feverish condition;
- Strong headache;
- begins to see double;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- blurred vision.
Strong headache
Symptoms of azocolia:
- lack of reaction to light in one pupil (normally it narrows),
- ptosis - drooping of the upper eyelid,
- eye pain,
- diplopia - double vision of visible objects,
- photophobia,
- decreased vision (one eye sees worse).
Diseases indicated by pupils of different sizes include:
- 1. Iritis is an inflammation of the iris of the eye. One of the symptoms is persistent constriction of the pupil and lack of reaction to light.
- 2. Horner's syndrome is a pathology associated with damage to the oculomotor nerve, which regulates the constriction of the pupils and the movement of the eyelids. It manifests itself as a triad of symptoms: ptosis, enophthalmos and miosis.
- 3. Eydi syndrome is a pathological condition caused by a violation of innervation, manifested by persistent mydriasis (dilated pupil) and lack of reaction to light.
- 4. Infectious eye lesions.
- 5. Thyroid cancer.
- 6. Injuries to the visual apparatus.
You should be especially careful if, in parallel with anisocoria, the following are observed:
- fever;
- decreased vision;
- double vision;
- fear of light;
- attacks of nausea;
- Pain in the eyes;
- vomit.
In itself, the changed size of only one pupil rarely causes any inconvenience other than aesthetic ones. More inconvenience is caused by the symptoms of the conditions that caused this disease. If anisocoria is a physiological condition, the main symptoms will be:
- pronounced manifestation in the dark;
- preserved and correct reaction to exposure to light;
- disappearance of symptoms when using pupil dilating drops;
- the difference in pupil size is no more than 1 millimeter.
If the cause of anisocoria is Horner's syndrome, then the symptoms will include:
- an increase in the difference in pupil sizes by more than 1 millimeter;
- slower dilation of the affected pupil in the dark;
- pupillary reactions are very slow;
- the sweating system does not work properly.
This damage to the nervous system is accompanied by a large number of symptoms that can be easily identified. If you suspect problems with your body's systems, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Another cause of anisocoria is oculomotor nerve palsy.
If this problem occurs, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- weaker dilation of one of the pupils;
- eye movement is limited;
- lack of pupil reaction to light, there is a response to movement;
- when the eyeball deviates, the upper eyelid rises;
- pain when moving the eyeball.
Sometimes anisocoria can be a characteristic reaction to taking medications: pilocarpine, atropine, adrenaline, naphazoline. This list is quite large; when choosing a product, you need to carefully read the instructions for the drug.
When using some formulations, symptoms may be as follows:
- lack of reaction of the dilated pupil to light;
- absence of other pathological changes in the iris;
- near vision impairment.
You should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- the pupil is dilated, the reaction to light is lost;
- Slit lamp examination confirms the presence of injury.
Questions and answers on the topic “dilated pupils”
Question: One of my friends had constantly dilated pupils during pregnancy. At the same time, she did not complain about her vision and did not see a doctor. After she gave birth, her pupils became normal again, but her vision gradually began to decline. She began to have difficulty seeing objects in the distance. Therefore, I had a question: is it normal for the pupils to be dilated during pregnancy and is this related to deterioration of vision?
- Answer: There is no direct connection between pregnancy and dilated pupils; apparently this physiological feature is a reaction to sunlight. In young children and adolescents, dilated pupils do not affect visual acuity, but during pregnancy it is better to consult an ophthalmologist for consultation. But, as a rule, visual acuity decreases for completely different reasons.
Question: Hello! I began to pay attention to the fact that my 4-year-old daughter periodically has dilated pupils of 5-6mm, maybe a little more. I looked on the forums and didn't find an answer. Tell me whether it is worth paying attention to this or not, if so, which doctor to contact. My eldest daughter was diagnosed with astigmatism at the age of 7.
- Answer: Hello. Astigmatism of the direct type up to 1.0 diopters, as a rule, does not require glasses correction and does not lead to decreased vision. Just in case, the youngest should undergo a routine examination by an ophthalmologist. Make sure everything is ok. The width of the pupil may depend on the characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. It is important that the doctor examines first the narrow pupil in connection with your complaints, and then the wide one, since only when the pupil is dilated can the refraction, including astigmatism, be correctly determined.
Classification of mydriasis
Depending on the factors that provoked the onset of the disease, the following types of dilated pupil are distinguished:
- Paralytic. It develops when the muscles responsible for the movement of the eyeball are damaged. As a result, the nerve endings are paralyzed and immobilization occurs. The muscles that control the diameter of the pupil are static, so it does not change in size. The causes of paralytic mydriasis lie in meningitis, tuberculosis or syphilis;
- Spastic. It is provoked by a spasm of the muscles responsible for widening the hole in the iris. For a while, the muscle loses its performance, however, this happens for a short period of time and goes away without outside intervention. This type of lesion is observed when the cervical sympathetic system is irritated or as a result of a large concentration of adrenaline entering the circulatory system. In rare cases, pathology is diagnosed in the presence of problems with the kidneys or liver;
- Medication. In some situations, it is deliberate; ophthalmologists specifically use eye drops that dilate the pupil to analyze the condition of the fundus. In other cases, this is a side effect from the use of certain medications;
- Traumatic. Diagnosed when the iris or nerve endings are damaged, as well as after surgery affecting the structures of the organ of vision;
- Arbitrary. It arises due to human willpower.
There is another type of pathology, which is characterized by the fact that the pupil dilates in daylight, but at night, on the contrary, decreases in size. This anomaly is caused by severe neuroses or lesions of the cerebral cortex.
Diagnostic procedures
If your pupils are significantly narrowed or constantly dilated, then you should see an ophthalmologist. The specialist asks the patient what other symptoms bother him and for how long. After this, a visual inspection of the damaged areas of the eye is carried out. To make a final diagnosis and find out the causes of narrowing and enlargement of the pupils, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
An examination by a neurologist is necessary for the patient to identify the cause of his condition.
- neurological examination;
- laboratory blood test to determine the inflammatory process;
- examination of the eyeball for mechanical damage;
- CT and MRI of the brain.
If the pupils are dilated or constricted for a long time, then additional consultation with a neurosurgeon may be required.
Mydriasis type
People who live here and now can be recognized by the large size of their pupils. Such people are responsive and easy-going. They are not very ambitious in the modern sense, but they are able to literally enjoy the very process of implementing their plans, ideas and initiatives. It’s as if they are playing at life, rejoicing in successes and not really reproaching themselves for failures. Normal pupil dilation looks like the result of a prevailing psychological state, which cannot be called anything other than positive. People belonging to this type run away from stress like the plague. In our area they are in the minority.
Causes of dilated pupils
The physiological norm for pupil diameter is 3–5 mm. The size changes depending on the level of illumination in the room and the mood of the person. The pupils dilate or contract for various physiological reasons. That is, this condition is considered normal.
During the day, the pupil constantly changes in diameter depending on the following natural factors:
- Emotions. When a person is in a state of panic, stress, fear and on the verge of a nervous breakdown, there is a reaction in the iris muscles; under the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system, a reflex increase in diameter occurs.
- Reaction to light. This is an important reflex mechanism that occurs when regulating the amount of light. When the light is too bright, narrowing occurs to prevent damage to the visual analyzer by UV radiation. In poor lighting, the pupil dilates, it tries to let in enough light so that a person can navigate in the dark. The diameter changes mechanically. In the dark they expand to 3.8 mm. After 5 seconds in a dark room up to 5.8 mm. This happens all the time.
- Feelings. A person cannot control the contraction and dilation of the pupil. These actions happen automatically. This is a more persistent channel, in which an instant reflex occurs, but the more persistent is the humoral one. For example, an increase in adrenaline (a component of the hormonal “love cocktail”) tends to expand them. Scientists have found that this reaction occurs when a man looks at a naked woman or his child. That is, hormones of happiness are released, a person experiences love and attraction.
- Drugs. To diagnose certain diseases, ophthalmologists use special drops. They are called mydriatics. Medicines dilate the pupil. Thanks to them, the ophthalmologist can examine the fundus of the eye. The effect after using eye drops lasts up to three days.
Mydriasis in children and its causes
Parents should be attentive and pay attention to the condition of the eyeballs of the child, who, due to his age, may not be able to articulate the symptoms that are bothering him. There can be many causes of mydriasis in childhood.
One of the most common is the presence of helminths. Children often have them, but the child will not always talk about how he feels. Helminthiasis requires timely treatment, since the presence of parasites threatens the health of the entire body. With this disease, the pupils are constantly dilated.
Poor lighting may be the cause. If children spend a lot of time in a poorly lit room at a computer, gadget, or book, without turning on bright light, their pupils will be constantly dilated. The eyes simply adapt to the conditions, and with good lighting they return to normal.
Altered psycho-emotional state: fear, irritation, excitement lead to expansion of the pupil. Perhaps the child has problems at school, but he hides them.
Children run a lot, climb trees, and often fall. A child can get a concussion without noticing symptoms. Enlarged pupils along with nausea and headache are a sign of a concussion.
This phenomenon may be a sign of other pathologies: fever, poisoning, infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, epilepsy, brain tumors, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. The baby himself cannot monitor the health of his eyes, so parents need to be careful.
The narrowing and expansion of the zenko several times during the day is a normal physiological phenomenon that occurs completely unnoticed by others. But if they are constantly increased, this indicates a problem with the body.
Signs
The phenomenon in question is considered a symptom in itself. If it develops as a result of any disease, it is complemented by a number of other signs. Symptoms of an enlarged pupil of one eye depend on the cause of the pathology. Let's look at the main features.
For pathologies of the visual apparatus:
- movement of the apple is limited on the side of the enlarged pupil or both eyes;
- pain;
- the upper eyelid is drooping; more about drooping eyelid→
- deterioration of visual acuity;
- migraine;
- heat;
- double vision.
Symptoms of pathology caused by systemic diseases:
- heat;
- feeling dizzy or in severe pain;
- nausea;
- swelling and drooping of the upper eyelid;
- split picture.
The appearance of accompanying symptoms requires immediate contact with a doctor.
Diagnostics
Various diagnostic methods are used to determine the causes. Only after a thorough study of the medical history, test results and other types of research does it become possible to diagnose the problem and draw up a correct treatment plan. The doctor performs or prescribes the following manipulations:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels;
- MRI;
- X-ray examination of the lungs;
- computed tomography of the head;
- eye pressure measurement;
- blood analysis;
- performing a spinal tap;
- X-ray of the neck and skull.
After identifying the pathology that provokes anisocoria, treatment is planned. This takes into account not only the diagnosis, but also the age group of the patient. Treatment for a child can be radically different from treatment for an adult.
Treatment
The condition, called physiological anisocoria, does not require special treatment. It does not affect visual acuity and the general health of the entire organ. Pathological anisocoria is treated in several ways. Preference is given to one method or another, depending on the main diagnosis and individual characteristics of the patient:
If the pupils are different due to brain infections, then the patient must be hospitalized. The basis of therapy is antibacterial and antiviral agents. When diagnosing vascular aneurysms and neoplasms in the brain, surgical intervention is required. The patient then undergoes a rehabilitation course. If the cause of the pathology is glaucoma, the doctor’s actions are aimed at stabilizing the level of normal pressure in the eye
Much attention is paid to preventive measures to prevent recurrence of attacks of the disease. Glaucoma is treated with medication or surgery. Inflammatory processes in the organs of vision are treated with a course of antibiotic therapy. A tumor in the eye is eliminated through surgery.
It is strictly forbidden to use any medications without a doctor's prescription. Self-medication often leads to unpleasant consequences.
Pupils are dilated: reasons why a child has constantly dilated pupils
It's no secret that such a reaction can occur in a child when consuming drugs, alcoholic beverages, or psychotropic drugs. Excessive and regular consumption of alcohol leads to a corresponding disease, which is difficult to get rid of.
And using drugs once will lead to repeated use, and then to systematic use. This will not affect your health. And constant intoxication and brain damage gradually leads to chronic mydriasis. It has been noticed that in people who have given up dangerous habits and begun to follow a healthy lifestyle, the size of the pupils remains at the same level - over 5 mm in circumference.
Prevention
Doctors suggest, first of all, to be attentive to your health. A balanced diet, giving up bad habits and playing sports strengthen the protective properties of the immune system.
It is also necessary to always follow safety rules both at home and at work. This especially applies to people working in dangerous, difficult conditions. Careful attention will reduce the likelihood of various injuries.
An important role in the prevention of not only anisocoria, but also other pathologies, is played by a timely visit to the clinic when the first signs of disease are detected.
Causes
There are many different reasons why one of a child’s pupils may dilate. This may be a major or minor expansion. A healthy child should have pupils of the same diameter. When exposed to bright light they narrow, in the dark they expand. This is a necessary adaptation of the eye to protect the internal structural elements from adverse factors.
Non-hazardous physiological
A child may have a congenital discrepancy between the sizes of the right and left pupils, which he inherited from one of the parents. This condition cannot be changed; it is a permanent norm for the child. Sometimes in children this condition can disappear closer to 7 years.
The influence of external causes is also possible, when eliminated, the shape of the pupil is restored.
- Use of medications. These include Atropine and similar drugs, psychostimulants. In early childhood, a child may accidentally use these drugs, following the example of adults.
- Emotional condition. Pupil dilation can cause severe fear, excessive emotions, stress, and nervous tension.
- Incorrect lighting in the room. Normally, the room where the child is constantly located should be well lit with natural or artificial light. If the lighting balance is not correct, 1 of your baby's eyes may dilate the pupil to better see things around them.
- Physiological anisocoria. In children with this phenomenon, both pupils narrow or dilate, but in some, one of them carries out these actions to a greater extent.
Dangerous pathological
If the patient's condition is caused by any disease or disorder in the body, the pupils will not only not correspond to each other.
The affected organ of vision also does not respond to bright light, that is, the pupil is in a constant state of dilation. The other eye functions normally, that is, it narrows when exposed to bright light and widens in the dark.
There are many reasons why this anomaly may appear:
- A disorder in the structure of the iris, as a result of which the muscle tissue of the eye is not properly stretched. Therefore, one pupil narrows sharply, while the other does not contract completely.
- Brain disease, underdevelopment during embryogenesis. As a result, nerve impulses do not enter the tissues of one of the eyes, so the pupil becomes permanently dilated.
- Birth injury. These could be blows, bruises, or curvature of the cervical spine.
- Traumatic brain injury. The symptom appears immediately after a child falls or gets a head injury. It can be used to determine which part of the brain is damaged.
- Benign or malignant neoplasm in the brain. If it is localized near the visual analyzer, it affects the conduction of impulses from the brain to the eyes. As a result, one of the organs of vision suffers, its pupil does not narrow.
- Infectious diseases. A discrepancy in the size of the pupils may occur if the infection has reached the brain and is localized in the visual analyzer. This often occurs with encephalitis and meningitis.
- Mechanical damage to the eyeball. Anisocoria occurs if the sphincter of the pupil has been damaged.
- Neurological disorders. This symptom is caused by pathologies of the autonomic nervous system, especially if the cranial nerves in the area of the third pair are affected.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure, which is formed due to a violation of the outflow of secreted fluid. As a result, the camera of the eye compresses the sphincter of the pupil, which leads to disruption of its function.
- Hereditary pathologies. These include Parinaud, Horner, and Argyle-Robertson syndrome. These are mutations in genes that lead not only to anisocoria, but also to other clinical manifestations.
For each of the above pathologies there is a specific treatment. Therefore, the doctor must not only determine the diagnosis of “anisocoria,” but also identify the pathology that led to it.
Why the pupil of the eye enlarges: the influence of emotions and the environment of women
The pupils may constrict or dilate depending on mood changes. When a person is excited, his pupils can be enlarged by as much as 4 times. Anger and irritation provoke narrowing. It is no coincidence that the expressions “snake eyes” or “beady gas” are painted in a negative tone. It is believed that light eyes are more attractive, this is due to the fact that the constriction and dilation of the pupils on them is easier to notice, and, therefore, to determine the emotional state of a person.
Scientists from the University of Chicago have proven that the degree of a person’s arousal is reflected in the size of the pupil. Heterosexual men react with pupil dilation to women, and to members of the same sex – with pupil constriction. During the study, people were asked to look at photos - pleasant and not so pleasant. They depicted beautiful landscapes, girls, politicians, scenes of bloodshed, and disabled people. And each time, the size of the pupil clearly showed what emotions this or that photo evoked in a person. Music directly affects pupil size.
Why do lovers love to look into each other's eyes? At an unconscious level, they try to notice the dilation of their partner’s pupil, and at the same time their mutual arousal increases.
Reference! Many will be surprised to learn that when seeing an attractive woman, a man's pupil size increases three times, not the size of any other part of the body.
Pupil dilation is actively used by marketers. Because a dilated pupil looks more attractive than a constricted one, women who advertise a cosmetic product deliberately dilate their pupils. It has been observed that this technique increases sales by 45%. Also, if you look at any children's toy or cute cartoon character, you can see that their pupil will definitely be dilated.
A man’s pupil may dilate under the influence of the following emotions:
- Severe fear and feeling of anxiety.
When a person is scared, his body begins to actively produce adrenaline. It is this hormone that provokes the dilation of the pupils and maintains their increased size until a state of rest occurs. In childhood, such a reaction can be observed when the child receives a bad grade or when he is scolded. - Breakdown.
The muscles located in the iris react to it. This process triggers a response from the parasympathetic nervous system, resulting in pupil dilation. - Active thought process.
When a person tries to answer a question posed as quickly as possible, his pupils often dilate, and the higher the degree of pupil dilation, the more intense the search for the desired answer is. - Sexual attraction.
When a man is surrounded by beautiful women and feels sympathy, the body reacts to this by dilating the pupil. In this case, the size of the pupil is influenced by the so-called love hormones - dopamine and oxytacin. A man's brain gets a boost from these hormones when he is sexually attracted to someone. This may also be due to the biological need for reproduction.
Reference! When sexual interest disappears, as well as when nervous or mental activity relaxes, the pupils immediately contract to normal size. Psychologists often use this ability of the pupil in their work.
Why do drugs make my pupils dilate? Why is a pupil needed?
The pupil is a round hole in the iris of the eye. The muscles of the iris can change the diameter of the hole, adjusting the flow of light. The opening narrows in bright light so as not to “blind” the light-sensitive receptors inside the eye. And in the dark, the eye needs to catch as much light as possible to accurately perceive the picture, so the hole increases.
These actions occur due to the pupillary reflex. Photoreceptors on the retina transmit information about light levels to the brain using nerve impulses. And it sends a corresponding signal to two muscles of the iris - the dilator (dilator) and the constrictor (sphincter).
Other factors also affect the size of the hole:
- Emotional stress. Strong fear, vivid emotions, sexual desire and love cause excitation of the sympathetic nervous system and the release of hormones - adrenaline, norepinephrine, oxytocin. These hormones stimulate the dilator muscle of the iris, so that in a stressful situation we can clearly perceive the surrounding reality.
- Concentration on the subject. When looking closely at a person or object, a wide pupil helps to better see the object of interest.
- Depression, depression, fatigue. By narrowing the diaphragm of the eye, the nervous system tries to reduce the flow of light and turn off the visual information channel, which sends negative signals. This is why many people lose their sight.
- Age characteristics. Teenagers have wider pupils than adults - due to the active functioning of hormones and increased tone of the nervous system. And in old age, the pupil area decreases because the overall level of brain activity decreases.
Human eye pupil
The pupil is a round hole located in the center of the iris. Through it, light rays penetrate into the eye and are transformed in the retina into visual energy. The number of light rays entering the eye is controlled by narrowing or widening the hole in the iris, which acts as a diaphragm.
The narrowing and expansion of the zenko can be caused by influences coming from various parts of the body, due to the presence of widespread nerve connections between the iris and these parts.
Causes
Reducing light levels
Expansion in the dark is a normal reaction. The eye tries to catch a little light so that a person can better navigate in a poorly lit room.
This is not a pathology. After moving to a bright room, the pupil remains dilated for some time.
Strong emotions and their effect on the eyes
Experiences, fear, joy or surprise cause the release of hormones into the blood. For this reason, the pupils automatically become larger. This is the norm. They can change size depending on their mental state. Sometimes the increase is one-sided.
Interest in a particular subject
They expand in an attempt to see something interesting. This is the psychological response of the pupils. Both or one may increase, depending on what a person is thinking about, what emotions he experiences while looking at an object (after all, different hemispheres are responsible for some).
Use of certain drugs (pharmaceutical mydriasis)
Abuse of psychotropic medications, narcotic drugs and solutions containing alcohol can lead to different diameters. Asymmetry is observed in exceptional cases, most often a bilateral increase.
Headaches with autonomic disorders
The symptom being studied is the cause of autonomic disorders, in which headaches and migraines are observed.
Asymmetry is accompanied by redness, blurred vision and vomiting.
Hereditary factors in the development of pathology
The occurrence factor is the pathology of the iris and other anomalies in the development of the visual organs. Causes:
- anisocoria;
- lagophthalmos;
- ptosis;
- intraocular hemorrhage;
- hypoplasia;
- malformations of the vascular tract of the eyes.
Compression of the oculomotor nerve
One pupil is more dilated as a result of loss of reaction to light, which causes sphincter paralysis.
Compression of the nerve trunk may be the cause. This sign is often the first symptom, ahead of other manifestations, indicating damage to the 3rd pair of cranial nerves due to dislocation of the brain stem. After a traumatic injury, aberrant regeneration develops. When looking up or down, the hole in the iris narrows. With a microinfarction of the nerve, this sign is not present, this refutes its presence.
Brain or eye injury with iris damage
If one of the pupils does not react to light, the doctor makes a diagnosis of severe damage to one of the brain hemispheres. If there is a reaction, but it is weak, the patient has a mild concussion.
Horner's syndrome
Develops with concomitant pathological conditions of the neck, head and lungs. It is caused by damage to the part of the nervous system that regulates breathing, digestion and blood circulation.
Horner's syndrome is characterized by a decrease in pupil size. Ptosis occurs, intraocular pressure decreases, and accommodation increases. The reaction to light and fixation of the gaze at a close point changes.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine as a cause in adults
The cervical region contains arteries that supply the brain. Due to wear of the intervertebral discs, they are compressed, that is, cerebral circulation is disrupted.
Because of this, different parts of the brain suffer, and the eyes may also suffer. There is a weak reaction to light, an enlargement of the hole in the iris.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome
Diagnosed if the pupil remains dilated for a month, but responds poorly to light signals. This is paralysis of the eye muscles.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome is characterized by an oval pupil and segmental damage to the iris. It slowly returns to its original size.
The syndrome can be congenital or acquired. The difference between the pupils is not noticeable; it increases by about 1.5 mm.
Nerve palsy as a consequence of stroke or malignant brain tumors
Malignant or benign formations of the central nervous system or brain affect visual functions. Cancer or an abscess, increasing in size, increases IOP, hence tissue compression and asymmetry.
People who are drug addicts: what they look like (photo)
The appearance of a drug addict is distinguished by its soreness. Of course, the presence of acne on the face, bruises under the eyes and pale skin does not always indicate the presence of drug addiction. To determine a possible dependence, it is necessary to pay close attention to many factors at once.
Article prepared by an expert
Terekhova Anna Vladimirovna
psychologist-consultant on socio-psychological work with addicted clients and their families. More than 9 years of experience.
Similar articles:
New drug NBOMe: symptoms, consequences, treatment
How to help a loved one with a salt overdose?
Similarities and differences between drug addiction and alcoholism
Alcoholism and drug addiction. Resistance to treatment
The drug salt: signs of use and treatment
One comment on ““External signs of a drug addict: face, gait, behavior””
- Lyudmila:
January 19, 2021 at 03:04
If you notice some of the above signs in your teen, try talking to him. During such a conversation, you can determine whether your suspicions are confirmed. If you start a conversation about drugs, the teenager will immediately become wary, and after your question there will be a long pause before the teenager answers it. Or maybe there will be no answer at all, or he will be slow to answer questions. During drug addiction, even the simplest question can cause difficulty for a teenager. Causes dry mouth, redness of lips and eyes, dilated pupils. The addict becomes restless and constantly moves. His speech is leisurely. The appetite is “wolfish”; after the intoxication wears off, there is intense thirst.
Answer
Diseases that cause changes in the pupil
Let's talk about pathologies, one of the symptoms of which is anisocoria. First, let's discuss paresis of the oculomotor nerve.
Oculomotor nerve palsy
The slightest changes in the functioning of the oculomotor nerve affect a person’s quality of life. Children suffer from this disease quite rarely. It is almost impossible to recognize the disease in the initial stages, since it does not manifest itself in any way.
The following reasons can cause nerve paresis:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- vasculitis;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- tumor process;
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- syphilis, diphtheria, encephalitis, meningitis;
- side effects of medications;
- injuries;
- ocular migraine.
With paresis of the upper eyelid, the eye closes completely or partially. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the form of a squint. Most often, the pathology has a one-sided process. In addition to physical inconvenience, the problem causes aesthetic discomfort. Paresis of the upper eyelid leads to deterioration of visual acuity.
Paresis of the oculomotor nerve is one of the causes of anisocoria
A birth defect is formed as a result of abnormalities in the formation of muscles or intrauterine nerve damage. Acquired pathology can be a manifestation of injuries, as well as neurological disorders.
With mydriasis, the pupil dilates. The disease occurs as a result of injuries, diseases of the nervous system, visual apparatus, as well as the use of potent drugs. Normally, pupil dilation is a natural reaction to lighting. This can also occur during severe emotional stress.
After the diagnosis of “oculomotor nerve palsy” has been established, the patient is registered with a specialist. To avoid mistakes, he is asked to undergo a repeat test. In general, the disease has positive dynamics. Doctors usually recommend doing strengthening exercises for the extraocular muscles. Patients are prescribed vitamins and medications. You may also need to wear bandages or glasses.
Full restoration of nerve mobility occurs after about six months. If there is no result, surgery may be required.
Bernard Horner syndrome
The development of the disease is based on damage to the sympathetic nervous system. The disease affects the muscle tissue of the body, including the visual apparatus. A number of provoking factors can cause the appearance of the syndrome:
- damage to brain tissue;
- cluster headache;
- injuries, including surgical ones;
- otitis media;
- aortic aneurysm.
Bernard Horner syndrome manifests itself in the form of drooping of the upper eyelid, decreased production of tear fluid, a haggard appearance of the face, unnatural constriction of the pupil, and sunken eyeball. The disease also causes heterochromia, in which the pupils have different colors. In addition, the eye loses its ability to adapt to light. The stronger the level of illumination, the more constricted the pupil, while in the dark it, on the contrary, expands.
In Bernard Horner syndrome, the pupil constricts in bright light and dilates in the dark
The treatment process may include electrical stimulation. Electrodes are attached to the affected areas. The essence of the technique is to stimulate muscles through short electrical impulses. This normalizes blood circulation and in some cases leads to complete recovery.
Problem areas can also be corrected using plastic surgery. Stimulation of affected facial tissues is also possible with the help of drug therapy.
Eydie syndrome
Patients have a slow reaction of the pupils to light, in some cases it is completely absent. Even if you shine a flashlight directly into your eyes, the same braking reaction will be observed. On the affected side, the pupil dilates and becomes deformed.
The disease can be congenital or acquired. The cause of Eydie syndrome can be ophthalmoherpes, atrophy of the eye muscles, meningitis, encephalitis, myotonia.
Treatment includes the use of Polycarpine. Regular use of these drops will help to achieve some improvement in the condition. Glasses are used to correct violations.
Long lasting effects after alcohol
In practice, there are cases when drinking alcohol results in serious pathological disorders of the functioning of the eyes. Among the most common changes in the body, the following processes should be highlighted:
A mobile application for sophisticated players is now always available without the need to search, of course on your smartphone with all the innovations introduced under the control of professional cappers and sports event analyzers.
- Often, people who drink are more likely to develop early cataracts. In this case, the disease develops at an increased rate;
- Drinking individuals are subject to macular degeneration, which in normal situations occurs exclusively with age. This fact was established after research by the US Optometric Association;
- Alcohol flushes essential minerals and vitamins from the body. As a result, people's vision decreases. If there is not enough vitamin B1, then paralysis of the pupils and eye muscles may develop, and if there is not enough vitamin A, then the risk of night blindness and thinning of the cornea increases. The worst thing for an alcoholic will be blindness, partial or complete;
- After drinking alcoholic beverages, there is a risk of developing optic neuropathy. What it is? This pathology is a serious disease leading to damage to the optic nerve.
Attention! Research shows that disturbances are also observed in other organs. Thus, due to the development of certain diseases, vision may deteriorate. In such cases, determining the cause is very difficult, and sometimes impossible.
Of course, it is worth considering that if you drank alcohol once or take it very rarely, then you should not have any health problems. The occurrence of such serious pathologies concerns only prolonged or frequent drinking bouts. Remember that alcoholic drinks have the same destructive effect on the eyes as they do on the liver and kidneys.
What happens to the body and blood when drinking alcohol?
Interesting fact! Scientists from the University of Chile have established a direct connection between drinking alcohol and color blindness. It turned out that women who suffer from alcoholism very often lose color vision.
Reasons for different pupil sizes in adults
Many people wonder whether it is possible to influence the size of their pupils on command. For example, you need to narrow or dilate your pupils during a photo shoot. In fact, there is nothing complicated about it. Below are step-by-step instructions, following which will lead you to the desired result.
Step 1. Go into a dark room. As noted earlier, in a dark room the pupils dilate as they try to “catch” more light. If it is not possible to completely turn off the light in the room, then simply turn away from the windows, thereby protecting yourself from light sources.
Go into a dark room
Step 2. To constrict your pupils, turn towards a light source in your home and remain in this position for a few seconds. If you are on the street, then all you need to do is look up. Of course, looking at the sun is bad for your eyes, so it's best to focus your gaze on something else.
Turn towards the light source
Step 3: Another easy way to constrict your pupils. Just look at the object that is located next to you. When focusing the gaze, the pupils constrict
Alternatively, you can place your finger in front of your eye and focus your attention on it.
Focus your gaze on a nearby object
Step 4: Tighten your abdominal muscles. Many people manage to dilate their pupils by keeping their muscles in constant tension. To test this method, you need to tense your stomach and look at yourself in the mirror. If your pupils are dilated, then this method is suitable for you, but if not, then try another method.
Tighten your abdominal muscles
If the period during which pupil dilation is determined has exceeded the four-week mark, and a weakened reaction to a light stimulus and slow dilation have been noted, then perhaps we are talking about the manifestation of Eydie syndrome.
This condition is characterized by disturbances in the innervation of the muscles of the pupil and, as a result, pupils of different sizes. Detection often occurs randomly due to lack of discomfort.
Mechanical damage usually includes damage to the nerves surrounding the eyeball. The cause is an unsuccessful ophthalmological procedure or a penetrating wound in the eye area.
If the reason for the change in the size of only one pupil in an adult is not injury or external damage, then we can talk about medicinal mydriasis. The pupil reacts poorly to light and does not contract when using pilocarpine.
In general, the causes of this condition are varied.
They are divided into two groups:
- Ophthalmological.
- Neurological.
A change in the pupil that occurs due to eye diseases has one of the following reasons:
- Uveitis.
- Iritis.
- Iridocyclitis.
- Operations and injuries on the eyes.
- Implanted lens.
If we talk about the causes of anisocoria being neurological diseases, then the following should be mentioned:
- Horner's syndrome: can develop with concomitant diseases of the neck, head, and lungs.
- Eydie syndrome: the causes of this disease are still unclear.
- Damage to the nerve fibers of the eyeball.
- Nerve palsy; often a consequence of a stroke or brain tumors.
- Herpes zoster.
- The use of certain drugs, including narcotic drugs.
It is recommended to immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms of anisocoria appear:
- decreased visual acuity;
- bifurcation;
- loss of vision;
- headache;
- feeling of fog in the visibility zone;
- temperature;
- nausea;
- eye pain;
- fear of light.
Why is one pupil larger than the other in a child? The occurrence of anisocoria in a child is a sign of a pathological state of the nervous system and is caused not by drowsiness or increased excitability of the child, but by congenital factors. Concomitant diseases include strabismus and drooping eyelids.
Reasons for changing pupil size:
- Brain injury.
- Brain swelling caused by meningitis, encephalitis.
- Eye injury with damage to the iris.
- Poisoning with certain types of poisons.
- Overdose of drugs.
- Brain tumor.
- Adie's syndrome.
- Heredity.
It should be borne in mind that sometimes children are born with a deviation. Manifestations of anisocoria are common for them. If the condition is stable and there is no effect on the quality of vision, there is no concern.
If the child’s condition exhibits the following symptoms: decreased visual acuity, double vision, deterioration in health, the parents go to the hospital.
You can often observe situations where a child born with normal pupils changes his condition, the reasons being previous infections or injuries. The unexpected occurrence of anisocoria is a cause for concern and a visit to the doctor.
Most dangerous condition
The following symptoms will indicate that delay in diagnosis and medical care is very dangerous: headache; depression of consciousness; irregular breathing rhythm; tilting the head to one side; impaired movement and sensitivity of all limbs.
If, in addition to eyes dilated in the light, one of these symptoms is observed, immediately contact a neurologist. This may be brain dislocation syndrome - a condition when the brain is displaced due to inflammation, tumors, hematomas, abscesses, traumatic brain injury, occlusion of the venous sinuses and many other reasons.
The danger is that when this main organ of the central nervous system gets some part into a large opening of the skull, it is pinched in it, that is, the vessels are squeezed by the bone ring. This causes a part of the brain to be destroyed and, if it is large or vital, such as the brain stem, the person dies.