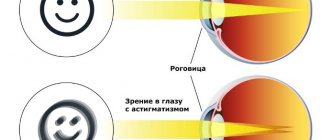
Miosis is a constriction of the pupil. It can be physiological, not associated with any diseases, and pathological. The pupil contracts and dilates depending on the light rays hitting it. In the dark it increases, and in the light it becomes narrower. If miosis occurs for other reasons, you should consult a doctor.
Miosis is considered normal in the following cases:
- in very bright light (the pupil narrows to reduce the negative impact of light on the retina);
- with convergence (bringing together the visual axes when viewing objects located close to the eyes);
- in older people and newborns, the pupils may be slightly narrower than normal (2-2.5 mm);
- during sleep in people with farsightedness;
- with severe fatigue (mental and physical).
The reduction in pupil diameter occurs due to the work of the ocular sphincter and dilator muscle. If, after the cessation of exposure to external factors on the eye, the pupil dilates to normal, then there is nothing to worry about. If he remains small for a long time and does not react to light, then we may be talking about some kind of pathology.
Causes of miosis
In medicine, miosis is understood as an abnormal persistent constriction of the pupil without a reaction to a transition to darker lighting.
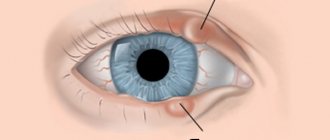
schematic representation of the structure of the eye
The pupils constrict in bright light or during sudden changes between darkness and light. This reason is natural and does not pose a threat to health. The constriction of the pupils is stable, they are the same size. As you move away from the light, the pupil enlarges. Congenital strabismus can be cured surgically.
Miosis can occur when people use pilocarpine to treat eye conditions.
This medicine reduces eye pressure and at the same time constricts the pupil. There's nothing wrong with that either. Read how to treat dirofilariasis here.
Medicines that contain morphine also cause pupil dilation.
The pupil also reacts to excessive use of drugs and alcohol, and sometimes tobacco.
Miosis is often observed in diseases such as:
- Diabetes. The constriction of the pupil is influenced by both the use of insulin and the course of the disease itself.
- Horner's syndrome. With this disease, the functioning of nerve cells is disrupted. Here the pupils constrict in the dark.
- Meningitis. The pupil becomes not only small, but also oblong.
- Encephalitis. Miosis is noticed already in the initial stage of the disease.
- Parkinson's disease. Changes that occur in the brain also affect frequent changes in pupil size.
- Epilepsy. The pupil becomes smaller during a seizure.
Miosis can also appear with aortic aneurysm, cervical osteochondrosis, multiple sclerosis, stroke, coma and increased intracranial pressure. Diagnosis of keratitis is carried out in a clinical setting by an experienced ophthalmologist.
Sometimes the pupils can become much smaller due to injuries, bruises, wounds, or when a foreign body enters the cornea. Injuries to the brain and spinal cord are very serious. All people should know safety rules in everything and everywhere. Children need to be taught this from an early age. Gononymous hemianopsia differs in the perception of the right or left half of vision.
Classification of miosis
Depending on the reasons that caused miosis, it can be:
- functional (normal reaction to light);
- paralytic (dilator palsy);
- medicinal (the result of using medications);
- toxic (caused by the use of alcohol, drugs, caffeine or exposure to other toxins);
- sympathetic (with spasms of the sphincters of the pupillary zone);
- syphilitic (miosis is the main symptom of the tertiary form of syphilis).
You need to treat any type of disease listed above, except functional and medicinal. In this case, it is not the miosis itself that needs to be eliminated, but the underlying disease that is accompanied by such a symptom.
Symptoms other than severe constriction of the pupil of the eye
pupil reaction to light
The ability to see objects clearly is lost with myopia and farsightedness. In such people, the pupils most often constrict when trying hard to see something without glasses. In infants and older people, the pupils constrict much more often. People who are intensely engaged in mental or physical labor also complain of periodic pupil reduction. To avoid this, you need to alternate types of work and take a break between them. If your eyes become infected, you should consult a doctor.
Miosis can be unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral may be a symptom:
- incipient and developing diseases of the nervous system;
- vagus nerve palsy;
- instilling medicine into one eye;
- eye damage;
- detection of a foreign object in it.
Bilateral miosis can also occur due to injuries, poisoning and other physical and biological relapses. It is observed in sleep, with increasing light intensity, and in certain brain diseases. What is hypermetropia and how to treat it, read our article.
Miosis - causes and treatment
Miosis
is a slight narrowing of the pupil (less than 2.5 mm in diameter), which is not always a pathology. Constriction of the pupil, in general, is a natural physiological reaction of the eye, which reflexively occurs in bright light. As a normal variant, miosis appears, for example, in older people and newborns, as well as when looking at different distances and during strong physical or mental stress. This condition can also occur in people with farsightedness.
Types: reactive, functional, paralytic
comparison of pupils in miosis and madriasis
Conventionally in medicine, miosis is divided into the following types (forms):
- Functional (natural) miosis. Constriction of the pupil is normal. It is affected by bright light.
- Reactive miosis (drug-induced). Medicine injected into the eyes or the use of narcotic substances affect the size of the pupil.
- Miosis is irritable (spastic). Convulsive compression of the muscular eye valve occurs due to brain diseases.
- Syphilitic miosis. It is caused by a sexually transmitted disease - syphilis.
- Paralytic miosis. Caused by pathological processes in the carotid artery or cervical spine.
Blindness before the eyes is one of the symptoms of retinal dystrophy.
What is miosis?
Miosis is a condition that occurs when the pupils remain constricted and do not respond to the amount of light entering the eye.
This occurs due to excessive contraction of the orbicularis muscle or pupillary sphincter , responsible for a decrease in pupil size or a deficiency in the activity of the dilator pupillary muscle.
Miosis is therefore the opposite of mydriasis or dilated pupils. It is also known as pinpoint pupil or pathological miosis.
Miosis can be a symptom of life-threatening drug poisoning. It also appears in other non-ocular diseases such as Horner's disease, due to a tumor at the apex of the lung.
The pupils are physiologically dilated in the dark or in low light conditions, when this does not happen, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Diagnostics
To properly treat miosis, you need to know exactly the causes of its occurrence. The correct diagnosis can be made by an experienced ophthalmologist. First he will conduct a visual examination. Look at the reaction of the pupil to light influence. Then he will start looking for the problem using a slit lamp. What kind of eye disease is cataract, read on our website.
The doctor may detect changes in the vascular system of the brain. Treatment can include vasoactive drugs and vitamins, carbohydrate metabolism measures.
Reasons for punctual students
The most common causes of miosis:
Drug abuse
Drugs such as heroin, methadone and cocaine can disrupt the central nervous system and cause bilateral miosis. Heroin poisoning constricts the pupils to such an extent that it is called pinpoint pupils due to their similarity.
Horner's syndrome
This is a brain condition that affects one side of the face and causes contraction of the pupil, drooping of the eyelid (ptosis), and decreased sweating due to a stroke, spinal cord injury, or the presence of a tumor affecting the sympathetic chain, such as a Pancoast tumor of the apex of the lung.
bleeding
Loss of blood in the brainstem pons can cause pinpoint pupils.
Chemical substances
Frequent contact with fertilizers or herbicides can cause pupillary miosis.
Treatment
Physiological miosis does not need to be treated . When the medicine is removed from the body, the constriction of the pupil will stop. Reviews about the treatment of blepharitis can be read here.
For paralytic and spastic miosis, treatment is necessary aimed at eliminating the causes that caused the disease.
If a foreign body gets into the eyes, it must be removed immediately. You need to understand that delay is fraught with negative consequences.
If the body is poisoned by toxins, it is necessary to carry out cleansing procedures (gastric lavage, IV drips, blood transfusions, and so on). And it is better to never eat food that is not fresh or questionable mushrooms. Tablets and over-the-counter medications must be used wisely.
Mechanical dilatation of the pupil is also possible. To do this, surgeons open the anterior chamber of the eye and inject special drugs. Constriction of the pupil is needed here to treat eye diseases. How to treat demodicosis of the eyelids can be found here.
General information
Miosis is a term used by ophthalmologists to designate a condition in which the pupil narrows significantly in diameter (less than 2.5 mm). This condition is both a variant of the norm (observed in certain groups of people and in certain situations) and a pathology.
The size of the pupil is regulated due to the tone of the internal muscles of the eye. The sphincter, innervated by parasympathetic fibers, ensures pupil contraction (miosis), and the dilator, innervated by sympathetic fibers, is responsible for pupil dilation (mydriasis).
Since the sphincter located in the iris and responsible for miosis is not controlled by human consciousness, it reflexively contracts:
- with a sudden increase in lighting intensity;
- during accommodation of the eye.
That is why miosis as a physiological norm is characteristic:
- for older people (accommodation changes as the lens loses elasticity);
- for infants in the first months of life;
- for people suffering from farsightedness;
- as a reflex reaction to the brightness of lighting;
- in case of physical or mental overstrain;
- for any person in a state of sleep.
Miosis also develops as a result of taking certain medications.
Prevention of miosis
diagram of the pupil's response to light
Prevention of miosis involves:
- careful use of medications;
- avoidance of traumatic situations (vigilance, attentiveness, caution);
- timely consultation with an ophthalmologist, neurologist, venereologist, therapist and other specialists;
- systematic blood sugar test;
- annual medical examination;
- use of protective equipment in work involving intense eye activity (glasses, mask).
Miosis needs and can be treated. If there is an unexpected and sudden change in the size of the pupils, consult a doctor. Monitor your health carefully. Do not allow chip dust, glass, or sand to get into your eyes. Protect your eyes from the bright sun with dark glasses. Wear protective masks when working with pesticides, paint, or welding. Choose eye drops according to a specialist’s prescription. Remember that healthy eyes are the mental and physical health of a person as a whole.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing miosis, you must follow simple rules:
- Any medications are used only as prescribed by a doctor;
- Do not start treatment for neurological diseases. These are very dangerous anomalies that can cause serious harm to health. Visit a neurologist regularly for preventive examinations;
- Elderly patients are advised to have their blood glucose levels checked more frequently;
- Wear safety glasses when working at the computer for long periods of time.
| Following simple rules will help maintain eye health for many years. |