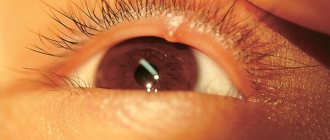
When the immune system is weakened, the opportunistic flora, which has peacefully existed for years on the surface of the skin, mucous membranes or inside the human body, is activated and can lead to various diseases. Among them is barley - or, scientifically, hordeolum: a condition familiar to many, which in more than 90% of cases is caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
The bacterial pathogen is not the only culprit of the disease. The appearance of stye can be caused by a fungus or the microscopic parasitic mite demodex, which likes to settle in or near the hair follicles.
According to statistics, most often barley is diagnosed in the age range from 20 to 50 years, but its manifestations are also common in childhood. The pathology manifested itself at least once in 90 people out of 1000.
Barley - (lat. hordeolum) - an acute inflammatory process affecting - depending on the location - one or more ciliary follicles or glands of the cartilage of the eyelids.
Barley classification
Typically, barley in adults and children is divided into external and internal - according to the location of the inflammatory process.
External stye
External stye occurs much more often than its internal “brother”. The location is the outer, visible surface of the eyelid.
External stye occurs due to infection of the eyelash follicles or glands that are located at the edge of the eyelids. It usually affects the Zeiss gland and the Moll gland. Zeiss' sebaceous glands are located in pairs around each follicle, into which they secrete their secretion. Moll's sweat glands are located there; their function is still not fully understood.
With external styes, an abscess with a white abscess on the top forms on the outside of the upper or lower eyelid. Over time, the abscess matures and opens. After this, tissue regeneration begins: most often, within a few days, not a trace of inflammation remains.
Symptoms of external styes
Usually the disease has a mild onset: a person may not even notice that a health problem has arisen. The primary symptoms of stye on the eye include:
- hyperemia of the eyelid;
- swelling;
- pain, tingling in the affected area;
- lacrimation;
After 2-4 days, the infiltrate bursts and the purulent contents come out. After this, the pain subsides and the healing process begins.
The symptoms of stye on the upper eyelid are no different from stye on the lower eyelid.
Internal stye
As for the internal styes, the zone of its destruction is the lobules of the meibomian glands located in the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid. These glands are named after Professor Meibom, who discovered them, and they belong to the sebaceous group. Their secretion is involved in the formation of the lipid layer of the tear film that lines the surface of the eyeball and the inside of the eyelids.
Symptoms of internal stye
The initial symptoms of internal and external stye are similar: the patient is plagued by pain, swelling, increased lacrimation, and a sensation of a foreign body. On the inside of the eyelid you can notice a hyperemic area with a yellowish center. Internal stye is usually more painful than external stye, and it takes longer to ripen.
The ripened internal barley opens into the conjunctival sac. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, a chalazion may form at the site of the stye - a chronic inflammation of the cartilage and gland, in which the gland duct is clogged and the secretion cannot come out. A chalazion looks like a dense, hyperemic ball the size of a millet grain to a pea. This condition requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
In rare cases, the formation of stye - both internal and external - may be accompanied by general malaise, fever, aching joints, muscle and headache, and enlarged lymph nodes located next to the affected eye. Typically, such a reaction of the body indicates a complicated course of the disease. Consult a doctor: you may need more serious treatment for stye or additional diagnostics.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of the appearance and development of internal styes (meibomitis) on the upper eyelid are pronounced and differ little from the symptoms of the development of internal styes on the opposite lower eyelid, only in the localization of the process.
Acute meibomitis is characterized by:
- At the initial stage, redness, thickening, and soreness form under the eyelid in the area of inflammation.
- Next comes swelling, a feeling of speck in the eye, which is accompanied by itching.
- An abscess is formed that can burst inside the eye, which is accompanied by purulent discharge.
- If a breakthrough does not occur, the process degenerates into a chronic course.
- The eyelid and the contents of the stye thicken.
- The swelling goes away, but the itching and burning remains.
- The cervical and submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged.
- A low-grade fever may persist.
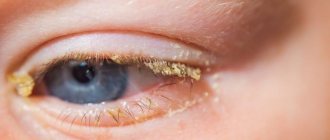
- Discharge from the sebaceous gland becomes thick, yellow, and has an unpleasant odor.
Causes of stye on the eye
The reasons leading to the occurrence of the disease include:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- using someone else’s or expired cosmetics, dirty brushes and applicators;
- untreated demodex;
- long stay in a dusty, dirty room;
- lack of vitamins;
- colds, hypothermia, decreased immunity;
- constant stress;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
Stages of development of stye on the eye
Why barley occurs, risk factors
It is often believed that inflammation on the eyelid can appear as a result of hypothermia, but this is not entirely true. Hypothermia is only a risk factor that leads to a weakened immune system and increased susceptibility to the bacterial environment.
Other causes and risk factors include:
- pathogen - Staphylococcus aureus or streptococcus in the body;
- blockage of the gland duct;
- colds;
- weak immunity;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene: using someone else's cosmetics, towels, dirty hands;
- hypothermia;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- viral infections (acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections) and other chronic diseases;
- digestive system disorders;
- demodicosis (eyelash mites) and blepharitis (inflammation of the edge of the eyelid);
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- furunculosis;
- helminthic infestations;
- pregnancy period.
Symptoms of stye
- The appearance of pain.
- Redness and swelling of the eyelid.
- Itching and burning in the area of inflammation along the ciliary edge of the eye.
- Tearing.
- A feeling that there is a blockage in the eye.
- The presence of an abscess on the edge of the eyelid is yellow in color.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Complications
- A chalazion is a dense nodule on the eyelid.
- Phlegmon of the orbit - the orbit of the eye, cornea and optic nerve become inflamed.
- Chronic infection – constant fatigue, frequent colds and relapses.
How to treat stye on the eye
Typically, barley ripens and opens on its own within a week. A disease without complications does not require medical intervention. To quickly get rid of the disease, you can resort to warming compresses: apply a towel soaked in warm water or a heated towel to the inflamed area 3-4 times a day. Compresses with aloe juice, a decoction of St. John's wort, and chamomile can also help. In addition, careful hygiene of the eyelids is important: if the discharge increases, you should clean the eyes of crusts and pus using sterile wipes and boiled water.
If there is severe pain, general malaise, or suspicion that the disease has become complicated, it is better to consult a specialist. The doctor may prescribe:
- a course of antibiotics (for the treatment of chalazion, phlegmon, or in case of frequent occurrence and severe course of the disease;
- local anesthetics, antiseptics, glucocorticoids;
- ultra-high frequency therapy;
- removal of the eyelash around which barley has formed;
- surgical removal of barley under local anesthesia. If the inflammation is too severe and treatment is ineffective, the surgeon will open the abscess and clean it of accumulated pus.
Stages of pussy development
The disease begins from the moment pathogens penetrate the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. The ciliary boil is one of the most favorable places for the accelerated reproduction of pathogenic organisms; with further advancement, they enter the Zeiss glands or the ducts of the meibomian gland. The inflammatory process develops quickly, healthy cells die, the inflamed area turns red and increases in volume. At the same time, severe itching appears, and the eyelid hurts when touched. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the eyelid, ulcers are localized in the lower part.
Pussy development
The abscess begins to form on the 3rd–4th day after intoxication; a light bulge with a very thin shell appears on the compaction. After 5–7 days it breaks through, the eyelid is freed from purulent masses and restores its normal structure. In the vast majority of cases, no intervention is required; complications arise due to the inept actions of patients.
Important. It is strictly forbidden to remove pus mechanically, as this can lead to blood poisoning.
Man with barley
There are rarely cases when the pussy does not open, but resolves on its own or turns into a chalazion. Chalazion is a chronic form of the disease; complete recovery will take 1–2 months.
Chalazion and stye on the eyes
Prevention of eye stye
Prevention of the disease consists of simple rules, the main one of which is hygiene. Not worth it:
- leave makeup on eyelashes and eyelids overnight;
- rub your eyes, comb them;
- use someone else's brushes to apply makeup;
- overwork, hypothermia;
- neglect the rules of wearing and caring for contact lenses.
By following these recommendations, you will not protect yourself from the appearance of barley 100%, but you will significantly reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
Complications
When an internal stye is identified, it is important to begin treatment as early as possible. During it, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Otherwise, serious complications may arise:
- the acute form can become chronic. In the future, the disease will regularly worsen and be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms;
- When barley becomes severe, a secondary infection may join it. All this will cause an abscess, which can be removed surgically;
- the appearance of conjunctivitis or blepharitis;
- thrombophlebitis of the orbital veins;
- thrombosis of the cavernous sinus;
- inflammation of the meninges;
- in severe cases, the disease can cause severe visual impairment or death.
Conservative treatment
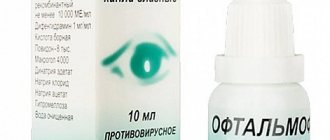
At the initial stage, medications help well. Most often, drops and ointments with an antibacterial effect are prescribed.
Drug therapy
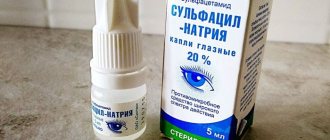
Treatment of barley involves the use of various drops and ointments that have a detrimental effect on bacteria. The following medications may be prescribed:
- Floxal drops and ointment.
- Tobrex drops.
- Albucid.
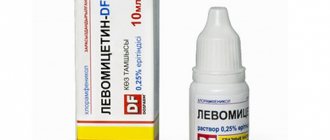
- Levomycetin drops.
All these medications are used several times a day. Hands are first thoroughly washed with soap. The lower eyelid is carefully pulled back, 1-2 drops of the medicinal solution are instilled, after which the eyes are closed and the eyelids are gently massaged so that the medicine disperses.
Eye ointment is used only after drops. Hydrocortisone and tetracycline ointment are suitable for treatment. It is placed 1 cm under the lower eyelid, after which the eyes are closed and the pupils are moved for several minutes to distribute the medicine evenly. If the doctor has prescribed the use of eye drops and ointment, then apply the ointment only after the drops, after waiting at least 15 minutes. Otherwise, the ointment prevents the absorption of the medicinal solution.
Before applying the medicine, remove all cosmetics from the eyes and wash the mucous membrane with a weak solution of boric acid or chamomile decoction. Solutions for eye treatment should be warm; the bottle of medication should be preheated in your hand.
You should not wear contact lenses until you are completely healed. During treatment you need to switch to glasses.
Treatment of internal stye
It is a mistake to believe that the abscess will resolve on its own; this will not happen if you do not consult a doctor and do not carry out timely treatment. With self-medication, a compaction may eventually form at the site of the abscess, which will sometimes make itself felt in the form of the manifestation of new purulent formations.
Important! Under no circumstances should you open the abscess yourself; this can lead to irreparable consequences, including death.
Treatment is prescribed by an ophthalmologist and carried out at home.
Diagnosis of the disease
Basically, the diagnosis of the disease is carried out directly during a visual examination by a doctor, but if relapses of the pathology occur, additional tests are prescribed in order to detect the hidden cause of the disease.
Additional tests and examinations
- An immunogram is an examination to identify the state of the body’s immune system in order to restore its normal functioning.
- Culture to detect staphylococcus, the main causative agent of the disease.
- A general blood test to identify hidden pathologies of the body, which serve as an impetus for the reappearance of internal stye.
- Measuring blood sugar, an elevated level indicates the presence of other diseases in the body that cause circulatory problems and lead to relapses of diseases.
Based on all the examinations performed, the doctor determines the stage of the pathology and prescribes the necessary course of treatment.
Prevention
To protect yourself from meibomitis and its dangerous consequences, it is worth observing prevention. It will help prevent the development of unpleasant symptoms, which often cause severe discomfort. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- Be sure to maintain hygiene when instilling drops or using ointments.
- There is no need to constantly rub or scratch your eyes, especially with dirty hands.
- Before contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes, you must wash your hands.
- It is worth ensuring proper nutrition.
- Start taking vitamins to increase and strengthen immunity;
- No need to overwork yourself;
- It is imperative to lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly.
Internal stye is a serious and unpleasant disease that can occur in anyone. It is important to carefully monitor your condition and, if you notice any suspicious symptoms, immediately consult a doctor. This disease should not be neglected, otherwise it can cause serious health complications. If you follow preventive measures, you can completely avoid this disease.
Author of the article: Olga Aleksandrovna Pecheritsa, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Prevention of disease relapse
To prevent relapse of the disease, it is necessary to follow some preventive measures. They include:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- giving up bad habits that reduce human immunity;
- avoid hypothermia;
- proper rest after physical activity;
- providing the body with sufficient vitamins;
- compliance with personal hygiene standards;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases.
To a greater extent, internal stye is considered a disease of a weakened immune system of the body, so the course of treatment should be aimed at strengthening the human immune system in order to prevent relapses.