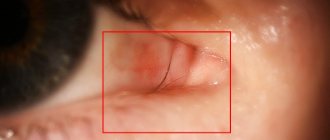
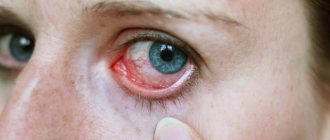
Eye inflammation is a reaction to infection or mechanical trauma. This process affects the internal and external structures of the eyeball, as well as nearby organs. It is important to distinguish between usually redness of the conjunctiva, which does not require medical intervention.
Any inflammation in the eye area is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- Redness;
- Soreness;
- Edema.
Due to the fact that the human eyes play an important role, their inflammation leads to a significant decrease in the quality of life. In this case, visual acuity, color perception, etc. may be impaired.
Allergic conjunctivitis
The nature of allergic conjunctivitis can be associated with various allergens. Depending on this, the symptoms of the disease change. If an allergy occurs in response to medications, then swelling, burning, and itching appear. Copious mucus secretion appears.
The atopic form of conjunctivitis is associated with seasonal flowering. Typically, illness is accompanied by rhinitis, pain, redness, swelling of the conjunctiva, itching and photophobia. For treatment, hormonal agents and antiallergic drugs for topical application are used.
Inflammation of the cornea
Keratitis is a fairly common eye disease, and it can be superficial (associated with external causes) or deep (associated with internal pathological processes). All these forms of the disease require immediate treatment, as complications may develop. Among the consequences, the most common are scleritis, adhesions on the pupil, decreased vision, and endophthalmitis.
Symptoms of keratitis are:
- lacrimation;
- Cutting pain;
- Narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- Photophobia;
- Swelling of the eyelids;
- Itching.
Treatment of keratitis is carried out with local and systemic drugs. In this case, antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral drugs are prescribed. Oral vitamin complexes are also used. Local therapy is carried out using anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, disinfectant, and hormone-containing eye drops.
If the lacrimal canals are involved in the pathological process, then they are washed with a solution of chloramphenicol.
In case of herpetic nature of keratitis, laser coagulation or diathermocoagulation can be additionally performed. In addition to traditional drugs, phytotherapeutic treatment is sometimes prescribed.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial pathogens affect the organs of vision upon contact with infected people. The proliferation of pathological microflora leads to pathologies:
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is provoked by pathological microflora of a viral or bacterial nature.
In case of a bacterial disease, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately, as complications may develop. Due to the active proliferation of bacterial microflora, perforation of the cornea is observed, which leads to complete blindness.
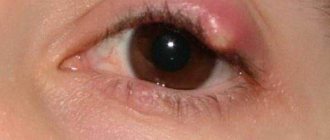
Barley
Barley is characterized by suppuration in the sebaceous gland area, which is provoked by streptococci or staphylococci. Symptoms of the disease are:
- pain syndrome;
- swelling;
- hyperemia of the eyelid.
The disease can affect one eye or two at the same time. Initially, a painful area forms on the eyelid, which in a few days will turn into an abscess.
Blepharitis
Inflammation spreads to the eyelash area on the eyelid. Among the symptoms of blepharitis, the most pronounced are:
- tearfulness;
- itching sensation;
- photophobia;
- eyelash loss;
- violation of proper growth.
Dacryocystitis
Inflammation of the tear duct is caused by staphylococci and streptococci. Due to swelling of the canal, stagnation of tear fluid is observed, which provokes inflammation. Symptoms observed with dacryocystitis:
- redness of the inner corner of the eye;
- pain syndrome;
- purulent discharge.
Abscess
The formation is characterized by severe pain and severe swelling. The development of an abscess is provoked by a pseudomonas pathogen or staphylococcus. An area of redness appears on the eyelid. Temporary hyperemia is possible.
Keratitis
Keratitis develops due to the progression of bacteria in the cornea. The disease is accompanied by general symptoms, as well as severe pain. A complication of the pathology is necrosis of the eyeball tissue and the development of an abscess.
Dacryoadenitis
Dacryoadenitis is a lesion of the lacrimal gland, which develops as a result of influenza, colds or sinusitis. When the disease occurs:
- swelling of the outer corner of the eye;
- severe pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the affected area;
- drooping eyelid;
- downward displacement of the eyeball.
Tuberculous keratitis
The cornea is affected due to the proliferation of the tuberculosis pathogen. One eye may be affected. With the active course of the disease, the formation of a cataract is observed.
Diphtheria conjunctivitis
The diphtheria bacillus provokes the development of a pathological condition. As a result of the disease, the following is observed:
- swelling;
- hyperemic mucosa;
- formation of gray plaque;
- discharge of cloudy secretion with flakes;
- gray coating.
Iridocyclitis
Iridocyclitis occurs due to an inflammatory reaction in the anterior part of the eye. There is a deterioration in the tolerance to bright lighting, the level of vision decreases, and increased secretion of tear secretion appears. An additional symptom of the disease is the appearance of plaque on the lens.
Inflammation of the eye socket
Typically, inflammation of the orbit leads to the formation of an abscess or cellulitis. The cause of this is infection. Symptoms of the disease are swelling, pain, redness of the eyelids, and decreased visual acuity. Against the background of phlegmon, the body temperature often rises, a headache appears, and the eye is often impossible to open. Treatment begins with antibiotic therapy (ampiox, erythromycin, gentamicin, penicillin). If treatment is not prescribed in time and the abscess is not opened, a complication may develop.
Who gets blepharitis more often?
Simple blepharitis, which occurs in an acute form, usually begins after infection in the eyes, hypothermia, or fatigue. It is treated quickly and does not cause complications. Chronic, recurrent blepharitis may indicate serious health problems. If a person’s inflammation frequently bothers him, he should undergo a comprehensive examination.
Anyone can get blepharitis. It affects women and men, children and adults equally often, but most often they suffer from this disease:
- girls using cosmetics;
- allergy sufferers, persons with gastrointestinal diseases, vitamin deficiency, diabetes mellitus;
- office workers, people who spend a lot of time at computers;
- people who have suffered serious illnesses.
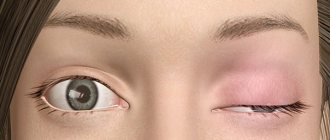
Inflammation of the eyelid
Inflammation of the eyelid can involve the lower or upper eyelid (sometimes both). In this case, the symptoms of the disease are redness and swelling. Among specific diseases, blepharitis, stye, chalazion and herpetic infection are more common. Sometimes the cause of inflammation is associated with the proliferation of small mites, increased sensitivity to cosmetics or dust, a decrease in the body's immune defenses, and systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, gastritis, cholecystitis, etc.). Inflammation of the eyelid may cause impaired eyelash growth, excessive loss of eyelashes, itching, watery eyes, and reddish nodules along the edge of the eyelid.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to see an ophthalmologist. To treat the disease, it is important to eliminate the cause of inflammation (allergen, micromites, etc.). You should also pay attention to maintaining hygiene measures, regularly washing the eyes with antiseptics after removing the discharge. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics or hormonal agents.
Inflammation of the blood vessels of the eye
Uveitis refers to any inflammation of the choroid. Depending on the location of the inflammation, various symptoms may be present:
- Iridocyclitis leads to photophobia, pain, decreased visual acuity, constriction of the pupil, and increased intraocular pressure.
- With peripheral damage to both eyes, blurred vision and decreased vision occur.
- Chorioretinitis is accompanied by pain and decreased vision.
The causes of uveitis can be infections, rheumatism, syphilis, dental pathology, diabetes.
The reaction of the pupil to light is usually slow, and miosis and darkening of the iris are present.
For treatment, hormonal, vasoconstrictor and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If inflammation is severe, then injections can be used (intravenous, intramuscular, subconjunctival, in the eyelid). You also need to focus your efforts on treating the underlying disease.
What can cause red eyes?
Before treating red eyes, you need to find out the root cause. There may be several of them:
- External influence of irritating factors: wind, pollen, smoke;
- Reaction to animal fur, flowering plants;
- Staying in a room with air conditioning for a long time;
- You can strain your eyesight for several reasons: sitting for a long time in front of a monitor or TV, reading in low light;
- Stress, fatigue, lack of sleep;
- The operating conditions of the lenses are violated: they are not changed regularly, they are not removed at night;
- Incorrect glasses selected;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Dry eye syndrome;
- Ophthalmological diseases.
Inflamed, red eyes can cause serious illness, so consultation with a doctor is necessary.
In some cases, this is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms: itching, burning, tingling.
You should definitely consult an ophthalmologist if red eyes are accompanied by more serious symptoms, including:
- Dizziness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Photophobia and lacrimation;
- Discomfort in the eye area, burning, tingling.
Inflammation of the tear ducts
When inflammation spreads to the lacrimal canals, we are talking about dacryocystitis. Since its patency is impaired, microbes accumulate in this area, which cause inflammation. The causes of the disease may be congenital characteristics, consequences of injury, or ophthalmological problems. Usually the inflammation is unilateral and is accompanied by redness, swelling and pain. There are also specific secretions. For treatment, adult patients are prescribed rinsing of the lacrimal canal with special disinfectant solutions. In childhood, massage of this area, antibacterial drops or tetracycline ointment are recommended. If conservative treatment is ineffective, then surgery is performed.
Prevention
Some inflammatory processes in the eye can be prevented. Prevention includes following the rules of hygiene; you should not touch your eyes with your hands or other objects. If the conjunctiva is irritated, you can wash your eyes with chamomile solution, saline solution or plain boiled water. You can protect your eyes from the bright sun with dark glasses.
It should be noted that using medications for prophylactic purposes is not advisable and can even be harmful. Inflammation of the eye is a very dangerous pathology and therefore requires immediate medical attention. If the disease is detected in the early stages, it is easier to cure.
Causes
Most often, the inflammatory process on the choroid is observed due to the influence of the following factors:
- mechanical damage to the eyeball, which can be minor or extensive;
- the entry of a foreign object into the eyes, which can vary in size, not only damages the mucous membrane, but also contributes to the spread of bacterial infection;
- infection with bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, gonococci, chlamydia, tuberculosis);
- spread of viruses to the choroid of the eyes, for example, adenovirus, herpes, influenza, parainfluenza;
- spread of helminths and other parasites to the visual area;
- the presence of seasonal or periodic allergies, which are formed due to animal hair, flowering plants, bird feathers, house dust, chemicals;
- the impact of excessively low temperatures on the organs of vision, especially in strong winds;
- exposure to a large amount of ultraviolet radiation on the organs of vision, which affects not only the retina, but also the outer structure of the eyes.
Each cause of the condition has its own treatment methods, so it is necessary to conduct diagnostic tests, only then use medications.