What are the causes of blepharospasm
The exact pathophysiology underlying the development of blepharospasm is still unknown, but it is thought to be multifactorial, with a likely genetic component and environmental triggers.
It has been suggested that it is associated with abnormalities in the basal ganglia and dopaminergic system of the brain. Etiology:
- Parkinson's disease;
- Regular use of antipsychotic and other medications;
- Trichiasis;
- Supranuclear palsy;
- Entry of a foreign body;
- Dry eye syndrome;
- Neoplasms;
- Cortical epilepsy;
- Inflammation of the sinuses, teeth, nasopharynx;
- Blepharitis.
Provoking factors:
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- Long work at the computer;
- Stress;
- Sleep disorders;
- Physical and mental fatigue.
Benign essential blepharospasm is associated with a family history of dystonia, head or facial trauma, and other neurological movement disorders (eg, Tourette's syndrome).
Secondary pathology manifests against the background of focal lesions in several areas of the brain or develops in patients with tardive dyskinesia. Finally, secondary blepharospasm often occurs as a result of conditions associated with eyelid weakness, such as facial palsy and myasthenia gravis.
What is blepharospasm
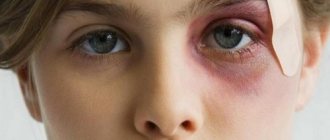
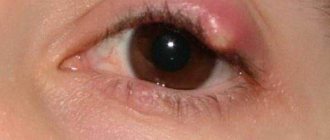
Blepharospasm is a pathology in which unilateral (bilateral) and episodic contraction of the eye muscles (orbicularis) occurs. It is believed that women suffer from this disease more often than men. In the 16th century, people with manifestations of blepharospasm were considered mentally unbalanced, and only in the 20th century it was established that there could be many reasons for the development of the disease.
The following stages of pathology are distinguished (according to the frequency of attacks):
- frequent blinking (occurs at the initial stage of the disease);
- frequent short-term episodes of blinking and muscle spasms;
- prolonged episodes of squinting;
- frequent rhythmic spasms of the orbicularis muscle and twitching of the eyelids;
- drooping of the eyelids (is a consequence of prolonged neglect of the disease or occurs against the background of serious neurological pathologies).
People popularly call blepharospasm a “nervous tic.” It is believed that muscle spasms can occur in any part of the body, but in the eye area it occurs many times more often. This is explained by the presence of a large number of nerve endings in the orbital zone and weakness of the muscles of the upper and lower eyelids.
This condition negatively affects the quality and standard of life of the patient. A person is not able to lead a normal lifestyle; he develops complexes. This also leads to the development of depression, which greatly aggravates the situation.
Symptoms of blepharospasm
Symptoms are characterized by stereotypical, bilateral and synchronous spasms of the orbicularis oculi muscles. The spasms can be brief or long lasting and can cause the eyelids to narrow or close.
Focal dystonia, manifested by involuntary closure of the eyelid, has two stages:
- Tonic;
- Clonic.
The clonic form is characterized by frequent involuntary blinking. The problem usually begins on one side and then moves to the second organ.
| It should be noted that unilateral lesions practically never occur. |
Over time, the duration and intensity of the clonic spasm gradually increases. In this case, the patient closes his eyes tightly and for a long time against his will. In this case, the nosology moved to another stage - tonic. In severe cases of the disease, mechanical blindness develops in 70% of patients. A person loses visual function because he cannot open his eyelids. Young girls suffering from hysterical seizures experience bilateral squinting that lasts for several hours.
A distinctive feature of hysteria is that when pressing on the exit points of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, the spasmodic state of the periocular muscles is stopped.
Main manifestations:
- Intense twitching of the eyelids;
- Frequent blinking;
- Excessive tearing;
- Photophobia, burning and itching;
- Involuntary squinting;
- Areas of maceration on the skin of the eyelids;
- Impaired outflow of tear fluid.
Psychiatric changes include depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. If the pathological process proceeds for a long time and is painful, then it becomes difficult for the individual to fulfill his professional duties, take care of himself at home, interpersonal interaction and emotional balance are disrupted.
| Sudden attacks interfere with driving and provoke emergency situations on the road. |
Types of blepharospasm
There are two types of blepharospasm: clonic
and
tonic
.
Clonic
The species is characterized by involuntary frequent blinking and impaired eyelid closure (fast or slow).
Tonic
Blepharospasm is characterized by impaired contraction of the circular ocular muscles, which is accompanied by persistent squinting. This spasm lasts from several hours to several days, and sometimes even weeks.
Tonic blepharospasm is divided into two subtypes: reflex and essential.
Reflex develops as a result of prolonged irritation of the trigeminal nerve receptors. This can occur with various diseases of the eyes, sinuses and nasopharynx, eyelid skin, and teeth.
The essential type of blepharospasm is observed, as a rule, in women and is explained by neurosis or hysteria.
Treatment of blepharospasm
Treatment of the disease depends on its cause and predisposing factors.
If dry eye syndrome is detected, the doctor prescribes “artificial tears” in the form of drops with a moisturizing effect. If a foreign body enters the organ of vision, the ophthalmologist very carefully removes it and prescribes anti-inflammatory and absorbable medications. If, after a comprehensive examination, it is not possible to determine the exact etiology of the closure of the palpebral fissure, then several microdoses of botulinum toxin are injected into the periocular muscles. Botox causes paralysis of muscle fibers, and thus eliminates blepharospasm. Side effects such as transient ptosis, blurred vision or diplopia are relatively rare and usually disappear spontaneously after a few weeks.
Symptom resolution from botulinum toxin injections is considered temporary and requires repeated injections every three months for the remainder of the patient's life. Many affected individuals develop a more severe form and/or clinical resistance to botulinum toxin.
If the injections do not lead to positive and lasting results, the spasm still persists, then surgical intervention is indicated. During the operation, the surgeon completely or partially removes defective muscles in the area of the eyebrows and eyelids.
Electromyographic studies help determine the best injection sites for optimal response and differentiate patients who require limited or complete myectomy.
Treatment
The beginning of the fight against the disease is carrying out diagnostic procedures. After the initial diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor selects the optimal treatment option based on the cause of the disease. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, you can greatly aggravate your condition!
Medication method
The most popular treatment for spasms is botulinum toxin (Botox, Dysport). The injection is performed directly into the eyeball every three months. The effect of the drug appears after two days, the maximum result from therapy is observed after a week. Lasts for three months.
In rare cases, muscle relaxants are prescribed (Phenibut, Clonazepam), which are characterized by a low degree of effectiveness. They can slightly improve the patient's condition and extend the time between botulinum toxin injections.
Doctors may recommend taking sedatives and pain medications. To eliminate anxiety and signs of depression, take a course of antidepressants. The therapy is temporary and contraindicated in older people.
Surgery
Surgery may be used to eliminate the spasm. The essence of the procedure is to excise the nerve endings associated with the muscles of the eye. The second option for the operation is complete or partial excision of the orbicular muscle, which is responsible for opening and closing the eyelid.
The first option does not guarantee a 100% cure, since after a while the excised nerves can recover and the spasm will reappear. The second method is considered less preferable, since the risk of complications increases, since it is very difficult to determine the required volume of muscle for cutting. Return to contents
Folk remedies
Grandma's recipes will help you cope with this unpleasant disease. Before using this or that method, be sure to consult your doctor. The following means are most effective:
- Take twenty grams of calendula, St. John's wort, yarrow and cinquefoil. Pour the mixture with two glasses of boiling water. Leave for a couple of hours, strain and take twenty milliliters three times a day;
- Combine ten grams of motherwort, linden, rue and twenty grams of mistletoe. Pour a glass of boiling water, divide into three parts and drink throughout the day;
- Take equal amounts of oregano, valerian, yarrow, and pine buds. Pour twenty grams of the mixture with the same volume of boiling water. Strain the mixture and take fifty milliliters three times a day;
- To reduce nervous excitability and fight insomnia, the following decoction will help: combine ten grams of mint, twenty grams of heather and lemon balm, forty grams of valerian. Pour boiling water (three hundred milliliters) over twenty grams of the mixture. Filter the composition and drink fifty milliliters twice a day;
- To combat swelling, prepare a mask of flour, honey and egg white. Apply the mixture to the affected eyelid and leave for ten minutes. Repeat the procedure three times during the day;
- Take equal amounts of lavender, linden and viburnum. Pour forty grams of the collection with half a liter of boiling water. Use one hundred milliliters of solution three times a day;
- Dissolve ten grams of valerian root in one hundred milliliters of water. Take the composition before bed;
- To eliminate swelling, try sage and chamomile compresses. Combine the ingredients in equal quantities and pour boiling water. Leave for two hours, strain the mixture and soak a cotton pad in it. Apply to your eyelid for ten minutes. Perform the procedure twice a day.
| Remember that treating blepharospasm is a protracted and difficult task, so be patient and calm. |
Prevention of blepharospasm
In modern medicine there are no specific ways to prevent blepharospasm. If the pathology has developed secondary, then it is necessary to avoid irritating factors as much as possible. Wear dark sunglasses in bright light. It is recommended to treat blepharitis and dry eyes with medication, eliminate stress if possible and reduce the dosage of the provoking drug. Ophthalmologists recommend excluding drinks that provoke stimulation of the central nervous system (coffee and strong tea). After working at the computer for a long time, it is better to do eye exercises.
If you notice that for some reason the frequency of blinking is increasing or you need to make an effort to close your eyelids, you should seek help from a neurologist or ophthalmologist.
At the Fedorov Clinic in Moscow, doctors will help diagnose the disease in a timely manner and prescribe treatment. Making an appointment Today: 17 registered
Diagnosis of blepharospasm
Blepharospasm can be diagnosed based on a person’s complaints and existing symptoms.
If there is a suspicion that the disease is hereditary, genetic testing is performed. A score of visual functions is also performed. In this case, the doctor gives the following points:
- 1 – blindness;
- 2 – dependence in case of staying outside the home;
- 3 – independence with poor visual functions;
- 4 – independence with insufficient visual functions;
- 5 – discomfort;
- 6 – normal visual functions.
Carrying out differential diagnosis is of no small importance. It is recommended to distinguish blepharospasm from myasthenia gravis, photophobia, tics, facial neuritis and other conditions with a similar clinical picture.
How to cure blepharospasm as quickly as possible?
We offer an innovative method of color pulse therapy, the discovery of which was awarded the Nobel Prize.
In order to answer the question of how to cure blepharospasm, it is necessary to restore the normal functioning of the brain centers responsible for regulating the nervous system. This is exactly the problem that the unique Neurodoctor device solves.
The device was developed based on the pulse therapy method. This method of treatment is considered by modern medicine, one of the most progressive and highly effective. Pulse therapy affects the regulatory centers of the brain and activates some areas of the nervous system, eliminating malfunctions in their work.
During the treatment of blepharospasm:
- The general condition of your body will improve.
- Muscle tension will decrease.
- Swelling and inflammation will disappear.
- The frequency and duration of reflex spasms will decrease.
- The psycho-emotional state will be restored.
- The risk of complications will be reduced.
Powerful and effective treatment with the Neurodoctor device will quickly eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, localize the foci of pathology, and reduce the dose of medications. This will allow you to live a full life and forget about your illness forever.
How it works?
Neurodoctor affects the control centers of the brain.
The brain begins to produce dozens of neurohormones and form “corrective” nerve impulses.
Neurohormones are many times more effective than the most powerful drugs in quickly curing the disease. Nerve impulses eliminate pathological processes at the cellular level and correct the functioning of other organs and systems of the body.
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE METHOD
Is it possible to get rid of blepharospasm forever?
“Neurodoctor” is today recognized as one of the most powerful methods for treating diseases of a wide variety of etiologies. Whether it is possible to get rid of blepharospasm forever is not completely known, but Neurodoctor combines perfectly with traditional methods of treatment and allows the body to recover better. Today the Neurodoctor device is:
- A treatment method that won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
- The development history of the device goes back more than 20 years.
- Neurodoctor takes part in medical exhibitions around the world.
- The press writes about the Neurodoctor device (publications such as KP and others).
- Neurodoctor is used by thousands of people in 26 countries around the world.
- Produced in Russia at enterprises of the military-industrial complex.
- Combines well with various medications without causing side effects.
- The device has no contraindications.
What happens if blapharospasm is not cured?
In most cases, if blepharospasm is not treated, it leads to severe complications that pose a real threat to your health and vision, including complete loss of visual function. Among these complications:
- Difficulty in tearing
- Swelling and maceration of the eyelids
- Eye inflammation
- Psychological and neurological disorders
- Disorders of adaptation in society
- Mechanical blindness
The main danger of the disease is related to the fact that in the absence of adequate treatment for blepharospasm, the development of so-called mechanical blindness, leading to permanent disability, is possible.
With blepharospasm, you experience a persistent, spasmodic closure of the eyelids, leading to severe discomfort and severe neurological and sometimes mental problems. The disease causes difficulties in communication, decreased performance, and in some cases, the inability to perform professional duties.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The diagnosis and treatment of blepharospasm is carried out by a neurologist and a surgeon. To determine the direction and causes of the disease, patients are referred for a brain study. In addition, the sore eye:
- examined using a slit lamp;
- subjected to electromyography;
- check for the presence of a blink reflex.
An important place at the initial stage of diagnosis is determined by the speed at which the impulse flows through the fibers of the facial nerves.
The disease manifests itself in the form of an altered reaction to:
- stretching;
- coupled muscle inhibition;
- dysfunction of the premotor cortex, which is responsible for external stimuli.
The main sign of blepharospasm is twitching of the eyelid, independent of a person’s desire. In the later stages, “mechanical blindness” appears - the eye simply cannot be opened. Sometimes, against the background of blepharospasm, problems arise with swallowing food, chewing it and speaking (spasms of the larynx, tongue, masticatory muscle), which is why the person begins to grimace.
Negative manifestations intensify in bright lighting and sharp sounds (a person blinks more often, his eyelids involuntarily close, this is how the nervous system reacts to external stimuli).
3.Types of eye twitches
There are three types of eyelid twitching:
- Twitching of the small eyelid;
- Benign essential blepharospasm;
- Hemifacial spasm.
Most common eyelid twitching
associated with
fatigue, stress, lack of sleep, drinking alcohol, caffeine and smoking.
The eye also twitches due to irritation of the surface of the eye or the membrane lining the eyelids (conjunctiva). Sometimes it is difficult to determine the cause of a tic, but almost always such twitching of the eyelid is harmless, painless and goes away quickly.
Benign essential blepharospasm
usually develops in middle-aged people and gradually progresses. In women, blepharospasm is diagnosed twice as often as in men. As a rule, benign essential blepharospasm begins with frequent blinking or irritation of the eyes caused by fatigue, stress or external irritants - bright light, wind, polluted air. As the disease progresses, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, and facial spasms may develop. In particularly severe cases, the spasms can become so severe that the eyelids remain closed for up to several hours. Gradually the eye stops twitching and the contractions go away. According to scientists, benign essential blepharospasm is a neurological disorder that develops due to a combination of environmental and genetic factors.
Hemifacial spasm
It is quite rare, and this disease does not just cause eye twitching. The tic usually affects the muscles around the mouth. Unlike other types of eyelid twitching, hemifacial spasm affects only one side of the face. The cause of tics in most cases is arterial pressure on the nerves of the facial muscles.
If your eye twitches, most likely nothing bad has happened. But you need to see a doctor if:
- The eye twitches for a week or longer;
- The eyelid twitches so violently that it closes completely;
- Spasms appeared not only in the eyes, but also in other facial muscles;
- There is redness, swelling, or discharge from the eyes.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Complications of blepharospasm
Pathology often occurs in people of working age. When blepharospasm appears, complications in the form of social maladjustment are often observed. If proper treatment is not started in time, the risk of associated disorders increases. These include depression, increased anxiety, and social phobia.
In addition, the likelihood of functional blindness increases, which can cause disability. Reflexive squinting causes falls or accidents. This results in traumatic injuries.
Why does blepharospasm occur?
Absolutely all processes in our body are controlled by the brain. Brain cells receive information from all organs and systems, process it, produce the required reaction, and transmit the appropriate orders through nerve fibers to various organs of the body. The cause of blepharospasm (like most other diseases) is a combination of many different factors.
These factors lead to a malfunction of some parts of the brain and disruption of neural connections. In other words, the brain stops giving the “correct” orders for the smooth operation of your neural system, which leads to blepharospasm, and then to more serious diseases.