First aid
The most common are superficial eye injuries associated with midges, specks, and eyelashes. In this case, the action plan is as follows.
Blink actively - perhaps the foreign body will come out on its own along with the tear fluid.
If you experience discomfort after this, go to the mirror and pull down your lower eyelid (or upper eyelid, depending on which part of the eye you feel discomfort in). If you find an eyelash or speck, remove it using the tip of a handkerchief soaked in water. A cotton swab is also suitable, which also needs to be wet.
You should not rub your eye. Otherwise, you can “drive” the speck deeper. In this case, only a doctor can remove the foreign body.
After removing a foreign body into the eye, it is recommended to instill drops with a disinfectant effect.
To the doctor!
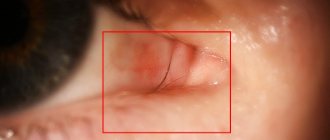
Often, a foreign object is not on the surface of the eye, but penetrates into the cornea or deeper. In this case, it must be removed by a specialist; you cannot act on your own! You can only cover your eye with a bandage and go to the doctor.
The help of an ophthalmologist is also required if a branch pokes into the eye or another injury occurs, even superficial. Typically, with such injuries, the eyelids reflexively close. They need to be opened slightly - carefully, without pressing on the eyeball - and antibacterial drops should be instilled. After this, you should cover your eye with a sterile napkin and immediately consult a doctor.
A visit to a specialist is also required if the speck was small and it seemed to have been removed, but the next day the redness of the eye, tearing, and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye persist.
First aid for eye injury: important treatment tips
Vision is a complex mechanism that allows a person to perceive the world around him.
If the organs of vision are damaged, complete or partial blindness may occur. There are several types of eye injuries in a child or an adult, depending on the nature of the origin of which, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Eye injury: what is it?
Eye injury is a violation of the integrity of the membrane of the eyeball due to exposure to external factors.
As a result of such damage, not only the integrity, but also the functionality of the organ of vision is impaired.
Depending on the depth and severity of the injury, the injury can be classified as superficial, deep, penetrating, or mechanical.
Burns of the cornea are placed in a separate category , since almost half of patients consult ophthalmologists with such eye injuries.
Classification and types
There are several types of eyeball injuries that can be classified according to the following characteristics:
- Getting foreign bodies (small objects, insects, chemicals) into the eye. In this case, the patient experiences lacrimation, pain and pain when blinking.
- External mechanical impact (concussion, compression, impact with blunt and sharp objects, gunshot and other wounds).
- Thermal burns from steam, smoldering and burning objects, flames.
- Frostbite. In contrast to thermal burns, in this case the eye is exposed to extremely low temperatures (cold liquids, exposure to wind, contact of the eye with chilled objects).
- Chemical burns. Occur upon contact with various chemical compounds , most often alkalis and acids, but in some cases eye injury is possible upon contact with adhesives, lime, cement mortar and solvents.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eye (this type of damage is possible both after prolonged exposure to the sun and under artificial light sources, including quartz or conventional lamps).
In most cases, injuries occur in domestic conditions , and in such situations, urgent assistance to the victim is necessary.
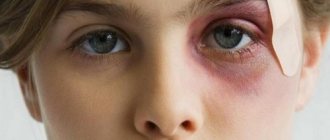
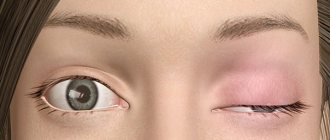
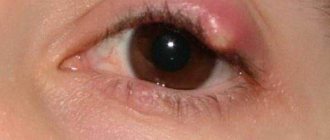
Eye injuries photo
Contusion
Eyeball bruise
Consequences of a fragmentation grenade explosion
Foreign body
Eye injury: treatment, causes and symptoms
Trauma to the cornea of the eye, depending on its origin, can be classified as superficial, penetrating, contusion-type injury and burn .
What to do if the eye is damaged depends on the type and the necessary treatment is selected accordingly.
Superficial (a special case of blunt eye injury)
This type of damage is the most common, it includes damage such as erosions of various types, non-penetrating small wounds, blunt trauma , as well as foreign bodies entering the surface of the eyeball.
The following signs are typical for these types of damage:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body under the eyelid;
- cutting pain in the affected eye;
- photophobia and excessive lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- decreased visual acuity and quality.
a specific treatment is prescribed in each specific case , since the injury can be of varying degrees of severity.
Ophthalmology, taking into account the origin of the injury, can determine the most effective and adequate treatment method.
Often, with superficial injuries, there is a violation of the integrity of the skin , and in such cases, primary surgical treatment of the wound is performed (sometimes it is necessary to apply sutures to the excised edges of the wound).
Most often, conservative medicinal treatment methods are used , in which the wound is treated with antibacterial and antiseptic ophthalmic drops; sometimes it is necessary to use ointment to place under the eyelid.
In case of blunt injury to the eye, a binocular bandage is applied to it , after which the patient must remain in bed for several days and remain at rest.
When hemorrhages form in the injured eye, procedures such as electrophoresis, autohemotherapy and subconjunctival injections of the drug dionin are prescribed - such measures can quickly eliminate eye hemorrhage after injury, providing a resolving effect.
Penetrating
With penetrating eye injuries, the patient usually experiences photophobia, lacrimation and pain.
Blepharospasm (impossibility of opening the eyelids) , redness in the eyelid area, redness of the conjunctiva and bleeding in damaged areas of the eye are also possible.
Severe cases carry the risk of possible loss of the membranes and contents of the eye.
In general, signs of penetrating injuries include:
- presence of a wound channel in the lens;
- a through wound in the cornea or sclera;
- presence of an air bubble in the vitreous;
- prolapse of the iris into the wound;
- prolapse of the ciliary and vitreous bodies;
- tear of the pupillary edge of the iris;
- severe hypotension of the eye ( drop in intraocular pressure );
- segmental opacification of the lens .
When treating this type of injury, sulfonamides are prescribed, which are taken orally or parenterally , as well as broad-spectrum antibiotics.
In most cases, anti-inflammatory and antifungal agents are prescribed in parallel to prevent the development of additional pathologies.
Shell shock
Ocular contusion is the result of impact on the eyeball, and the injury in such cases can be direct or indirect.
In the first case, this is the result of a direct impact on the eyeball , and in the second, it is the result of a person’s body being shaken during a fall .
Also, the result of contusion can be cataracts , which must be removed.
Burns
Burns can be either thermal or chemical in nature , and in the first case, the main treatment consists of treating the damaged eye with medications .
After this, the patient must remain in bed for several days .
Chemical burns mainly occur due to contact of the eyeball with acids and alkalis (or chemicals containing such components).
This kind of damage does not necessarily occur in any manufacturing plants: alkalis and acids are also found in many household cleaners and detergents that people use every day .
burns occur when the eye comes into contact with soda, ammonia solutions, lime and any detergents.
Acid burns do not cause such damage as alkalis, which quickly destroy the mucous membrane. Basically, when acids come into contact with the surface of the eye, superficial destruction of the outer layer of the mucous membrane occurs, which secretes protein.
This protein, reacting with acid, coagulates, forming a barrier to acid access to the deep layers of the eye and the retina. In most cases, acid burns do not cause significant damage to vision, while alkali burns reduce the quality of vision.
Associated eyelid injuries and their classification
When the eye is damaged, there are almost always concomitant eyelid injuries , the danger of which is not so great, but can contribute to the development of additional pathologies.
Such injuries include:
- Erosion. It is expressed in damage in the form of abrasions and scratches of the outer layer of the eyelid , and the affected area may bleed. Damage is always accompanied by pain , but seeing a doctor for such damage may not be necessary: you can relieve pain and stop bleeding on your own by treating the damaged area with any antibacterial agent and applying cold to it .
- After a blow to the closed eye with a blunt object, a contusion of the eyelid is possible , in which pronounced swelling of the soft tissues is observed. In this case, hematomas and bruises can form under the eye , and pain is felt not only when the eyeball moves, but also at rest. In case of severe eye injuries, a rupture of the conjunctiva, rupture of the lacrimal canals and their displacement are possible. As first aid for such an injury, it is necessary to apply a cold object to the damaged eyelid, then consult a doctor. If necessary, a specialist can inject an anesthetic into the injured area.
- It is possible to form puncture, cut and lacerated wounds of the eyelid , which can be both superficial and affect the deep layers of the eyelid.
Diagnosis of eye injuries
Diagnosis of eye injury allows us to identify the cause and extent of damage, which in turn is necessary to prescribe adequate treatment.
Sometimes an X-ray examination is required (this method is especially relevant for penetrating wounds and helps determine the presence of a foreign body in the eye).
During the diagnostic process, the ophthalmologist can not only determine the type of injury and the degree of damage , but also give a prognosis regarding the condition in which the patient’s vision will remain after treatment.
First aid for eye injuries
First aid for an eye injury is to immediately call a doctor or go to the nearest medical facility yourself , but while waiting for a specialist, you should try to remove the foreign body if the injury is caused by it.
To do this, you need to pull back the lower or upper eyelid and try to carefully remove the foreign object with the corner of a folded scarf or piece of fabric. Do not rub your eyes - this will lead to even greater irritation.
Eye injury treatment at home
After removing the foreign body, it is necessary to drop 2-3 drops of albucid into the affected eye.
You can also use the following eye drops for eye injury for treatment at home and during rehabilitation after injury in accordance with the instructions for use:
- Korneregel;
- Solcoseryl;
- Balarpan-N;
- Vitasik;
- Hyphenation.
Before using such drugs, you should consult with your doctor , who will help you plan a course of treatment and recommend the appropriate type of drops.
Pain-relieving eye drops after injury
Drops such as alcaine, inocaine, lidocaine can be used as anesthetic drops after an injury. After application, they begin to act in one to two minutes and will provide an analgesic effect for 15-20 minutes.
In the video you will learn about first aid for eye injuries:
Self-medication in the form of using decoctions, infusions and lotions for eye injuries is not recommended: such methods will be ineffective and can worsen the situation, and this is fraught with complete and irreversible loss of vision, not to mention the restoration of the eye.
Was the article helpful?
Source: https://zrenie1.com/bolezni/travma-glaza.html
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). Its cause may be an allergic reaction, the penetration of viruses or bacteria. In any case, the symptoms are similar. This is redness, lacrimation and discharge from the eyes, pain in the eyes.
Important
Treatment for conjunctivitis should be selected by an ophthalmologist. But if in the first days of the illness there is no access to a doctor, you can independently wash your eyes with a warm tea solution and instill antiseptic drops.
For conjunctivitis treatment to be effective, it is important to follow a number of rules.
If one eye is affected, the drops should be in both.
If you have conjunctivitis, you should not put a bandage on your eye - this creates favorable conditions for the spread of infection.
If there is pus or mucus in the eye, before instilling drops you need to remove them using a cotton pad soaked in tea, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin.
In most cases, conjunctivitis is contagious, so it is important that the sick person wipes his face only with his own towel and uses his own washing gel.
| Drugs | ||
| Preparations for the prevention and treatment of eye diseases | ||
| Vision support products |
Remember, self-medication is life-threatening; consult a doctor for advice on the use of any medications.
First aid for various injuries
First aid is an immediate course of action before medical assistance is provided. It is aimed at eliminating a factor that threatens the health or life of the patient, relieving pain and minimizing possible complications.
Expert opinion
Danilova Elena Fedorovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category, Doctor of Medical Sciences. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children.
In case of eye injury, first aid will depend on the depth of the damage. However, regardless of the severity of the injury, you should consult a doctor, even if the situation seems very ordinary. For example, when struck with a fist in the eye area or head, visual acuity may suddenly decrease, dizziness and headache may appear.
This is how retinal detachment manifests itself, which cannot be treated at home, so you should know the procedure for providing assistance before the medical team arrives or the patient is taken to a medical facility.
At home, any type of assistance should be provided with clean hands so as not to introduce infection into the mucous membrane. The wounded person needs to be reassured, and if the wound is penetrating, then you should immediately seek help from an ophthalmologist.
First aid for an adult and a child if a branch gets into the eye
It's not that hard to stumble upon a branch..
This is facilitated by haste, too active play, inattention, and insufficient lighting.
Even an adult, returning home from work, can accidentally “crashe” into a branch, being immersed in his thoughts.
Such a collision is a common injury to the cornea, so the eye naturally hurt . What to do to get rid of unpleasant sensations faster?
Symptoms
In case of minor injuries, as a rule, it is the cornea that suffers.
In more serious cases, the deep layers of the eye are damaged , right down to the lens.
Superficial eye injuries are the easiest to treat and, as a rule, have a favorable outcome, and a blow from a branch is specifically superficial.
It is extremely difficult to imagine that a person ran into a branch with enormous force and that it penetrated deep into it.
The symptoms are:
- pain when blinking;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- redness of the eye and tissues around it;
- swelling;
- tearfulness;
- cutting pain at rest;
- difficulty opening the eye;
- photophobia;
- decreased visual acuity.
Causes of eye injuries
Acute injuries often occur when glasses or masks, i.e., equipment that is supposed to protect, are damaged. Shards of broken glass or plastic cause many penetrating wounds to the eyeball, incised wounds to the eyelids and face. Acute injuries can also be caused by nails, tree branches, and in some sports, such as basketball, water polo, rugby, and wrestling.
However, most eye injuries are blunt (contusions). Any object traveling at high speed can cause blunt force trauma. If the object is large, part of the energy is absorbed by the surrounding tissues, which can also be damaged (up to a fracture of the nose, cheekbone).
However, even a large and relatively “soft” soccer ball can protrude deep into the orbit and injure the eye. The eyeball is quite elastic, and when it “restrains” the blow, the kinetic energy is transferred further to the thin walls of the orbit and the so-called. a fracture of the orbital floor, and part of the contents of the orbit moves into the maxillary cavity. Such damage leads to the “drowning” of the eyeball into the orbit and limits its mobility, which causes diplopia.
Injuries to the eyes and eyelids most often occur during sports competitions (13% of all cases). The most traumatic sports in this regard, according to Norwegian statistics: football (up to 35%), bandy (13%), squash (up to 11%), handball (up to 7%). In Scotland, football also leads (up to 33%), followed by squash (up to 30%), ice hockey (up to 10%), tennis (up to 10%) and badminton (up to 8%).
In the US, basketball takes first place, and paintball comes in second (up to 21%). Perhaps the real danger of these sports is not so high, but the whole point is their popularity.
First aid at home
But the victim can be given first aid before going to the emergency room.
For an adult
The first thing you need to do is calm down and wash your hands well .
Next, you need to open your eye and see if there is any speck or sliver left inside.
If they are present, you will need to carefully remove them using a clean cloth or cotton wool moistened with water.
If a foreign object has penetrated into the deep structures of the eye and is stuck there, under no circumstances should you remove it yourself.
If the eye is very swollen, you can apply something cold to it (ice, a cold spoon) while you travel to a medical facility.
To kid
An eye injury will greatly frighten the child and he will most likely scream and cry.
An adult needs to calm the child down and carefully examine the eye .
If there are small specks under the upper or lower eyelid, you should try to remove them using one of the following methods:
- roll a clean handkerchief into a thin tube, moisten it with water and gently rub it along the inner surface of the lower or upper eyelid;
- douche: rinse the eye with cool water.
When should you see a doctor?
In case of minor injury , when the integrity of the skin of the eyelids is not broken, there are no spots, wounds, or bleeding on the eye, you can cope with the injury yourself.
It is only necessary to periodically (every 3-4 hours) use antiseptic and antibacterial drops.
To relieve swelling, you can apply compresses and lotions.
If a branch penetrates the eye and gets stuck there, you should immediately take the victim to the emergency room.
Medical assistance is required in some cases:
- a branch hit a child in the eye;
- there are traces of injury on the surface of the eye;
- small particles remain on the surface of the eye or penetrate inside;
- the eyeball is red (hemorrhage);
- the branch remained in the eye.
Symptoms and consequences
With a non-penetrating eye injury, the following occurs:
- severe bleeding inside the eye;
- rupture of the retina and choroid;
- retinal disinsertion;
- traumatic cataract.
This is often possible after a severe bruise or blow with a blunt object.
Manifestations:
- severe pain in the eye;
- uncontrollable lacrimation begins;
- pain syndrome, if the patient looks at the light, visual acuity is greatly reduced;
- a bloody spot may appear on the eye.
With penetrating trauma, complete destruction of the damaged eyeball, damage to the lens, and loss of vision are possible. The patient must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible.
Blunt eye trauma is divided into the following degrees: mild, moderate, severe.
Consequences of such an injury:
- erosion of the tissues that are located around the cornea;
- damage to the corneal epithelium;
- inflammation and infection may develop;
- the level of visual acuity may decrease;
- pain in the eye due to damage to the nerve endings.
Symptoms of blunt trauma:
- when an infection occurs, swelling develops after a few days;
- purulent discharge is formed;
- post-traumatic keratitis and corneal ulcer are possible;
- Visual acuity will decrease as a result.
The eye can also be damaged due to injury or bruise to the bones, tissues, and muscles located near the eye organ.
As a result of a fracture and crack in the wall of the orbit, air can penetrate under the skin, causing severe swelling of the eyelid and protrusion of the eyeball. The optic nerve can become damaged and the person may go blind .
Treatment
Treatment at home consists of several points:
- Use antibacterial and antiseptic drops simultaneously (with a break of 20 minutes). For example, these could be Albucid, Tobrex and Okomistin drops. Drip morning and evening for 5 days.
- Using eye gel (Actovegin, Solcoseryl). Before going to bed, place a thin strip of gel behind the lower eyelid.
- After each eye drop, place a strip of behind the retracted lower eyelid .
The course of treatment should be 5-7 days . If after this the discomfort does not disappear completely, you should visit a doctor.
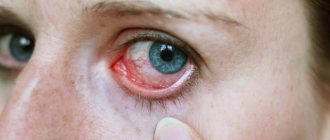
Redness of the eyeball after a blow
Eyes are very delicate and most unprotected organs that are vulnerable to mechanical irritations. They especially suffer from direct blows. In general, the eyeball itself has an elastic structure, thanks to which it can withstand even the strongest blows.
After the blow, the eyeball becomes red and swollen. Complications of injury are not only external manifestations; damage can cause significant harm to the entire visual apparatus. Trauma can damage the lens, cornea, retina, and even the optic nerve.
A direct injury is one in which a person hits his eye with a blunt object. If he received a concussion of the torso, then the eye is injured against the bony walls of the orbit - an indirect injury. During the impact and after it, the person experiences severe pain. In the first hour after injury, headache, dizziness and nausea often occur.
Unfortunately, few people know how to treat a red eye after an injury. A competent specialist will help answer this question. Before we talk about what to do in case of a concussion, let's look at the characteristic signs of eye damage.
Lens displacement
Displacement of the lens occurs with blunt trauma to the eye. Here, damage to the ligament of Zinn occurs, unevenness of the anterior chamber appears, which leads to trembling of the iris (iridodonesis). The edge of the dislocated lens is visually determined. With ophthalmoscopy, we see two optic discs.
Displacement of the lens is combined with cataracts of traumatic origin, secondary glaucoma, and iridocyclitis. In the case of complete separation of the ligament of Zinn, the lens is dislocated and displaced into the anterior chamber of the eye, and sometimes into the vitreous body. At the same time, the anterior chamber of the eye deepens, the pupil narrows. In such cases, iridocyclitis and an acute attack of glaucoma suddenly appear.
The main symptom of lens displacement is iris trembling, or iridodonesis. Iris tremors can sometimes be seen with the naked eye. But it is better to observe this in the light of a slit lamp. But iris trembling may not always occur. In such cases, symptoms such as different depths of the anterior and posterior chambers of the eyes due to pronounced pressure, as well as movement of the vitreous anteriorly, to where the support of the lens is weakened, help to identify the displacement of the lens.
Lens subluxations most often occur in the upper inner quadrant. When the lens is dislocated, degenerative processes develop, followed by clouding, and in rare cases, its complete resorption.
Treatment of the eye after injury
Since with uncomplicated displacement of the lens, vision decreases insignificantly, no treatment is required. But in case of complications as a result of eye injury (lens opacification, secondary glaucoma), it is required to remove it and replace it with an artificial lens.
Classification of bruise
Eye injuries are divided depending on the degree of damage:
- Easy. Does not affect the quality of visual function.
- Average. Causes short-term visual impairment.
- Heavy. Characterized by a persistent decrease in visual function.
- Particularly heavy. Can lead to complete blindness.
Despite the elasticity of the eyeball, a bruise can cause various types of damage, namely:
- trauma to the anterior chamber of the eye and cornea. If the eye was closed during the impact, then the eyelid may also be damaged. Swelling, hematoma, bleeding, and closure of the palpebral fissure appear. If the pathological process affects the cornea, its structures and transparency are destroyed, and erosions also appear;
- bruising of the eyelids can lead to damage to the adhesions, which manifests itself in the form of continuous tearing. If the cartilaginous structure of the eyelid has been damaged, this causes the formation of a defect and drying of the cornea;
- damage to the iris of the eye. This leads to the fact that the iris loses its ability to narrow and expand, and therefore cannot respond to light. The process may also involve the nerve endings of the iris. The hemorrhage appears as a dark red spot in front of the pupil;
- when the vitreous body is bruised, blood permeates the entire surface of the eye, which is why a person is only able to distinguish light;
- Injury to the ligaments can cause disruption in the functioning of the lens that they support. This is fraught with clouding of the lens, that is, the development of cataracts;
- retinal damage. It may even peel off. This usually happens when hit with great force;
- contusion of the optic nerve threatens complete loss of vision.
Mechanism of injury
At the moment of contusion, the eyeball is displaced and the structures that make it up are compressed.
At the same time, intraocular pressure increases and the pupil sharply dilates. Fluid rushing into the anterior chamber can cause tears in the iris along the pupillary edge or in the corners of the chamber.
The lens shifts, the ligament supporting it may not withstand the load and may break. Subluxation or dislocation of the lens occurs, and it falls out into the vitreous or anterior chamber. Ruptures of the lens capsule cannot be ruled out.
From vessels damaged by trauma, blood flows under the mucous membrane, chorionic membrane, retina, or into the chambers of the eye. The degree of hemorrhage that occurs varies.
Due to the tension of the structures at the time of injury, separation, ruptures or detachment of the retina is possible.
With severe injuries, rupture of the fibrous capsule of the eyeball may occur. More often this happens at the border of the limbus or at the attachment points of the extraocular muscles.
Ruptures or compression of the optic nerve are possible when the bone structures of the orbit are damaged.
Clinical symptoms
Contusion of the visual organ manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- impaired movement of the eyeball;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- hemorrhage into the white of the eye;
- swelling, pain, pain;
- worsening reaction to light;
- bulging or sinking of the eyeball;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- blurred vision;
- diplopia – double vision;
- the palpebral fissure does not close;
- continuous tearing;
- involuntary closing of the eyelids;
- nausea, dizziness, headache;
- in severe cases, loss of consciousness is possible.
A minor contusion does not always manifest itself as typical symptoms of eye injury. For example, a branch that hits the eye or a bounced ball can only hit the superficial layers and not cause pain.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of the disease depend on the severity of the injury.
Frequently encountered complaints:
- pain is sharp or aching, constant or appears when moving the eyeball, radiating to the temporal, superciliary region;
- hyperemia of the sclera, local or total;
- disturbance of motor activity of the eye;
- photophobia;
- blepharospasm;
- lacrimation;
- visual impairment, manifested by fog, spots before the eyes, decreased visual acuity, diplopia;
- blindness;
- exophthalmos;
- dizziness, nausea.
During the examination, the ophthalmologist will identify specific symptoms of disruption of individual structures of the eyeball.
For diagnosis, complaints, anamnesis, and an objective examination with examinations are important:
Additional instrumental studies include ultrasound, MRI, radiography, computed tomography.
First aid
Let's look step by step what needs to be done after an impact:
- Give your eyes complete rest. Any physical activity should be avoided. Don't even turn your head or move your eyeball.
- Apply cold. You can wet a towel with cold water or wrap ice cubes in a cloth. Cold is applied to the eye through closed eyelids, and the temporal part should also be involved. Apply the towel for fifteen minutes and repeat after ten minutes.
- Place disinfectant drops into the conjunctival sac.
- A sterile bandage must be applied to the eye. This will relieve hypersensitivity to light.
- For acute pain, you can apply cold compresses, which are changed every fifteen minutes.
- In case of severe pain, take an analgesic.
- Immediately take the victim to a specialized facility.
- Use Polimedel electret film. It can be used for up to four hours. The device normalizes blood circulation, tissue nutrition and metabolism. As a result, the healing process is accelerated.
Injuries to the cornea of the eye
Most often, corneal injuries are caused by scratching with a fingernail or other foreign body, but more serious injuries, such as chemical burns, can also occur.
All corneal wounds are divided into linear and patchwork. They can be of various sizes and shapes. Clinical manifestations: lacrimation, photophobia, eye pain, blepharospasm. If an infection occurs, inflammatory infiltration of the wound edges can be detected.
To diagnose a non-perforated corneal wound, in addition to anamnestic and clinical data, the following method is used: drops of a fluorescein solution (1%) are instilled into the conjunctival sac, followed by rinsing with a sodium chloride solution (isotonic). The injured area of the cornea will turn yellow-green.
Treatment
Analgesics are not used for injury to the cornea of the eye, because this delays the healing process. Epithelization occurs within a few days without leaving a trace. If the damage was deep, it is possible that after healing there will be an area of cloudiness, which (sometimes) reduces visual acuity. In general, the prognosis for corneal injuries is favorable.
Features of treatment
A red eye is not the only sign of mechanical damage. During the examination, other manifestations may be noticed that are noticeable only to a specialist. That's why you shouldn't self-medicate!
In case of eyelid defect, primary surgical treatment is performed. To strengthen the walls of blood vessels, Ascorutin tablets are prescribed. If the blow is severe, the doctor may prescribe bed rest. Hemostatic agents (hemostatic agents) and calcium supplements help speed up the healing process. Sometimes antibiotics are required.
Important! Self-medication is fraught with irreversible consequences on the visual system and complete loss of vision.
Surgical intervention is indicated in the following cases:
- retinal detachment;
- damage to the eyeball;
- lens displacement;
- corneal damage;
- disturbance in the functioning of the adnexal apparatus.
Classification
The disease is classified according to the nature of the damage and the degree of its severity.
There are 4 degrees of severity of concussion:
- The first degree is characterized by minor hemorrhages in the orbital tissue, under the conjunctiva of the eyeball without ruptures or violation of the integrity of internal structures.
- In the second degree, swelling of the cornea is observed, tears of the iris from the pupillary edge, and minor damage to the surface layers of the sclera are possible.
- The third degree of severity implies severe damage to the eyeball and adjacent soft tissues and bone structures of the orbit. There are defects in the cornea, iris, sclera, massive hemorrhages in the chambers of the eye, under the conjunctiva, and retina. Fractures of the orbital walls are noted.
- The fourth degree includes extremely severe lesions. Multiple gross destruction of eye structures with loss of the iris, lens, bone fractures, internal and external bleeding, separation or compression of the optic nerve are characteristic of this stage.
ethnoscience
Let's consider effective traditional medicine recipes that will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of an eye injury:
- Mix a teaspoon of calendula tincture with a third of a glass of water. The resulting solution is used in the form of a compress, which should be applied three to four times a day;
- Mix turmeric and ginger in equal proportions and then add a little water. The resulting pulp is applied to the hematoma, wrapped in cellophane and a warm scarf;
- Mash a fresh cabbage leaf until the juice appears, and then apply to the affected area;
- Finely chop the parsley and add a small amount of sour cream. Apply the resulting mass to the skin around the eyes.
So, redness of the eye after a blow is a natural phenomenon. Along with this, vision may deteriorate, photophobia, lacrimation, pain, a feeling of sand, and more may occur. Left untreated, it can lead to complete blindness. Timely, qualified help will help you avoid serious complications and recover faster!
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body of the eye: symptoms and treatment
A blow to the vitreous area results in hemorrhage. Blood in the retrolental space of the vitreous expands it, and blood in the orbicular space leads to the formation of a specific rim (stripe) that surrounds the periphery of the lens behind.
Retrolental hemorrhage takes longer to resolve than orbicular hemorrhage. Sometimes minor hemorrhages may be invisible and are discovered later, when they “descend” to the lower part of the anterior chamber.
Hemophthalmos is understood as massive hemorrhage into the vitreous body, occupying a significant part of the latter.
Approximately on the third day after injury, the blood in the vitreous body undergoes a process of hemolysis with the loss of hemoglobin by red blood cells, as a result of which they become colorless and later disappear. And the hemoglobin of erythrocytes takes on the form of grains, which are subsequently absorbed by phagocytes. Hemosiderin is formed, which has a toxic effect on the retina. Sometimes the blood does not completely resolve and a blood clot is formed and replaced by connective tissue moorings. The clinical picture of hemophthalmos is dominated by loss of visual acuity from the state of light perception to complete blindness. Focal illumination and biomicroscopy make it possible to see behind the lens a dark brown granular, sometimes with a reddish tint, mass of blood that permeates the vitreous body. Ophthalmoscopy shows the absence of a fundus reflex. Later, when the blood clot dissolves, one can observe deformation of the vitreous with its liquefaction. Hemophthalmos must be distinguished from partial hemorrhage into the vitreous body, which quickly and completely resolves.
Hemophthalmos leads to the development of degenerative processes in the vitreous body.
Treatment
In case of vitreous hemorrhage, bed rest and a cold bandage are prescribed on the affected eye. Calcium preparations (tablets, eye drops and intramuscular injections), hemostatic agents (Vicasol) are used. To speed up the resorption of hemorrhage, heparin is used (subconjunctivally on days 1–2) and enzyme preparations and potassium iodide. Treatment of hemophthalmia: bed rest with the head end elevated. Use a binocular bandage for 2–3 days. Calcium chloride, pilocarpine 1% 2 times a day, glucose with ascorbic acid are used, and a solution of dicinone (12.5%) is injected subconjunctivally. Then, after 2-3 days, absorbable drugs are used: dionin, potassium iodide, lidase. Corticosteroids (under the conjunctiva) and fibrinolysin are also indicated. In the late period of treatment, ultrasound and physiotherapy help a lot. If there is no positive effect from therapy, then it is necessary to suction the vitreous, and sometimes excise part of it. The removed vitreous body is replaced with luronite (a hyaluronic acid preparation).
We must not forget that with somatic diseases (cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, hypertension, blood diseases, endocrine pathology), the development of hemophthalmos is possible. But in these diseases, hemophthalmos occupies a small part of the vitreous body.
The prognosis depends on the area of hemorrhage. If the hemorrhage covers 1/8 of the vitreous body, it often resolves. With an area of 1/8-1/4 of the vitreous, moorings are formed, which leads to retinal detachment. In terms of restoring visual functions and preserving the organ in total hemophthalmia, when a blood clot occupies more than ¾ of the vitreous, the prognosis is unfavorable. Irreversible destructive changes occur in the vitreous body (organization of a blood clot, formation of adhesions). Tractional retinal detachment and atrophy of the eyeball may develop.