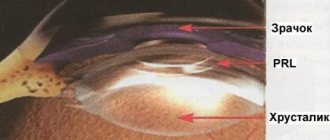
Phakic intraocular lens
The history of intraocular (that is, implanted inside the eye) lenses began in the middle of the twentieth century.
The first successful implantation of this type of lens was carried out in Italy in the 1960s. In those days, only one option for placing and fixing the lens was possible - in the anterior chamber of the eye. The material for the manufacture of the implant was a solid polymer, polymethyl methacrylate. After the operation, the patient received excellent quality of vision, without experiencing discomfort or feeling a foreign body in the eye. However, in the long term, many patients developed various complications - and the operation became unpopular. In the 1980s, when there was a quantum leap in the development of medical technology, ophthalmologists returned to the practice of using phakic lenses. New methods of positioning and fixing implants, as well as more advanced materials for their manufacture, appeared.
Today, the largest manufacturers of optics for phakic lenses are companies from the USA, Switzerland, Germany, England and Russia.
Modern phakic intraocular lenses (PIOLs) have a number of undoubted advantages:
- Complete reversibility of the operation:
if such a need arises, the doctor can remove the lens without damaging the cornea and lens. - Biocompatibility:
the implant is not rejected by the body. - Minimal trauma:
the microscopic incision heals on its own, vision is restored within a few hours after the procedure, the anatomy of the eye is not disturbed. - Manufacturing according to individual parameters:
each phakic lens is manufactured for a specific patient, according to individual measurements. - Eye protection from ultraviolet radiation.
We can say that such lenses are similar to contact lenses, only they are implanted inside the eye, and not put on top.
Advantages of posterior chamber phakic IOLs
- Posterior chamber phakic IOLs, while in the eye, do not contact the cornea or iris, which prevents dystrophic changes.
- The lenses are biocompatible with body tissues.
- PIOLs protect the retina from the negative effects of ultraviolet rays.
- Visual function is restored quickly.
- The integrity of the cornea is preserved.
The main difficulty in using intraocular phakic lenses is the high requirements for calculation accuracy and flawless work of the ophthalmic surgeon. This is why a full ophthalmological examination is performed before surgery. Detailed diagnostics, during which a whole range of procedures are carried out, allows the specialist to draw up a detailed picture of the condition of the patient’s visual analyzer and optimally select lenses.
Specifics of image perception
Over the years of research, the bionic eye has undergone many changes and improvements. In early models, the image was transmitted from a video camera directly to the patient's eye. The signal was recorded on the photosensor matrix and passed through the nerve cells to the brain. But there was one drawback in this process - the difference in the perception of the image by the camera and the eyeball. That is, they did not work synchronously.
Another approach was to first send video information to a computer, which converted the visible image into infrared pulses. They were reflected from the lenses of the glasses and hit the photosensors through the lens into the retina. Naturally, the patient cannot see IR rays. But their effect is similar to the process of obtaining an image. In other words, a perceptible space is formed in front of a person with bionic eyes. And it happens like this: the image received from the active photoreceptors of the eye is superimposed on the image from the camera and projected onto the retina.
Indications and contraindications for implantation of intraocular phakic lenses
The use of phakic lenses is possible only in cases where the visual system has not lost the ability to natural accommodation. First of all, this concerns the lens of the eye - it must function fully. Implantation is guaranteed to help with farsightedness, nearsightedness or high degree of astigmatism.
Phakic lenses are suitable for people who are prohibited from laser correction (for example, due to a very thin cornea or other pathologies).
Although the operation is considered low-traumatic and does not require general anesthesia, it is a penetrating type of surgery and has a number of contraindications:
- glaucoma, intraocular pressure disorder;
- history of eye surgery (eg, affecting the vitreous or retina);
- systemic pathologies (cataracts, corneal dystrophy, lens subluxation, chronic inflammation of the vessels of the eye and others);
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- age-related changes in the lens;
- diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent type).
It is most effective and safe to perform implantation before the age of 50 years.
What is a phakic lens?
Thanks to the development of technology, most people suffering from myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism can count on laser vision correction. But in case of medical contraindications, laser correction may be contraindicated. These cases include myopia and farsightedness, high-degree astigmatism, as well as the category of people who, for whatever reason, do not have the opportunity or desire to undergo excimer laser vision correction.
In our Clinic, this problem can be solved by implanting a phakic lens.
The method involves implanting an additional (positive or negative) intraocular lens inside the eye with the natural lens preserved, resulting in focusing the image directly on the retina (and not in front of it, which happens with myopia, or behind the retina, which happens with farsightedness).
There are three types of phakic lenses that are implanted to correct refractive errors. Their name is determined by their location in the eye: anterior chamber phakic lens, iridofixation phakic lens and posterior chamber phakic lens.
An intraocular lens is a CONTACT LENS, used in adults and children since 1992 after official confirmation of safety and approval of this technique.
The proposed technique makes it possible to obtain an accurate, safe and stable refractive effect even in children over the age of 3 years. The intraocular lens corrects myopia from –3.0 to –29.0 and farsightedness from +3.0 to +11.0 diopters.
The developed software makes it possible to calculate the optical power of the PIOL depending on the anatomical and optical parameters of the eye, the patient’s age and the expected refraction in the early and late postoperative period.
Chinese scientists have created an artificial eye comparable in characteristics to a human eye
The human eye is an extremely complex and finely tuned mechanism. Making a copy of it turned out to be very difficult, but scientists from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology managed to get as close to it as no one had ever come before. They created an artificial eye that is similar to a human eye in shape and size, as well as in light sensitivity, viewing width and receptor reaction speed. An article about this was published in Nature.
The front convex part of the eye is made of aluminum, there is also a lens that transmits and focuses light. The outer surface of the back is made of polymer, and the inner surface contains an artificial retina. The retina is a membrane embedded with nanofilaments that mimic photoreceptor cells; they capture photons and transmit signals through wires to an external computing device. The space inside, between the lens and the retina, is filled with a fluid similar to the vitreous (a clear, gel-like substance that makes up two-thirds of the volume of the eyeball). This liquid provides the electrochemical activity of the nanowires.
Everything works in much the same way as a normal human eye: light passes through a lens (lens) and a special liquid (vitreous body), is focused, then photoreceptor cells (nanofilaments) capture photons and transmit a signal through nerve fibers (wires) to a computing device (brain). ), which forms the final picture.
Of course, Chinese scientists were not the first to think of replicating the structure of the eye. However, they came up with a device that is significantly superior in performance to its analogues.
First, its sensors capture light over a wide range of intensities. Even if the light intensity is the lowest, they will register 86 photons per second - this is comparable to the capabilities of the human eye. The device owes this sensitivity to the perovskite from which the nanowires are made. This mineral is used to create solar cells.
Secondly, the response speed of the sensors is very high. They are capable of generating current in response to stimulation with a delay of 19.2 milliseconds, and recovery - returning to an inactive state - takes only 23.9 milliseconds. This is an extremely important parameter because it characterizes how quickly the artificial eye can perceive and transmit information about light signals. Photoreceptors in the human eye have excitation and recovery response times ranging from 40 to 150 milliseconds.
Third, the hemispherical artificial retina accommodates many more sensors than a flat or slightly curved surface. As a result, the resolution of the device has significantly increased. And finally, the viewing angle of the artificial eye, thanks to its design, reaches 100 degrees (in humans, the field of view of one eye is about 130 degrees).
However, despite all the advantages, the device is far from ideal. For example, the quality of the picture leaves much to be desired - it turns out blurry, measuring 10x10 pixels. In addition, engineers will have to somehow reduce the size of the wires through which information is received from nanofilaments, and find out how long the device can function without loss of performance. All we know now is that during nine hours of continuous operation its quality did not suffer.
The development of Chinese scientists is not yet capable of blowing up the market for robotics or eye prostheses, if only because the production of even one such eye requires a huge amount of money. However, it showed how the use of perovskite and a hemispherical retina improves the performance of such devices.
What implantation methods are there?
A phakic intraocular lens (PIOL) can be placed in the anterior or posterior chamber of the eye. Lens models differ in size, shape of support mounts, and material. Accurate calculations when making an implant are the key to the success of the entire operation, so the doctor must conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and take into account all the individual parameters of the patient’s eye chamber. The main task is to secure the lens so that it does not touch the lens and does not affect the natural circulation of fluid inside the eye.
Lenses are made to order and can take quite a long time - up to several months.
Features of implantation in the anterior chamber:
- There is enough free space in this part of the eye for stable fixation of the lens, so this procedure is considered to be an operation of medium complexity.
- Optical calculations and measurements are relatively simple.
- The material for the implant can be either hard or flexible, elastic.
- The lens can be placed in the corner of the camera or on the iris itself.
- Possible complications: risk of damage to the iris or lens, reduction in the number of endothelial cells, changes in the shape of the pupil, chronic inflammation.
Another feature of anterior chamber lenses: they can be visible to others due to glare.
Features of implantation in the posterior chamber:
- This implantation method is technically more difficult, because there is much less free space in the posterior chamber of the eye.
- Optical calculations are complex and require very precise special measurements.
- The lens material must be elastic, repeating the shape of the lens.
- Possible complications: impaired free circulation of intraocular fluid and the risk of developing cataracts.
Posterior chamber lenses cannot be seen from the outside; they are visible only with special examination.
As you can see, both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Modern clinics usually practice implanting posterior chamber lenses if the patient’s vision level is up to -14 diopters. But the final choice can only be made by a qualified doctor after carefully studying all the features of the patient’s visual system.
What is premium phakic lens correction?
Implantation of phakic intraocular lenses is used in our clinic in cases where it is impossible to correct vision using excimer laser methods. Most often this occurs when the cornea is insufficiently thick.
During this operation, an artificial lens is placed inside the eye in front of the lens, while the remaining internal structures of the eyeball must remain intact. Therefore, PIOLs are made extremely thin, and the material from which such a lens is made must have a high refractive index. In addition, the lens must be placed inside the eye through small punctures in the cornea, so it must have high elasticity. Each such lens is a high-tech product and is often made individually, taking into account the size of the patient's intraocular structures.
Currently, lenses from STAAR (Switzerland) are certified for use in Russia. You can view details about the phakic lens on the manufacturer’s website - https://www.staar.com/. Lenses from this manufacturer allow you to correct not only myopia or farsightedness, but also astigmatism.
Like any surgical intervention, implantation of phakic intraocular lenses has its indications and contraindications, therefore the final decision on the possibility of implanting a phakic lens is made by the surgeon only after a thorough examination of the patient.
Argus II
This bionic eye was designed and made in the USA. 130 patients with retinitis pigmentosa took advantage of its capabilities. Argus II consists of two parts: a mini-video camera built into the glasses and an implant. All objects in the surrounding world are recorded on camera and transmitted to the implant through a processor wirelessly. Well, the implant, using electrodes, activates the patient’s existing retinal cells, sending information directly to the optic nerve.
Users of the bionic eye can clearly distinguish between horizontal and vertical lines within a week. In the future, the quality of vision through this device only increases. Argus II costs £150,000. However, research does not stop, as developers receive various cash grants. Naturally, artificial eyes are still quite imperfect. But scientists are doing everything to improve the quality of the transmitted image.
Features of the operation
Let's talk about how the operation itself to implant intraocular lenses takes place. The procedure is very demanding on the level of training of the ophthalmic surgeon, as well as on the technical equipment of the clinic. What features of the operation does the patient need to know:
- Before the operation, local anesthesia (drip) will be administered.
- The procedure cannot be called painful, but rather psychologically unpleasant.
- The incision for lens implantation is microscopic and heals independently, without sutures.
- The operation lasts only 10-15 minutes.
- It is impossible to carry out implantation in both eyes at once.
- Vision restoration occurs within a few hours after surgery.
The recovery period is very short and painless. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drops, which must be taken independently. Restrictions in everyday life are minimal - almost all of them are related to hygiene procedures.
Advantages of PIOL implantation over laser vision correction
- The structure of the cornea is not disturbed when implanting phakic lenses;
- The operation is reversible - it is possible to remove (explant) the lens if necessary;
- Accommodation is preserved;
- Visual acuity is better than with glasses or contact lenses
| Recommended for the correction of visual impairment in patients under 40 years of age. |
ISLSTAAR phakic lenses are produced in Switzerland and certified by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Implantation of phakic lenses in the clinic is carried out by ophthalmic surgeon, Professor Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Sheludchenko.
The surgeon is a proctor of the STAARSURGYCAL company in the Russian Federation, an expert in the technology of implanting phakic lenses ISL and can train ophthalmologists in surgical techniques.
To date, over 300 PIOL implantation operations have been performed.
Operation stages:
- Patient preparation. Local anesthesia. Installation of an eyelid speculum;
- Corneal puncture for lens installation;
- Implantation of a phakic lens behind the iris in front of the native lens.
No stitches are required. Outpatient management.
Good vision the next day.
The period of complete recovery and healing under the supervision of an ophthalmologist takes one month.
Our advantages
"Moscow Eye Clinic" is a modern medical institution that provides a full range of professional services in the field of ophthalmology. The clinic has at its disposal the best examples of modern equipment from the world's leading manufacturers.
The Clinic employs leading domestic specialists with extremely broad practical experience. So, a surgeon of the highest category Natalia Ivanovna Fomenko consults at the clinic. Thanks to the high professionalism of doctors and the use of modern technologies, MGC guarantees the best treatment results and the return of vision. By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you can be sure of quick and accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Result of the operation
Phakic lenses are a very effective method of refractive correction. After the operation, the patient receives the maximum possible visual acuity in his case. Of course, in case of serious ophthalmological disorders, implantation will not return one hundred percent vision, but the result will be very noticeable.
Predictability of the result is another advantage of the operation for the patient. The doctor can provide accurate information about possible vision improvements already during the calculation of the optical characteristics for lens manufacturing.
And after the procedure, on the same day, a person will see the world around him in a new way, in all its richness of colors and details.
Prices
At the Moscow Eye Clinic you can undergo a full diagnostic examination and receive recommendations on the most effective treatment methods. A comprehensive examination of the patient (including such methods as testing visual acuity, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry, ophthalmoscopy with a narrow pupil, pneumotonometry) is 3500
rubles
The cost of artificial iris implantation for aniridia in the MGK is 50 000
rubles (for 1 eye).
Irido-lens MIOL-Iris is made individually (after making an advance payment, production time is four weeks), paid separately. The price of the implant is 40,000
rubles.
Arguments for and against surgery
The main disadvantage of implanting intraocular lenses is the financial side of the issue. High-quality diagnostics, ordering optics, implantation itself - all this costs a lot of money. Therefore, very often people choose other methods of vision correction.
Another difficulty is choosing a clinic and a qualified ophthalmic surgeon. Many people are frightened by the very fact of surgical intervention and the possible risks.
However, phakic lenses also have their advantages:
- modern implantation methods reduce the risks of postoperative complications to a minimum;
- the operation is reversible: if problems arise, the lens can always be removed;
- if laser correction is contraindicated, phakic lenses become an ideal alternative;
- the procedure does not violate the natural anatomy of the eye;
- The operation is well tolerated at any age and does not affect the heart and blood vessels.
There is a common myth that after implantation you will have to give up sports and physical activity. We inherited this belief from past, imperfect medical technologies. But today, operations to implant intraocular lenses are carried out at such a level that optics become an organic part of the eye, and a person can live a full life without fear of complications.
Bionic eyes
In 2013, the FDA approved the first bionic implant to treat retinitis pigmentosa, an inherited disease that causes degeneration of the photoreceptors in the retina. Users of this technology wear a pair of glasses equipped with a tiny video camera. The data goes from the camera to the video signal processing unit and to a group of electrodes implanted in the retina. The electrodes convert the data into electrical impulses that stimulate the retina to produce images.
The procedure, designed to treat age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in people over 55, removes the eye's natural lens and replaces it with a pea-sized telescopic object that magnifies the object and projects images onto the remaining healthy area of the retina.
Such technologies have already helped restore the sight of thousands of people, but many issues remain to be resolved to make bionic vision equivalent to ideal human vision. Patients with retinal or lens implants complain of poor resolution, difficulty seeing when moving at high speeds, and a limited field of vision.
With breakthroughs in biological vision treatments and artificial solutions like bionic eyes, blindness may one day become a disease of the past.
The experience of using such artificial iris already includes dozens of successful operations that have achieved high vision and excellent cosmetic effects. At the same time, achieving a unique cosmetic effect becomes possible due to the fact that the artificial iris production technology uses an individual approach to selecting the color of the implant.
This is done according to the following scheme:
1. First, a digital photograph of the healthy fellow eye is taken. 2. Then computer processing of the resulting image of a healthy iris is carried out. 3. Afterwards, the image is printed using a special polymer film. 4. At the final stage, the structure of the artificial iris is assembled into a single complex with an artificial lens.
The operation of artificial iris implantation is performed only by a qualified ophthalmological surgeon and belongs to the field of microsurgery. Unlike existing conventional implants, the artificial iris includes a haptic part made in the shape of a disk. Its end surface contains three additional arcuate support elements, whose internal surfaces are congruent with the end ones. Each of these arc-shaped elements contains a through slot made in the form of two arcs connected to each other. The opposite corners of both arcs are sharp, and each arc-shaped element has an installation hole. The use of just such an invention can significantly reduce operating rooms, as well as potential postoperative complications, and significantly reduce the time of surgical intervention.
It is worth noting that to eliminate a cosmetic defect, implantation of an artificial iris can be carried out even in an eye that is completely blind.