Increased intraocular pressure is often observed after 40 years, but can also occur at an early age.
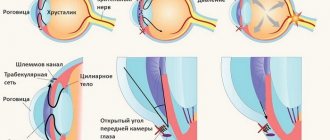
A persistent condition leads to the development of glaucoma, disruption of the movement of intraocular fluid and deterioration of vision, first in the periphery, then in the center.
To correct the condition, eye drops are used to lower intraocular pressure.
Their selection is made by an ophthalmologist based on diagnostic results, individual patient data, the presence of concomitant diseases, and additional medications used.
Causes of intraocular pressure
An increase in this indicator can be observed in some cases or constantly, especially in old age.
Factors that provoke increased intraocular pressure are:
- stress, emotional instability, increased excitability and disruption of the central nervous system;
- chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels - atherosclerosis, hypertension;
- chemical poisoning;
- some medications;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys;
- constant eye fatigue caused by heavy load on the organ of vision, the presence of diseases of this system (farsightedness, myopia);
- oncology, various eye injuries, etc.
If there is a constant increase in intraocular pressure, you must contact an ophthalmologist to prescribe treatment.
What is eye pressure?
Pressure in the eyes is a fairly common pathology, however, it is also very dangerous, as it can provoke the spread of a disease such as glaucoma and completely deprive a person of vision. When talking about signs of eye pressure, experts first of all name headaches, often migraines, which tend to intensify during a cold.
What pressure is normal? Most ophthalmologists are inclined to the following indicators: 8-26 mm Hg. Art. If for some reason the body experiences stress, the eye secretion increases, which, in turn, entails disruption of the cardiovascular system. It is at this time that the pressure inside the eyes begins to increase.
Symptoms
With this condition, patients note the following symptoms:
- fatigue, heaviness in the eyes, redness, swelling of the eyelids;
- pain in the temples and eyebrow area, migraine;
- severe pain in the eyes;
- deterioration and blurred vision, seeing “spots” before the eyes;
- decreased twilight vision;
- deterioration of lateral vision, loss of central vision if not treated in a timely manner.
Additionally, there is discomfort when reading and working at the computer.
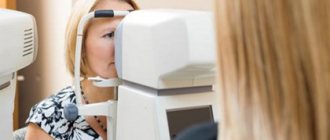
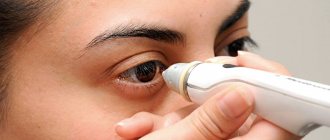
How to measure and lower eye pressure
Eye pressure is measured by the most well-known method - palpation. When palpating a closed eye, it is discovered that if the organ is normal, it is quite elastic and has a strict round shape. If the pressure is high, any touch can cause pain, and the shape will be very hard. When IOP is less than normal, the ball of the eye will dent quite strongly when touched.
In cases where eye pressure is outside the normal range, a tonometric examination is prescribed. Their working methods are quite difficult to explain. But they show the exact units of measurement of the fundus pressure condition.
To prevent eye pressure, doctors recommend first of all balancing your diet. The use of food additives – salt, sugar and other carbohydrates – is minimized. They should be replaced with nuts and dried fruits, as well as foods high in protein. It is necessary to add vitamins E and beta-carotene to the diet. On the contrary, bad habits need to be reduced. Among them, the most dangerous are: prolonged work at the computer, smoking, alcohol and eating fatty foods.
In addition, patients take medications in the form of drops and tablets for IOP. We will talk about pharmacological drugs below.
Classification of drugs
Drops that reduce intraocular pressure are used continuously. They can additionally reduce the production of aqueous humor, improve fluid outflow, or have a complex effect.
The following groups of drugs are used.
- Cholinomimetics - constrict the pupil and improve contractility of the eye muscles, lower intraocular pressure, and remove excess fluid from the eyeball. Side effects when using them are temporary blurred vision (can last up to 6 hours), burning sensation. The group includes Pilocarpine and Aceclidine drops.
- Beta blockers - reduce the production and regulate the movement of aqueous humor. Pharmacies offer medications based on the substances Timolol (Oftan-Timolol, Okumed, Arutimol, Glautam, Okumol), Betaxolol (Betoptik, Betoftan, Xonef, Optibetol). Restriction on use: bronchial asthma.
- Alpha2-adrenergic agonists - reduce the amount of moisture and are represented by drugs with the active ingredient Brimonidine (Alfagan R, Luxfen, Alfabrim).
- Prostaglandins and their analogues improve and normalize the outflow of moisture from the mucous membrane. This group of drugs is the safest and is often prescribed; the only drawback is the relatively high price. These include drops with the active ingredients Latanoprost, Travoprost, Tafluprost.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce moisture production. The pharmacy offers the drugs Azopt (Brinzopt), Dorzopt (Trusopt, Glaukopt, Dorzolamide-Nativ, Dorzolan Solo).
- Combined drops contain several active ingredients and have a complex effect (Dorzopt plus, Azarga, DuoTrav, Fotil and Fotil forte, Xalacom, etc.).
The choice of drops is influenced by the clinical picture of the disease: often increased intraocular pressure is accompanied by a violation of the outflow of aqueous humor or its production.
Classification
Drugs used for high eye pressure affect the amount of intraocular fluid. Drops that improve the outflow of fluid from the eye chambers include:
- prostaglandins – stimulate prostaglandin receptors and improve fluid excretion along the uveoscleral pathway, have the most pronounced hypotensive effect compared to other types of drops;
- cholinomimetics – cause contraction of the ciliary muscle of the eye, reduce the thickness of the iris, thereby ensuring the outflow of fluid, reducing ophthalmotonus;
- alpha-blockers - affect the receptors of the autonomic nervous system and stimulate the opening of pathways for the release of excess fluid.
Among the drops, the action of which is aimed at reducing the production of aqueous humor in the eyeball, there are:
- beta-blockers - act on ciliary epithelial cells and can be used for all forms of glaucoma;
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – block the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, resulting in reduced fluid production inside the eye.
Combined products contain several active substances and have a complex effect. Most often, drops for high eye pressure are a combination of cholinomimetics and beta-blockers; they are more effective and have a more convenient instillation regimen (once a day).
List of safe eye drops
Drugs that include Timolol, Betaxolol and Pilocarpine have a lower cost, but a large number of side effects. Timolol and Betaxolol can lead to bronchospasm, disruption of sinus rhythm and breathing, and dizziness. Pilocarpine causes pupil dilation, which is undesirable during dangerous activities, driving, or industrial management.
The following drugs are the safest.
Latanoprost
Drops containing this active ingredient are produced under the following trade names:
- Xalatan (Belgium);
- Glaumaks (Estonia);
- Glauprost (Romania);
- Xalatamax (Croatia);
- Lanotan (Ukraine);
- Latanomol (Korea);
- Latanoprost-Teva (Italy);
- Prolatan (India);
- Trilactan (Russia).
The effect of lowering intraocular pressure lasts for a day, after instillation it occurs within 3 hours. The drug enhances the outflow of aqueous humor and does not affect its production. Drops must be stored in the refrigerator at temperatures up to 8 degrees Celsius. Can be used as prescribed by a doctor for children over one year of age (Xalatan).
When used with contact lenses, you must first instill the medicine, then install the product after 15 minutes. This is due to the preservative Benzalkonium chloride included in the composition, which can remain on the surface of the CL.
When using Latanoprost, a temporary improvement in eyelash growth and a change in the color of the iris of the eyes is possible.
Brimonidine
Produced under the trade names Alfabrim (India), Alphagan R (USA), Luxfen (Lithuania).
The drug reduces the formation and increases the outflow of intraocular fluid, lowers intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Drops are used every 8 hours 3 times a day. It cannot be used in children under 2 years of age; careful use is required from 2 to 7 years of age due to the possible occurrence of bradycardia, decreased muscle tone, decreased pressure and temperature, and dysfunction of the respiratory system.
In adults, it can cause allergic manifestations (conjunctivitis, lacrimation, burning sensation and discomfort), dry mouth, drowsiness, headache, gastrointestinal disorders.
Travoprost
The substance is part of the drugs Travapress (Romania) and Travatan (Belgium).
The antiglaucoma drug improves the outflow of aqueous humor and reduces intraocular pressure; it is prescribed exclusively for adults (from 18 years of age) in the evening once a day. With regular use, it can cause eye pain, irritation, dry eye syndrome, and changes in the color of the iris.
Tafluprost
The drug is presented in pharmacies under the name Taflotan in disposable droppers and Taflotan Multi, produced in Finland. Its action is similar to the drugs Travapress and Travatan. The difference is that it can be used by people with an allergic reaction to preservatives. To reduce the phenomenon of darkening of the eyelids, the remaining drops after use should be removed from the skin with a cotton pad.
Brinzolamide
There are 2 drugs with this active ingredient in pharmacies - Azopt (USA) and Brinzopt (Romania).
The peculiarity of the drops is that they are used twice a day. You may experience a runny nose, blurred vision, or an unusual, bitter or sour taste in your mouth.
Complex drugs
Combination medications contain several substances:
- Timolol and Latanoprost (Duoprost, Xalacom);
- Brimonidine and Timolol (Combigan);
- Travoprost and Timolol (DuoTrav);
- Tafluprost and Timolol (Tapticom);
- Brinzolamide and Timolol (Azarga);
- Dorzolamide and Timolol (Dorzopt Plus).
These drugs are effective and safe, but restrictions on their use include children under 18 years of age, the presence of bronchial asthma and diabetes mellitus. They are prescribed in cases where treatment with one substance does not bring the desired result.
Contraindications
Eye drops for high intraocular pressure should be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor, and it is important to follow the rules of instillation, frequency and dosage.
Contraindications to the use of the products are children under 18 years of age, individual intolerance to the main active and additional substances. Many drugs have not been studied in pregnant and lactating women.
Drops based on Timolol cannot be used for diabetes, bronchial asthma, severe stages of heart and vascular diseases.
List of names of the best blood pressure drops
Drops to reduce intraocular pressure in different forms of glaucoma differ in composition, dosage method, contraindications and side effects.
1. Timolol. The active ingredient is timolol. Prescribed according to the following regimen: at the beginning of therapy, 1–2 doses, 2 times a day. After normalization of IOP - 1 dose 2 times a day for a long time. Cannot be used for cardiac diseases, lung diseases, severe vasomotor rhinitis.
2. "Betoptik". Eye pressure drops must be shaken first. The active ingredient is betaxolol. Instill 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac, 2 times a day. Immediately after this, press the area of the inner corner of the eye with your fingers for 2 minutes. Do not use if you have heart disease. The contraindications are the same.
Video: Is it necessary to instill Betoptik for glaucoma?
3. "Arutimol". The active ingredient is timolol maleate. Treatment regimen: 1 dose, 2 times a day, after stabilization of IOP - 1 time a day. Contraindications: heart disease, lung disease, dystrophic changes in the cornea.
4. "Xalatan". The active substance is latanoprost. Dosage regimen: 1 dose in each eye 1 time per day. The drug is approved for use not only in adults, but also in children over 1 year of age.
Video: Xalatan - indications for use
5. "Travatan". The active ingredient is travoprost. Method of application: 1 k. – 1 r/d. Not prescribed for allergic conditions.
6. "Pilocarpine". The action develops due to pilocarpine hydrochloride. Directions for use: 1–2 drops, 2–4 times a day. Contraindications: iritis, iridocyclitis, retinal detachment/threat of retinal detachment.
7. "Trusopt". The action is due to dorzolamide hydrochloride. Instill 1 drop in the morning, afternoon, evening. Contraindications: allergic reactions.
Video: Trusopt - indications for use
8. Azopt. The active ingredient is brinzolamide. Prescribed 1 k. 2 times a day. Contraindicated for people with severe kidney disease.
9. "Cosopt". Active ingredients: dorzolamide, timolol. 1 k. 2 r/d. Do not use for corneal dystrophy, respiratory tract hyperresponsiveness, severe kidney damage, sinus bradycardia, sinoatrial or atrioventricular block of the 2nd-3rd degree without a pacemaker, severe heart failure, cardiogenic shock.
Video: Kosopt - indications for use
10. "Fotil". Drops for combined type glaucoma. They combine 2 active ingredients - pilocarpine hydrochloride, timolol maleate. Dosage: 1 dose – 2 times a day. It is prohibited to prescribe for anterior uveitis, after surgical interventions on the eye organ, for cardiac pathologies, and lung diseases.
A general contraindication for all of the above drugs is increased hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Prohibited for children under 18 years of age (except for Xalatan drops), pregnant and lactating women.
Side effects from the organ of vision: blurred vision, double vision, lacrimation, discomfort or burning in the eyes, photophobia, inflammatory processes of the organ of vision.
Side effects from other organs rarely occur, since eye drops for eye pressure are poorly absorbed into the systemic circulation. Possible: nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath, bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, allergic reactions.
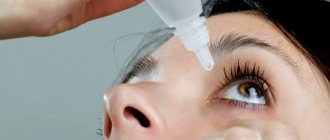
How to apply drops correctly
The dosage and time of instillation are determined by the doctor.
The procedure is carried out with clean hands, if possible, removing any remaining makeup and dust particles from the eyelids. Then you need to take a comfortable position, lying or sitting, tilt your head back, pull down your lower eyelid and look as high as possible.
Drop the medication into the corner of the eye, then close the eyelid and lightly press the inner corners of the eyes, if desired, massage for better distribution of the medication.
When using drops, it is important not to touch the tip to the mucous membrane or other surfaces, so as not to cause an infection.
Features of application
When using eye pressure drops, you should follow a number of rules to achieve optimal effect and prevent side effects:
- the instillation procedure is carried out strictly according to the instructions for the specific drug (once or twice a day) at the same time no later than 20.00;
- the sequence of using drops and a five-minute break between instillations (when prescribing several drugs) is a prerequisite for treatment;
- to increase the effectiveness of the product, immediately after instillation, you should close your eyes and lightly press your eyelids towards the inner corners (to improve the penetration of liquid into the lacrimal sac);
- drops are used on an ongoing basis daily;
- skipping is not a reason to increase the dose of medication the next day;
- To prevent addiction, a drug with another active ingredient is prescribed 2-3 times a year for a month.
Source
Reviews from doctors
Olga Vasilievna, ophthalmologist: For increased intraocular pressure, I prescribe modern drops based on Latanoprost, Brinzolamide, Brimonidine. The disease mainly develops in older people who have heart and vascular diseases and take other medications. The drops are well tolerated; at a high price, they can be replaced with available analogues.
Alexey Viktorovich, ophthalmologist: For glaucoma and eye pressure, I prescribe Xalatan and its cheaper analogues. The cost is average and above average, it is convenient to use - only once a day in the evening, patients have practically no side effects.
Consumer Reviews
Antonina Egorovna: 3 years ago I was diagnosed with the initial stage of glaucoma, the doctor recommended a choice of Xalatan or Glauprost. The first one is more expensive, so I decided to drip it. I use it daily at 8 pm, the disease does not progress. The only drawback is the expensive price, but I don’t want to exchange them for analogues.
Anton: My grandmother has high intraocular pressure and sees very poorly. At first, cheap drops Okumed, Pilocarpine, and Arutimol were used. When they stopped helping, the doctor prescribed Azarga. Expensive, but it helps. Sometimes watery eyes and blurred vision bother me, but this goes away.
Useful video
The video describes the symptoms of glaucoma and the principles of treating the disease.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2029
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 16 ratings, average: 4.25 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.