Intraocular pressure is created by the contents of the eyeball on the wall. Among the deviations from the norm, there is an increase and decrease in the indicator. And although both conditions are dangerous, people more often face the consequences of eye hypertension - glaucoma. Intraocular pressure is measured during the initial visit to a therapist, even if the person has no complaints. It is recommended to repeat the examination every three years.
The technique for measuring pressure is constantly being improved. From a rough assessment of ophthalmotonus by palpation, doctors moved to an accurate determination of the indicator using electronic devices and laser technology. Some manipulations can be carried out at home.
Methods for measuring intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure is measured by several methods.
- Palpation through the eyelids makes it possible to estimate the pressure approximately and understand whether there are currently significant deviations from the norm. The result of palpation is determined depending on the tone according to the degree of hardness of the eye.
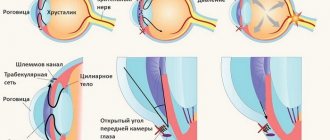
- More accurate results using the instrumental method. There are several fundamentally different types of tonometers that use contact and non-contact methods for measuring intraocular pressure. Any hardware tonometry uses the principle of the relationship between the force applied to deform the cornea by pressing and V.D. The difference lies in the methods of applying force and the way results are measured.
Methodology
There are many methods for measuring intraocular pressure. Depending on the methodology, the final results may differ.
According to Maklakov
During the examination, an anesthetic is instilled into the eye and a weight with paint is placed. An imprint is made on paper and, using a ruler, the area of paint removed from the surface of the eye is measured. The lower the pressure, the greater the volume of contact, so less paint should remain on the eyes.
Non-contact tonometry
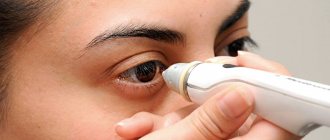
This test evaluates changes in the cornea, which is a response to air flow. There is absolutely no contact with the eyes, and therefore there is no risk of infection or pain.
The procedure lasts literally a few seconds: a person puts his head in a special apparatus and looks at the burning point with wide open eyes. The intermittent flow of air changes the shape of the cornea. As a result, an indicator of intraocular pressure appears on the computer.
Applanation tonometry
During the procedure, a person is given eye drops and a strip of fluorescent dye is held to the eye. The selection should be placed on a special stand and then looked at through a microscope. The doctor will hold the tonometer to the eye and measure the intraocular pressure. You should not rub your eyes for half an hour after the procedure.
Daily tonometry
This research method is very important for assessing the initial stage of glaucoma. It is based on an assessment of daily pressure changes. Typically, measurements are performed in the morning immediately after waking up, in the afternoon - from 12 to 16 o'clock, in the evening - at 18-20 o'clock. As a result, not only the difference between the obtained indicators is assessed, but also the magnitude of the peaks. The type of daily pressure curve is of great importance.
Methods for measuring intraocular pressure
Non-contact tonometry is a computer measurement, the principle of which is based on the reaction of the cornea under the influence of air flow. This takes into account the degree and rate of change in the cornea. The non-contact method is the most gentle and non-traumatic, there is no direct contact with the eye and no painful effect for the patient, and there is no risk of infection. The procedure takes a few seconds, no preparation of the patient is required, and he does not feel any discomfort.
Applanation tonometry is a measurement of intraocular pressure based on the Amber-Fick law. According to this law, internal pressure is defined as the ratio of external force and the size of the area of influence.
Impression tonometry - indentation of the cornea with a rod with a rounded end. The method is mainly used for increased V.D. and for measuring pressure when the surface of the cornea is curved, when it is impossible to capture a large area.
Dynamic contour tonometry is a contact tonometry method based on measuring intraocular pressure along the contour of the cornea. A probe with an integrated pressure sensor based on integral sensitive elements made of single crystals is placed in the central part of the cornea. The force of pressure of the probe on the cornea is constant. The sensor records eye resistance and receives up to 100 results/sec. Based on these data, the measurement result is displayed.
Non-contact tonometry
Contact tonometry
Indications and measurement results
Normal true intraocular pressure is approx. 16.2 mmHg Art. Readings from 10 to 21 are not considered a deviation from the norm. During the day, its level changes slightly, after waking up it is higher, and then begins to decrease slightly. Daily fluctuations can range from 1 to 5 mmHg.
Maklakov’s tonometers do not show true V.D., but the so-called tonometric one. The readings are somewhat inflated due to the squeezing out of a certain amount of fluid from the eye chambers. Therefore, the norm for tonometric pressure according to the Maklakov method was adopted in the range of 12-25 mmHg.
It is also necessary to take into account when measuring V.d. the fact that each method and type of instrument produces slightly different data. It makes no sense to compare readings - this is a feature of each measurement method. Therefore, if it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of the patient’s eye condition, then the check must be carried out using the same method. Only in this case can we compare the results and draw a conclusion. In particular, this is very important for patients with glaucoma.
The results of measurements using non-invasive methods are influenced by the thickness of the cornea. With a dense and thick cornea, the likelihood increases that the data obtained will be slightly higher than the true V.D. With a thin cornea, the opposite picture is observed.
Contact methods
Intraocular pressure can be measured using mechanical tonometers. The method is based on the property of the cornea of the eye to flatten under the influence of external force. Depending on the specifics of the measurements, the normal ranges will differ for each method.
Maklakov tonometer
The applanation method according to Maklakov was developed in 1884. Tonometric pressure is determined by the ratio of the force of impact and the size of the contact area.
The tonometer kit includes:
- 2 weights weighing 10 g,
- holder,
- stamp pad,
- ruler.
During the procedure, the patient is in a lying position. They put dicaine in his eyes for anesthesia. The specialist applies a dye to the smooth surface of the applant and places it on the cornea of the eye. Upon contact, some of the paint is removed. The more compacted the eye is, the worse it bends and the smaller the mark it leaves.
Afterwards, an imprint is made on paper using a weight. Its dimensions are measured with a special Nesterov-Wurgaft-Vagin ruler, with the help of which the units of length are converted into the corresponding pressure.
Normal eye pressure according to Maklakov’s method is considered to be from 12 to 25 mmHg. Errors occur in patients with thickened or thinned corneas and children.
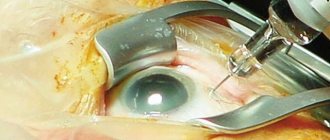
Goldman tonometry
The method combined applanation techniques and slit lamp observation. A prism is in contact with the patient's eye. The pressure force is adjusted using a lever. The reaction of the cornea is observed through a binocular microscope. To make the procedure comfortable, the eyes are instilled with anesthetic drops (Proximetacaine).
The measurement results are taken from the instrument scale on the lever immediately in mmHg. For the Goldman method, the highest limit of normal is 21 mmHg.
A manual version of the Goldmann device is the Perkins tonometer. It is convenient for bedridden patients. The algorithm for measuring ophthalmotonus with this device does not differ from Goldman tonometry.
Impression dimension
The author of the method, Schiotz, used a rod of a certain cross-section and a set of weights of 5.5, 7.5 and 10 g to measure intraocular pressure. The result is obtained in mm, and then converted to mmHg according to the table. The disadvantage of the impression tonometer is its low accuracy compared to applanation instruments. But the method is suitable for patients with uneven corneas.
The general disadvantages of contact methods with ruler assessment are:
- discomfort when carrying out
- limited accuracy,
- the possibility of errors in assessing the results,
- the likelihood of microdamage to the cornea,
- difficulty in children.
Dynamic contour tonometry
The modern contact method for measuring ophthalmotonus combines the principles of operation of mechanical instruments and electronic interpretation of the results. The applant is replaced with a corneal contour. It creates a pressure of 1 g. The piezoelectric sensor responds to changes in electrical resistance upon contact with the eye. It takes readings 100 times per second for 8 seconds. The duration of measurements is related to the cardiac cycle.
The method is accurate for any thickness of the eyeball wall and eliminates errors associated with heartbeats, but its reliability for people with abnormal corneal curvature is low.
Rebound blood pressure monitors
Rebound or rebound tonometers belong to the group of contact ones. A magnetized metal probe with a plastic tip touches the cornea of the eye. The phenomenon of induction is used to measure pressure. During the reverse movement, the probe enters the area of the induction coil. The strength of the generated current is used to calculate ophthalmotonus.
Rebound tonometers are used for individual use at home. Pharmacies offer the Finnish model Icare HOME.
Electronic contact devices
A thin rod (diameter up to 1.5 mm) touches the cornea of the eye. The mechanical signal is converted into an electrical one. Several micro-impacts occur in one session. Indicators are recorded in digital and graphical form.
The following work on the principle of identification tonometry:
- Mackay-Marg tonometer,
- pencil,
- Langham membrane device,
- Behrens-Tolman IOP indicator,
- Brunn-Jensen glaucotest,
- Zeimer device.
Types of ophthalmic tonometers
Non-contact tonometers are modern automatic devices that allow you to quickly and accurately measure intraocular pressure. They have a number of advantages over contact ones. In particular, pneumotonometers do not require the use of eye anesthesia and dyeing solutions. This is the most gentle and non-traumatic research method for the patient, eliminating the risk of corneal damage and infection. Also, the advantage of non-contact tonometers is that the procedure is not labor-intensive and does not require calculations, since the measurement and output of results are carried out automatically. Using a non-contact tonometer, you can measure intraocular pressure in children and patients with hypersensitivity, as well as allergy sufferers and those who have individual intolerance to drugs.
Applanation tonometers – measurement according to the Maklakov and Goldman method. To measure according to Maklakov, a cylindrical tonometer with glass plates is used. A dye is applied to the disinfected surface of the glass plates. The measurement is carried out under local anesthesia. After sensitivity disappears, a colored tonometer plate is lowered onto the central part of the cornea. The paint gets onto the surface of the cornea, and an unpainted spot appears on the plate. Its size depends on the degree of flattening of the cornea, which, in turn, shows the amount of pressure. The larger the contact area, the softer the eye and the less pressure. Then repeat the measurement with the opposite plate of the tonometer. The readings are transferred to paper - an imprint is made and measured using a ruler.
The Goldmann tonometer is a more modern version of the applanation tonometry method. This is a tonometer mounted on a slit lamp. A prism is installed on the tonometer, which, after anesthesia of the eye and instillation of a fluorescein solution, is applied to the cornea. The prism is illuminated with blue light and makes it possible to clearly see the tear menisci, which are due to the refraction of light passing through the prism into the upper and lower half ring. Next, use the knob to slowly adjust the pressure of the prism on the cornea, flattening it until the sodium fluorescein-stained half rings converge at one point. V.d. pressure is determined by the scale of the device.
An impression tonometer is a tonometer that uses the Schiotz method (the most successful and accurate impression tonometer, although the author of the technology belongs to Graefe). According to Schiotz, pressure is measured by pressing a rod of a certain mass on the cornea. Before measurement, local anesthesia is administered. Then a tonometer rod (piston) with a load of a certain mass is placed on the eye, which can move freely along the rod. Under the influence of the force of intraocular pressure, the piston moves and deflects the arrow on the scale. To determine the value of V.d. using a Schiotz tonometer, it is necessary to compare the readings with calibration tables (taking into account the mass of the load on the piston).
Dynamic contour tonometer – “Pascal” tonometer. Its advantage is that it is possible to carry out measurements practically ignoring the properties of the cornea. "Pascal" is somewhat similar to the Goldmann tonometer, since the device is also mounted on a lamp. The contact plane of the tip is concave in shape and degree of curvature of the cornea of the eye. In this case, the cornea does not flatten, as in other contact tonometers. The device records a series of data and calculates on their basis a certain average value, which is accepted as true.