The process of measuring the concentration of various substances by measuring refraction and determining the refractive index got its name - refractometry
. Devices that use the principle of refractometry in their work are called refractometers. Refractometers are widely used in various industries: for identifying chemical compounds, determining physicochemical parameters, for quantitative and structural analysis. In the food industry - to measure the alcohol content in alcoholic products, control the sugar content in sugar production - in general, to establish the quality of food products. In pharmacology, refractometers are used to determine the amount of glucose in biological fluids and drugs in solutions. The advantages of refractometric methods of chemical quantitative analysis are the speed of measurements, low consumption of substances and high accuracy.
Objective of the work: Refractometric method as a method for analyzing medicinal substances. The relevance of using ATAGO refractometers and polarimeters in pharmaceuticals and, in particular, in pharmacies.
Indications for autorefractometry
Doctors prescribe a diagnostic test in the following cases:
- suspicion of myopia - a visual impairment when a person sees well near, but poorly in the distance, which is formed when a beam is projected in front of the retina;
- suspicion of hypermetropia - a condition in which a person sees well in the distance, but poorly near, which is formed due to the projection of a light beam behind the retina;
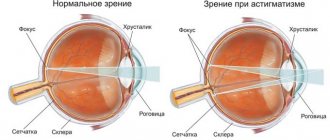
- astigmatism is a violation of the shape of the eyeball, as a result of which the patient incorrectly perceives the shape of an object, visual acuity often decreases towards myopia or hypermetropia;
- selection of corrective optics (contact lenses, glasses);
- A vision test is mandatory for people at risk (elderly people, recent injury to the eyeball);
- preparatory stage before surgery or laser correction;
- control examination of visual function after surgery or laser correction;
- a sharp decrease in visual function due to unknown reasons;
- condition after mechanical injuries, bruises, cuts and other conditions that can lead to decreased vision function.
Autorefractometry helps to obtain the most reliable information, since the data is determined by analyzers according to specified parameters.
Automatic refractometers of the RX, ATAGO series.
Automatic Refractometers
Automatic laboratory refractometers of the RX series with microprocessor control are designed to study the concentration of a wide range of liquid media of both low and high viscosity, regardless of transparency and color. The RX series provide high measurement accuracy, precise temperature control. The entire measurement process (heating/cooling) takes place automatically. Simply press the Start key. The device automatically measures the refractive index of a solution sample, calculates its concentration and displays the result on a digital LCD screen. The RX-I series is equipped with a screen that is made using Touch Screen technology - a touch screen, all control of the device is carried out from the screen. Automatic refractometers of the RX series can both heat/cool the sample using built-in Peltier elements, and use the automatic temperature compensation function when performing measurements. The ideal instrument for pharmacists in this series is the RX-9000-i and RX-5000-i Plus automatic refractometer.
Determination of alcohol concentration in dosage forms by refractometric method.
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol, Spiritus aethylicus) is one of the most widely used organic solvents in medical and pharmaceutical practice. Ethanol has bacteriostatic and bactericidal properties. Widely used to obtain tinctures, extracts, dosage forms for external use. The quality of alcohol solutions depends on the concentration of alcohol in which the drug is dissolved. In each case, an optimal concentration is required at which the drug substance does not precipitate. Therefore, water-alcohol solutions with different alcohol concentrations are prepared. The quantitative content of ethyl alcohol is easily determined by the refractometric method. There is a clear relationship between the concentration of ethyl alcohol and the refractive index. It is known that the refractive index depends on temperature, wavelength of light, the nature of the substance and solvent, and the concentration of the substance. So, the refractive index of aqueous alcohol solutions from 1% to 70% has a linear characteristic, which means you can easily measure the concentration with a refractometer. ATAGO produces special refractometers for measuring alcohol concentration. In general, these are ordinary refractometers, but a special correction factor is built into the processor, which allows you to immediately display the concentration of an aqueous-alcohol solution on the display, bypassing the refractive index. At concentrations from 70% to 96%, the relationship is nonlinear. Thus, the refractometric method can determine the strength of alcohol in the range from 1% to 70%.
Practical part.
Let's consider the use of refractometers in the manufacture and analysis of a 10% glycerin solution for injection: 10% glycerin solution Glycerin (in terms of anhydrous) 100 g 1. Sodium chloride 9.0 g. Water up to 1 liter.
Manufacturing. Glycerin (highest grade, dynamite) with a quantitative content of 86-90%, 94-98% or more is purchased from suppliers. Therefore, in order to calculate the amount of initial glycerin, it is necessary to know exactly what the mass fraction of anhydrous substance is in it. A refractometer is used to accurately measure glycerol concentration. The refractive index of the original glycerol n=1.4569 corresponds to a mass fraction of anhydrous substance of 89%. The initial amount of glycerin required to make the solution, according to the recipe, is 68:
2. Mass of glycerin = 100 g / 0.89 = 112.36 g.
Quantitative determination of glycerol in solution. We calculate the concentration of glycerol: Sglyts = / Fglyts
where n is the refractive index of the solution; n0 is the refractive index of purified water, measured at the same temperature; СNaCl is the concentration of sodium chloride in solution, determined by argentometry; FNaCl is the refractive index factor of the sodium chloride solution for the found concentration; Fglyc is the refractive factor of a 10% glycerol solution (0.001156).
In the pharmaceutical industry, ATAGO refractometers can be used to study aqueous solutions of various drugs: calcium chloride (0% and 20%); novocaine (0.5%, 1%, 2%, 10%, 20%, 40%); ephedrine (5%); glucose (5%, 25%, 40%); magnesium sulfate (25%); sodium chloride (10%); cordiamine, etc.
Note:
If for one of the substances included in the solution the refractive index factor is unknown or its insignificant concentration does not allow obtaining accurate data, then prepare a control solution containing this substance in the concentration that was determined by the titrometric method.
Refractometers and polarimeters from the Japanese company ATAGO have found application in all industries of the Russian Federation. ATAGO refractometers and polarimeters are included in the state register of measuring instruments of the Russian Federation. This allows the use of ATAGO devices in the most tightly controlled areas of production - such as, for example, pharmaceuticals.
Contraindications
Autorefractometry is not recommended in the following cases:
- children under 3 years of age, since bright ultraviolet rays can negatively affect the state of the central nervous system;
- a psychiatric illness that leaves the patient unable to sit still for several minutes;
- violation of the transparency of the lens, vitreous body, cornea, as a result of which the procedure is impossible;
- intraocular hemorrhage, which complicates the examination;
- bedridden patients to whom it is impossible to bring an eye examination device.
There are no side effects from the procedure, so it can be performed for any category of patients, in the absence of contraindications. The method can be used even by people suffering from hypersensitive eyes. It is carried out within 2-3 minutes, during which time a person will be able to withstand ultraviolet radiation.
Preparation for autorefractometry
There is no specific preparation for the technique. It is recommended to carry it out when the patient does not have conjunctivitis; purulent discharge will complicate the examination and make the results unsuccessful. With conjunctivitis, there is additionally increased sensitivity to the action of bright light, which is used in aftorefractometry.
If the procedure is performed with a narrow pupil, doctors do not prescribe any medications. If the ophthalmologist decides to dilate the pupil for extensive access to the retina, Atropine or similar drugs are prescribed.
Refractometers best suited for pharmacies: Abbe type refractometers, NAR/DR-A1 series, ATAGO.
NAR-1T Liquid
DR-A1
NAR or DR-A1 series refractometers are designed to measure the refractive index and average dispersion of non-corrosive liquids. These are very high quality devices. Easy to maintain. Minimal in content. In fact, the consumable material for these refractometers is a light bulb (light source). ATAGO refractometers of the NAR or DR-A1 series are used:
- In medical institutions to determine protein in urine, blood serum, urine density, analysis of brain and joint fluid, density of subretinal and other eye fluids. The use of a refractometer can significantly reduce time spent during mass examinations of patients.
- In the pharmaceutical industry, ATAGO refractometers can be used to study aqueous solutions of various drugs: calcium chloride (0% and 20%); novocaine (0.5%, 1%, 2%, 10%, 20%, 40%); ephedrine (5%); glucose (5%, 25%, 40%); magnesium sulfate (25%); sodium chloride (10%); cordiamine, etc.
- In the food industry, ATAGO refractometers are used at sugar and bread factories, confectionery factories to analyze products and raw materials, semi-finished products, culinary and flour products, to determine the moisture content of honey (up to 30%). ATAGO polarimeters are widely used in sugar production. Polarimeters in a sugar factory measure the concentration and purity of sugar in sugar beets or sugar cane at the raw material acceptance stage.
To determine the proportion of dry substances in various worts (GOST 5900-73), sugar agar syrup, syrup for marmalade, marshmallows, creams and gingerbreads.
To determine the mass fraction of soluble solids by sucrose (% Brix) in processed fruits and vegetables, to determine the percentage of fat in solid foods (gingerbreads, waffles or baked goods) and salt concentrations.
4. When servicing equipment, ATAGO refractometers are used to determine with greater accuracy the volumetric concentration of anti-crystallization liquid “IM”, which is added to aviation fuel in an amount of 0.1 to 0.3%. Further processing of the results is carried out in accordance with the “Methodological recommendations for analyzing the quality of fuels and lubricants in civil aviation” Part II p. 159. Experience in using refractometers has shown that these devices significantly reduce the time and increase the reliability of obtaining analyzes on the percentage of IM liquid in aviation fuel.
How is autorefractometry performed?
To carry out the technique, the patient enters a dark room and sits on a chair. The chin is placed on a special holder so that the head does not move while the beam is shining.
Ultraviolet light emerges from the autorefractometer, reaches the cornea and is reflected from it. It is the reflected beam that fixes the device and records the results. The device issues them on a research form.
Since the function of each eye may be different, the device records measurements first for one organ of vision, then for the other. The results are immediately handed over to the attending physician or patient, who must provide the form to the ophthalmologist.
With a narrow pupil
There is no preliminary preparation for the examination. The device directs ultraviolet rays through the patient's pupil, which is in its natural state. It narrows even in a dark room, as it is affected by light.
The technique is incorrect because the pupil can be affected by fatigue, overexertion, nervousness and other factors. Ultraviolet light may not penetrate fully into the eyeball. The same applies to beam reflection. The doctor will not be able to fully rely on these data to make a diagnosis.
Using cycloplegia
2 days before the study, the patient is prescribed a drug that blocks the functions of the muscles of the iris. When the drug accumulates, a long-lasting effect is formed, so the pupil does not constrict even under the influence of bright light. The doctor will be able to use not only autorefractometry, but also completely examine the fundus of the eye.
The data obtained is considered reliable. Based on them, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment. After therapeutic actions, it is recommended to repeat the procedure to determine the presence or absence of improvements.
The essence of the refractometry technique
Research using this method was first carried out in Germany back in the 19th century. At that time, an ophthalmoscopic mirror and interchangeable lenses were used as a refractometer. The technique has been constantly improved, and today ophthalmologists use computerized automatic refractometers.
If the study is carried out using an autorefractometer, the device sends infrared pulses into the eye, which are reflected from the fundus of the eye and read by the sensor. Special software then analyzes the raw and reflected signal data to determine the clinical refraction of the eye being examined.
What is very important is that this study does not violate the integrity of tissues and is absolutely painless.
Decoding the results
The patient is given a study form in which Latin abbreviations and data expressed in numbers are written down. Before going to the treating ophthalmologist, a person will be able to independently determine the quality of his vision:
- Ref – refractometry, that is, data obtained from the examination;
- R/od - data from the right eye;
- R/os – data from the left eye;
- Sph – optical power of the eye, expressed in diopters;
- Pd – distance between pupils;
- R1 and R2 – largest and smallest corneal meridians;
- Vd is the distance from the cornea to the back of the lens;
- # - inaccurate data;
- Cyl is the optical power of the cylindrical eye lens;
- Ax – axis of the cylindrical lens;
- Ave – average refraction;
- Ker – corneal thickness;
Using the data obtained, the doctor can determine how much myopia, hypermetropia, and astigmatism are developed. Next, visual acuity is corrected using a laser device, surgical technique, and optical devices (lenses, glasses).
An indicator of the electrical power of the cylindrical lens of the eyes is necessary to detect astigmatism. This indicator must be within certain limits, beyond which the shape of the eyeball changes.
The optical power value is necessary to detect myopia, hypermetropia, and astigmatism. The doctor determines the distance between the eyes to prescribe glasses; this indicator is mandatory. If the patient is undergoing laser or surgical surgery, it is necessary to measure the thickness of the cornea. If the patient has keratoconus (a protrusion of the cornea resulting in thinning), the procedure will be contraindicated for the individual.
The doctor determines mild, moderate, and severe degrees of visual impairment. Depending on the data received, the ophthalmologist will make a diagnosis. The sooner autorefractometry is performed, the greater the patient’s chances of completely restoring visual function without complications.
With astigmatism, the patient's visual acuity often decreases. The procedure can determine astigmatism together with hypermetropia or myopia.
The procedure is mandatory for each eye separately. On one of them, a person may have a decrease in visual acuity, the other may be normal. Then the doctor will prescribe corrective lenses, glasses, surgery. The method will be chosen by the patient himself.
Determination of the concentration of a substance in a solution
In refractometry, two methods are used to calculate the concentration of a substance in a solution from the measured refractive index.
1. Calculation of concentration using the formula. The dependence of the refractive index on the concentration of a substance in percentage is expressed:
n=n0+С·F, hence (15),
where n and n0 are the refractive indices of the solution and solvent;
F – refractive index factor.
2. Calculation of concentration using refractometric tables . Having measured the refractive index, the corresponding concentration value is found in the table. If the measured refractive index is not given in the table, interpolation is carried out.
| Refractometry is an analysis method based on measuring the index (coefficient) of refraction of light (n) as it passes from one medium to another. Refraction of light, that is, a change in its original direction, is due to different speeds of light distribution in different media. In this case, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence of the beam (α) to the sine of the angle of refraction (β) for two contacting media is a constant value called the refractive index (n). The refractive index is also equal to the ratio of the speed of propagation of light in these media: In laboratory conditions, the so-called relative refractive index of the substance is usually determined in relation to the air of the room where the measurement is being taken. The refractive index is measured using refractometers of various systems. The value of the refractive index depends on factors affecting the speed of light propagation in the test substance (the nature of the substance, the wavelength of the light, the temperature at which the measurement is carried out, the concentration of the substance in the solution) and the medium in relation to which it is measured. The refractive index measurement is carried out at a light wavelength of 589.3 nm (line D of the sodium spectrum). A prerequisite for determining the refractive index is compliance with the temperature regime. Usually the determination is performed at 20±0.30C. As the temperature increases, the refractive index decreases, and as the temperature decreases, it increases. The correction is calculated using the following formula: n1=n20+ (20-t)·0.0002 The range of values of the measured refractive index is 1.3 - 1.7. Measurement accuracy +2·10-4. The amount of increase in refractive index with each percent increase in concentration is called the refractive index factor (F). The F value is determined experimentally for each substance and each concentration percentage. |
| Example 16: Determine the concentration of a calcium chloride solution using refractometric tables if the measured refractive index of a calcium chloride solution is 1.3442. Solution: The closest table values are 1.3434 and 1.3445, corresponding to concentrations of 9% and 10%. The difference in the table refractive indices corresponds to one percent of the concentration. 1.3445 – 1.3434 = 0.0011. The difference between the found refractive index and one of the table values (for example, for a 10% solution) 1.3445-1.3442=0.0003 corresponds to x%. Hence 0.0011 – 1% 0.0003 – x The concentration of the solution under study will be: 10-0.27 = 9.73%. You can take the difference between the table value for a 9% solution and the found refractive index: 1.3442-1.3434=0.0008 The end result is the same: 9+0.73=9.73% Conclusion : C(%) calcium chloride is 9.73% |
| ! | When the concentration of a substance is less than 3 - 4%, it is not recommended to use the refractometry method for the quantitative determination of substances. |
If there is a need to express the drug content in grams, then in the basic formula the value of the total volume (ml) of the drug is substituted in the numerator, and the number 100 is substituted in the denominator.
(16),
The given examples of concentration calculations are applicable only for single-component drugs. Most often they are used to determine the content of drugs in concentrated solutions.
The refractive index of a multicomponent solution is the sum of the refractive index of the solvent and the refractive indices of the dissolved substances. For solutions containing two or more substances, the formula will be as follows:
n=n0+n1+n2+…= n0+С1·F1+ С2·F2+ С3·F3+…
The concentration of one of the components in a multicomponent solution can be calculated based on refractometric measurements using the formula:
(17),
If necessary, express the content in grams:
(18),
where C1, C2, Cn are the concentrations of substances (%) found by chemical (for example, titrimetric) methods;
F1, F2, Fn – factors of refractive index of solutions of substances determined by chemical methods;
F is the factor of the refractive index of a substance determined by the refractometric method.
Which doctor conducts the examination?
Initially, the patient consults an ophthalmologist. He may send him to a laboratory where another doctor will perform the procedure or perform it himself. Only the attending ophthalmologist can decipher the data in order to prescribe further examination or treatment.
The examination can be done at a clinic or hospital; there is always an autorefractometer there. If the patient makes an appointment at a private clinic, you must first find out about the equipment of the ophthalmologist’s office.
What is the principle of autorefractometry based on?
In healthy people, a light beam passes through the pupil, is refracted in the cornea and lens, and is projected on the retina. If the refractive power is disrupted, a decrease in visual acuity occurs. When a light beam is projected in front of the retina, myopia occurs. If it projects behind the retina, the patient suffers from farsightedness.
The doctor measures the internal structure of the eyeball by determining the wavelength of ultraviolet light that is sent to and reflected from the retina.