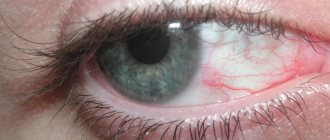
What is unilateral visual impairment?
Ophthalmic diseases usually affect both organs of vision. But sometimes a person notices that his vision has become worse in only one eye. You can determine that only one visual organ sees poorly by alternately closing each eye.
A functional disorder where one eye sees worse than the other is called amblyopia. The symptom is associated specifically with dysfunction of the visual analyzer. The brain cannot compare two different images coming from the visual organs and turns off one of them. The eye becomes lazy.
Watch the video about what amblyopia is:
Why does one eye see worse than the other?
If the deterioration of vision is not associated with trauma to the visual organ or other physical damage, then the phenomenon in which poor vision is observed in one eye is called amblyopia. The pathology also has another name, common among the population - “lazy eye”.
With amblyopia, dysfunction of the visual centers is observed, characterized by a disruption in the interaction of the optic nerve of the “lazy eye” with the brain. The corresponding part of the brain does not synchronize signals from both eyes - binocular (volume) vision is impaired.
This happens because the perception of the surrounding world by the “lazy eye” differs from the information provided by the second organ of vision. The brain, in order to create a clear, familiar image, takes the “picture” only from the healthy eye, and ignores the “lazy” one.
Amblyopia is a reversible condition. Sometimes it goes away on its own, in other cases it can be easily treated if you consult an ophthalmologist in a timely manner.
Causes and symptoms of the disorder
People suffering from refractive errors, strabismus, working in hazardous industries, and athletes are predisposed to have poor vision with one eye. The risk increases with hereditary predisposition.
A person does not immediately notice that he has begun to see poorly in one eye. This indicates the formation of ophthalmological diseases, complications of chronic diseases of internal organs. If one eye suddenly begins to see worse, a foreign body has probably entered the visual organ. Common reasons why one eye sees worse than the other:
- Overstrain of the organ of vision due to long periods of watching TV, working at a computer, reading while driving or in low light.
- Impaired blood flow, nerve compression after sleeping in an awkward position, with carotid artery stenosis, temporal arteritis.
- Ophthalmological diseases: strabismus, cataracts, glaucoma, refractive errors, infectious diseases.
- Chronic diseases: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, atherosclerosis, oncology.
- Injuries to the head and visual organ, foreign body.
Poor vision in one eye may result in blurred or unclear images. May occur at certain times of the day. Sometimes it occurs after surgical treatment. Let's look at the features of the symptoms.
Other reasons:
- The eye sees poorly in the dark. When one eye sees worse in the dark, this is due to a lack of vitamin A, severe infectious diseases, excessive physical activity, glaucoma, and pregnancy. Both visual organs can be affected evenly or to varying degrees. This is called night blindness.
- Pain and blurred vision. If one eye hurts and has poor vision, the cause may be infectious lesions (conjunctivitis, barley, abscess), late stages of cancer.
- Headache and blurred vision. The combination of headache and poor vision on one side occurs with neuralgia, migraine, hypertension, and glaucoma.
- Visual impairment in the morning. Impaired blood flow due to thickening of the blood, after long-term infectious diseases, after sleeping in an uncomfortable position leads to the fact that a person has difficulty seeing in the morning.
- Poor vision after correction. Unilateral visual impairment after correction occurs due to swelling after surgical treatment. This is a temporary side effect. If a person sees poorly for a long period after surgery, then it is worth contacting a specialist.
- Refractive errors. With myopia, the right or left eye has blurry vision into the distance. With farsightedness, on the contrary, the image is difficult to see up close. Visual impairment is possible on both sides to varying degrees.
Cataract
With cataracts, clouding of the lens occurs, which leads to a decrease in its accommodative function. It usually appears with age, but in some cases the disease occurs after an injury or illness.
Most often, with cataracts, a person is bothered by blurred vision, manifested in blurred contours of objects, and photosensitivity may also be observed.
The disease can only be treated with surgery. Drug therapy in the form of eye drops only helps to slow down the development of cataracts. During the operation, the real lens is replaced with an artificial one, which allows the patient to regain vision.
Features in children
The child’s organs and systems are at the stage of formation. Prolonged visual stress can lead to poor vision in one eye or both. You should limit prolonged reading, long computer games, and hours of watching cartoons.
For children, it is common for small dust particles to enter the visual organ. Sand often gets in while playing on the playground. This causes lacrimation, redness of the conjunctiva, and blurred images. After removal of the foreign body, the symptoms disappear.
Strabismus
With strabismus, vision in one eye often deteriorates. In most cases, this disease manifests itself in childhood. Strabismus is characterized by double vision, headaches and dizziness. Also, with this disease, the patient often experiences refractive errors (myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism). To improve vision, the doctor prescribes wearing glasses. Additionally, the patient is prescribed a special set of eye exercises. If such treatment is ineffective, surgery is indicated; it can be performed no earlier than the age of three.
How to fix when one eye sees worse than the other
Therapy for functional disorders includes treatment with the Amblyocor device. A person watches a movie on a computer, while brain signals are recorded. If incorrect operation of the visual analyzer is detected, the film is turned off. A person needs to normalize his vision through his own effort, then the film will turn on.
Physiotherapy is effective: electrical stimulation, light-color stimulation, laser stimulation, computer stimulation methods, medicinal electrophoresis. The success of treatment depends on treatment of the underlying cause that caused poor vision on one side.
Treatment of functional disorders is auxiliary.
- Anti-fatigue drops will help relieve symptoms of visual fatigue and improve poor vision: Visine, Artificial Tear, Systane.
- If a foreign body gets in, it must be removed.
- For strabismus, apply an occlusive bandage to the healthy side. This makes the lazy eye work. Treatment with Amblyocor and physiotherapy are used.
- The basis of therapy for ophthalmic infectious diseases is the effect on the pathogen. For viral infections, “Ophthalmoferon” and “Aktipol” drops are effective. For bacterial infections – drops “Tobrex”, “Albucid”; eye ointments "Tetracycline", "Erythromycin".
- To treat cataracts, the clouded lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
- Glaucoma is treated with drops that reduce IOP: Azopt, Cosopt, Betoptik.
- Myopia and farsightedness are corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
- Chronic diseases. Therapists treat hypertension with antihypertensive drugs. Atherosclerosis is treated with statins. Migraine and neuralgia - painkillers. To treat diabetes mellitus, endocrinologists prescribe insulins or glucose-lowering drugs.
- Oncologists treat oncological diseases with surgical removal of the tumor, radiation and chemotherapy.
Retinal disinsertion
The main causes of retinal tears are possible injuries, heavy lifting and severe myopia. Characteristic symptoms of this process are:
- the appearance of flies or veils before the eyes;
- distortion of the letters and objects in question;
- the appearance of scotomas (loss of visual fields in the form of black spots in front of the eyes).
Treatment of retinal detachment is only possible with surgery. During the operation, the ophthalmic surgeon performs a filling, strengthening the eye membrane, which helps eliminate tears.
Prevention
To see better, eat more fruits and vegetables. Carrots, blueberries, fish, cherries, and broccoli are especially rich in vitamins. In spring and autumn, when the body lacks vitamins, take a course of vitamins and dietary supplements. Blueberry Forte tablets have proven themselves well.
Maintain hygiene, do not rub your eyelids with dirty hands, and wash off your makeup at night. Get a good night's sleep on an orthopedic pillow. Take regular walks in the fresh air, do physical exercise, and strengthen your immune system.
When working hard for a long time, take breaks and do eye exercises. Do not read in low light, lying down, or while traffic is moving. Limit your computer use and reduce your TV viewing.
If you have good vision in one eye and poor vision in the other, we recommend that you consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will examine the visual organ and assess the condition of the visual structures. This will allow the disease to be detected at an early stage.
Tell us about your story in the comments. Share the article with your friends on social networks. Be healthy. All the best. What to do with eye pressure, you will find the answer in the link.
Amblyopia - types, causes, who is susceptible
There are different types of amblyopia depending on the cause:
- Dysbinocular amblyopia develops with strabismus.
- Refractive - when you refuse to wear glasses or contact lenses due to myopia, strabismus, as a result of which a blurry image is formed on the retina of one eye.
- Obscurational - inherited.
- Anisometropic - gradually develops if one eye sees a little worse than the other.
- Hysterical - develops with a mental disorder.
Amblyopia is also caused by other pathologies that require medical intervention. To identify them in time, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
According to statistics, people who are predisposed to strabismus are most often susceptible to amblyopia.
With strabismus, different eyes produce different images and send dissimilar information to the brain. The brain does not accept an out-of-focus image and “turns off” the one that is unable to focus on the object.
In addition to strabismus, there are other factors that provoke the development of the symptom:
- heredity;
- eye injury;
- high blood pressure;
- congenital pathologies of the visual apparatus;
- traumatic brain injury;
- problems with blood circulation;
- inflammatory diseases of the organs of vision;
- nerve compression;
- advanced myopia, farsightedness;
- prematurity;
- cerebral paralysis.
The risk group also includes children under 6 years of age, among whom there is a high percentage of people suffering from amblyopia.
Myopia
The essence and reasons. A condition in which the image is focused in front of the retina rather than on it, causing distant objects to become blurred. Myopia most often develops during primary school age. In the future, vision continues to deteriorate.
Question and Answer Why are many children myopic?
Symptoms. The child does not distinguish distant objects, but sees those nearby well. Headaches and increased visual fatigue are common when looking into the distance for a long time (for example, during sports games).
Treatment. Wearing glasses, contact lenses.
Treatment
As with any other pathology, it is better to combat the development of amblyopia at an early stage.
The key to successful treatment here is early diagnosis. You need to understand that the violation does not go away on its own. Therefore, the sooner qualified medical care is provided, the greater the chances of a full recovery. Diagnostic procedures aimed at identifying amblyopia involve performing an examination, which makes it possible to establish the root cause of the formation of the pathology. Subsequently, the ophthalmologist prescribes surgical or conservative therapy, based on the factors that lie at the root of the development of the disease.
If parents have vision problems, children should definitely undergo a full ophthalmological examination at the age of 3-5 years. It is during this period that it is easiest to cope with the development of amblyopia.
To strengthen the weak optic nerve, special contact lenses, glasses or laser correction are used. The eye sees worse than the other until the effects of cataracts or strabismus are eliminated. With the right approach to organizing therapy, these methods make it possible to cope with the presented disorders quite quickly.
Children are often prescribed to wear the so-called pirate bandage. To do this, the old glasses frame is covered with cardboard or opaque plastic. Covering the “strong” eye makes the “weak” visual organ work more actively. As an alternative to the device, some ophthalmologists prescribe patients to wear opaque contact lenses and instill atropine into the healthy eye, which leads to the formation of a blurred image.